Abstract
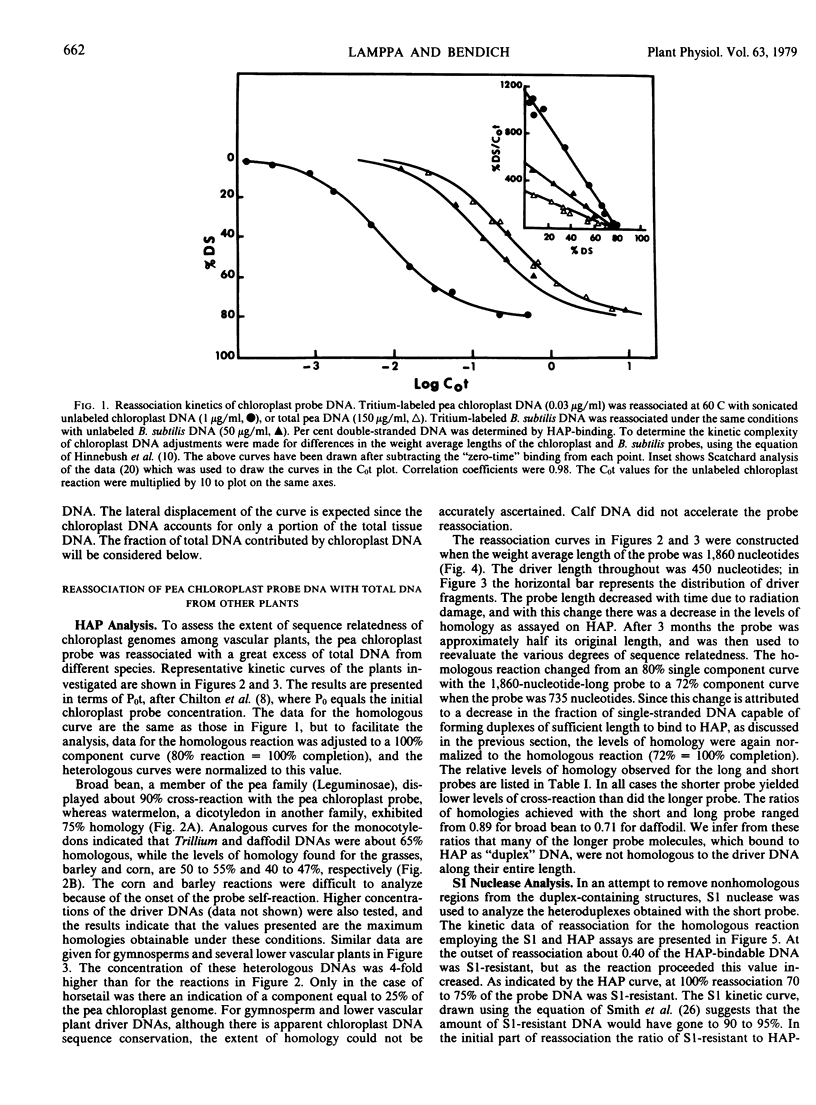
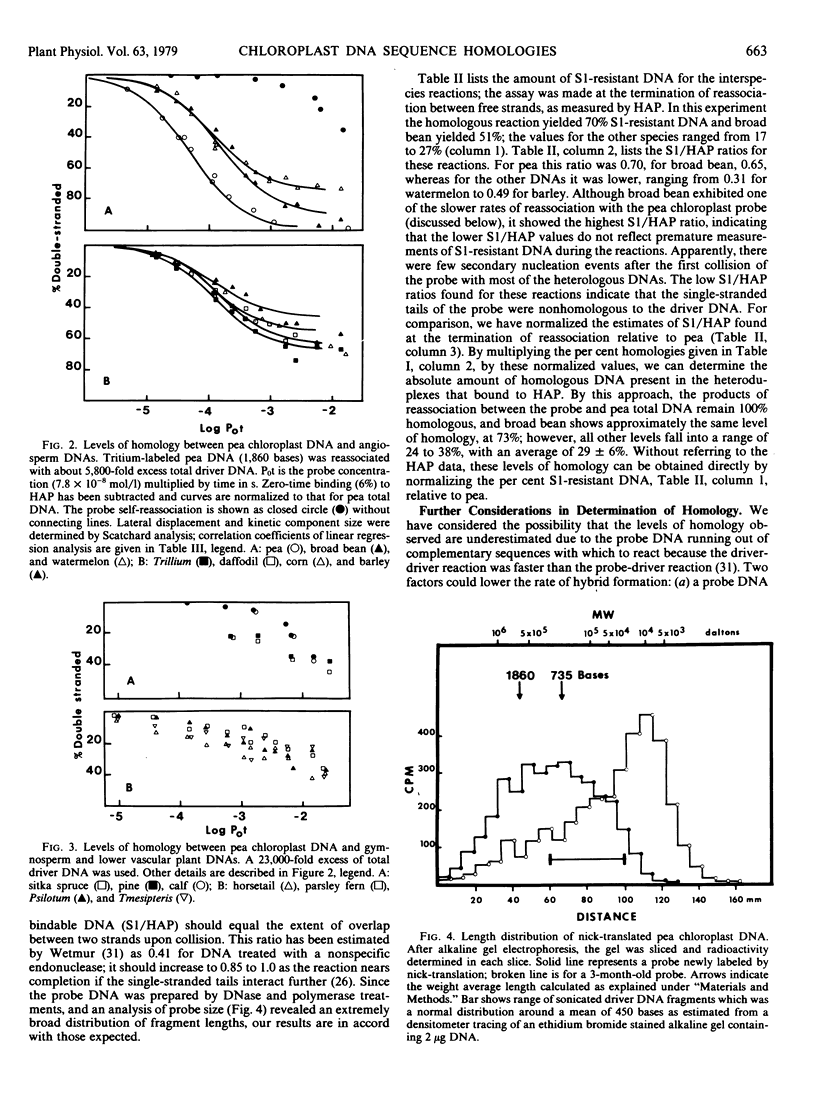
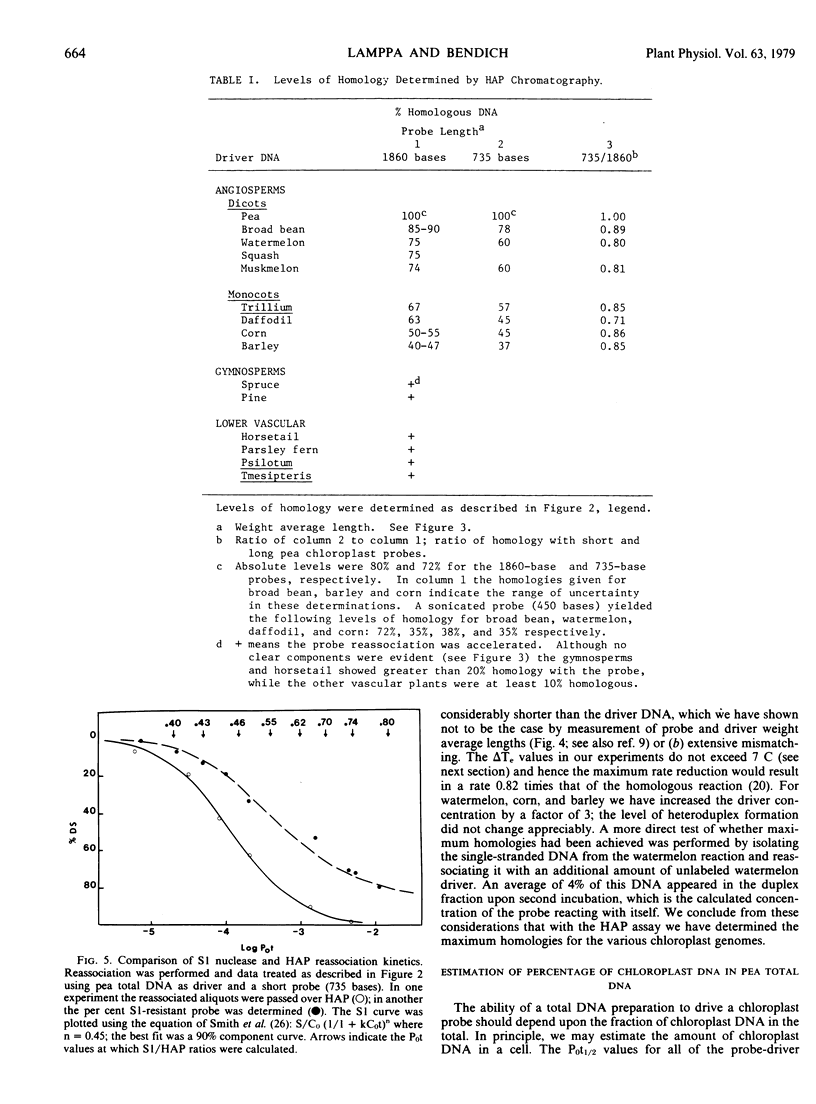
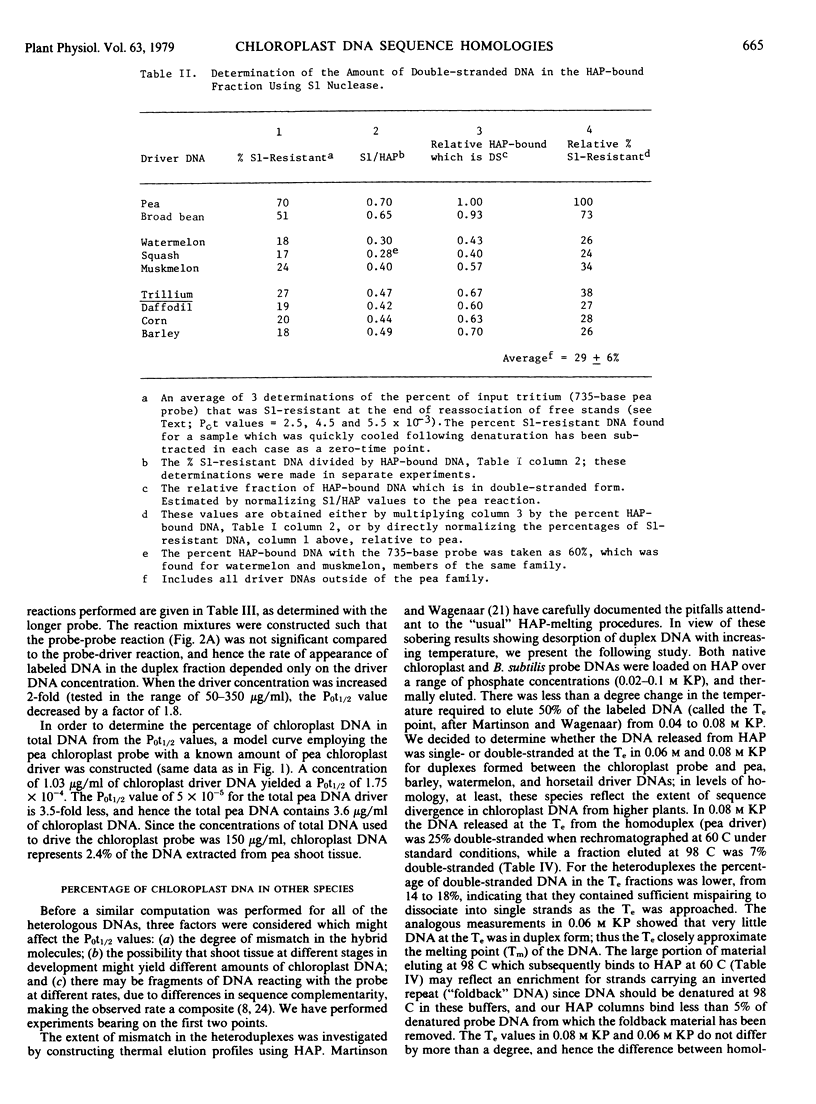
The extent of sequence conservation in the chloroplast genome of higher plants has been investigated. Supercoiled chloroplast DNA, prepared from pea seedlings, was labeled in vitro and used as a probe in reassociation experiments with a high concentration of total DNAs extracted from several angiosperms, gymnosperms, and lower vascular plants. In each case the probe reassociation was accelerated, demonstrating that some chloroplast sequences have been highly conserved throughout the evolution of vascular plants. Only among the flowering plants were distinct levels of cross-reaction with the pea chloroplast probe evident; broad bean and barley exhibited the highest and lowest levels, respectively. With the hydroxylapatite assay these levels decreased with a decrease in probe fragment length (from 1,860 to 735 bases), indicating that many conserved sequences in the chloroplast genome are separated by divergent sequences on a rather fine scale. Despite differences observed in levels of homology with the hydroxylapatite assay, S1 nuclease analysis of heteroduplexes showed that outside of the pea family the extent of sequence relatedness between the probe and various heterologous DNAs is approximately the same: 30%. In our interpretation, the fundamental changes in the chloroplast genome during angiosperm evolution involved the rearrangement of this 30% with respect to the more rapidly changing sequences of the genome. These rearrangements may have been more extensive in dicotyledons than in monocotyledons. We have estimated the amount of conserved and divergent DNA interspersed between one another.
From the reassociation experiments, determinations were made of the percentage of chloroplast DNA in total DNA extracts from different higher plants; this value remained relatively constant when compared with the large variation in the diploid genome size of the plants.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedbrook J. R., Kolodner R., Bogorad L. Zea mays chloroplast ribosomal RNA genes are part of a 22,000 base pair inverted repeat. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendich A. J., Anderson R. S. Characterization of families of repeated DNA sequences from four vascular plants. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4655–4663. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendich A. J., Anderson R. S. Novel properties of satellite DNA from muskmelon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1511–1515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton M. D., Currier T. C., Farrand S. K., Bendich A. J., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Agrobacterium tumefaciens DNA and PS8 bacteriophage DNA not detected in crown gall tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3672–3676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H. Viral DNA in transformed cells. II. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 2 DNA IN NINE LINES OF TRANSFORMED RAT CELLS USING SPECIFIC FRAGMENTS OF THE VIRAL GENOME;. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Clark V. E., Klotz L. C. Length dependence in reassociation kinetics of radioactive tracer DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1521–1529. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingle J., Timmis J. N., Sinclair J. The Relationship between Satellite Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Ribosomal Ribonucleic Acid Gene Redundancy, and Genome Size in Plants. Plant Physiol. 1975 Mar;55(3):496–501. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.3.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavenoff R. Characterization of the Bacillus subtilis W23 genome by sedimentation. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):801–806. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz L. C., Zimm B. H. Size of DNA determined by viscoelastic measurements: results on bacteriophages, Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):779–800. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. Molecular size and conformation of chloroplast deoxyribonucleic acid from pea leaves. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6355–6364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. Presence of displacement loops in the covalently closed circular chloroplast deoxyribonucleic acid from higher plants. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8840–8847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. The molecular size and conformation of the chloroplast DNA from higher plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 1;402(3):372–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., McCarthy B. J. Effect of reaction conditions on the reassociation of divergent deoxyribonucleic acid sequences. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3382–3388. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson H. G., Wagenaar E. B. Thermal elution chromatography and the resolution of nucleic acids on hydroxylapatite. Anal Biochem. 1974 Sep;61(1):144–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees H., Jones R. N. The origin of the wide species variation in nuclear DNA content. Int Rev Cytol. 1972;32:53–92. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60338-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Pettersson U., Sambrook J. Viral DNA in transformed cells. I. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 2 DNA in a line of transformed rat cells using specific fragments of the viral genome. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):709–726. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Studies on nucleic acid reassociation kinetics: reactivity of single-stranded tails in DNA-DNA renaturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4805–4809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R., Tewari K. K. Conservation of 70S ribosomal RNA genes in the chloroplast DNAs of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3147–3151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B. Estimation of DNA sequence divergence from comparison of restriction endonuclease digests. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1257–1265. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walbot V. The dimorphic chloroplasts of the C4 plant Panicum maximum contain identical genomes. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetmur J. G. Hybridization and renaturation kinetics of nucleic acids. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1976;5:337–361. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.05.060176.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



