Abstract
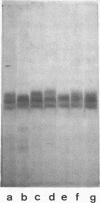
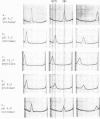
Electrophoretic analysis of the major seed protein, G1 globulin, from four strains of Phaseolus vulgaris L. revealed a three-banded pattern for two strains having a high methionine content (BBL 240 and PI 302,542). The other two strains (PI 207,227 and PI 229,815) known to have a lower seed methionine content, had a two-banded subunit pattern for the G1 globulin. Analytical ultracentrifugation confirmed that globulin from the two-banded strains underwent pH-dependent reversible dissociation similar to that previously found for a three-banded cultivar; additionally, the protomer molecular weight showed that three subunits of about 50,000 molecular weight each were present in the G1 globulin of the two-banded strain. Gel patterns of G1 globulin from the two strains used as parents, BBL 240 and PI 229,815, showed differences in the largest subunit, which appeared as either a 53,000 molecular weight polypeptide known to be present in the three-banded strain, or as a shorter polypeptide having a molecular weight close to 47,000. Analysis of G1 protein from portions of single hybrid seeds showed a banding pattern intermediate between the two- and three-banded types. The subunit pattern from all seeds with intermediate-banded parents segregated in a manner consistent with that expected for control of the polypeptide by a single Mendelian gene. The remaining portions of the seeds were grown to confirm that they represented true crosses. The procedures used are essentially nondestructive, and can be used as a basis for selecting seeds having different protein characters.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews A. T., Jayne-Williams D. J. The identification of a phytohaemagglutinin in raw navy beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) toxic for Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Br J Nutr. 1974 Jul;32(1):181–188. doi: 10.1079/bjn19740068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R. Differential activation of maternal and paternal loci in seed development. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 5;245(140):30–32. doi: 10.1038/newbio245030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusztai A., Watt W. B. Glycoprotein II. The isolation and characterization of a major antigenic and non-haemagglutinating glycoprotein from Phaseolus vulgaris. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 23;207(3):413–431. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2795(70)80005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. M., Buchbinder B. U., Hall T. C. Cell-free Synthesis of the Major Storage Protein of the Bean, Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1975 Dec;56(6):780–785. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.6.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. M., Hall T. C. Application of Remazol dye for isolation of protein subunits by preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1974 Sep;61(1):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. M., Hall T. C. Solubility characteristics of globulins from Phaseolus seeds in regard to their isolation and characterization. J Agric Food Chem. 1975 Mar-Apr;23(2):184–189. doi: 10.1021/jf60198a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. M., McLeester R. C., Bliss F. A., Hall T. C. Reversible and irreversible dissociation of globulins from Phaseolus vulgaris seed. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2118–2121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. J., Boulter D. Purification and subunit structure of legumin of Vicia faba L. (broad bean). Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):413–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1410413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]