Abstract
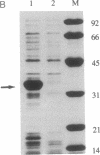
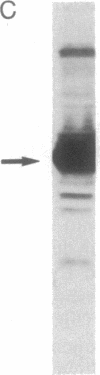
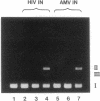
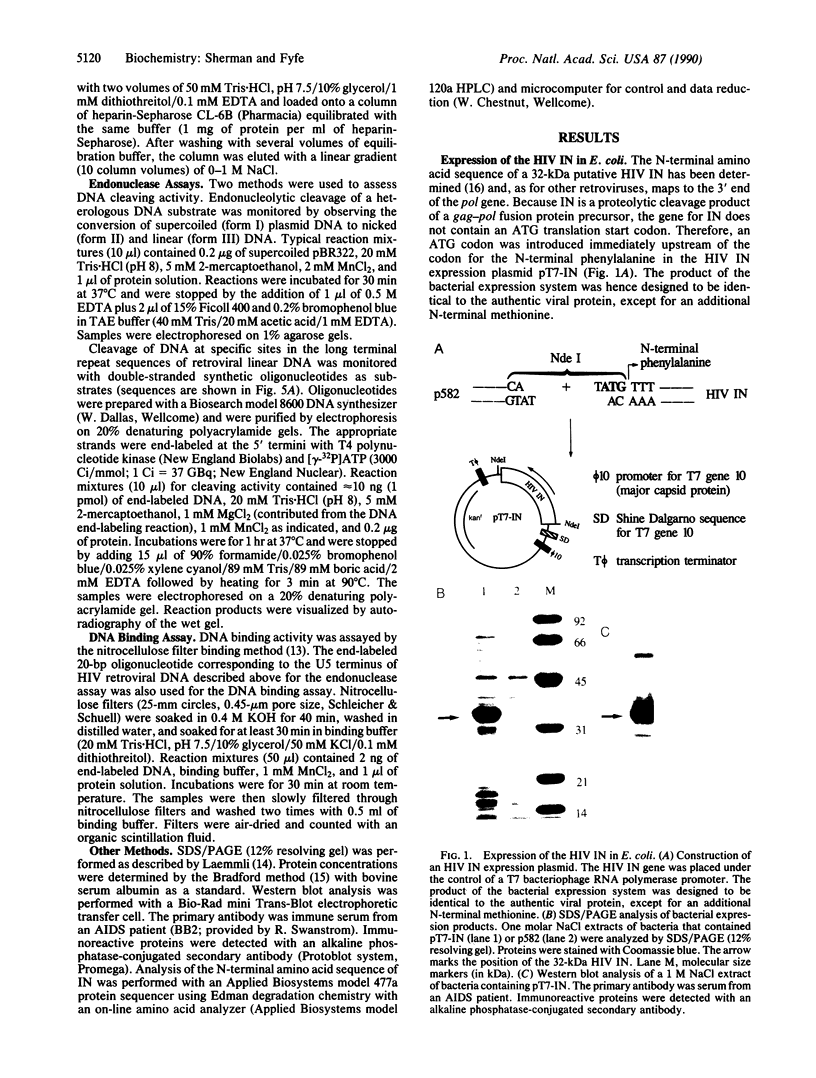
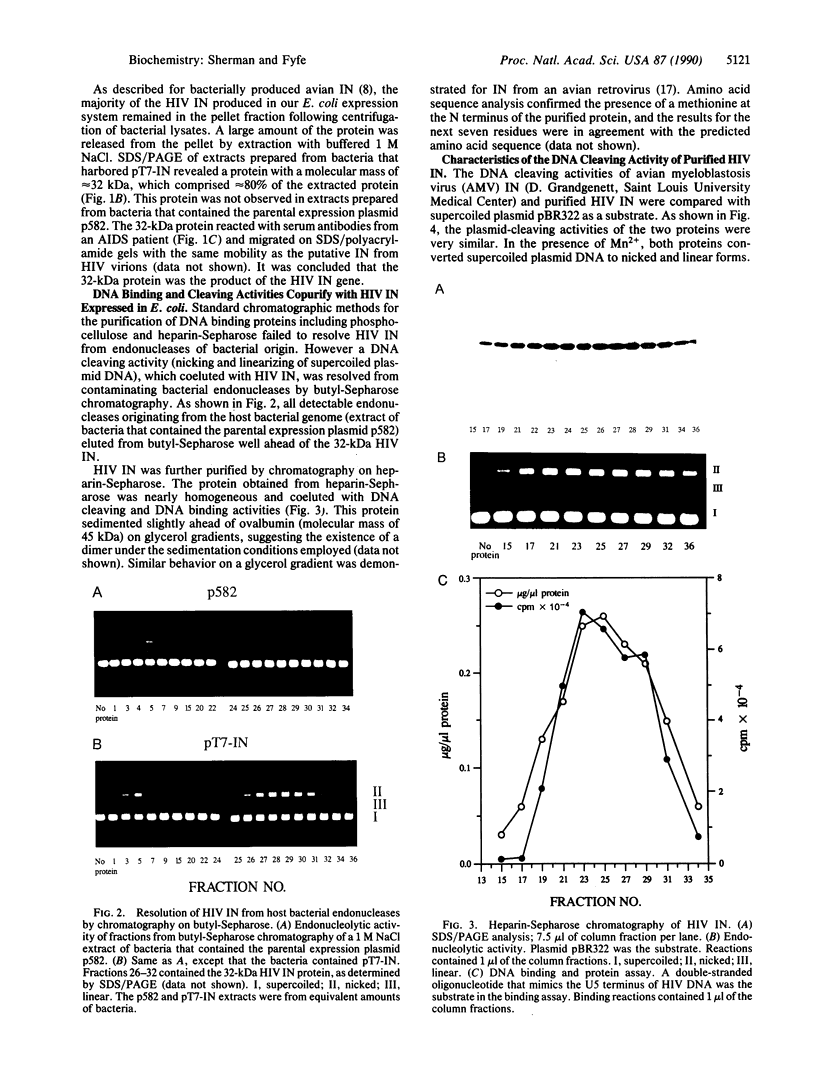
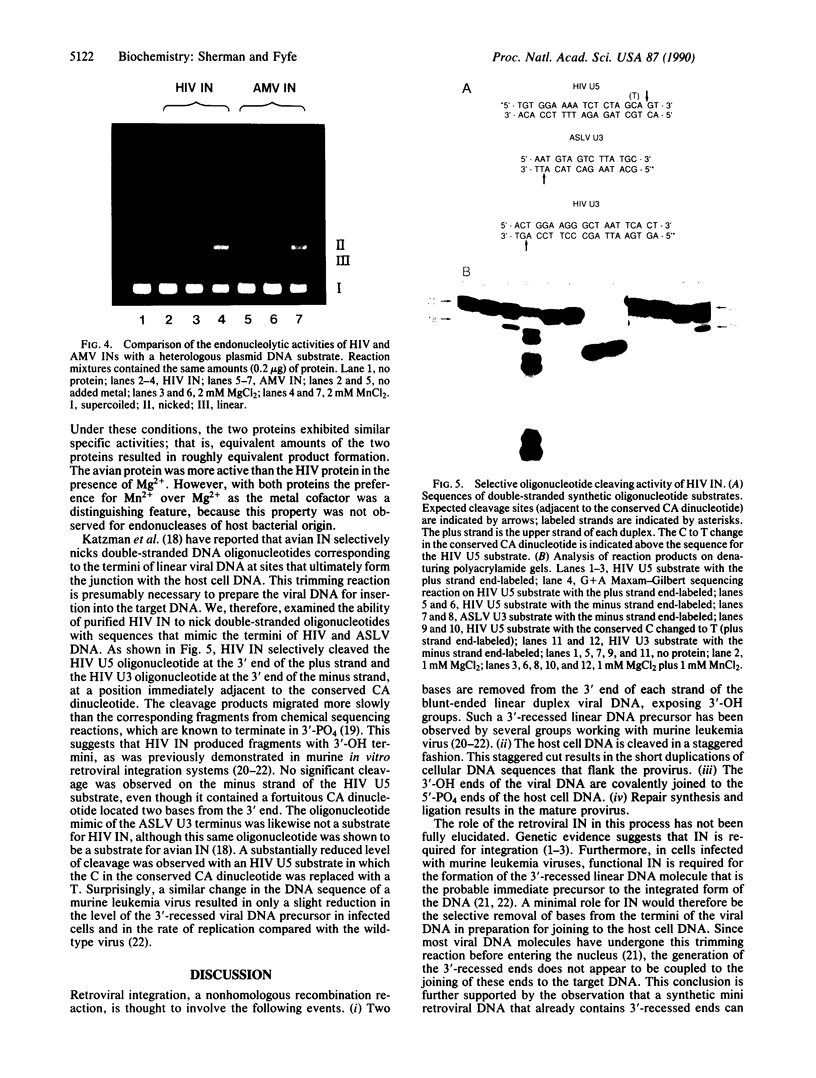
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integration protein, a potential target for selective antiviral therapy, was expressed in Escherichia coli. The purified protein, free of detectable contaminating endonucleases, selectively cleaved double-stranded DNA oligonucleotides that mimic the U3 and the U5 termini of linear HIV DNA. Two nucleotides were removed from the 3' ends of both the U5 plus strand and the U3 minus strand; in both cases, cleavage was adjacent to a conserved CA dinucleotide. The reaction was metal-ion dependent, with a preference for Mn2+ over Mg2+. Reaction selectivity was further demonstrated by the lack of cleavage of an HIV U5 substrate on the complementary (minus) strand, an analogous substrate that mimics the U3 terminus of an avian retrovirus, and an HIV U5 substrate in which the conserved CA dinucleotide was replaced with a TA dinucleotide. Such an integration protein-mediated cleavage reaction is expected to occur as part of the integration event in the retroviral life cycle, in which a double-stranded DNA copy of the viral RNA genome is inserted into the host cell DNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Varmus H. E. A mutant murine leukemia virus with a single missense codon in pol is defective in a function affecting integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6461–6465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyk G., Leis J., Longiaru M., Skalka A. M. Selective cleavage in the avian retroviral long terminal repeat sequence by the endonuclease associated with the alpha beta form of avian reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6745–6749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Integration of mini-retroviral DNA: a cell-free reaction for biochemical analysis of retroviral integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3065–3069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C., Schiff R. D. A 32,000-dalton nucleic acid-binding protein from avian retravirus cores possesses DNA endonuclease activity. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C. Site-specific nicking at the avian retrovirus LTR circle junction by the viral pp32 DNA endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6205–6221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., Hughes S. H. Expression of the Moloney murine leukemia virus and human immunodeficiency virus integration proteins in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):634–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoote M. M., Coligan J. E., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Martin M. A., Venkatesan S. Structural characterization of reverse transcriptase and endonuclease polypeptides of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):771–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.771-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K., Grandgenett D. P., Parsons J. T. Avian retrovirus pp32 DNA-binding protein. I. Recognition of specific sequences on retrovirus DNA terminal repeats. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):330–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.330-343.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. The retrovirus pol gene encodes a product required for DNA integration: identification of a retrovirus int locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7885–7889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Fisher A., Jagodzinski L. L., Mitsuya H., Liou R. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Complete nucleotide sequences of functional clones of the AIDS virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Spring;3(1):57–69. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A., Kikuchi Y., Nash H. Interaction of int protein with specific sites on lambda att DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90049-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Schwartzberg P. L., Goff S. P. Structure of the termini of DNA intermediates in the integration of retroviral DNA: dependence on IN function and terminal DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff R. D., Grandgenett D. P. Virus-coded origin of a 32,000-dalton protein from avian retrovirus cores: structural relatedness of p32 and the beta polypeptide of the avian retrovirus DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):279–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.279-291.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Construction and analysis of deletion mutations in the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus: a new viral function required for productive infection. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R., Soltis D. A., Katzman M., Cobrinik D., Leis J., Skalka A. M. Properties of avian sarcoma-leukosis virus pp32-related pol-endonucleases produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2358–2365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2358-2365.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]