Abstract
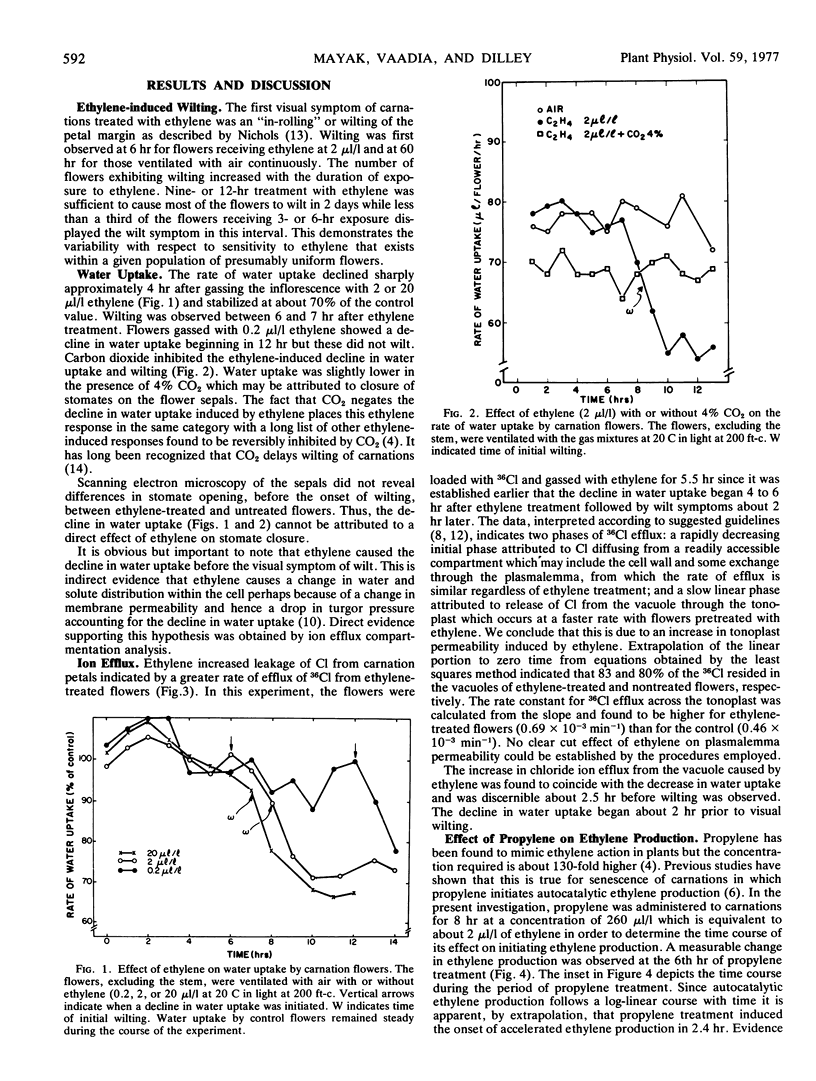
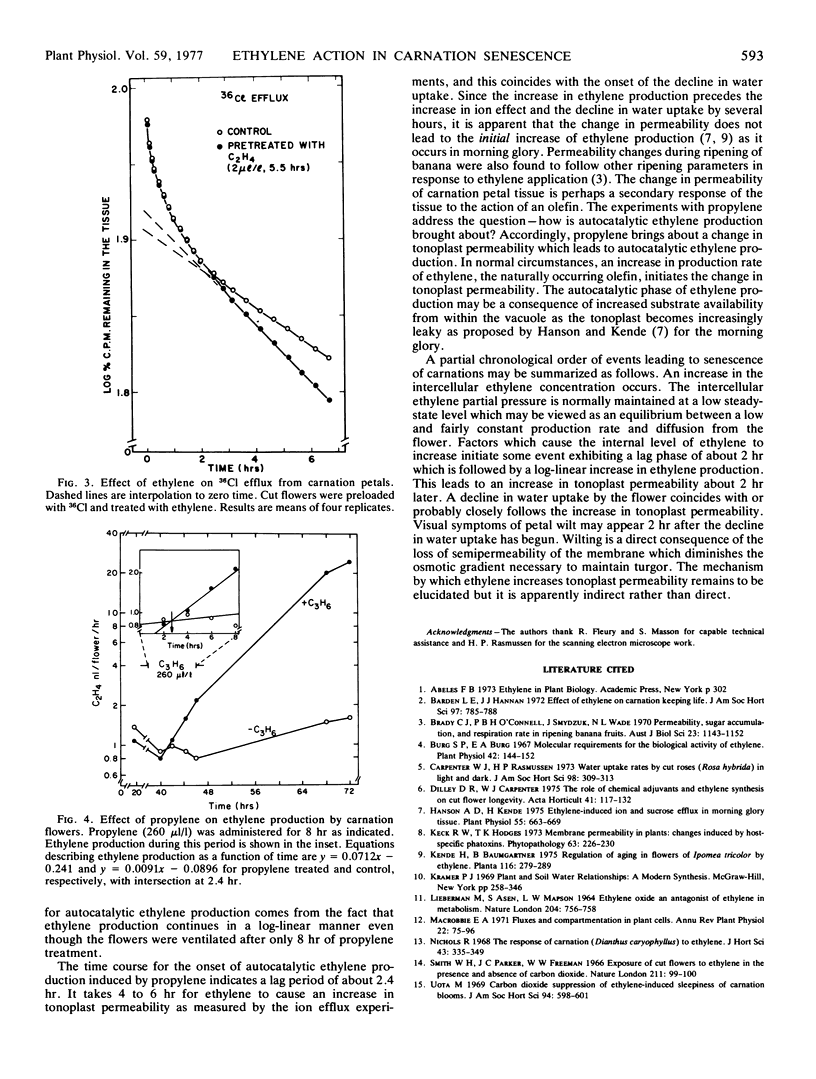
Carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus) flowers were exposed to 2 μl/l ethylene and examined at intervals to determine the time course of wilting, decrease in water uptake, and increase in ionic leakage in response to ethylene. A rapid decrease in water uptake was observed about 4 hours after initiating treatment with ethylene. This was followed by wilting (in-rolling of petals) about 2 hours later. Carbon dioxide inhibited the decline in water uptake and wilting and this is typical of most ethylene-induced responses. Ethylene did not affect closure of stomates. Ethylene enhanced ionic leakage, as measured by efflux of 36Cl from the vacuole. This was judged to coincide with the decrease in water uptake. Gassing flowers with propylene initiated autocatalytic ethylene production within 2.4 hours. Since the increase in ethylene production by carnations preceded the increase in ionic leakage and the decline in water uptake by several hours, it is apparent that the change in ionic leakage does not lead to the initial increase in ethylene production as reported (Hanson and Kende 1975 Plant Physiol 55:663-669) in morning glory but may explain the autocatalytic phase of ethylene production.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burg S. P., Burg E. A. Molecular requirements for the biological activity of ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jan;42(1):144–152. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Kende H. Ethylene-enhanced Ion and Sucrose Efflux in Morning Glory Flower Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):663–669. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallier R. Morphogenetic effects of acidic glycoproteins on the development of sea urchin eggs. Nature. 1966 Jul 2;211(5044):99–99. doi: 10.1038/211099a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


