Abstract
Introduction
Individuals with aphasia symptoms due to neurodegenerative disease are under-referred for speech–language therapy (SLT) services. We sought to determine the feasibility of utilizing telepractice, via Internet videoconferencing, to connect individuals with progressive aphasia to a speech–language pathologist (SLP) for treatment.
Methods
Participants received an initial evaluation, 8 person-centered Internet-based SLT sessions, and 2 post-therapy evaluations. The feasibility of providing Web-based SLT, strategies used and their compliance, functional gains, and the duration of benefit were assessed.
Results
Thirty-four participants from 21 states and Canada were enrolled. Thirty-one participants completed the 6-month evaluation. SLP-assessed and self-reported functional gains and increased confidence in communication were documented at 2 months and maintained at 6 months postenrollment.
Discussion
Internet-based SLT using person-centered interventions provides a feasible model for delivering care to individuals with dementia and mild and/or moderate aphasia symptoms who have an engaged care-partner and prior familiarity with a computer.
Keywords: Primary progressive aphasia, Frontotemporal dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Speech–language pathology, Apraxia of speech
1. Introduction
Language impairment (aphasia) is a common symptom in clinical dementia of the Alzheimer's type (DAT) and is the defining feature of primary progressive aphasia [1], [2] (PPA). There is currently no cure for DAT or PPA; however, initial research suggests speech–language therapy (SLT) may enhance quality of life (for reviews, see [3], [4], [5]). Despite positive research, individuals with aphasia because of dementia are under-referred for SLT services [6], [7]. This may be in part because of a lack of evidenced-based data and formal training for speech–language pathologists (SLPs) for providing SLT to individuals with dementia [8]. Additionally, there is the misconception [3], [9], [10] that SLT services are not appropriate for individuals with neurodegenerative syndromes because of its progressive nature and the heterogeneity of language and other cognitive symptoms among individuals. As a result, evidence-based research on the effectiveness of SLT in dementia has been limited to small group and case studies. This study was designed to circumvent both geographic limitations and poor access to care by delivering Internet-based SLT for individuals with progressive aphasia through a personalized, interactive, Web application.
The primary goal was to determine if Internet-based delivery of SLT was feasible for individuals with progressive aphasia symptoms. The SLT intervention focused on three primary areas: 1) impairment-based approaches (i.e., targeting lexical retrieval and motor speech production of personally relevant words) integrated into a home exercise program; 2) activity and/or participation strategies to facilitate communication in daily life; and 3) disease education, counseling, and care-partner training. Home exercises were used to support the intervention sessions. Each of these three components occurred throughout the treatment sessions because this model resembles the clinical setting. Rationale for including these components is supported by the previous studies (e.g., see Holland et al. [11] and Murray [12]) and by Croot et al. [3] who acknowledge that care for individuals with progressive language decline will need to be comprehensive, including combined approaches. The goal of this study is not to determine which component produces better outcomes, but instead is guided by the notion that each component is essential for providing clinical care for individuals with progressive aphasia.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
Thirty-four participants with a clinical diagnosis of dementia due to neurodegenerative disease (e.g., PPA) and prominent aphasia symptoms and their care partners were enrolled. Participants were required to have a diagnosis of dementia (progressive decline from a prior level in one or more cognitive and/or behavioral domains [e.g., memory, language], to the extent that activities of daily living were impacted) and a prominent aphasia [13]. The root diagnosis of PPA was made on the basis of isolated and progressive language impairment according to the research criteria [1], [2], [14]. Participants provided medical records to confirm the clinical diagnoses.
Care partners were encouraged to be present during each treatment session. Three SLPs provided treatment for this study. One SLP was assigned to each participant who completed all SLT evaluations and treatment sessions. Trained research assistants administered neuropsychological tests, a post-therapy interview, and provided technical support.
2.2. Standard protocol approvals, registrations, and patient consents
Participants were recruited from the Northwestern University PPA Research Program, Clinicaltrials.gov, clinical referral, and the Cognitive Neurology and Alzheimer's Disease Center (CNADC) Web site (www.brain.northwestern.edu). The Institutional Review Board of the Northwestern University approved the study. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant.
2.3. Visit components
Participants received an initial evaluation, eight 1-hour Internet videoconference treatment sessions with an SLP, followed by two evaluations (2- and 6-month postenrollment) to determine the duration of therapy benefit. Initial and 6-month evaluations occurred in-person at the CNADC to establish rapport and to complete neuropsychological testing. The 2-month evaluation and eight treatment sessions occurred via Internet videoconferencing.
The initial evaluation included three components: 1) informed consent, demographics, neuropsychological testing, and questionnaires (described subsequently); 2) initial SLP evaluation; and 3) an orientation session for the Communication Bridge Web application.
The 2-month evaluation had three components: 1) completion of questionnaires (described subsequently); 2) SLP evaluation via Internet videoconferencing; 3) semistructured post-therapy interview to assess participant and/or care-partner satisfaction.
The 6-month evaluation included the same neuropsychological measures and questionnaires as the initial evaluation. Participants also received an assessment by the SLP, which was identical to the 2-month evaluation, except it was in-person.
2.3.1. SLP evaluations
The initial evaluation included a review of standardized test scores to determine participant profile of expressive and/or receptive language strengths and weaknesses; person-centered, structured interview and appraisal of different language domains including the participant's self-reported areas of communication challenge; and counseling and disease education for the participant and care partner.
The 2- and 6-month evaluations included an assessment of language domains targeted in treatment (e.g., personally relevant word accuracies); an assessment of which of the recommended strategies the participant was using in daily life via participant and care-partner report; and modifications to strategies and home exercises, based on the participant's changing needs.
2.4. The Communication Bridge Web application
An important component of the study was the use of the personalized Communication Bridge Web application, developed in collaboration with Northwestern University's Center for Behavioral Intervention Technologies (http://cbits.northwestern.edu/). An account was created for each participant so that the content of the Web application could be personalized.
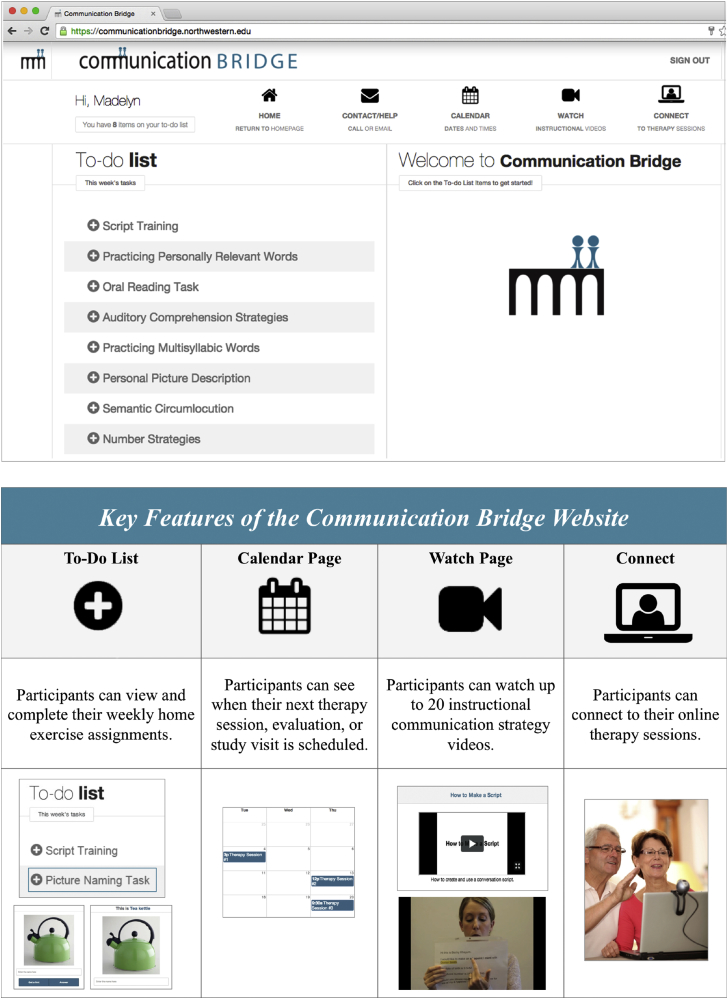
Fig. 1 shows an example homepage and key features. The “To-Do List,” located on the home screen, was updated weekly with SLP-assigned home exercises. The “Watch Page” featured instructional SLT strategy videos to reinforce strategies (e.g., Use of Semantic Circumlocution in Conversation and Practicing Personally Relevant Words), which were assigned on the participant's weekly To-Do List. Participants clicked a link on the “Calendar” or “Connect” pages to start videoconferencing sessions.
Fig. 1.
An example of the personalized Communication Bridge Web application homepage (top) and its key features (bottom).
2.5. Treatment approach
The intervention session regimen included impairment-based approaches, activity- and/or participation-based approaches, and ongoing disease education, counseling, and support. These were all personalized to the needs of each participant and family (i.e., person-centered care) [3], [15], [16], [17]. Impairment-directed interventions target areas of weakness in a rehabilitation approach to improve function in a specific cognitive domain (e.g., improving lexical retrieval for targeted words). Activity- and/or participation-based interventions, in comparison, aim to increase an individual's ability to participate in desired life activities through the use of compensatory strategies and care-partner training on appropriate cueing techniques (e.g., using a communication wallet). All impairment-based and activity- and/or participation-based interventions used in this pilot study were evidence-based interventions that have been previously established for stroke-induced aphasia. During treatment, feedback from both the participant and the care partner was elicited weekly by the SLP to ensure that strategies were understood and implemented appropriately. Modifications to strategies and further education were provided throughout the course of treatment to ensure care partners and participants gained independence in implementing the strategies in daily life. Strategies were initially introduced during structured language tasks (e.g., rehearsing a telephone script) and then gradually applied to functional contexts to promote generalization (e.g., using a script during a telephone call). This model of individualized care is consistent with the Life Participation Approach for Aphasia [17], [18], [19] and the CARE pathway model [16]. Both of these models recognize the importance of identifying each individual's challenges to tailor interventions to their needs. The rationale for our person-centered approach is to maximize impact on the participant's quality of life by teaching strategies that can be implemented in everyday life situations.
After each SLT session, the SLP-assigned home exercises. These exercises were listed under the To-Do List (e.g., Fig. 1) of the participant's personalized Communication Bridge homepage. Participants were encouraged to practice at least three times per week.
2.6. Outcome measures
The outcome measures were administered to each participant allowing for quantification of within-subject gains and comparisons at the group level while providing personalized therapy, which acknowledges the variability of language deficit profiles across participants.
Functional communication was assessed at the initial and 2- and 6-month evaluations with the American Speech–Language–Hearing Association functional communication measures (ASHA-FCM) [20] and the Communication Confidence Rating Scale for Aphasia (CCRSA) [21].
The ASHA-FCM measures the participant's level of functioning for different cognitive-communication domains (e.g., expressive language, writing, and so forth), using a 7-point scale, with higher numbers indicating better functioning. This scale corresponds with Medicare claims-based reporting requirements. As in the clinical setting, the SLP identified the participant's most challenging domain in daily life at the initial evaluation and appraised their level of functioning for that domain at each evaluation (i.e., assessing lexical retrieval accuracies and the level of cueing needed for the expressive language domain).
The CCRSA was used to assess confidence, using a 100-point scale (0 [not confident] to 100 [very confident]), in response to 10 questions that address different communication situations (e.g., “How confident do you feel about your ability to talk with family or friends?”).
A semistructured post-therapy interview was completed to assess participant and care-partner satisfaction with Internet-based therapy and the Web application and to determine if the treatment had any impact on their quality of life.
For each participant, the therapist documented strategy recommendations and whether the participant was using the strategies in their daily lives (i.e., compliance) at the 6-month evaluation. Compliance was determined based on the SLP evaluation and self-report from the participant and care partner. These data were used to determine which therapy approaches were assigned and used over time for each participant and if there were gains.
Data will be presented for two of the most commonly recommended interventions: lexical retrieval and motor speech production strategies. For this intervention, the SLP asked participants and their care partners to identify personally relevant words that were challenging to retrieve or pronounce in daily conversations. Participants were unable to independently retrieve or accurately pronounce these target words before starting the home exercise program. Participants were encouraged to provide personal pictures of target words rather than stock photos; they could also write a description of the word if no picture was available or if the word was not easily represented by a picture. A home exercise program was developed for each participant. The lexical retrieval program focused on use of a hierarchical cueing approach, where a series of semantic, phonological, and orthographic cues were systematically presented until the participant was able to retrieve the target word [22]. For motor speech production, evidence-based interventions used for stroke-induced apraxia were applied to promote successful motor sequencing of personally relevant multisyllabic words. The participant was presented with maximal visual cues for each target word to promote production (e.g., syllable segmentation and orthographic phonetic cues, in addition to visual and/or audio cues from a care partner or recording when needed) [23]. Participants were assigned a lexical retrieval home program, a motor speech home program, or both depending on their symptoms.
A subset of their personally relevant target words were evaluated by the SLP at the 2- and 6-month evaluations. For each word, either motor speech production or lexical retrieval accuracy was assessed. For assessment of lexical retrieval, the SLP provided participants with verbal descriptions of their personally relevant target words to elicit oral production, and accuracy was determined by whether the individual could independently retrieve the target word, without semantic, phonemic, or orthographic cues being provided by the care partner or SLP. For assessment of motor speech production, the written form of the target word was presented to the participant to elicit an oral production; accuracy was based on intelligibility, measured by whether the SLP could accurately understand the word during testing (rather than based on exact percentage of correct syllables).
2.7. Statistical analysis
Mean scores on the CCRSA across the three time points were analyzed with a repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by pairwise post hoc t tests, with a Tukey adjustment for multiple comparisons. We expected improvement on the CCRSA between baseline and 2 months and maintenance of gains at 6 months. For the ASHA-FCM, we quantified the number of participants who declined, improved, or maintained at the 2- and 6-month evaluations compared with their initial evaluation.
To determine which strategies might be useful for future interventions for individuals with dementia, the most frequently assigned strategies were identified and their compliance of whether they were being used was tracked (via self-report) at the 6-month evaluation. Therapy strategy compliance over time was measured for each strategy category (no. of participants using the strategy at 6 months/no. of participants assigned the strategy during the treatment sessions) and summarized as a percentage for each participant.
3. Results
Of the 34 participants, 2 discontinued because of severity and 1 because of noncompliance and inadequate computer abilities. Thus, 31 individuals with early-to-mid-stage dementia and their care partners were included in this analysis (Table 1). All participants were fluent in English. Twenty-seven of the care partners were spouses, two were adult children, one was a niece, and one was a friend. Participants enrolled from 21 different states and Canada.
Table 1.
Demographic, clinical, and neuropsychological characteristics
| No. of participants | 31 | |
| Age at onset, years | 62.5 (6.8) | Range: 53–76 |
| Age at enrollment, years | 67.2 (6.9) | Range: 56–83 |
| Gender | Male: 13 | Female: 18 |
| Handedness | Right: 30 | Left: 1 |
| Education, years | 16.1 (2.4) | |
| Symptom duration, years | 4.3 (2.2) | |
| Clinical diagnosis |
PPA: 28 |
Other dementia diagnosis: 3 |
| Initial evaluation |
6-Month evaluation |
|
| WAB-R-AQ (%) | 81.3 (13.9)* | 76.7 (17.5) |
| MMSE (out of 30) | 24.1 (5.0) | 23.7 (5.5) |
| BNT (%) | 60.9 (29.5)∗ | 54.7 (31.0) |
Abbreviations: BNT, Boston Naming Test; MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination; PPA, primary progressive aphasia; WAB-R-AQ, Western Aphasia Battery Revised.
NOTE. Numbers are provided as means (standard deviations [italicized]). Other dementia diagnosis consisted of one person with prominent apraxia of speech, one with apathy and aphasia, and one with aphasia, working memory, and processing speed deficits. Clinician-rated aphasia severity is based on the initial evaluation. All participants were fluent in English. English was the native language for 29 of the participants. Spanish and Arabic were the native languages for the other two participants. The aphasia quotient from the WAB-R-AQ was used as a global measure of aphasia severity [31]. The BNT was used to assess the naming of objects [32]. Because of participant language deficits, a modified multiple-choice version of the MMSE [33] was used for 12 individuals at the initial evaluation and 20 individuals at the 6-month evaluation.
Pairwise t tests indicated significant decline (P < .05).
3.1. Feasibility and functional outcomes
Participant, care partner, and therapist feedback were overwhelmingly positive with 16 participant and/or care-partner pairs reporting that therapy ‘exceeded’ expectations.
Thirty of the 31 individuals completed the post-therapy interview. During the post-therapy interview, participants and their care partners were asked “If you could change anything about the Web-based therapy sessions, what would you change?.” The most common response was “nothing,” followed by “add more therapy sessions” (37% and 20% of the participants, respectively).
Expressive language was the most commonly identified domain that was impaired and targeted (n = 24 of 31) in the ASHA-FCM. All participants maintained or improved their level of functioning in their most challenging domain as measured by the ASHA-FCM from the initial evaluation to 2 months (65% improved and 35% maintained). At the 6-month evaluation, only 13% declined by one level on the ASHA-FCM compared with the initial evaluation.
A repeated-measures ANOVA showed significant change in CCRSA scores across the three evaluations (P = .02). Post hoc t-tests revealed significant improvement in their confidence in communication from baseline to the 2 months (mean scores at baseline = 68.2 ± 2.7, 2 months = 73.3 ± 2.6, P = .018) and no significant decline at 6 months (mean score = 70.9 ± 2.9, P > .4).
3.2. SLT interventions: Gains and compliance
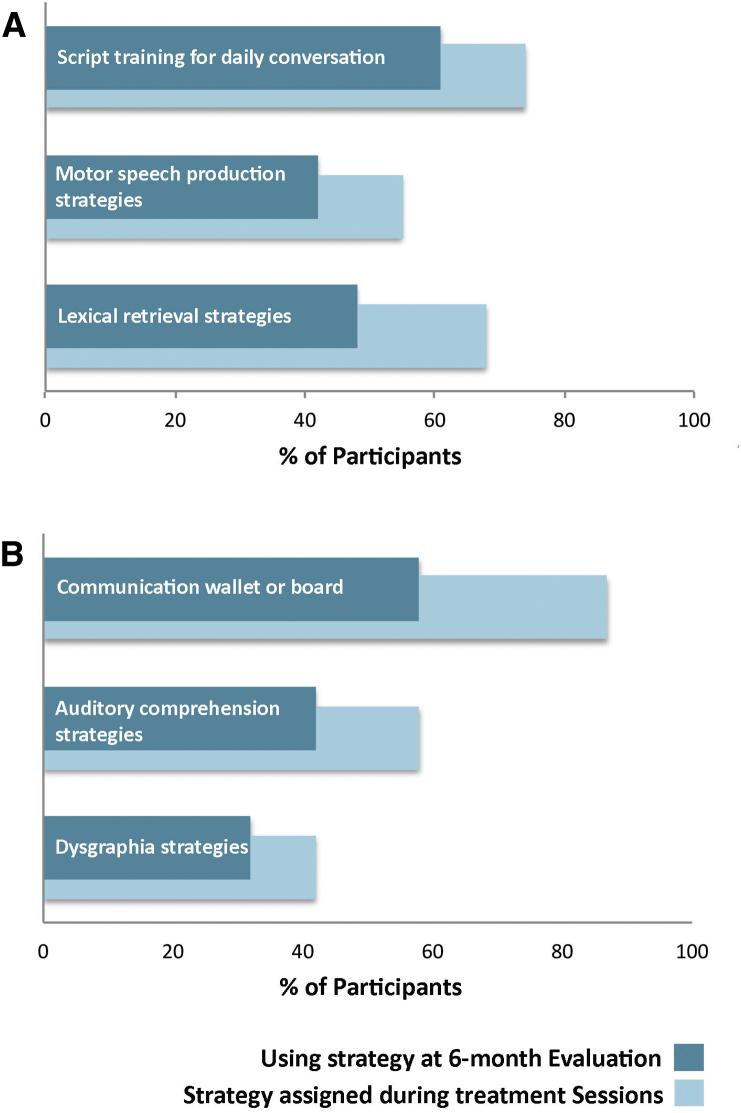
The three most frequent impairment-directed interventions were 1) lexical retrieval program for personally relevant words; 2) motor speech production program for personally relevant words; and 3) script training tasks to facilitate daily conversations (e.g., ordering at a restaurant, describing your condition to others). The three most common activity- and/or participation-directed interventions included 1) creation of personalized communication wallets and boards; 2) functional writing strategies, including use of assistive technology and/or apps; and 3) auditory comprehension strategies for daily conversations, including participant and care-partner education on how to eliminate environmental distractions and how to increase the use of positive communication strategies (e.g., slowing speech rate and repetition). Table 2 provides descriptions of these strategies. Overall, compliance for the six most commonly assigned strategy categories was good; 74% of those assigned during therapy were still being used at 6 months (range: 67%–83%, see Fig. 2 for the percentage of individuals assigned each strategy category and their compliance at the 6-month evaluation).
Table 2.
Description of the most commonly used interventions
| Description of strategy | |
|---|---|
| Impairment-based interventions | |
| Lexical retrieval of personally relevant words | Participants used personally relevant picture or word-based flashcards to target active encoding of target words. Treatment focused on use of a hierarchical cueing approach, where a series of semantic, phonological, and orthographic cues were systematically presented until the participant was able to retrieve the target word [22]. |
| Motor speech production of personally relevant words | Participants used paper-based flashcards with orthographic cues to rehearse motor speech production of words that were difficult for them to pronounce. The participant was presented with maximal visual cues for each target word to promote production (e.g., syllable segmentation, orthographic phonetic cues, in addition to visual and/or audio cues from a care partner or recording when needed) [23]. Cues were systematically removed as pronunciation improved (i.e., modified version of Rosenbeck eight-step program). |
| Script training for daily conversation | Participants developed written scripts to facilitate speech for specific functional contexts (e.g., answering the phone, describing their condition to friends or strangers, and so forth). Scripts were orally rehearsed to increase automaticity in functional contexts. |
| Activity- and/or participation-based interventions | |
| Communication wallets and/or boards for daily conversation | Participants created low-tech electronic or paper-based communication aids that were word based and/or picture based using personally relevant stimuli. |
| Auditory comprehension strategies for daily conversation | Participants were educated to make environmental modifications (e.g., eliminating environmental distractions). Care partners received training on increased use of positive communication strategies (e.g., repetition, use of orthographic, or picture cues). |
| Dysgraphia strategies for functional use in daily conversation | Participants and care partners were trained to use paper-based (e.g., pocket dictionary and templates and/or visual aids) and technology-based (e.g., spell and/or grammar checks on word processing programs, voice-recognition technology to dictate words to aid in spelling ability, and word-prediction technology) supports for functional writing tasks in daily life. |
Fig. 2.
The most frequently assigned and used speech–language therapy strategies. (A) Percentage of participants assigned and using their impairment-directed strategies at the 6-month evaluation. Script training was assigned to 23 of 31 participants and 19 of those participants were still using the strategy at the 6-month evaluation. Motor speech production strategies were assigned to 17 of 31 participants and 13 of those participants were still using the strategy at the 6-month evaluation. Lexical retrieval strategies were assigned to 21 of 31 participants, and 15 of those participants were still using the strategy at the 6-month evaluation. (B) Percentage of participants assigned and using their activity- and/or participation-directed strategies at the 6-month evaluation. Communication wallets or boards were assigned to 27 of 31 participants, and 18 of those participants were still using the strategy at the 6-month evaluation. Auditory comprehension strategies were assigned to 18 of 31 participants, and 13 of those participants were still using the strategy at the 6-month evaluation. Dysgraphia strategies were assigned to 13 of 31 participants, and 10 of those participants were still using the strategy at the 6-month evaluation.
Lexical retrieval and/or motor speech production interventions targeting personally relevant words were assigned for 29 of 31 individuals (lexical retrieval alone: 12 of 31, motor speech production alone: 8 of 31, and both lexical retrieval and motor speech production: 9 of 31). Participants identified words (range: 10–150 words per participant) that were difficult to retrieve or pronounce during conversation in daily life and the SLP-probed accuracy of a subset of these words at the post-treatment evaluations. Because the number of words targeted and probed (range: 5–47 probed words) differed by participant, the average accuracy was summarized as a percent correct. Average accuracy for lexical retrieval was 87% ± 13 at the 2-month evaluation and 84% ± 19 at the 6-month evaluation. Average accuracy for motor speech production was 89% ± 9 at the 2-month evaluation and 81% ± 13 at the 6-month evaluation. For participants where both lexical retrieval and production was targeted the average accuracy was 80% ± 17 at the 2-month evaluation and 90% ± 10 at the 6-month evaluation (personally relevant words were not assessed for one participant at 6 months).
4. Discussion
This pilot study used a novel Internet-based delivery of SLT strategies and dementia education for individuals with progressive aphasia and their care partners. The feasibility of using the Internet to connect an individual with a dementia diagnosis to an SLP has rarely been documented in neurodegenerative disease and is currently not reimbursed by Medicare or most health insurance policies. Our results suggest that Web-based SLT is feasible and that some statistically significant gains (e.g., in communication confidence) can be made after eight (weekly) sessions. Therapy reached participants in 21 states and Canada, highlighting that an Internet-based model of therapy has the potential to improve access to care.
Our focus on functional goals is desirable because it allows for the inclusion of individuals with different language deficit profiles (e.g., naming and grammar deficits) and levels of symptom severity and identifies optimal strategies according to the participant's communication strengths and weaknesses. It also allowed us to gain experience with the delivery of the Internet-based intervention among participants with progressive aphasia. One challenge with this model is it makes it difficult to isolate which treatment strategy is contributing to functional gains. Several participants reported improvements in completing functional daily tasks they had abandoned. Scripts enabled one participant to order food at a favorite restaurant. Another participant was able to generate her own paper To-Do List with the use of assistive speech recognition technology to aid with spelling. Systematic assessment of functional gains in daily life may be an important quantitative measurement for future studies.
Results from this pilot study are consistent with the preliminary reports indicating that SLT strategies are useful for individuals with dementia [24], [25], [26], [27], [28], [29], [30]. Participants with different language deficit profiles and individuals with mixed or unclassified dementia diagnosis were able to participate and benefit from SLT, suggesting this approach may be useful across dementia phenotypes. The most severe participant in this study discontinued participation, suggesting that Web-based SLT may be most feasible for mild- or moderate-stage dementia.
Evidence-based approaches traditionally used for stroke aphasia or speech apraxia were modified and helpful irrespective of the clinical language profile. For example, elements from the treatment approach of Rosenbeck et al. [23] were used to successfully facilitate pronunciation of personally relevant multisyllabic words for not only individuals with an agrammatic profile displaying motor-sequencing errors but also for individuals displaying phonological errors.
Many participants reported that they enjoyed working on their home exercises. The care partner of a participant who practiced their personally relevant words almost daily reported at the 2-month evaluation: “I really did see an improvement in those words …” referring to the personally relevant words. “Overall compared to where he was, it's better. I think that his speech impairment, the way it was going, I think this halted it. Today compared to 6 months ago, he's better.” It will be important to identify whether the frequency with which individuals practice their home exercises influence outcomes.
Several participants provided unsolicited feedback that the strategy videos available on the Web application were helpful, with >600 views among participants. One participant reported the videos were particularly useful for home exercises with several steps because “it was easier to recall the details of the exercise with the videos.” Another participant used the “How to create a communication book” video to successfully create a communication notebook 10 months after their last session. Systematic tracking of video views and usage by participant may be useful to determine if they promote increased functional gains.
An advantage of Web-based SLT was the flexibility of location. SLT could occur anywhere with strong Internet, avoiding logistical challenges (e.g., transportation and geographic) associated with an outpatient clinic. Some participants completed sessions while on vacation (e.g., Europe and Hawaii). Likewise the therapist completed sessions when she had a cold because there was no risk of spreading germs.
Our Web-based SLT program had some limitations. Video and/or audio quality was suboptimal in some sessions. Increasing Internet speed and/or using a hardline connection resolved most of these issues. Having prior familiarity with a computer was essential. During the course of the study, we implemented a brief technology screening, which helped to identify participants with adequate computer skills for participation.
As a first step to determine feasibility of providing personalized Web-based care, a within-subject design and outcome measures that were common across the group was used rather than a randomized control design. In future trials, it will be important to document gains from the participants, their therapists, and blinded raters to minimize bias and also to establish a stable baseline for all personally relevant target words. Use of an appropriate control condition in future studies will help disentangle whether the gains reported here are because of the intervention or increased stimulation and engagement.
Care-partner participation was common (77% [n = 24 of 31] of the care partners were consistently present at the intervention sessions). However, their level of engagement varied. SLPs commented that actively engaged care partners were beneficial to treatment. Systematic ratings of the level of care-partner engagement in the treatment may be an important variable to include in future trials because it may influence outcomes. The SLPs reported that at times participants and/or their care partners became emotional and/or tearful during sessions and felt that the inability to provide a consoling personal touch was a limitation to Web-based SLT.
In the absence of a cure for neurodegenerative diseases, it is important to offer interventions that help individuals maintain an optimal quality of life and full-life participation for as long as possible. Data from this study suggest Internet-based SLT using person-centered impairment-directed and activity- and/or participation-based interventions and disease education provides a feasible method for improving access to care for individuals with mild and/or moderate aphasia symptoms who have an engaged care-partner and prior familiarity with a computer. Improving access to SLT care is important because it may contribute to prolonging the period of independence for the individual with a dementia diagnosis and decrease care-partner burden.
Research in Context.
-
1.
Systematic review: The existing literature was reviewed (e.g., PubMed, Google Scholar) and is cited in the article. Most speech–language therapy (SLT) studies for individuals with dementia have been case or small group reports, and none provide SLT over the Internet.
-
2.
Interpretation: Our results provide initial evidence that person-centered Internet-based SLT is feasible for improving access to supportive services for individuals with mild and/or moderate aphasia symptoms because of dementia who have an engaged care-partner and prior familiarity with a computer.
-
3.
Future directions: A substantial To-Do List remains and includes a randomized controlled trial. Collectively, these data can be used to create guidelines for best practices in intervention and management for individuals with dementia.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Smita Mahajan who was the SLP for some of the participants and Amanda Rueter who designed the Communication Bridge logo. E.J.R. had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. E.J.R. and A.R. conducted and are responsible for all data analyses for this study. This project was supported by DC008552 from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (M.-M.M.); AG13854 (Alzheimer Disease Center) from the National Institute on Aging (M.-M.M.); NS075075 from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) (E.J.R.); the Alzheimer's Association (E.J.R.); and the Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration (E.J.R.), this is not an industry-sponsored study. B.K. is the President of MemoryCare Corporation, and K.B. is an employee of MemoryCare Corporation. The authors have no additional disclosures to report.
References
- 1.Mesulam M.M., Rogalski E.J., Wieneke C., Hurley R.S., Geula C., Bigio E.H. Primary progressive aphasia and the evolving neurology of the language network. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014;10:554–569. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mesulam M.M. Primary progressive aphasia: a language-based dementia. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1535–1542. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra022435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Croot K., Nickels L., Laurence F., Manning M. Impairment- and activity/participation-directed interventions in progressive language impairment: clinical and theoretical issues. Aphasiology. 2009;23:125–160. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Carthery-Goulart M.T., da Silveira A.D., Machado T.H., Mansur L.L., Parente M.D., Senaha M.L. Nonpharmacological interventions for cognitive impairments following primary progressive aphasia. Demen Neuropsychol. 2013;7:121–131. doi: 10.1590/S1980-57642013DN70100018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Murray L.L., Paek E.J. Behavioral/nonpharmacological approaches to addressing cognitive-linguistic symptoms in individuals with dementia. Perspect ASHA Spec Interest Groups. 2016;1:12–25. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Taylor C., Kingma R.M., Croot K., Nickels L. Speech pathology services for primary progressive aphasia: exploring an emerging area of practice. Aphasiology. 2009;23:161–174. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Riedl L., Last D., Danek A., Diehl-Schmid J. Long-term follow-up in primary progressive aphasia: clinical course and health care utilisation. Aphasiology. 2014;28:981–992. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Douglas N.F., Hinckley J.J., Haley W.E., Andel R., Chisolm T.H., Eddins A.C. Perceptions of speech-language pathologists linked to evidence-based practice use in skilled nursing facilities. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2014;23:612–624. doi: 10.1044/2014_AJSLP-13-0139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nickels L., Croot K. Progressive language impairments: intervention and management. Aphasiology. 2009;23:123–124. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kortte K.B., Rogalski E.J. Behavioural interventions for enhancing life participation in behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia and primary progressive aphasia. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2013;25:237–245. doi: 10.3109/09540261.2012.751017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Holland A.L., McBurney D.H., Moossy J., Reinmuth O.M. The dissolution of language in Pick's disease with neurofibrillary tangles: a case study. Brain Lang. 1985;24:36–58. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(85)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Murray L.L. Longitudinal treatment of primary progressive aphasia: a case study. Aphasiology. 1998;12:651–672. [Google Scholar]
- 13.McKhann G.M., Knopman D.S., Chertkow H., Hyman B.T., Jack C.R., Jr., Kawas C.H. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:263–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gorno-Tempini M.L., Hillis A.E., Weintraub S., Kertesz A., Mendez M., Cappa S.F. Classification of primary progressive aphasia and its variants. Neurology. 2011;76:1006–1014. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31821103e6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.American Geriatrics Society Expert Panel on Person-Centered Care Person-Centered Care: A Definition and Essential Elements. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016;64:15–18. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Morhardt D., Weintraub S., Khayum B., Robinson J., Medina J., O'Hara M. The CARE pathway model for dementia: psychosocial and rehabilitative strategies for care in young-onset dementias. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2015;38:333–352. doi: 10.1016/j.psc.2015.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kagan A., Simmons-Mackie N., Rowland A., Huijbregts M., Shumway E., McEwen S. Counting what counts: a framework for capturing real-life outcomes of aphasia intervention. Aphasiology. 2008;22:258–280. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kagan A., Simmons-Mackie N. Beginning with the end: outcome-driven assessment and intervention with life participation in mind. Top Lang Disord. 2007;27:309–317. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Simmons-Mackie N., Damico J.S. Intervention outcomes: a clinical application of qualitative methods. Top Lang Disord. 2001;22:21–36. [Google Scholar]
- 20.American Speech-Language-Hearing Association . National Center for Evidence-Based Practice in Communication Disorders; Rockville, MD: 2009. National Outcomes Measurement System: Adults in Healthcare - Inpatient National Data Report 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cherney L.R., Babbitt E.M., Semik P., Heinemann A.W. Psychometric properties of the communication Confidence Rating Scale for Aphasia (CCRSA): phase 1. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2011;18:352–360. doi: 10.1310/tsr1804-352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Henry M.L., Rising K., DeMarco A.T., Miller B.L., Gorno-Tempini M.L., Beeson P.M. Examining the value of lexical retrieval treatment in primary progressive aphasia: two positive cases. Brain Lang. 2013;127:145–156. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2013.05.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rosenbek J.C., Lemme M.L., Ahern M.B., Harris E.H., Wertz R.T. A treatment for apraxia of speech in adults. J Speech Hear Disord. 1973;38:462–472. doi: 10.1044/jshd.3804.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Beeson P.M., King R.M., Bonakdarpour B., Henry M.L., Cho H., Rapcsak S.Z. Positive effects of language treatment for the logopenic variant of primary progressive aphasia. J Mol Neurosci. 2011;45:724–736. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Henry M.L., Beeson P.M., Alexander G.E., Rapcsak S.Z. Written language impairments in primary progressive aphasia: a reflection of damage to central semantic and phonological processes. J Cogn Neurosci. 2012;24:261–275. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Henry M.L., Beeson P.M., Rapcsak S.Z. Treatment for anomia in semantic dementia. Semin Speech Lang. 2008;29:60–70. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1061625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rapp B., Glucroft B. The benefits and protective effects of behavioural treatment for dysgraphia in a case of primary progressive aphasia. Aphasiology. 2009;23:236–265. doi: 10.1080/02687030801943054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tsapkini K., Hillis A.E. Spelling intervention in post-stroke aphasia and primary progressive aphasia. Behav Neurol. 2013;26:55–66. doi: 10.3233/BEN-2012-110240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jokel R., Anderson N.D. Quest for the best: effects of errorless and active encoding on word re-learning in semantic dementia. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2012;22:187–214. doi: 10.1080/09602011.2011.639626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Macoir J., Leroy M., Routhier S., Auclair-Ouellet N., Houde M., Laforce R., Jr. Improving verb anomia in the semantic variant of primary progressive aphasia: the effectiveness of a semantic-phonological cueing treatment. Neurocase. 2015;21:448–456. doi: 10.1080/13554794.2014.917683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kertesz A. Pearson Canada Assessment Inc.; Toronto, Ontario: 2006. Western Aphasia Battery—Revised. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kaplan E., Goodglass H., Weintraub S. Lea and Febiger; Philadelphia, PA: 1983. The Boston Naming Test. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Folstein M.F., Folstein S.E., McHugh P.R. “Mini-mental state.” A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12:189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]