Abstract
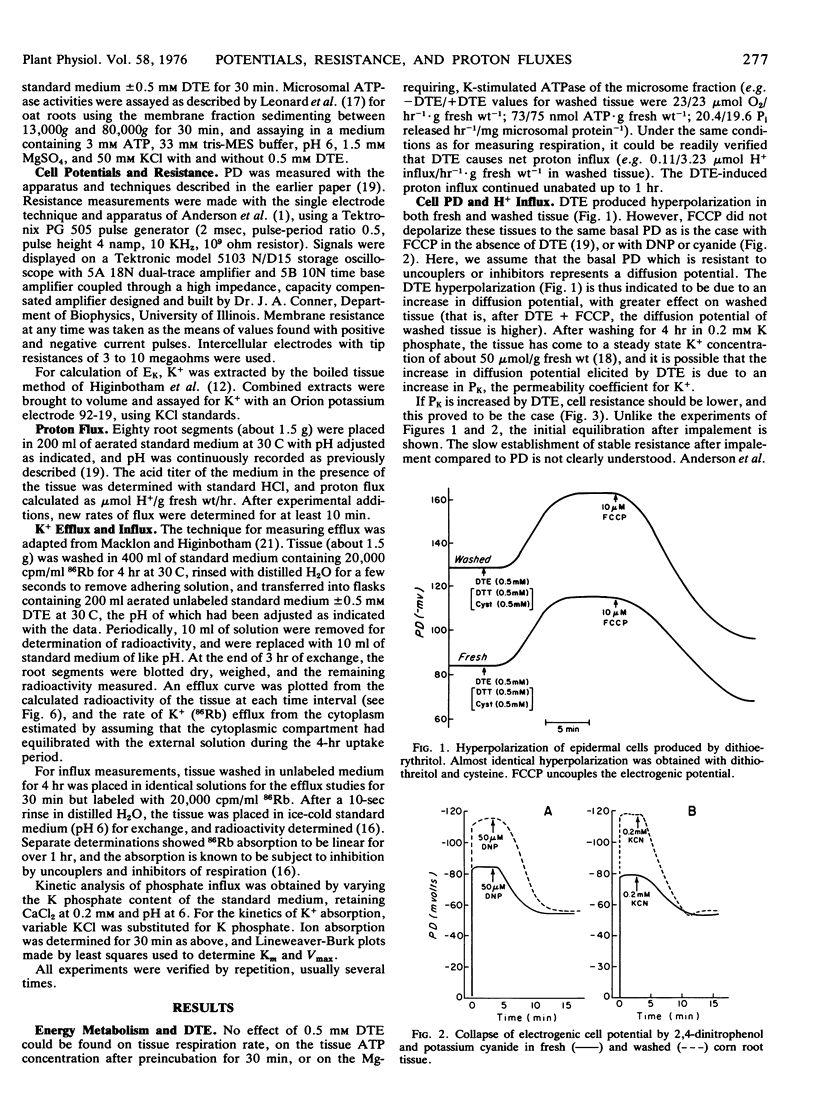
Studies were made of the effect of dithioerythritol on net proton flux, potassium influx and efflux, cell potential, and cell resistance in fresh and washed corn (Zea mays L. WF9XM14) root tissue. Dithioerythritol induces equal proton influx and potassium efflux rates, decreases membrane resistance, and hyperpolarizes the cell potential. Greater effects on H+ and K+ fluxes are secured at pH 7 than at pH 5. Other sulfhydryl-protecting reagents produced the same responses. No evidence could be found that dithioerythritol affected energy metabolism or membrane ATPase, and proton influx was induced in the presence of uncoupling agents.
We deduce that dithioerythritol activates a passive H+/K+ antiport, driven in these experiments by the outwardly directed electrochemical gradient of K+. The net effect on H+ and K+ fluxes is believed to reside with the combined activity of a polarized H+/K+ exchanging ATPase and the passive H+/K+ antiport. A model is presented to show how the combined system might produce stable potential differences and K+ content.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. P., Hendrix D. L., Higinbotham N. Higher plant cell membrane resistance by a single intracellular electrode method. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jan;53(1):122–124. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertagnolli B. L., Hanson J. B. Functioning of the adenine nucleotide transporter in the arsenate uncoupling of corn mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1973 Nov;52(5):431–435. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.5.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. L., Boyer P. D. The rapid labeling of adenosine triphosphate by 32P-labeled inorganic phosphate and the exchange of phosphate oxygens as related to conformational coupling in oxidative phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 28;14(2):392–398. doi: 10.1021/bi00673a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demiel R. A., Guerts van Kessel W. S., van Deenen L. L. The properties of polyunsaturated lecithins in monolayers and liposomes and the interactions of these lecithins with cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 14;266(1):26–40. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass A. The regulation of potassium absorption in barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1975 Sep;56(3):377–380. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.3.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson J. B., Bertagnolli B. L., Shepherd W. D. Phosphate-induced Stimulation of Acceptorless Respiration in Corn Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1972 Sep;50(3):347–354. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.3.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. A., Rosing J., van de Stadt R. J., Slater E. C. Tight binding of adenine nucleotides to beef-heart mitochondrial ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 31;314(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensley J. R., Hanson J. B. The action of valinomycin in uncoupling corn mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jul;56(1):13–18. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higinbotham N., Etherton B., Foster R. J. Effect of External K, NH(4), Na, Ca, Mg, and H Ions on the Cell Transmembrane Electropotential of Avena Coleoptile. Plant Physiol. 1964 Mar;39(2):196–203. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.2.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higinbotham N., Etherton B., Foster R. J. Mineral ion contents and cell transmembrane electropotentials of pea and oat seedling tissue. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jan;42(1):37–46. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON P. C., ADAMS H. R. Cation-anion balance during potassium and sodium absorption by barley roots. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Jan;46:369–386. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hansen D., Hodges T. K. Membrane-bound Adenosine Triphosphatase Activities of Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1973 Apr;51(4):749–754. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hanson J. B. Induction and development of increased ion absorption in corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):430–435. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Hanson J. B. Increase in electrogenic membrane potential with washing of corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1974 Nov;54(5):799–801. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.5.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Hanson J. B. Phosphate absorption rates and adenosine 5'-triphosphate concentrations in corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):250–256. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macklon A. E., Higinbotham N. Active and passive transport of potassium in cells of excised pea epicotyls. Plant Physiol. 1970 Feb;45(2):133–138. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz S. M., Higinbotham N. Transmembrane electropotential in barley roots as related to cell type, cell location, and cutting and aging effects. Plant Physiol. 1976 Feb;57(2):123–128. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.2.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman M. G. Adaptation of barley roots to low oxygen supply and its relation to potassium and sodium uptake. Plant Physiol. 1969 Sep;44(9):1233–1240. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.9.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman M. G., Mertz S. M., Graves J. S., Pierce W. S., Higinbotham N. Electrical potential differences in cells of barley roots and their relation to ion uptake. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jan;47(1):76–80. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayman C. L., Slayman C. W. Depolarization of the plasma membrane of Neurospora during active transport of glucose: evidence for a proton-dependent cotransport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1935–1939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


