Abstract
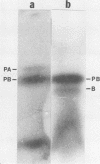
The messenger ribonucleic acid fraction isolated from a protein bodyenriched fraction of developing corn (Zea mays L.) endosperm stimulated the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into at least five polypeptides when added to a wheat germ extract capable of protein synthesis. Of these, the two major polypeptides formed with messenger from freshly frozen corn were identified as precursors to zein A and B, the two major polypeptides of the prolamine fraction of corn meal (21,600 and 19,600 molecular weight). The identification was based on the relative incorporations of radioactive leucine, lysine, and methionine, and the susceptibility of the zein A precursor, but not the zein B precursor to cleavage with cyanogen bromide. Using extracts from stored frozen corn, a third polypeptide of 14,500 molecular weight was identified as a major in vitro product. It was preferentially labeled with methionine and slightly larger than a similar peptide in the zein fraction of corn meal. Two other polypeptides of still lower molecular weight could be detected above the background of probably incomplete polypeptides.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A., Rubenstein I., Simon M. N. Purification and translation of zein messenger RNA from maize endosperm protein bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):696–700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A. Zein synthesis in maize endosperm by polyribosomes attached to protein bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):515–519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry J., Moureaux T. Hétérogénéité des glutélines du grain de mais: extraction sélective et composition en acides amines des trois fractions isolées. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1970;52(10):1021–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkins B. A., Dalby A. In vitro synthesis of zein-like protein by maize polyribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):1048–1054. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90746-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkins B. A., Jones R. A., Tsai C. Y. Isolation and in vitro translation of zein messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 14;15(25):5506–5511. doi: 10.1021/bi00670a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Jones R. A., Dalby A., Tsai C. Y. Genetic regulation of storaage protein content in maize endosperm. Biochem Genet. 1976 Aug;14(7-8):641–650. doi: 10.1007/BF00485842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K., Dudock B. Characterization of a highly efficient protein synthesizing system derived from commercial wheat germ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1385–1397. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A., Efron D., Weeks D. P. The wheat embryo cell-free system. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:749–754. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A., Seal S. N., Weeks D. P. Protein chain initiation in wheat embryo. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:94–101. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melcher U., Uhr J. W. Cell surface immunoglobulin. XVI. Polypeptide chain structure of mouse IgM and IgD-like molecule. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):409–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANS D., LIPMANN F. Amino acid transfer from aminoacyl-ribonucleic acids to protein on ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Apr 15;47:497–504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulis J. W., Bietz J. A., Wall J. S. Corn protein subunits: molecular weights determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Agric Food Chem. 1975 Mar-Apr;23(2):197–201. doi: 10.1021/jf60198a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulis J. W., Wall J. S. Fractionation and properties of alkylated-reduced corn glutelin proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct;251(1):57–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarragó A., Monasterio O., Allende J. E. Initiator-like properties of a methionyl-tRNA from wheat embryos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Nov 9;41(3):765–773. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]