Abstract
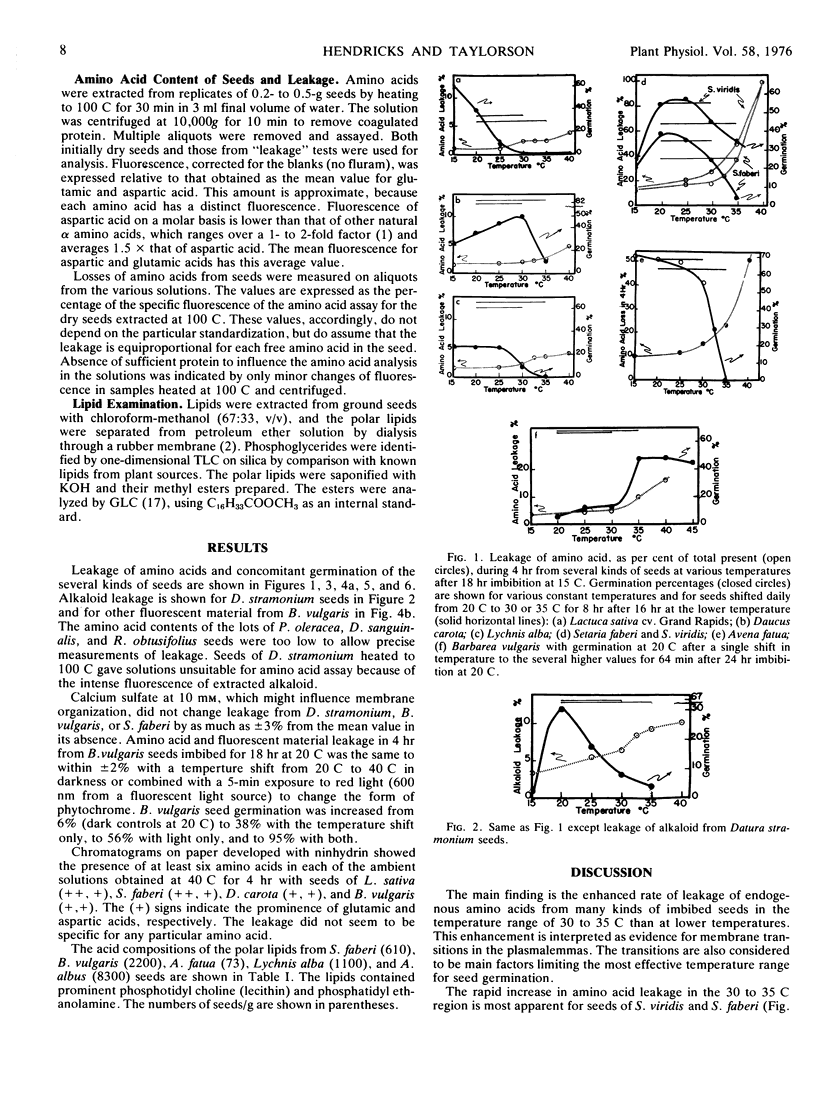
Leakages of amino acids and/or fluorescent material as functions of temperature between 15 and 40 C are reported for imbibed seeds of Avena fatua L., Lactuca sativa L., Barbarea vulgaris R. Br., Amaranthus albus L., Abutilon theophrasti Medic., Lychnis alba Mill., Daucus carota L., Setaria faberi Herrm., Setaria viridis (L.) Beauv., and Datura stramonium L. The leakage indicates prominent increase in permeability of the plasmalemma in the 30 to 35 C range for 8 of the 10 kinds of seeds studied. Germination of the seeds at constant temperatures or with daily shifts in temperature is related to the membrane transition temperature for permeation by amino acids. Seeds of A. albus and A. theophrasti, which did not show membrane changes in the 25 to 40 C range, germinated best at 35 to 40 C; the other seeds germinated best below 30 C. Seeds of B. vulgaris showed rapid permeation of limiting membranes upon initial wetting with water, which was indicative of membrane disorder when dry. Leakage under anaerobiosis was observed for S. faberi seeds.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D. Phase transitions and fluidity characteristics of lipids and cell membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1975 May;8(2):185–235. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser A. F., Souza K. A. Correlation between thermal death and membrane fluidity in Bacillus stearothermophilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4111–4115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiatt A. J., Lowe R. H. Loss of organic acids, amino acids, k, and cl from barley roots treated anaerobically and with metabolic inhibitors. Plant Physiol. 1967 Dec;42(12):1731–1736. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.12.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenaz G. Lipid-protein interactions in the structure of biological membranes. Subcell Biochem. 1974 Sep;3(3):167–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Träuble H. Phase transitions in cells, membranes, and lipids of Escherichia coli. Detection by fluorescent probes, light scattering, and dilatometry. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2625–2634. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinert J. C., Steim J. M. Calorimetric detection of a membrane-lipid phase transition in living cells. Science. 1970 Jun 26;168(3939):1580–1582. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3939.1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


