Abstract
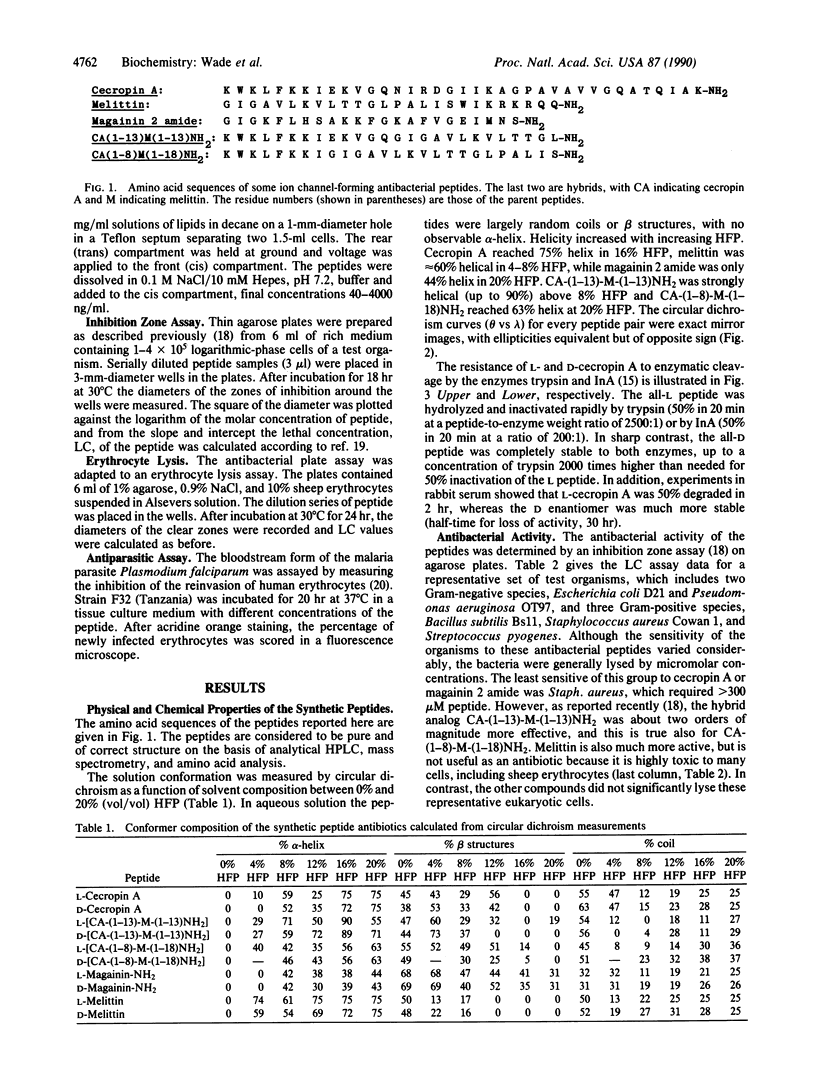
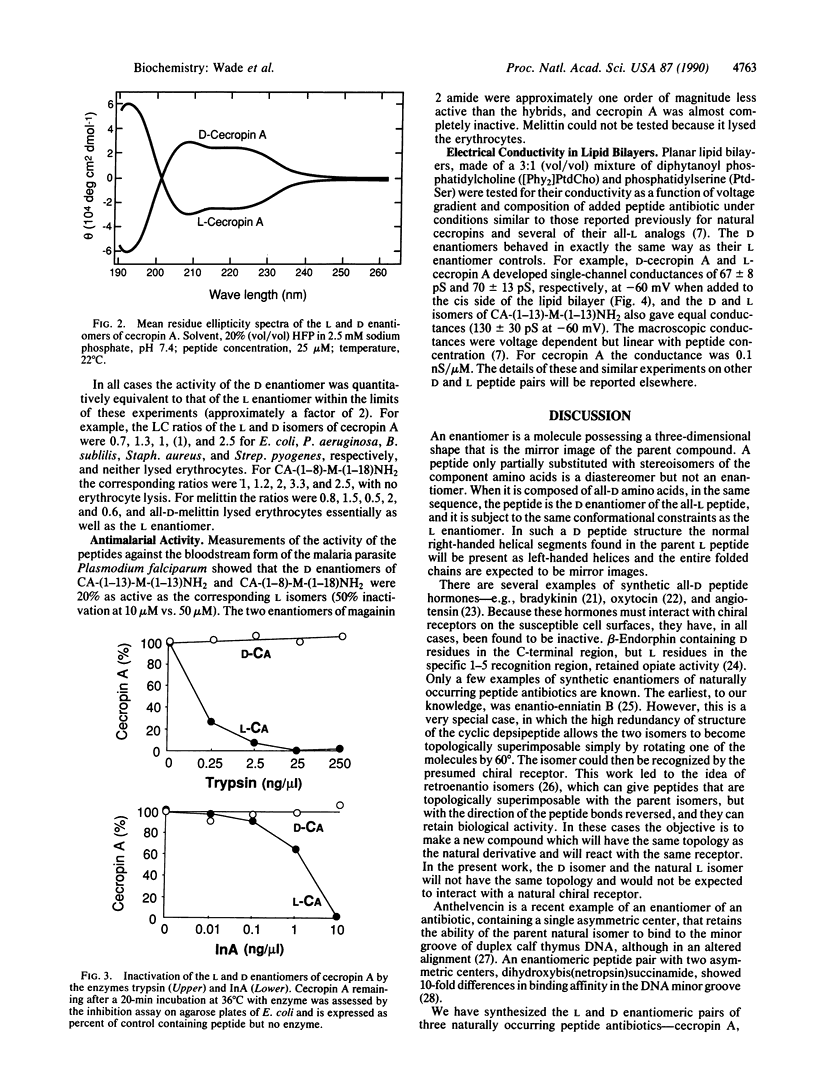
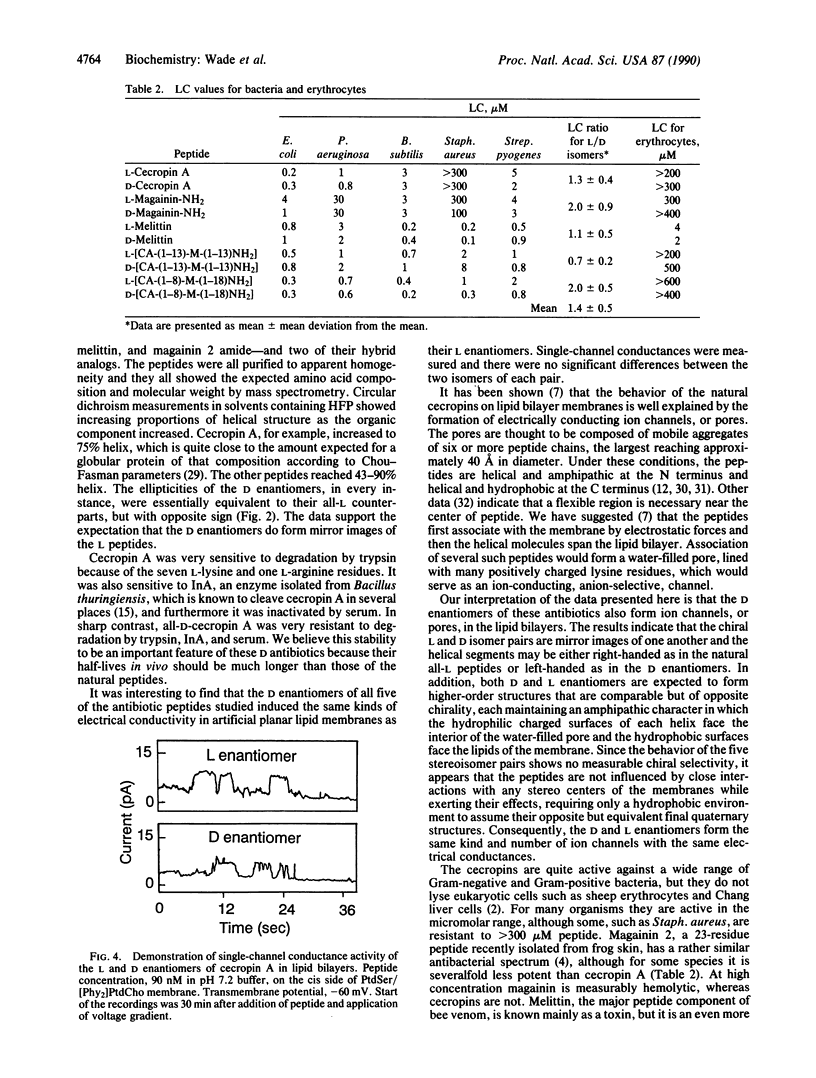
The D enantiomers of three naturally occurring antibiotics--cecropin A, magainin 2 amide, and melittin--were synthesized. In addition, the D enantiomers of two synthetic chimeric cecropin-melittin hybrid peptides were prepared. Each D isomer was shown by circular dichroism to be a mirror image of the corresponding L isomer in several solvent mixtures. In 20% hexafluoro-2-propanol the peptides contained 43-75% alpha-helix. The all-D peptides were resistant to enzymatic degradation. The peptides produced single-channel conductances in planar lipid bilayers, and the D and L enantiomers caused equivalent amounts of electrical conductivity. All of the peptides were potent antibacterial agents against representative Gram-negative and Gram-positive species. The D and L enantiomers of each peptide pair were equally active, within experimental error. Sheep erythrocytes were lysed by both D- and L-melittin but not by either isomer of cecropin A, magainin 2 amide, or the hybrids cecropin A-(1-13)-melittin-(1-13)-NH2 or cecropin A-(1-8)-melittin-(1-18)-NH2. The infectivity of the bloodstream form of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum was also inhibited by the D and L hybrids. It is suggested that the mode of action of these peptides on the membranes of bacteria, erythrocytes, plasmodia, and artificial lipid bilayers may be similar and involves the formation of ion-channel pores spanning the membranes, but without specific interaction with chiral receptors or enzymes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanc J. P., Kaiser E. T. Biological and physical properties of a beta-endorphin analog containing only D-amino acids in the amphiphilic helical segment 13-31. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9549–9556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Hultmark D. Cell-free immunity in insects. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:103–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Wade D., Boman I. A., Wåhlin B., Merrifield R. B. Antibacterial and antimalarial properties of peptides that are cecropin-melittin hybrids. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81505-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T. A new approach to the calculation of secondary structures of globular proteins by optical rotatory dispersion and circular dichroism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Sep 17;44(6):1285–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80225-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen B., Fink J., Merrifield R. B., Mauzerall D. Channel-forming properties of cecropins and related model compounds incorporated into planar lipid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5072–5076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalhammar G., Steiner H. Characterization of inhibitor A, a protease from Bacillus thuringiensis which degrades attacins and cecropins, two classes of antibacterial proteins in insects. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 1;139(2):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drain C. M., Christensen B., Mauzerall D. Photogating of ionic currents across a lipid bilayer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6959–6962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOURET G., DUVIGNEAUD V. THE SYNTHESIS OF D-OXYTOCIN, THE ENANTIOMER OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY HORMONE, OXYTOCIN. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Aug 20;87:3775–3776. doi: 10.1021/ja01094a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J., Boman A., Boman H. G., Merrifield R. B. Design, synthesis and antibacterial activity of cecropin-like model peptides. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1989 Jun;33(6):412–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1989.tb00217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Jentsch J. Sequenzanalyse des Melittins aus den tryptischen und peptischen Spaltstücken. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Jan;348(1):37–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holak T. A., Engström A., Kraulis P. J., Lindeberg G., Bennich H., Jones T. A., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. The solution conformation of the antibacterial peptide cecropin A: a nuclear magnetic resonance and dynamical simulated annealing study. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7620–7629. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Engström A., Andersson K., Steiner H., Bennich H., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Attacins, a family of antibacterial proteins from Hyalophora cecropia. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):571–576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01465.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Steiner H., Rasmuson T., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Purification and properties of three inducible bactericidal proteins from hemolymph of immunized pupae of Hyalophora cecropia. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb05991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L., Selsted M. E., Ganz T., Lehrer R. I. Antimicrobial defensin peptides form voltage-dependent ion-permeable channels in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):210–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B., Vizioli L. D., Boman H. G. Synthesis of the antibacterial peptide cecropin A (1-33). Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):5020–5031. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin V. K., Kent S. B., Tam J. P., Merrifield R. B. Quantitative monitoring of solid-phase peptide synthesis by the ninhydrin reaction. Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemyakin M. M., Ovchinnikov Y. A., Ivanov V. T. Topochemical investigations of peptide systems. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1969 Jul;8(7):492–499. doi: 10.1002/anie.196904921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenyakin M. M., Ovchinnikov Y. A., Ivanov V. T., Evstratov A. V. Topochemical approach in studies of the structure-activity relation: enantio-enniatin B. Nature. 1967 Jan 28;213(5074):412–413. doi: 10.1038/213412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H., Andreu D., Merrifield R. B. Binding and action of cecropin and cecropin analogues: antibacterial peptides from insects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 7;939(2):260–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H. Secondary structure of the cecropins: antibacterial peptides from the moth Hyalophora cecropia. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 25;137(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80368-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. M., Woolley D. W. All-D-bradykinin and the problem of peptide antimetabolites. Nature. 1965 May 8;206(984):619–620. doi: 10.1038/206619b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Alvarez O., Tosteson D. C. Peptides as promoters of ion-permeable channels. Regul Pept Suppl. 1985;4:39–45. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(85)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogler K., Studer R. O., Lergier W., Lanz P. Synthese von All-D-Val-5-Angiotensin II-Asp-1-beta-Amid. Helv Chim Acta. 1965 Sep 20;48(6):1407–1414. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19650480621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wåhlin B., Wahlgren M., Perlmann H., Berzins K., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Human antibodies to a Mr 155,000 Plasmodium falciparum antigen efficiently inhibit merozoite invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7912–7916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M. Magainins, a class of antimicrobial peptides from Xenopus skin: isolation, characterization of two active forms, and partial cDNA sequence of a precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



