Abstract
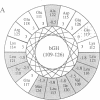
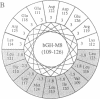
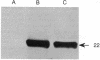
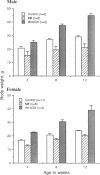
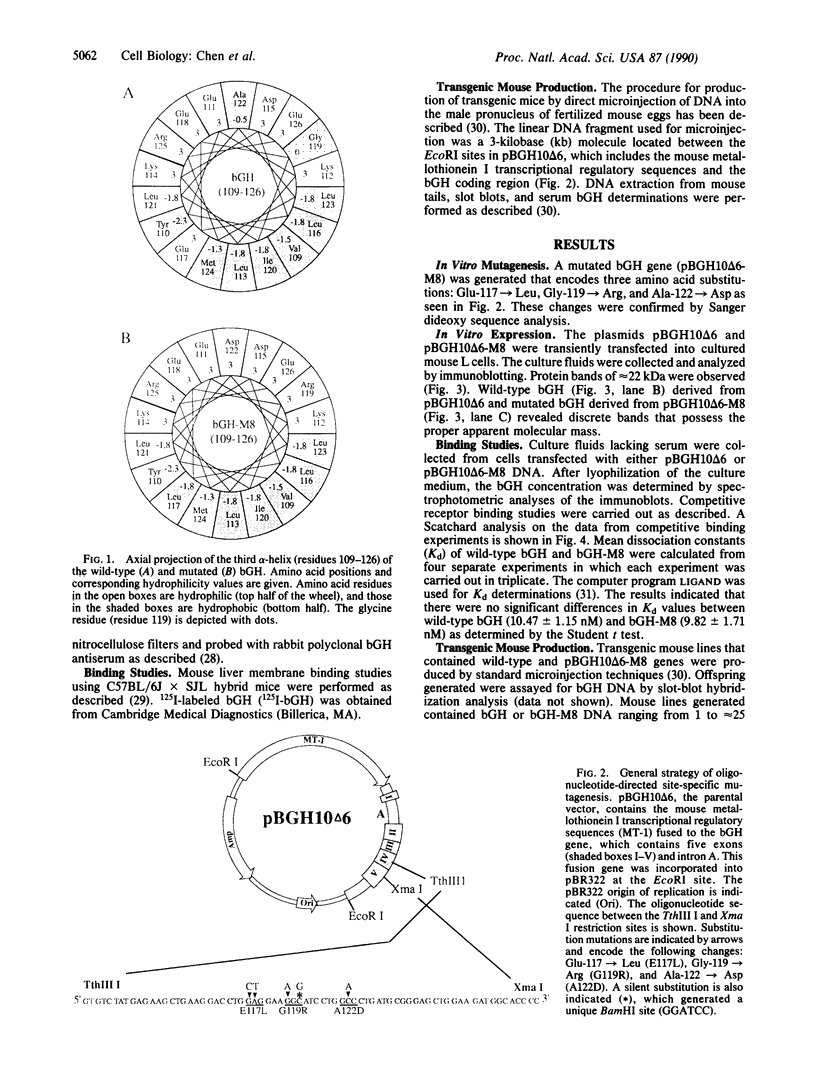
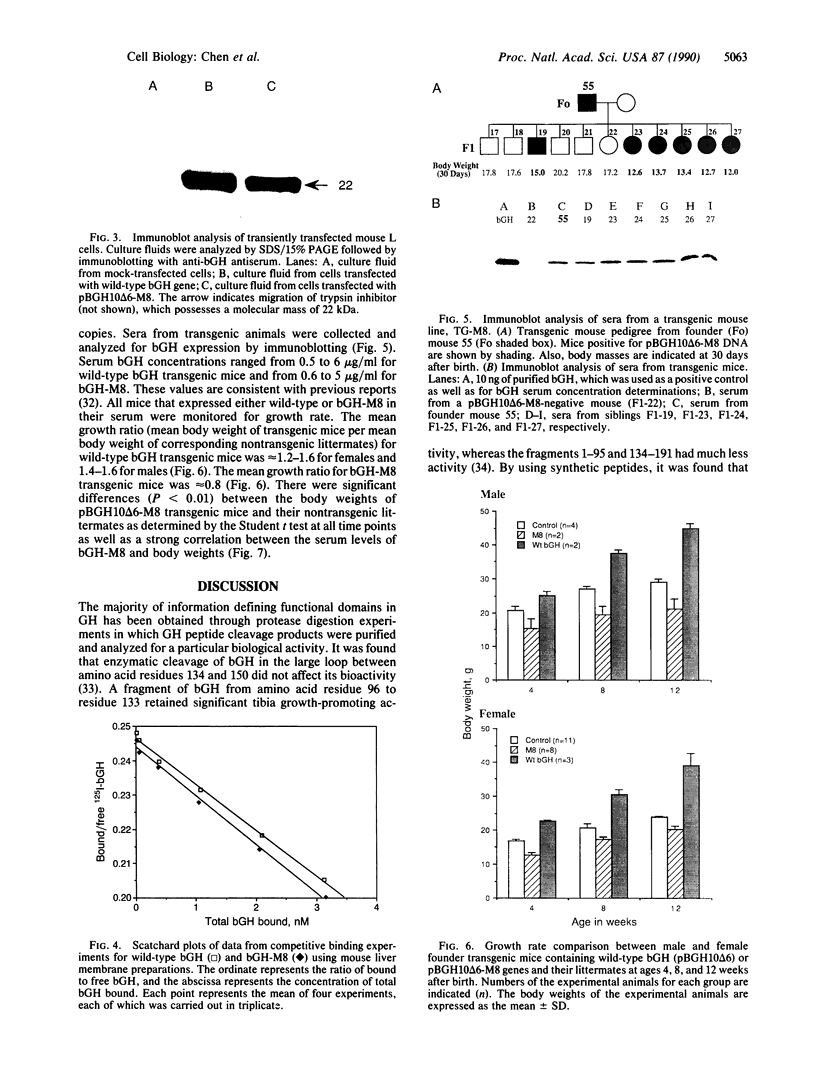
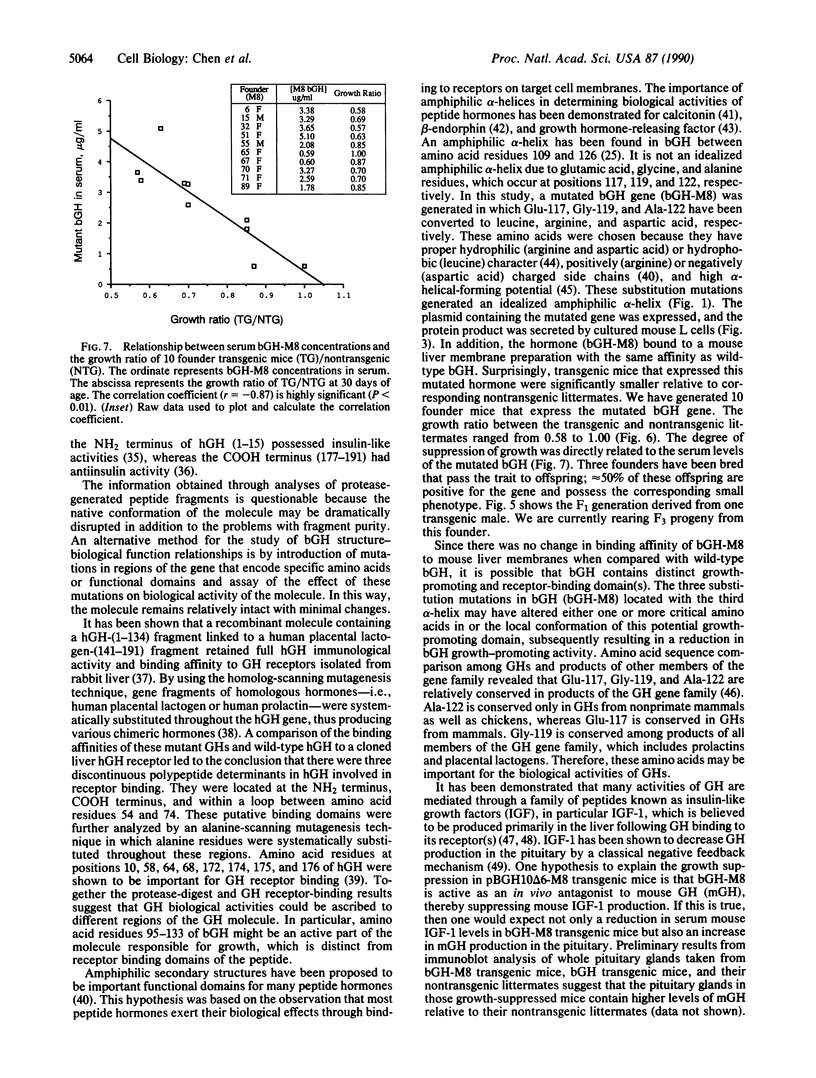
To determine the importance of the third alpha-helix in bovine growth hormone (bGH) relative to growth-related biological activities, the following experimental approach was used: (i) mutagenesis of helix III of bGH to generate an idealized amphiphilic helix; (ii) in vitro expression analyses of the mutated bGH gene in cultured mouse L cells; (iii) mouse liver membrane binding studies of wild-type and mutated bGH; and (iv) expression of the mutated gene in the transgenic mouse. An altered bGH gene (pBGH10 delta 6-M8) was generated that encodes the following changes: glutamate-117 to leucine, glycine-119 to arginine, and alanine-122 to aspartate. The plasmid pBGH10 delta 6-M8 was shown to be expressed in, and its protein product secreted by, mouse L cells. The altered hormone possessed the same binding affinity to mouse liver membrane preparations as wild-type bGH. Transgenic mice containing the mutated bGH gene, however, showed a significant growth-suppressed phenotype. The degree of suppression was directly related to serum levels of the altered bGH molecule.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Shieh H. S., Smith W. W., Dayringer H. E., Violand B. N., Bentle L. A. Three-dimensional structure of a genetically engineered variant of porcine growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6434–6437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Molecular weights of prolactins and pituitary growth hormones estimated by gel filtration. Nature. 1966 Jan 8;209(5019):155–157. doi: 10.1038/209155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brems D. N., Plaisted S. M., Havel H. A., Tomich C. S. Stabilization of an associated folding intermediate of bovine growth hormone by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3367–3371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Jhurani P., Ng P., Wells J. A. Receptor and antibody epitopes in human growth hormone identified by homolog-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1330–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.2466339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Wells J. A. High-resolution epitope mapping of hGH-receptor interactions by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1081–1085. doi: 10.1126/science.2471267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellacha J. M., Enero M. A., Faiferman I. Molecular weight of bovine growth hormone. Experientia. 1966 Jan 15;22(1):16–17. doi: 10.1007/BF01897741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Heyneker H. L., Hozumi T., Arentzen R., Itakura K., Yansura D. G., Ross M. J., Miozzari G., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. Direct expression in Escherichia coli of a DNA sequence coding for human growth hormone. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):544–548. doi: 10.1038/281544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara K., Hsu Chen C. J., Sonenberg M. Recombination of the biologically active peptides from a tryptic digest of bovine growth hormone. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):550–556. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjalmarson A., Ahrén K. Sensitivity of the rat diaphragm to growth hormone. II. Early and late effects of growth hormone on amino acid and pentose uptake. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Oct;56(2):347–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson O. G., Edén S., Jansson J. O. Mode of action of pituitary growth hormone on target cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:483–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J. Amphiphilic secondary structure: design of peptide hormones. Science. 1984 Jan 20;223(4633):249–255. doi: 10.1126/science.6322295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelder B., Chen H., Kopchick J. J. Activation of the mouse metallothionein-I promoter in transiently transfected avian cells. Gene. 1989 Mar 15;76(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyo J. L., Nutting D. F. Acute in vivo effects of growth hormone on protein synthesis in various tissues of hypophysectomized rats and their relationship to the levels of thymidine factor and insulin in the plasma. Horm Metab Res. 1973 May;5(3):167–172. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb I. C., Galehouse D. M., Foster D. N. Chicken growth hormone cDNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9339–9339. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung F. C., Jones B., Steelman S. L., Rosenblum C. I., Kopchick J. J. Purification and physiochemical properties of a recombinant bovine growth hormone produced by cultured murine fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1986 Oct;119(4):1489–1496. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-4-1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis U. J. Variants of growth hormone and prolactin and their posttranslational modifications. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:33–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILMAN A. E., RUSSELL J. A. Some effects of purified pituitary growth hormone on carbohydrate metabolism in the rat. Endocrinology. 1950 Aug;47(2):114–128. doi: 10.1210/endo-47-2-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. B. Neural regulation of growth hormone secretion. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jun 28;288(26):1384–1393. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197306282882606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrane M. M., de Vente J., Yun J., Bloom J., Park E., Wynshaw-Boris A., Wagner T., Rottman F. M., Hanson R. W. Tissue-specific expression and dietary regulation of a chimeric phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase/bovine growth hormone gene in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11443–11451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. Molecular cloning of DNA complementary to bovine growth hormone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7521–7524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe G. R., Kaiser E. T. Design, synthesis, and characterization of a model peptide having potent calcitonin-like biological activity: implications for calcitonin structure/activity. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1971–1976. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng F. M., Bornstein J. Insulin-potentiating action of a synthetic amino-terminal fragment of human growth hormone (hGH 1--15) in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1979 Dec;28(12):1126–1130. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.12.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Norstedt G., Gelinas R. E., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L. Metallothionein-human GH fusion genes stimulate growth of mice. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):809–814. doi: 10.1126/science.6356363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J., Sherwood L. M., Kowalski K., Schneider A. B. Recombinant hormones from fragments of human growth hormone and human placental lactogen. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):296–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWISLOCKI N. I., SZEGO C. M. ACUTE REDUCTION OF PLASMA NONESTERIFIED FATTY ACID BY GROWTH HORMONE IN HYPOPHYSECTOMIZED AND HOUSSAY RATS. Endocrinology. 1965 Apr;76:665–672. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-4-665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem M. A. Effects of the amino-terminal portion of human growth hormone on glucose clearance and metabolism in normal, diabetic, hypophysectomized, and diabetic-hypophysectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1988 Sep;123(3):1565–1576. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-3-1565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Shine J., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence and amplification in bacteria of structural gene for rat growth hormone. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):486–494. doi: 10.1038/270486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Sias S., Adelman J., de Boer H. A., Hayflick J., Jhurani P., Goeddel D. V., Heyneker H. L. Efficient bacterial expression of bovine and porcine growth hormones. DNA. 1983;2(1):37–45. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1983.2.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smal J., Closset J., Hennen G., De Meyts P. The receptor binding properties of the 20K variant of human growth hormone explain its discrepant insulin-like and growth promoting activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90541-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swislocki N. I., Sonenberg M., Yamasaki N. In vitro metabolic effects of bovine growth hormone fragments in adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 1970 Nov;87(5):900–904. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-5-900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum G. S., Guyda H. J., Posner B. I. Insulin-like growth factors: a role in growth hormone negative feedback and body weight regulation via brain. Science. 1983 Apr 1;220(4592):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.6338593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Miller R. J., Kaiser E. T. Structural characterization of beta-endorphin through the design, synthesis, and study of model peptides. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):657–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tou J. S., Kaempfe L. A., Vineyard B. D., Buonomo F. C., Della-Fera M. A., Baile C. A. Amphiphilic growth hormone releasing factor (GRF) analogs: peptide design and biological activity in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):763–770. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. D., Pullin C. O., Ng F. M., Bornstein J. The synthesis and hyperglycaemic activity of the amino acid sequence 172-191 of human growth hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 23;78(2):827–832. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watahiki M., Yamamoto M., Yamakawa M., Tanaka M., Nakashima K. Conserved and unique amino acid residues in the domains of the growth hormones. Flounder growth hormone deduced from the cDNA sequence has the minimal size in the growth hormone prolactin gene family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):312–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Camper S. A., Lyons R. H., Horowitz S., Goodwin E. C., Rottman F. M. Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the bovine growth hormone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7197–7210. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors/somatomedins: structure, secretion, biological actions and physiological role. Horm Res. 1986;24(2-3):121–130. doi: 10.1159/000180551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]