Abstract
A simple, rapid procedure is described for evaluating ozone injury to leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Pinto. Leaf chlorophyll is extracted with ethanol and analyzed spectrophotometrically; the concentration is expressed on the basis of leaf dry weight.
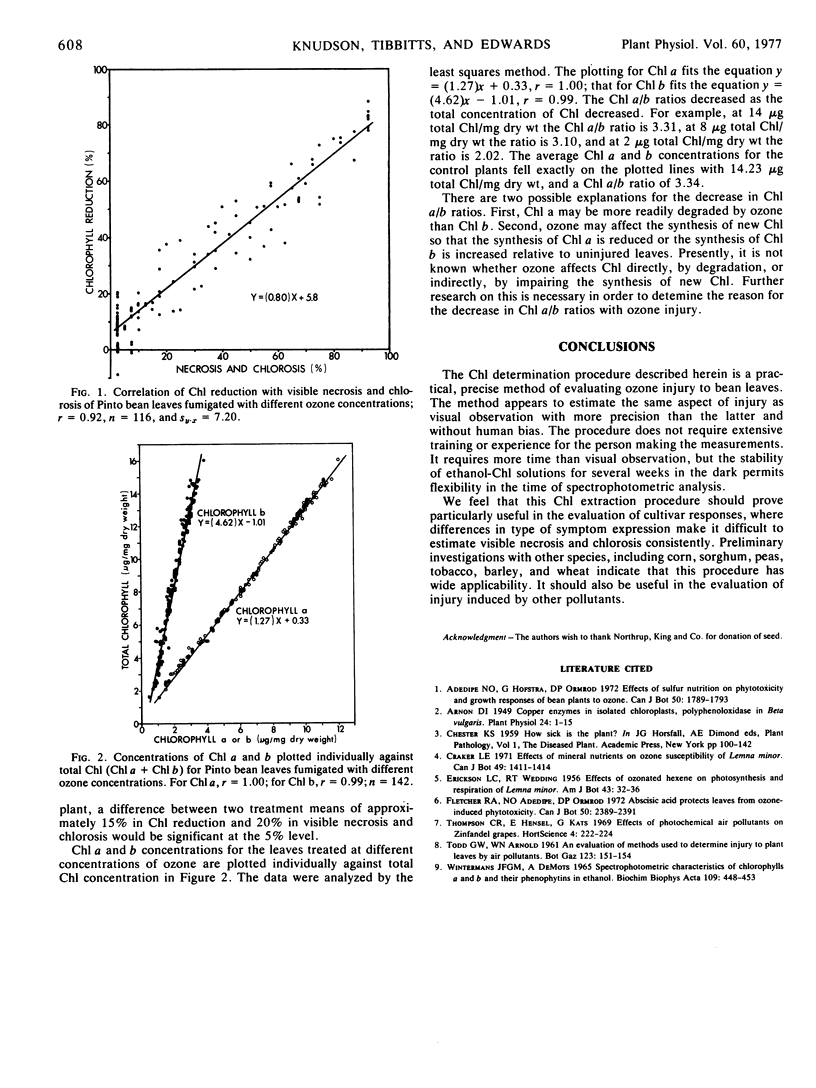
The per cent chlorophyll reduction of ozone-injured leaves was highly correlated with the per cent visible necrosis and chlorosis (r = 0.96). The variability in injury estimates with chlorophyll analysis was slightly less than with visual evaluation. An evaluation of chlorophyll a and b concentrations separately showed that the chlorophyll a/b ratio decreased with increasing amounts of injury. Chlorophyll determinations made for leaves harvested at intervals after an ozone treatment indicated that maximum chlorophyll reduction had occurred by 4 days.
This procedure for measuring ozone injury should be useful in eliminating the human bias associated with visible estimates of injury.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintermans J. F., de Mots A. Spectrophotometric characteristics of chlorophylls a and b and their pheophytins in ethanol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 29;109(2):448–453. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


