Abstract
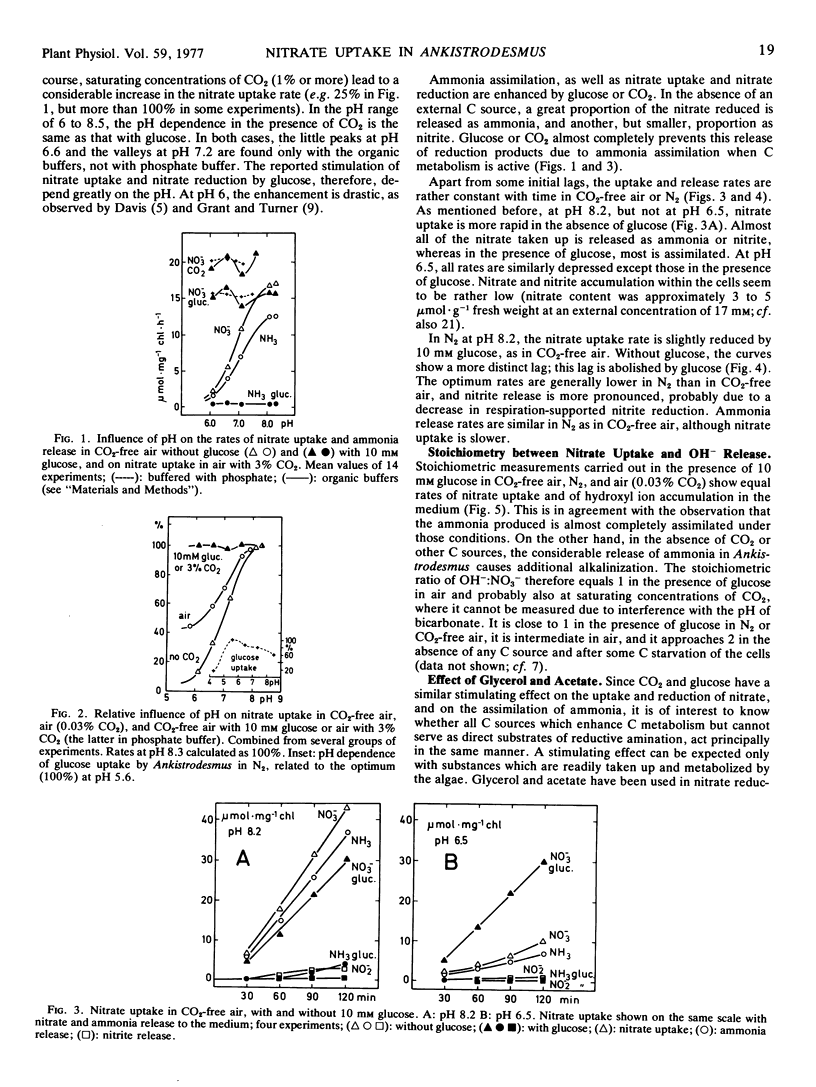
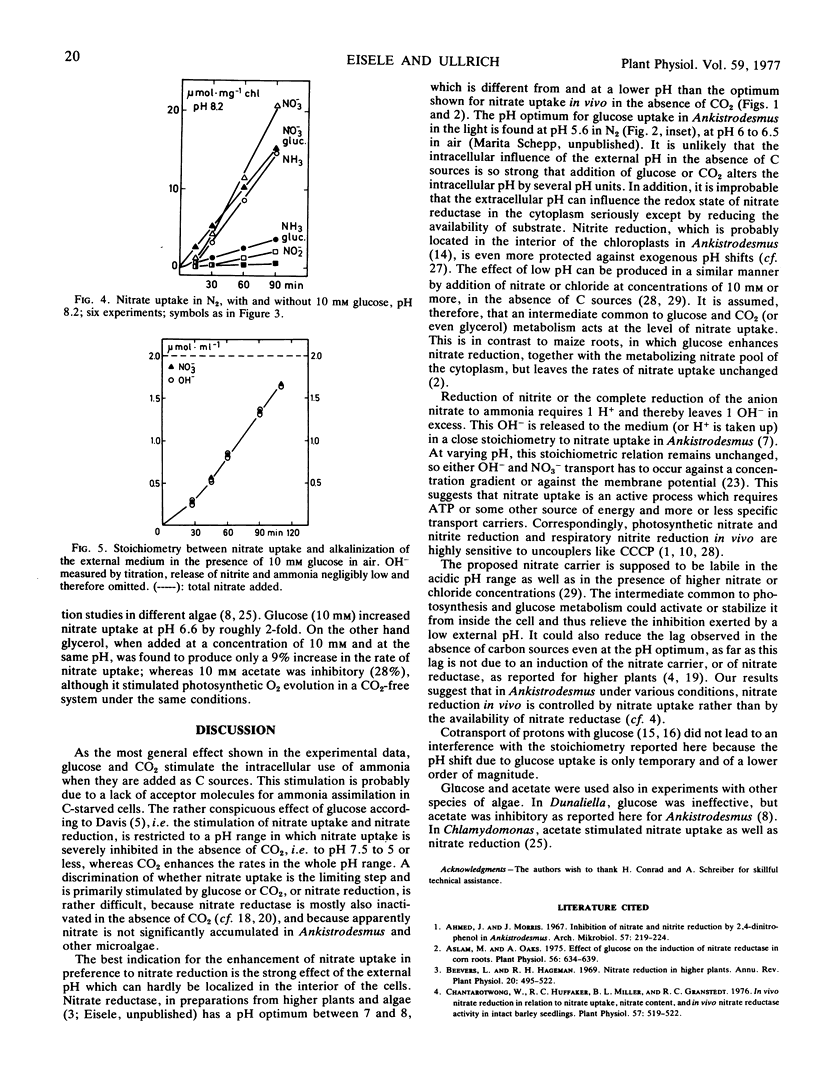
In Ankistrodesmus braunii, in the absence of CO2, i.e. in CO2-free air or N2, photosynthetic nitrate uptake and nitrate reduction were inhibited, especially at low pH. Under such conditions, glucose stimulated nitrate uptake and reduction to almost the same level in the pH range between 6 and 8.5. CO2 at 0.03% effected an intermediate pH dependence of nitrate uptake; saturating CO2 concentration (more than 1%) eliminated the pH dependence, as did glucose, but the rates were enhanced compared with glucose. Glucose and, even more, CO2, drastically reduced the release of nitrite and ammonia to the medium, the stoichiometry between alkalinization of the medium and nitrate uptake (OH−/NO3−) approached 1.
Due to the lack of storage vacuoles in Ankistrodesmus, nitrate uptake and nitrate reduction were closely coupled processes whose experimental separation is difficult. The relieving effect of glucose and CO2 suggests a carrier-mediated nitrate uptake which is more limiting than nitrate reduction and is sensitive to low pH, but which is stabilized by some intermediate originating from an active carbon metabolism.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aslam M., Oaks A. Effect of glucose on the induction of nitrate reductase in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1975 Nov;56(5):634–639. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.5.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantarotwong W., Huffaker R. C., Miller B. L., Granstedt R. C. In vivo nitrate reduction in relation to nitrate uptake, nitrate content, and in vitro nitrate reductase activity in intact barley seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):519–522. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. A. Nitrate Reduction by Chlorella. Plant Physiol. 1953 Jul;28(3):539–544. doi: 10.1104/pp.28.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant B. R. The effect of carbon dioxide concentration and buffer system on nitrate and nitrite assimilation by Dunaliella tertiolecta. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):327–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komor E. Proton-coupled hexose transport in Chlorella vulgaris. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 15;38(1):16–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80501-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komor E., Tanner W. The hexose-proton cotransport system of chlorella. pH-dependent change in Km values and translocation constants of the uptake system. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Nov;64(5):568–581. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.5.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyra C. A., Hageman R. H. Nitrate uptake and induction of nitrate reductase in excised corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1975 Nov;56(5):692–695. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.5.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


