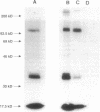
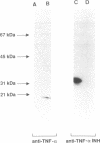
Abstract
Previous studies have shown that urine of febrile patients contains a tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibiting activity (TNF-alpha Inh) when tested in a cytotoxicity assay using the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)-susceptible cell line L929. In the present study, we investigated the relationship between the TNF-alpha Inh and a potential soluble form of the receptor, as the former has been shown to block TNF-alpha activities by binding to the ligand. We demonstrate that human TNF-alpha is affected to a greater extent than is murine TNF-alpha. This species specificity of the inhibitor correlates with the binding studies of TNF receptor interactions already reported. We raised a polyclonal antibody to TNF-alpha Inh that neutralizes its activity and does not recognize TNF-alpha. Solubilized cross-linked 125I-labeled TNF-alpha receptor complex could be immunoprecipitated by using either anti-TNF-alpha or anti-TNF-alpha Inh antibody, suggesting immunological cross-reactivity between the receptor and the inhibitor. By using fluorescein isothiocyanate-coupled TNF-alpha, it was possible to visualize by fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis the TNF-alpha receptor on phytohemagglutinin/interleukin 2-activated T cells. A similar increase of immunofluorescence intensity of the activated T cells was observed by using anti-TNF-alpha Inh antibody revealed with a fluorescein isothiocyanate-coupled goat anti-rabbit IgG1 conjugate, suggesting that the TNF-alpha Inh is also expressed as a membrane protein. Taken together, our results suggest that the TNF-alpha Inh originally described might be a soluble form of the TNF receptor itself.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Hass P. E. Characterization of receptors for human tumour necrosis factor and their regulation by gamma-interferon. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):665–667. doi: 10.1038/318665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:505–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eck M. J., Sprang S. R. The structure of tumor necrosis factor-alpha at 2.6 A resolution. Implications for receptor binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17595–17605. doi: 10.2210/pdb1tnf/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Aderka D., Rubinstein M., Rotman D., Wallach D. A tumor necrosis factor-binding protein purified to homogeneity from human urine protects cells from tumor necrosis factor toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11974–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Novick D., Wallach D. Two tumor necrosis factor-binding proteins purified from human urine. Evidence for immunological cross-reactivity with cell surface tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1531–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Remy R., Brockhaus M., van Loon A. P. Two different cell types have different major receptors for human tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha). J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14927–14934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel S., Hahn T., Holtmann H., Wallach D. Binding of human TNF-alpha to high-affinity cell surface receptors: effect of IFN. Immunol Lett. 1986 Apr;12(4):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(86)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. Y., Stuart D. I., Walker N. P. Structure of tumour necrosis factor. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):225–228. doi: 10.1038/338225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer S. M., Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., McCabe S. M., Ferraiolo B. L., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Characterization of the in vitro and in vivo species preference of human and murine tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):920–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Cellular receptor for 125I-labeled tumor necrosis factor: specific binding, affinity labeling, and relationship to sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5756–5760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewit-Bentley A., Fourme R., Kahn R., Prangé T., Vachette P., Tavernier J., Hauquier G., Niers W. Structure of tumour necrosis factor by X-ray solution scattering and preliminary studies by single crystal X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):389–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley B., Beckmann M. P., March C. J., Idzerda R. L., Gimpel S. D., VandenBos T., Friend D., Alpert A., Anderson D., Jackson J. The murine interleukin-4 receptor: molecular cloning and characterization of secreted and membrane bound forms. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):335–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Engelmann H., Wallach D., Rubinstein M. Soluble cytokine receptors are present in normal human urine. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1409–1414. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Lantz M., Nilsson E., Peetre C., Thysell H., Grubb A., Adolf G. Isolation and characterization of a tumor necrosis factor binding protein from urine. Eur J Haematol. 1989 Mar;42(3):270–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1989.tb00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Schaub L. B., Crump W. L., 3rd, Morin G. I., Grimm E. A. Regulation of lymphocyte tumor necrosis factor receptors by IL-2. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2236–2241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Hayflick J. S., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the cDNA for murine tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6060–6064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Zlotnik A., Espevik T., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Palladino M. A., Jr Tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin is a growth factor for thymocytes. Synergistic interactions with other cytokines. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1472–1478. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich P., Thoma B., Ucer U., Pfizenmaier K. Immunoregulatory activity of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha: induction of TNF receptors on human T cells and TNF-alpha-mediated enhancement of T cell responses. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1786–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich P., Ucer U., Krönke M., Pfizenmaier K. Quantification and characterization of high-affinity membrane receptors for tumor necrosis factor on human leukemic cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1986 Jul 15;38(1):127–133. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. A human inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1511–1516. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. Purification and biologic characterization of a specific tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11966–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Tanaka Y., Ota T., Suzuki H., Eto S., Yamashita U. Expression of interleukin 1 receptors on human peripheral T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4243–4248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Baglioni C. The active form of tumor necrosis factor is a trimer. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6951–6954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber G. B., Aggarwal B. B. Characterization and affinity cross-linking of receptors for human recombinant lymphotoxin (tumor necrosis factor-beta) on a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line, U-937. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3573–3576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber G. B., Aiyer R. A., Aggarwal B. B. Human tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor. Purification by immunoaffinity chromatography and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19098–19104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. L., Kurosaka M., Lipsky P. E. Phenotype of the accessory cell necessary for mitogen-stimulated T and B cell responses in human peripheral blood: delineation by its sensitivity to the lysosomotropic agent, L-leucine methyl ester. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2282–2290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingfield P., Pain R. H., Craig S. Tumour necrosis factor is a compact trimer. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81432-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]