Abstract
ATPase activity of the plasma membrane fraction from primary roots of corn (Zea mays L. WF9 × M14) was activated by Mg2+ and further stimulated by monovalent cations (K+ > Rb+ > Cs+ > Na+ > Li+). K+-stimulated activity required Mg2+ and was substrate-specific. Maximum ATPase activity in the presence of Mg2+ and K+ was at pH 6.5 and 40 C. Calcium and lanthanum (<0.5 mm) were inhibitors of ATPase, but only in the presence of Mg2+. Oligomycin was not an inhibitor of the plasma membrane ATPase, whereas N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide was. Activity showed a simple Michaelis-Menten saturation with increasing ATP·Mg. The major effect of K+ in stimulating ATPase activity was on maximum velocity. The kinetic data of K+ stimulation were complex, but similar to the kinetics of short term K+ influx in corn roots. Both K+-ATPase and K+ influx kinetics met all criteria for negative cooperativity. The results provided further support for the concept that cation transport in plants is energized by ATP, and mediated by a cation-ATPase on the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF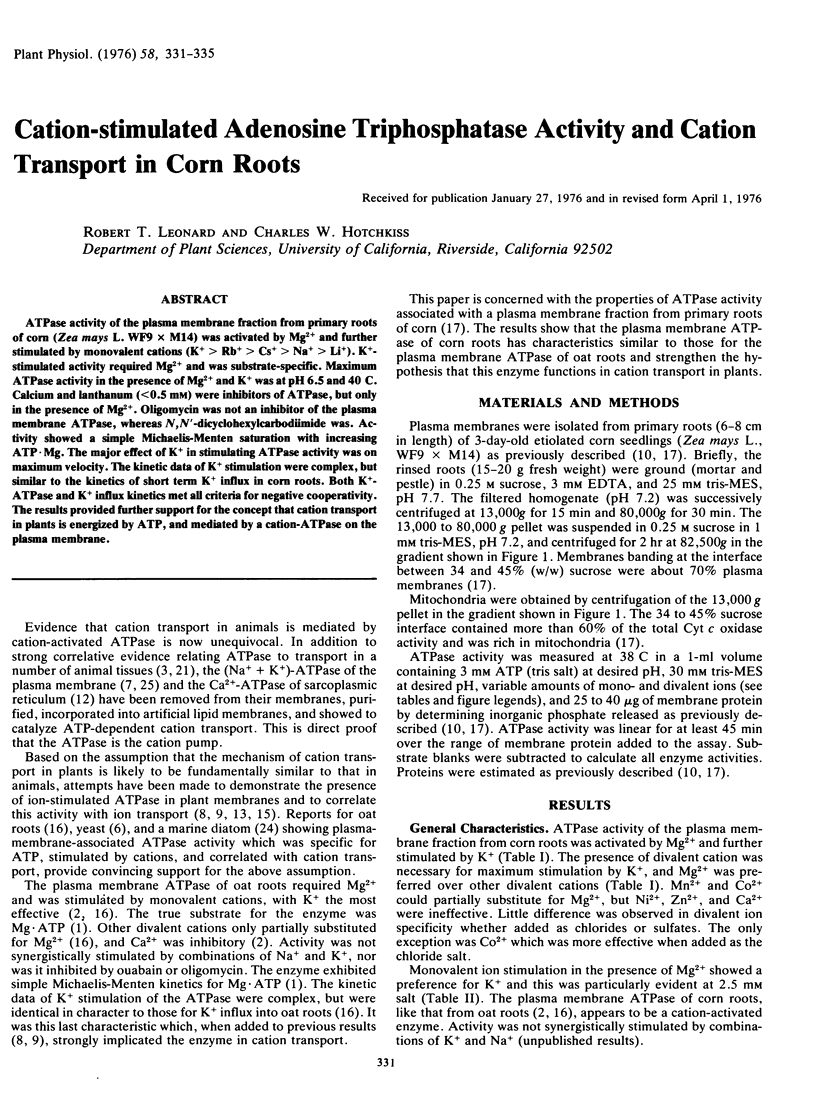


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balke N. E., Hodges T. K. Plasma membrane adenosine triphosphatase of oat roots: activation and inhibition by mg and ATP. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jan;55(1):83–86. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWD J. E., RIGGS D. S. A COMPARISON OF ESTIMATES OF MICHAELIS-MENTEN KINETIC CONSTANTS FROM VARIOUS LINEAR TRANSFORMATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:863–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl J. L., Hokin L. E. The sodium-potassium adenosinetriphosphatase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):327–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann G. F., Wehrli E., Boehm C. Preparation and identification of yeast plasma membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 23;363(3):295–310. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilden S., Hokin L. E. Active potassium transport coupled to active sodium transport in vesicles reconstituted from purified sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase from the rectal gland of Squalus acanthias. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6296–6303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T. Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:392–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles A. F., Kandrach A., Racker E., Khorana H. G. Acetyl phosphatidylethanolamine in the reconstitution of ion pumps. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1809–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh R. A., Williamson F. A., Jones R. G. Presence of Two Different Membrane-bound, KCl-stimulated Adenosine Triphosphatase Activities in Maize Roots. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):678–685. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hanson J. B. Increased Membrane-bound Adenosine Triphosphatase Activity Accompanying Development of Enhanced Solute Uptake in Washed Corn Root Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):436–440. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hodges T. K. Characterization of Plasma Membrane-associated Adenosine Triphosphase Activity of Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jul;52(1):6–12. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Nagahashi G., Thomson W. W. Effect of lanthanum on ion absorption in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1975 Mar;55(3):542–546. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Vanderwoude W. J. Isolation of plasma membranes from corn roots by sucrose density gradient centrifugation: an anomalous effect of ficoll. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):105–114. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A., Koshland D. E., Jr The role of negative cooperativity and half-of-the-sites reactivity in enzyme regulation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;10:1–40. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152810-2.50008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Hanson J. B. Phosphate absorption rates and adenosine 5'-triphosphate concentrations in corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):250–256. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. Membrane transport during development in animals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 31;415(3):311–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. D. Nucleotide and divalent cation interactions with the (Na+ plus K+)-dependent ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 21;341(1):232–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan C. W., Volcani B. E. Synergistically stimulated (Na+,K+)-adenosine triphosphatase from plasma membrane of a marine diatom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4376–4380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J., Goldin S. M. Reconstitution of active ion transport by the sodium and potassium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase from canine brain. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4022–4024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


