Abstract
Signaling pathways are critical modulators of a variety of physiological and pathological processes, and the abnormal activation of some signaling pathways can contribute to disease progression in various conditions. As a result, signaling pathways have emerged as an important tool through which the occurrence and development of diseases can be studied, which may then lead to the development of novel drugs. Accumulating evidence supports a key role for extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) signaling in the embryonic development of the central nervous system (CNS) and in the regulation of adult brain function. ERK1/2, one of the most well characterized members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase family, regulates a range of processes, from metabolism, motility and inflammation, to cell death and survival. In the nervous system, ERK1/2 regulates synaptic plasticity, brain development and repair as well as memory formation. ERK1/2 is also a potent effector of neuronal death and neuroinflammation in many CNS diseases. This review summarizes recent findings in neurobiological ERK1/2 research, with a special emphasis on findings that clarify our understanding of the processes that regulate the plethora of isoform-specific ERK functions under physiological and pathological conditions. Finally, we suggest some potential therapeutic strategies associated with agents acting on the ERK1/2 signaling to prevent or treat neurological diseases.
Keywords: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling, brain, stroke, neurodegeneration, drug addiction
1. Introduction
Over the past several years, intracellular signaling targets have been intensely studied as a measure of the cellular processes that occur following specific conditions. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) ligands interact with their receptor and/or corrector in the cell and subsequently activate the intracellular ERK1/2 signaling pathway. In vertebrates, ERK1/2 signaling begins during development and acts to regulate cell proliferation, differentiation and fate decisions in the mature individual. Dysfunction of ERK1/2 signaling is associated with several human diseases, such as cancer, asthma, stroke and Alzheimer's disease (AD) (1–4). Due to the importance of ERK1/2 in a wide range of biological processes in central nervous system (CNS) disease, better understanding of the precise mechanisms of ERK1/2 signaling may provide fundamental insight into its role in disease development as well as help identify novel targets for therapeutic applications.
2. ERK1/2 pathway
ERK1/2, like other protein kinases, contains unique N- and C-terminal extensions that provide signaling specificity. Human ERK1 consist of 378 amino acid residues while ERK2 consists of 360 amino acid residues. ERK1 and 2 differ from one anther among various species. Gene ablation studies have provided evidence that ERK1 and 2 are not entirely functionally identical. A study showed that the erk1 gene is dispensable for the development of mice, whereas ablation of the erk2 gene is embryonic lethal (5). However, ERK1 was found to play an essential role in thymocyte development in a ERK1-knockout (KO) mouse study (6). Whether functions exist that are unique or preferred to ERK1 or 2 is unknown. Maybe at one time or another during the development of an animal, ERK1 or 2 performs functions unique to that isoform. Even so, ERK1 and 2 have a high degree of similarity, with >95% amino acid identity among humans, mice and rats (7). These two kinases share many physiological and biological functions and are commonly referred to together as ERK1/2. All known cellular stimulants of the ERK1/2 pathway lead to parallel activation of ERK1 and 2 (8). The ERK1/2 activation ratio in cells corresponds with their expression ratio, indicating that the isoforms are activated in parallel (9).
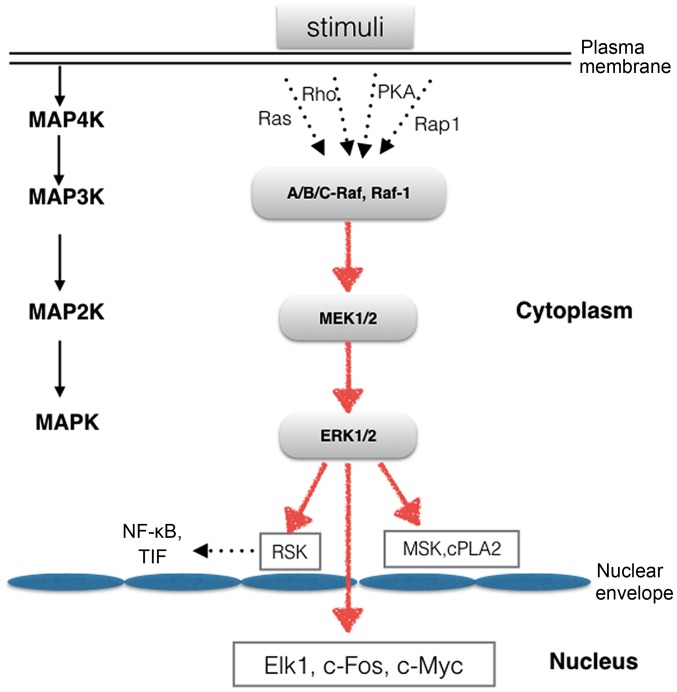
ERK1/2 cascade
A wide variety of extracellular stimuli are capable of activating the ERK1/2 cascade. Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK)1 and 2 are the immediate upstream kinases that phosphorylate and activate ERK1/2. MEK1 and 2 are dual-specificity protein kinases that mediate the phosphorylation of tyrosine and threonine residues. The activity of MEK1/2 is also regulated by phosphorylation, as MEK1 and 2 are phosphorylated by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinases (MAP3Ks). The most extensively studied MAP3Ks are the Raf proteins, including A-Raf, B-Raf, C-Raf and Raf-1 (10). They are activated by MAP4K proteins, such as Rap1, Ras, PKA and Rho (Fig. 1). ERK1/2 is a ubiquitously expressed hydrophilic non-receptor protein that participates in the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signal transduction cascade, which is involved in various diseases, including cancer, cardiac hypertrophy, pain and neuroinflam-mation (11–14). Therefore, this cascade is an interesting target for basic and translational research, including the development of drugs for therapeutic purposes.
Figure 1.
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade. The ERK1/2 MAP kinase, which occur in the cytoplasm and can be translated into the nucleus, catalyze the phosphorylation of many cytosolic proteins and nuclear transcription factors.
ERK1/2 substrates
Once activated, p-ERK1/2 can translocate into the nucleus to activate a wide array of transcription factors or can simply remain in the cytoplasm, where it regulates other subcellular functions (Fig. 1). ERK1 and 2 have more than 175 documented cytoplasmic and nuclear substrates (15). ERK1/2 nuclear targets include the ternary complex factor family of transcription factors. These proteins mediate the expression of immediate early genes, whose products contribute to cell survival, division and motility (16,17). Elk1 is one of the most thoroughly studied targets of the ERK1/2 MAPK kinase cascade, and Elk1 activation leads to increased transcriptional activity (15). Members of the ERK1/2 family of protein kinases participate in a wide variety of cellular processes. To date, more than 50 cytoplasmic substrates have been identified, including the ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) family of protein kinases, apop-totic proteins and cytoskeletal proteins. The RSK family consists of four human RSK isoforms (RSK1-4), mitogen- and stress-activated kinase (MSK)1 and 2, which are directly activated by ERK1/2 in response to stimuli. RSK1-4 are key components downstream of the Raf-MEK-ERK signaling cascade. The RSK family regulates transcription by mediating the phosphorylation of various types of transcription factors, including nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), serum response factor (SRF) and transcription initiation factor (TIF), in cells (18).
ERK1/2 scaffolds
Scaffolds are proteins that bind to multiple components of signaling modules. Scaffolds regulate and integrate overall signal transduction and play a pivotal role in the spatial and temporal regulation of the ERK1/2 signaling cascade. In response to stimulus exposure, ERK1/2 binds to a variety of cytoplasmic scaffold and anchor proteins, including the suppressor of Ras (KSR1/2), MEK partner 1 (MP1), IQ motif-containing GTPase activating protein 1 (IQGAP1) and MAP/ERK kinase kinase 1 (MEKK1) (19,20). MP1, which is also known as MAP kinase scaffold protein 1 and LAMTOR3, was identified as a scaffold protein that potentiates MAPK signaling by binding to MEK1 and ERK1. MP1 is localized to endomembrane compartments as part of larger signaling complexes and modulates the Raf-MKK1/2-ERK1/2 pathway together with its partner, p14 (21,22). In fact, IQGAP1 is a well-known regulator of signaling events involved in the MAPK pathway. The interaction between IQGAP1 and ERK1/2 plays a critical role in tumor formation, as competition for ERK1/2 binding between IQGAP1 and a peptide that encompasses the WW domain inhibits Ras and Raf-driven tumorigenesis (23). MEKK1, a MAP3 kinase, catalyzes the phosphorylation of MEK1 and 2, which are components of the ERK pathway. Xu et al (24) and Karandikar et al (25) both showed that MEKK1 binds to C-Raf, MEK1 and ERK2 of the ERK1/2 MAPK signaling module. Recent studies have suggested that KSR1 and 2 possess catalytic activity and that KSR2 participates in the assembly of a MEK1/KSR2/B-Raf ternary complex that is responsible for promoting rabbit MEK1 phosphorylation by mouse B-Raf (26,27).
3. ERK1/2 as effectors of physiological brain functions
ERK1/2 is abundant in the adult brain, and its activation can play multiple roles in the activity-dependent regulation of neuronal function. Mounting evidence indicates that ERK1/2 signaling plays an essential role in the development of the CNS (28). ERK1 and 2 are also involved in neuroinflammation, neural death, learning and memory formation and the regulation of synaptic plasticity in the adult nervous system.
Synaptic plasticity
Synaptic plasticity is thought to be crucial for information processing in the brain and to underlie many complex behaviours. The best studied forms of synaptic plasticity in the CNS are long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). The regulation of protein phosphorylation has an important role in the process of LTP and LTD.
Several recent studies have implicated the ERK1/2 pathway in the control of synaptic plasticity in the adult nervous system (29,30). English and Sweatt (31) investigated the role of MAPKs in regulating synaptic plasticity in adult rat neurons, with a particular focus on the modulatory role of ERK1/2 in hippocampal LTP. They provided the first demonstration of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-receptor dependent activation of ERK2 in rat hippocampal area CA1 in response to LTP-inducing high-frequency stimulation and suggested a crucial regulatory role of ERK2 in synaptic plasticity. Kanterewicz et al (32) further confirmed the role of ERK1/2 in NMDA receptor-independent LTP in the hippocampus. Over the past few years, a number of studies have demonstrated that ERK1/2 activity is required for several forms of synaptic plasticity in the amygdala which is associated with fear-dependent learning (33,34). Ratto and Pizzorusso (35) offered evidence, both in vivo and in vitro, that ERK1/2 plays a crucial role in controlling synaptic plasticity in the visual cortex. Inhibition of ERK1/2 can prevent the induction of various forms of LTP and LTD in the hippocampus and amygdala (33,36). These studies indicated that a requirement for ERK1/2 activation is common to many forms of synaptic plasticity but that the precise targets of ERK1/2 may differ between different types of plasticity.
Brain and development
Evidence has shown that total ERK1/2 activity controls the proliferation of certain late-born progenitor cells and the differentiation of neurons and glia during fetal brain development and that the two may compensate for each other during this process, at least in part, due to their overlapping functions (37,38). Samuels et al (39,40) also found that mutations that increase ERK1/2 activity can result in macrocephaly, while mutations that decrease ERK1/2 activity can result in microcephaly, suggesting that the ERK1/2 pathway is involved in the expansion of human neural progenitor cells. Furthermore, evidence indicates that ERK1/2 also takes part in regulating the proliferation and differentiation of astrocytes in the developing brain. Li et al (41) found that MEK/ERK signaling regulated the generation of glia from radial progenitors in the developing cortex, leading to a major increase in the number of astrocytes in the brain. This finding provides insight into the mechanisms involved in ERK1/2-mediated regulation of normal and abnormal astrocyte function during brain development. Recent evidence has consistently demonstrated that the ERK1/2 pathway is one of the dominant intracellular pathways for the regulation of oligodendroglial development, myelination and remyelination (38,42–44).
Neuronal cell death
Although ERK1/2 activation has generally been associated with brain cell differentiation and proliferation, a number of studies have shown that the activation of ERK1/2 can mediate cell death in several neuronal systems (45,46). The different effects of ERK1/2 on brain cells may be owing to the various stimuli and cell types involved. The activation of ERK1/2 was observed in glutamate- and heme-induced neuronal cell death and the neuronal injury (47,48) and loss of function (49,50) were reduced when suppressing ERK1/2 activation. ERK1/2 was found to play a caspase-independent role in promoting neuronal cell death in several other models. Okadaic acid has been shown to induce pyramidal cell death in hippocampal area CA3 in a manner dependent on ERK1/2 activation but not consistent with apoptosis (51). These findings may help us design strategies that can specifically attenuate ERK1/2-promoted neuronal pathologies.
Neuroinflammation
ERK1/2 is expressed in microglia, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Microglial cells are the primary immune cells in the CNS and promote host defense by destroying invading pathogens (52). Intra-glial signaling, including ERK1/2 pathway cascades, controls the regulation of inflammatory cytokine production and iNOS expression in activated microglia. Many in vitro experiments have demonstrated that the ERK1/2 signaling pathway contributes to the inflammatory response in microglia that is induced upon stimulation with radiation, thrombin or LPS (53–55). ERK1/2 is also involved in the inflammatory response in astrocytes (56,57). Furthermore, accumulating evidence indicates that many of the pharmaceutical-based therapies used to reduce neuroinflammation in stroke, neurodegenerative disorders, intracranial infections and other diseases act by suppressing the ERK1/2 pathway (58–61).
Learning and memory
ERK1/2 is localized in the soma and dendritic trees of neurons in the neocortex, hippocampus, striatum and cerebellum (62). An increase in ERK1/2 activation, as measured as the ratio of phosphorylated to total (phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated) ERK1/2, is necessary for learning and the formation of memory as well as for affect and arousal. In a seminal paper, Atkins et al (63) were the first to show that ERK1/2 is involved in memory processing in rat after fear conditioning. Later studies showed that activation of the ERK1/2 pathway is also required for the development of short-term memory and long-term memory consolidation (64,65). Treatment with ERK1/2 inhibition can impair long-term memory retention and prevents the formation of lasting memories of an event or association, including object recognition memory (66,67). Spatial learning and fear conditioning are the types of long-term memory in which the involvement of ERK1/2 has been best characterized (68). Studies of ERK1/2 KO mice demonstrated that ERK1/2 is involved in various aspects of learning and memory formation (69). ERK1 KO mice at first appear to be neurologically normal, whereas ERK2 KO is embryonic lethal; ERK2 KO mice die at embryonic day 6.5 (5,70,71). Selcher et al (70) showed that the ERK1 isoform is not required for associative learning in mice; instead, they found that the ERK2 isoform plays a predominant role in the synaptic plasticity that underlies learning and memory. Short-term memory is retained in ERK1-KO mice, but a marked enhancement of long-term memory was found in a one-trial inhibitory avoidance task (72). The results of a re-consolidation study also support the pivotal role of ERK2 in memory process (73). These results suggest that ERK1/2 may be a target for therapeutics to treat disorders of learning and memory.
4. ERK1/2 as effectors of stroke, neurodegeneration and drug addiction
Consistent with its critical role in key cellular activities, including cell proliferation, differentiation, survival and death, the ERK1/2 signaling pathway has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many CNS diseases, including stroke, AD, and Parkinson's disease (PD), among others (74–78). The activation of ERK1/2 cascades contributes to disease progression through the regulation of neuronal apoptosis, neuroinflammation and synaptic plasticity.
Stroke
ERK1/2 pathway activation is also known to play physiological and pathological roles post-development, and a large body of evidence suggests that ERK1/2 also contributes to the regulation of inflammatory responses, cytokines, cell apoptosis and death in ischemic and hemorrhagic brain injury (78–82). Several pharmacological studies have also demonstrated that suppression of ERK1/2 activation frequently downregulates features of apoptosis and inflammation and reduces neurological damage after stroke (49,81–83). Madami and Edvinsson showed that the elevated microvascular pro-inflammatory cytokine expression observed following focal ischemia in MCAO models also involved the ERK1/2 pathway (82). Moreover, Shioda et al (3) found that ERK1/2 signaling plays an important role in neurogenesis following brain ischemia. Substantial evidence has suggested that the ERK1/2 pathway is involved in regulating the changes in inflammation, cyto toxicity and cerebral vasospasm that occur after hemorrhagic stroke (76,84). Recently, Feng et al (85) showed that Ras/Raf/ERK signals participate in the neuronal apoptosis observed in the hippocampus in early post-subarachnoid hemorrhage brain injury. Taken together, these results suggest that therapies targeted at suppression of the ERK1/2 pathway may be beneficial in stroke.
PD
PD is the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disease after AD and is characterized by selective dopaminergic neuronal loss in the substantial nigra. The ERK1/2 pathway is known to play a major regulatory role in PD-related cellular processes. Accumulating evidence indicates that microglial cells play a crucial role in the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in animal models of PD. Recent studies have shown that the oxidative stress response plays a central role in the etiology of PD (86,87). The oxidative stress response that occurs in microglia is mediated by the activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway upon stimulation with pro-inflammatory stimuli. Furthermore, ERK1/2 has been shown to participate in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia through striatal synaptic plasticity (75,88). In addition, in the dopamine-depleted striatum, ERK1/2 plays an important role in the development of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in both mouse and non-human primate models of PD (75,89). The inhibition of ERK1/2 attenuated LID and completely inhibited all markers of angiogenesis in rat and mouse models of LID (75,90). Therefore, the modulation of ERK1/2 in response to dopamine in PD patients may be therapeutic for motor complications.
AD
AD is a neurodegenerative disease that is characterized by progressive cognitive decline and memory dysfunction as well as the presence of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) and senile plaques composed primarily of β-amyloid. ERK1/2 is one of the kinases known to phosphorylate tau and has been shown to be associated with NFTs and senile plaques (74). Increased levels of activated ERK1/2 have been found in AD brains, and inhibition of the pathway can reduce β-amyloid neurotoxicity (91–93). Activated ERK1/2 is found specifically in intracytoplasmic punctate structures and intracellular NFTs, primarily in the subpopulation of neurons that exhibits early AD-related protein deposition. As mentioned above, ERK1/2 is known to play a critical role in hippocampus synaptic plasticity and learning and memory. Abnormal ERK1/2 activation in the hippocampus may impair hippocampal function and contribute to memory deficits in AD patients. Therefore, improving regulation of the ERK1/2 pathway may be a central facet for the development of potential treatments for AD.
Drug addiction
Drug addiction is recognized as a type of neuroadaptive disorder. Because the ERK1/2 pathway plays an important role in neuronal plasticity in the adult brain, understanding of the role of this pathway is critical for overall understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying drug addiction and relapse. Exposure to a variety of substances with abuse potential, including nicotine, alcohol, amphetamine and cocaine, acutely active ERK1/2 in the striatum and other brain areas (94–97). Many of the enduring behavioral effects of acute drug exposure depend on ERK1/2 signaling. Studies have suggested that ERK1/2 is dynamically regulated following repeated drug exposure and withdrawal and that changes in ERK1/2 activation directly affect striatal cell excitability (98,99). These effects may be responsible for the expression of addictive behavior, and alterations of this pathway may contribute to the drug's rewarding effects and to the long-term maladaptation induced by drug abuse. Evidence indicates that ERK1/2 plays a dual role in gene regulation and drug addiction through direct activation of transcription factors, including Elk1 and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB), and by chromatin remodeling via MSK1 and histone H3 phosphorylation (100,101). Because ERK1/2 activation is a key molecular process in drug self-administration, targeting it may be a potential treatment strategy for drug addiction.
Other neurological diseases
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a CNS disease that causes the death of motor neurons and that can be either sporadic or familial origin. Mutant SOD1 is one of the genetic factors that contribute to the etiology of ALS, and mutant SOD1 induces motor neuron vulnerability. Phosphorylated ERK1/2 has been shown to be increased in the hippocampus and cerebellum in SOD1 G93A transgenic models (102). Apolloni et al (103) showed that ERK1/2 also participates in P2X7 receptor-induced enhancement of oxidative stress in ALS microglia, together with the NOX2 pathway. A previous study also identified ERK1/2 as a novel player in the pathogenesis of ALS associated with transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) (77). A recent study also showed that depletion of TDP-43 in microglia strikingly upregulated the production of COX-2 and PGE2 through the activation of ERK1/2 signaling (61).
Huntington's disease (HD), a devastating neurodegenerative disease that is characterized by progressive and severe cognitive, psychiatric and motor dysfunction, is caused by an expanded CAG repeat in the huntingtin (Htt) gene. MAPK signaling, and particularly the Ras-ERK cascade, is among the pathways that have been implicated in HD. In response to mutant huntingtin, ERK1/2 is activated and directs a protective transcriptional response and inhibits apoptotic caspase-3 and -7 activation (104,105). Data from different model systems indicate that ERK1/2 is involved in HD excitotoxicity at both the intercellular and intracellular level (106–108). Pharmacological interventions that promote ERK1/2 activation could suppress the adverse effects of mutant Htt by activating pro-survival mechanisms and suppressing apoptotic responses. Thus, studies in both cells and animal models suggest that the ERK1/2 cascade may be a potential target for therapeutic interventions for currently untreatable disorders.
5. Therapeutic inhibitors of the ERK1/2 signaling cascade
ERK1/2 pathway regulated kinase is a central point in the signaling network and is firmly established as an attractive target for pharmacological intervention in many diseases. Currently, inhibitors of the kinase function of Raf and MEK represent the most studied and advanced approaches for blocking the ERK1/2 pathway, with several inhibitors under evaluation in clinical trials and additional inhibitors in preclinical analyses. Morever, many neurological disease-related studies have investigated the effects of ERK1/2 pathway inhibitors, whose main mechanism of action is to prevent the phosphorylation of ERK1 and 2 by the upstream kinases, MEK1 and 2. A number of highly selective MEK1/2 inhibitors have been development, and many of them have been tested in a clinical setting. PD98059 and U0126 are first-generation small-molecule inhibitors of MEK1/2. In preclinical study, they feature potency and high specificity, with no or little inhibitory effects on other kinase. Most Raf inhibitors target mutant B-Raf and the most extensively studied B-Raf inhibitor in neurological disease is SB386023-b. Both Raf and MEK inhibitors have been widely applied in many experimental studies to better understand this pathway and explore its roles in neurological diseases (Table I). Other selected new and emerging MEK inhibitors have not been well studied in neurological diseases, such as PD0325901, selumetinib, cobimetinib, refametinib and trametinib. The main results obtained to date strongly suggest that the ERK1/2 pathway may represent a valid therapeutic target in neurological disorder conditions. Finally, it has also been proposed that ERK1/2 pathway may be a significant tool through which to study stroke, neurode-generative disease and drug addiction.
Table I.
Brief overview of recent studies concerning the involvement of the ERK1/2 pathway in neurological disease.
| Disease | Model | Effect | Inhibitor | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke | MCAO model | Regulates the expression of TNF-β, IL-1β, IL-6 and iNOS | U0126 | Reduces infarct size and improves neurological scores | (82) |
| Stroke | MCAO model | Regulates the expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in the vessel | U0126 | Reduces infarct volume and improves neurological function | (109) |
| Stroke | MCAO; organ culture of cerebral arteries | Regulates the expression of vascular endothelin type B receptor | U0126 | Attenuates cerebral vasoconstriction and improves long-term neurologic outcome | (110) |
| Stroke | MCAO model; organ culture of isolated cerebral arteries | Regulates the level of IL-1β, TNF-α, iNOS, IL-6, cxcl2, MMP9 and MMP13 | U0126 | Attenuates the expression of inflammatory and extracellular matrix-related genes in the smooth muscle cells of cerebral arteries | (111) |
| Stroke | MCAO model; organ culture of isolated cerebral arteries | Regulates the expression of TNF-α and TNF-α receptor 1 and 2 | U0126 | Reduces the expression of TNF-α, TNF-R1 and TNF-R2 in the wall of cerebral arteries | (112) |
| Stroke | Thrombin injection-induced brain injury | Involved in thrombin-induced striatal neuronal death | PD98059 | Reduces the size of the injured area | (79) |
| Stroke | ICH model | Involved in ICH-induced neuronal injury | PD98059 | Blocks striatal tissue injury | (81) |
| Stroke | Cultured human cerebral arteries | Regulates the expression of vascular contractile receptors | SB386023; SB590885 | Decreases vasoconstriction | (76) |
| Stroke | SAH model | Regulates cerebrocascular inflammatory mediators IL-1β, IL-6, iNOS, MMP-9 and TIMP-1 | SB386023-b | Prevents the reduction in cerebral blood flow | (80) |
| Stroke | SAH model | Regulates cerebrovascular expression of pro-inflammatory mediators IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and MMP-9 | U0126 | Improves neurological function | (83) |
| Stroke | SAH model | Regulates the expression of cerebrovascular smooth muscle cell receptors | SB386023-b | Prevents reductions in regional cerebral blood flow and neurological scores | (84) |
| Stroke | SAH model | Regulates the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and NF-κB activation as well as the level of IL-1β, IL-6, COX-2, MMP-9 | BAY 43-9006 | Reduces vasospasm, cerebral edema and blood brain barrier permeability | (113) |
| Stroke | SAH model | Regulates endothelium B and 5-hydroxytryptamine 1B receptors | SB386023-b | Prevents cerebral blood flow reduction | (114) |
| PD | PC12 cells culture | Regulates ERK1/2 phosphorylation and apoptosis in PC12 cells | GW5074; U0126 | Ameliorates cell toxicity induced by 6-hydroxydopamine | (115) |
| AD | AD model | Regulates the time exploring a novel object | PD98059 | Reverses memory impairment | (78) |
| AD | Culture of lymphoblasts from AD patients | Control cell survival or death decision under trophic factor withdrawal | PD98059 | Prevents cell death induced by serum starvation | (116) |
| AD | Metabolically competent rat brain slice | Regulates the phosphorylation of tau at Ser198/Ser199/Ser202, Ser262/Ser356 and Ser422 | U0126 | A lesser extend of tau hyperphophorylation in OA-treated rat brain slice | (117) |
| AD | Hippocampal slice culture | Regulates the activation of caspase-3 and tau cleavage | U0126 | Attenuates the neurotoxic effects of soluble Aβ oligomer in the hippocampus | (118) |
| AD | Rat brain synaptosome fraction | Regulates the activation of cPLA2 and arachidomic acid release | U0126 | Reduces the amyloid beta peptide fragment beta A(25–35)-induced formation of reactive oxygen species | (119) |
| Drug addiction | Cocaine- treated rat | Mediates cocaine-induced reduction of GABAergic inhibition and facility of LTP induction | U0126; SL327 | Reduces the level of D2 receptor (U0126) and blocks cocaine-induced faciliation of LTP induction (SL327) and I-LTD (U0126 and SL327) | (120) |
| Drug addiction | Ethanol- treated mice | Regulates binge-like alcohol consumption | SL327 | Increases ethanol bing-like consumption and home-cage alcohol consumption | (97) |
| ALS | Microglia culture | Regulates AP-1 activity, COX-2 expression and PGE2 production | U0126 | Inhibition of COX-2 expression and PGE2 production by celecoxib reduces the neurotoxicity triggered by TDP-43-deficient microglia | (61) |
ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; AD, Alzheimer's disease; PD, Parkinson's disease; IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; MCAO model, middle cerebral artery occlusion model; ICH model, intracerebral hemorrhage; SAH model, subarachnoid hemorrhage.
6. Summary and perspectives
In summary, the link between the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and a variety of neurological diseases, including stroke, neuro-degenerative diseases and drug addiction, demonstrates the importance of studying the ERK1/2 pathway to human health. More detailed knowledge of the physiological and pathological functions of ERK1/2 in the adult nervous system may not only provide insight for the development of new therapeutic drugs for neurological disorders but also achieve clinical benefits for patients. Over the next several years, additional novel therapeutic strategies that utilize ERK1/2 signaling inhibitors will likely be developed for neurological disease clinical trials.
References
- 1.Zhu X, Castellani RJ, Takeda A, Nunomura A, Atwood CS, Perry G, Smith MA. Differential activation of neuronal ERK, JNK/SAPK and p38 in Alzheimer disease: the 'two hit' hypothesis. Mech Ageing Dev. 2001;123:39–46. doi: 10.1016/S0047-6374(01)00342-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Roberts PJ, Der CJ. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3291–3310. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shioda N, Han F, Fukunaga K. Role of Akt and ERK signaling in the neurogenesis following brain ischemia. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;85:375–387. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(09)85026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alam R, Gorska MM. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling and ERK1/2 bistability in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011;41:149–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yao Y, Li W, Wu J, Germann UA, Su MS, Kuida K, Boucher DM. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 is necessary for mesoderm differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:12759–12764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2134254100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pagès G, Guérin S, Grall D, Bonino F, Smith A, Anjuere F, Auberger P, Pouysségur J. Defective thymocyte maturation in p44 MAP kinase (Erk 1) knockout mice. Science. 1999;286:1374–1377. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5443.1374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Charest DL, Mordret G, Harder KW, Jirik F, Pelech SL. Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of the human mitogen-activated protein kinase p44erk1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13:4679–4690. doi: 10.1128/MCB.13.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lefloch R, Pouysségur J, Lenormand P. Total ERK1/2 activity regulates cell proliferation. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:705–711. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.5.7734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lefloch R, Pouysségur J, Lenormand P. Single and combined silencing of ERK1 and ERK2 reveals their positive contribution to growth signaling depending on their expression levels. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:511–527. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00800-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Raman M, Chen W, Cobb MH. Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene. 2007;26:3100–3112. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ji RR, Gereau RW, IV, Malcangio M, Strichartz GR. MAP kinase and pain. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2009;60:135–148. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.12.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lorenz K, Schmitt JP, Vidal M, Lohse MJ. Cardiac hypertrophy: targeting Raf/MEK/ERK1/2-signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;41:2351–2355. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cui Y, Wu J, Jung SC, Park DB, Maeng YH, Hong JY, Kim SJ, Lee SR, Kim SJ, Kim SJ, et al. Anti-neuroinflammatory activity of nobiletin on suppression of microglial activation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33:1814–1821. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhu C, Qi X, Chen Y, Sun B, Dai Y, Gu Y. PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathways are involved in IGF-1-induced VEGF-C upregulation in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137:1587–1594. doi: 10.1007/s00432-011-1049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yoon S, Seger R. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase: multiple substrates regulate diverse cellular functions. Growth Factors. 2006;24:21–44. doi: 10.1080/02699050500284218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Murphy LO, Blenis J. MAPK signal specificity: the right place at the right time. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31:268–275. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3279–3290. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Anjum R, Blenis J. The RSK family of kinases: emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:747–758. doi: 10.1038/nrm2509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yao Z, Seger R. The ERK signaling cascade - views from different subcellular compartments. Biofactors. 2009;35:407–416. doi: 10.1002/biof.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lavoie H, Therrien M. Regulation of RAF protein kinases in ERK signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16:281–298. doi: 10.1038/nrm3979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schaeffer HJ, Catling AD, Eblen ST, Collier LS, Krauss A, Weber MJ. MP1: a MEK binding partner that enhances enzymatic activation of the MAP kinase cascade. Science. 1998;281:1668–1671. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5383.1668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Brahma A, Dalby KN. Regulation of protein phosphorylation within the MKK1-ERK2 complex by MP1 and the MP1•P14 heterodimer. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007;460:85–91. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.11.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jameson KL, Mazur PK, Zehnder AM, Zhang J, Zarnegar B, Sage J, Khavari PA. IQGAP1 scaffold-kinase interaction blockade selectively targets RAS-MAP kinase-driven tumors. Nat Med. 2013;19:626–630. doi: 10.1038/nm.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Xu S, Robbins D, Frost J, Dang A, Lange-Carter C, Cobb MH. MEKK1 phosphorylates MEK1 and MEK2 but does not cause activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:6808–6812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Karandikar M, Xu S, Cobb MH. MEKK1 binds raf-1 and the ERK2 cascade components. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:40120–40127. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005926200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brennan DF, Dar AC, Hertz NT, Chao WC, Burlingame AL, Shokat KM, Barford D. A Raf-induced allosteric transition of KSR stimulates phosphorylation of MEK. Nature. 2011;472:366–369. doi: 10.1038/nature09860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hu J, Yu H, Kornev AP, Zhao J, Filbert EL, Taylor SS, Shaw AS. Mutation that blocks ATP binding creates a pseudo-kinase stabilizing the scaffolding function of kinase suppressor of Ras, CRAF and BRAF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:6067–6072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102554108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim EK, Choi EJ. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1802:396–405. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Impey S, Obrietan K, Storm DR. Making new connections: role of ERK/MAP kinase signaling in neuronal plasticity. Neuron. 1999;23:11–14. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80747-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Di Cristo G, Berardi N, Cancedda L, Pizzorusso T, Putignano E, Ratto GM, Maffei L. Requirement of ERK activation for visual cortical plasticity. Science. 2001;292:2337–2340. doi: 10.1126/science.1059075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.English JD, Sweatt JD. A requirement for the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in hippocampal long term potentiation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19103–19106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.31.19103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kanterewicz BI, Urban NN, McMahon DB, Norman ED, Giffen LJ, Favata MF, Scherle PA, Trzskos JM, Barrionuevo G, Klann E. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade is required for NMDA receptor-independent LTP in area CA1 but not area CA3 of the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2000;20:3057–3066. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-09-03057.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Huang SS, He J, Zhao DM, Xu XY, Tan HP, Li H. Effects of mutant huntingtin on mGluR5-mediated dual signaling pathways: implications for therapeutic interventions. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2010;30:1107–1115. doi: 10.1007/s10571-010-9543-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schafe GE, Atkins CM, Swank MW, Bauer EP, Sweatt JD, LeDoux JE. Activation of ERK/MAP kinase in the amygdala is required for memory consolidation of pavlovian fear conditioning. J Neurosci. 2000;20:8177–8187. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-21-08177.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ratto GM, Pizzorusso T. A kinase with a vision: role of ERK in the synaptic plasticity of the visual cortex. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;557:122–132. doi: 10.1007/0-387-30128-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Thiels E, Kanterewicz BI, Norman ED, Trzaskos JM, Klann E. Long-term depression in the adult hippocampus in vivo involves activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphorylation of Elk-1. J Neurosci. 2002;22:2054–2062. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-06-02054.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Imamura O, Pagès G, Pouysségur J, Endo S, Takishima K. ERK1 and ERK2 are required for radial glial maintenance and cortical lamination. Genes Cells. 2010;15:1072–1088. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2010.01444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fyffe-Maricich SL, Karlo JC, Landreth GE, Miller RH. The ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates the timing of oligodendrocyte differentiation. J Neurosci. 2011;31:843–850. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3239-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Samuels IS, Karlo JC, Faruzzi AN, Pickering K, Herrup K, Sweatt JD, Saitta SC, Landreth GE. Deletion of ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase identifies its key roles in cortical neurogenesis and cognitive function. J Neurosci. 2008;28:6983–6995. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0679-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Samuels IS, Saitta SC, Landreth GE. MAP'ing CNS development and cognition: an ERKsome process. Neuron. 2009;61:160–167. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Li X, Newbern JM, Wu Y, Morgan-Smith M, Zhong J, Charron J, Snider WD. MEK is a key regulator of gliogenesis in the developing brain. Neuron. 2012;75:1035–1050. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.08.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Domercq M, Alberdi E, Sánchez-Gómez MV, Ariz U, Pérez-Samartín A, Matute C. Dual-specific phosphatase-6 (Dusp6) and ERK mediate AMPA receptor-induced oligodendrocyte death. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:11825–11836. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.153049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Newbern JM, Li X, Shoemaker SE, Zhou J, Zhong J, Wu Y, Bonder D, Hollenback S, Coppola G, Geschwind DH, et al. Specific functions for ERK/MAPK signaling during PNS development. Neuron. 2011;69:91–105. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Fyffe-Maricich SL, Schott A, Karl M, Krasno J, Miller RH. Signaling through ERK1/2 controls myelin thickness during myelin repair in the adult central nervous system. J Neurosci. 2013;33:18402–18408. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2381-13.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Satoh T, Nakatsuka D, Watanabe Y, Nagata I, Kikuchi H, Namura S. Neuroprotection by MAPK/ERK kinase inhibition with U0126 against oxidative stress in a mouse neuronal cell line and rat primary cultured cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2000;288:163–166. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01229-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Subramaniam S, Unsicker K. ERK and cell death: ERK1/2 in neuronal death. FEBS J. 2010;277:22–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Jiang Q, Gu Z, Zhang G, Jing G. Diphosphorylation and involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) in glutamate-induced apoptotic-like death in cultured rat cortical neurons. Brain Res. 2000;857:71–77. doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(99)02364-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Benvenisti-Zarom L, Chen-Roetling J, Regan RF. Inhibition of the ERK/MAP kinase pathway attenuates heme oxygenase-1 expression and heme-mediated neuronal injury. Neurosci Lett. 2006;398:230–234. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Namura S, Iihara K, Takami S, Nagata I, Kikuchi H, Matsushita K, Moskowitz MA, Bonventre JV, Alessandrini A. Intravenous administration of MEK inhibitor U0126 affords brain protection against forebrain ischemia and focal cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:11569–11574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.181213498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhao Y, Luo P, Guo Q, Li S, Zhang L, Zhao M, Xu H, Yang Y, Poon W, Fei Z. Interactions between SIRT1 and MAPK/ERK regulate neuronal apoptosis induced by traumatic brain injury in vitro and in vivo. Exp Neurol. 2012;237:489–498. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rundén E, Seglen PO, Haug FM, Ottersen OP, Wieloch T, Shamloo M, Laake JH. Regional selective neuronal degeneration after protein phosphatase inhibition in hippocampal slice cultures: evidence for a MAP kinase-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci. 1998;18:7296–7305. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-18-07296.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Perry VH, Teeling J. Microglia and macrophages of the central nervous system: the contribution of microglia priming and systemic inflammation to chronic neurodegeneration. Semin Immunopathol. 2013;35:601–612. doi: 10.1007/s00281-013-0382-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Weinstein JR, Zhang M, Kutlubaev M, Lee R, Bishop C, Andersen H, Hanisch UK, Möller T. Thrombin-induced regulation of CD95(Fas) expression in the N9 microglial cell line: evidence for involvement of proteinase-activated receptor(1) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. Neurochem Res. 2009;34:445–452. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9803-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Deng Z, Sui G, Rosa PM, Zhao W. Radiation-induced c-Jun activation depends on MEK1-ERK1/2 signaling pathway in microglial cells. PLoS One. 2012;7:e36739. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kim S, Lee MS, Lee B, Gwon WG, Joung EJ, Yoon NY, Kim HR. Anti-inflammatory effects of sargachromenol-rich ethanolic extract of Myagropsis myagroides on lipopolysac-charide-stimulated BV-2 cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:231. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Park GH, Jeon SJ, Ryu JR, Choi MS, Han SH, Yang SI, Ryu JH, Cheong JH, Shin CY, Ko KH. Essential role of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in protease activated receptor 2-mediated nitric-oxide production from rat primary astrocytes. Nitric Oxide. 2009;21:110–119. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2009.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fields J, Cisneros IE, Borgmann K, Ghorpade A. Extracellular regulated kinase 1/2 signaling is a critical regulator of interleukin-1β-mediated astrocyte tissue inhibitor of metallopro-teinase-1 expression. PLoS One. 2013;8:e56891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wang YJ, Zheng YL, Lu J, Chen GQ, Wang XH, Feng J, Ruan J, Sun X, Li CX, Sun QJ. Purple sweet potato color suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced acute inflammatory response in mouse brain. Neurochem Int. 2010;56:424–430. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2009.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Shao J, Liu T, Xie QR, Zhang T, Yu H, Wang B, Ying W, Mruk DD, Silvestrini B, Cheng CY, et al. Adjudin attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- and ischemia-induced microglial activation. J Neuroimmunol. 2013;254:83–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2012.09.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhao H, Wang SL, Qian L, Jin JL, Li H, Xu Y, Zhu XL. Diammonium glycyrrhizinate attenuates Aβ(1-42)-induced neuroinflammation and regulates MAPK and NF-κB pathways in vitro and in vivo. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013;19:117–124. doi: 10.1111/cns.12043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Xia Q, Hu Q, Wang H, Yang H, Gao F, Ren H, Chen D, Fu C, Zheng L, Zhen X, et al. Induction of COX-2-PGE2 synthesis by activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway contributes to neuronal death triggered by TDP-43-depleted microglia. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1702. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Fiore RS, Bayer VE, Pelech SL, Posada J, Cooper JA, Baraban JM. p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase in brain: prominent localization in neuronal cell bodies and dendrites. Neuroscience. 1993;55:463–472. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90516-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. doi: 10.1038/2836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Feld M, Dimant B, Delorenzi A, Coso O, Romano A. Phosph-orylation of extra-nuclear ERK/MAPK is required for long-term memory consolidation in the crab Chasmagnathus. Behav Brain Res. 2005;158:251–261. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2004.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Igaz LM, Winograd M, Cammarota M, Izquierdo LA, Alonso M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH. Early activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in the hippocampus is required for short-term memory formation of a fear-motivated learning. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006;26:989–1002. doi: 10.1007/s10571-006-9116-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kelly A, Laroche S, Davis S. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase in hippo-campal circuitry is required for consolidation and reconsolidation of recognition memory. J Neurosci. 2003;23:5354–5360. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-12-05354.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Villarreal JS, Barea-Rodriguez EJ. ERK phosphorylation is required for retention of trace fear memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2006;85:44–57. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2005.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Shalin SC, Zirrgiebel U, Honsa KJ, Julien JP, Miller FD, Kaplan DR, Sweatt JD. Neuronal MEK is important for normal fear conditioning in mice. J Neurosci Res. 2004;75:760–770. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Satoh Y, Endo S, Ikeda T, Yamada K, Ito M, Kuroki M, Hiramoto T, Imamura O, Kobayashi Y, Watanabe Y, et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) knockdown mice show deficits in long-term memory; ERK2 has a specific function in learning and memory. J Neurosci. 2007;27:10765–10776. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0117-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Selcher JC, Nekrasova T, Paylor R, Landreth GE, Sweatt JD. Mice lacking the ERK1 isoform of MAP kinase are unimpaired in emotional learning. Learn Mem. 2001;8:11–19. doi: 10.1101/lm.37001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Saba-El-Leil MK, Vella FD, Vernay B, Voisin L, Chen L, Labrecque N, Ang SL, Meloche S. An essential function of the mitogen-activated protein kinase Erk2 in mouse trophoblast development. EMBO Rep. 2003;4:964–968. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Mazzucchelli C, Vantaggiato C, Ciamei A, Fasano S, Pakhotin P, Krezel W, Welzl H, Wolfer DP, Pagès G, Valverde O, et al. Knockout of ERK1 MAP kinase enhances synaptic plasticity in the striatum and facilitates striatal-mediated learning and memory. Neuron. 2002;34:807–820. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00716-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Cestari V, Costanzi M, Castellano C, Rossi-Arnaud C. A role for ERK2 in reconsolidation of fear memories in mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2006;86:133–143. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2006.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ferrer I, Blanco R, Carmona M, Ribera R, Goutan E, Puig B, Rey MJ, Cardozo A, Viñals F, Ribalta T. Phosphorylated map kinase (ERK1, ERK2) expression is associated with early tau deposition in neurones and glial cells, but not with increased nuclear DNA vulnerability and cell death, in Alzheimer disease, Pick's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. Brain Pathol. 2001;11:144–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2001.tb00387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Santini E, Valjent E, Usiello A, Carta M, Borgkvist A, Girault JA, Hervé D, Greengard P, Fisone G. Critical involvement of cAMP/DARPP-32 and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase signaling in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. J Neurosci. 2007;27:6995–7005. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0852-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ahnstedt H, Säveland H, Nilsson O, Edvinsson L. Human cerebrovascular contractile receptors are upregulated via a B-Raf/MEK/ERK-sensitive signaling pathway. BMC Neurosci. 2011;12:5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ayala V, Granado-Serrano AB, Cacabelos D, Naudí A, Ilieva EV, Boada J, Caraballo-Miralles V, Lladó J, Ferrer I, Pamplona R, et al. Cell stress induces TDP-43 pathological changes associated with ERK1/2 dysfunction: implications in ALS. Acta Neuropathol. 2011;122:259–270. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0850-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Feld M, Krawczyk MC, Sol Fustiñana M, Blake MG, Baratti CM, Romano A, Boccia MM. Decrease of ERK/MAPK overac-tivation in prefrontal cortex reverses early memory deficit in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;40:69–82. doi: 10.3233/JAD-131076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Fujimoto S, Katsuki H, Ohnishi M, Takagi M, Kume T, Akaike A. Thrombin induces striatal neurotoxicity depending on mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in vivo. Neuroscience. 2007;144:694–701. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Maddahi A, Ansar S, Chen Q, Edvinsson L. Blockade of the MEK/ERK pathway with a raf inhibitor prevents activation of pro-inflammatory mediators in cerebral arteries and reduction in cerebral blood flow after subarachnoid hemorrhage in a rat model. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011;31:144–154. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ohnishi M, Katsuki H, Fujimoto S, Takagi M, Kume T, Akaike A. Involvement of thrombin and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in hemorrhagic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2007;206:43–52. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Maddahi A, Edvinsson L. Cerebral ischemia induces microvascular pro-inflammatory cytokine expression via the MEK/ERK pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2010;7:14. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Maddahi A, Povlsen GK, Edvinsson L. Regulation of enhanced cerebrovascular expression of proinflammatory mediators in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage via the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:274. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ansar S, Maddahi A, Edvinsson L. Inhibition of cerebro-vascular raf activation attenuates cerebral blood flow and prevents upregulation of contractile receptors after subarachnoid hemorrhage. BMC Neurosci. 2011;12:107. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Feng D, Wang B, Ma Y, Shi W, Tao K, Zeng W, Cai Q, Zhang Z, Qin H. The Ras/Raf/Erk pathway mediates the subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons through phosphorylation of p53. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53:5737–5748. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9490-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Liu Y, Qin L, Li G, Zhang W, An L, Liu B, Hong JS. Dextromethorphan protects dopaminergic neurons against inflammation-mediated degeneration through inhibition of microglial activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;305:212–218. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.043166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Qian L, Tan KS, Wei SJ, Wu HM, Xu Z, Wilson B, Lu RB, Hong JS, Flood PM. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity is inhibited by morphine through an opioid receptor-independent reduction of NADPH oxidase activity. J Immunol. 2007;179:1198–1209. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.2.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Valjent E, Pascoli V, Svenningsson P, Paul S, Enslen H, Corvol JC, Stipanovich A, Caboche J, Lombroso PJ, Nairn AC, et al. Regulation of a protein phosphatase cascade allows convergent dopamine and glutamate signals to activate ERK in the striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:491–496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408305102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Santini E, Sgambato-Faure V, Li Q, Savasta M, Dovero S, Fisone G, Bezard E. Distinct changes in cAMP and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase signalling in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. PLoS One. 2010;5:e12322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Lindgren HS, Ohlin KE, Cenci MA. Differential involvement of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in L-DOPA-induced angiogenic activity in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;34:2477–2488. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Pei JJ, Braak H, An WL, Winblad B, Cowburn RF, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I. Up-regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and MEK1/2 is associated with the progression of neurofibrillary degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2002;109:45–55. doi: 10.1016/S0169-328X(02)00488-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Zhu X, Lee HG, Raina AK, Perry G, Smith MA. The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosignals. 2002;11:270–281. doi: 10.1159/000067426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Liu F, Su Y, Li B, Ni B. Regulation of amyloid precursor protein expression and secretion via activation of ERK1/2 by hepatocyte growth factor in HEK293 cells transfected with APP751. Exp Cell Res. 2003;287:387–396. doi: 10.1016/S0014-4827(03)00152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Lu L, Koya E, Zhai H, Hope BT, Shaham Y. Role of ERK in cocaine addiction. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:695–703. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2006.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Hoffmann HM, Nadal R, Vignes M, Ortiz J. Chronic cocaine self-administration modulates ERK1/2 and CREB responses to dopamine receptor agonists in striatal slices. Addict Biol. 2012;17:565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Pascoli V, Cahill E, Bellivier F, Caboche J, Vanhoutte P. Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2 activation by addictive drugs: a signal toward pathological adaptation. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;76:917–926. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Agoglia AE, Sharko AC, Psilos KE, Holstein SE, Reid GT, Hodge CW. Alcohol alters the activation of ERK1/2, a functional regulator of binge alcohol drinking in adult C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015;39:463–475. doi: 10.1111/acer.12645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Boudreau AC, Reimers JM, Milovanovic M, Wolf ME. Cell surface AMPA receptors in the rat nucleus accumbens increase during cocaine withdrawal but internalize after cocaine challenge in association with altered activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Neurosci. 2007;27:10621–10635. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2163-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Schumann J, Yaka R. Prolonged withdrawal from repeated noncontingent cocaine exposure increases NMDA receptor expression and ERK activity in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci. 2009;29:6955–6963. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1329-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Brami-Cherrier K, Roze E, Girault JA, Betuing S, Caboche J. Role of the ERK/MSK1 signalling pathway in chromatin remodelling and brain responses to drugs of abuse. J Neurochem. 2009;108:1323–1335. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Ciccarelli A, Giustetto M. Role of ERK signaling in activity-dependent modifications of histone proteins. Neuropharmacology. 2014;80:34–44. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Chung YH, Joo KM, Lim HC, Cho MH, Kim D, Lee WB, Cha CI. Immunohistochemical study on the distribution of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in the central nervous system of SOD1G93A transgenic mice. Brain Res. 2005;1050:203–209. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.05.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Apolloni S, Parisi C, Pesaresi MG, Rossi S, Carrì MT, Cozzolino M, Volonté C, D'Ambrosi N. The NADPH oxidase pathway is dysregulated by the P2X7 receptor in the SOD1-G93A microglia model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Immunol. 2013;190:5187–5195. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Apostol BL, Illes K, Pallos J, Bodai L, Wu J, Strand A, Schweitzer ES, Olson JM, Kazantsev A, Marsh JL, et al. Mutant huntingtin alters MAPK signaling pathways in PC12 and striatal cells: ERK1/2 protects against mutant huntingtin-associated toxicity. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:273–285. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Varma H, Cheng R, Voisine C, Hart AC, Stockwell BR. Inhibitors of metabolism rescue cell death in Huntington's disease models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:14525–14530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704482104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Liévens JC, Rival T, Iché M, Chneiweiss H, Birman S. Expanded polyglutamine peptides disrupt EGF receptor signaling and glutamate transporter expression in Drosophila. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14:713–724. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Huang YY, Martin KC, Kandel ER. Both protein kinase A and mitogen-activated protein kinase are required in the amygdala for the macromolecular synthesis-dependent late phase of long-term potentiation. J Neurosci. 2000;20:6317–6325. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-17-06317.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Ribeiro FM, Paquet M, Ferreira LT, Cregan T, Swan P, Cregan SP, Ferguson SS. Metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated cell signaling pathways are altered in a mouse model of Hunti-ngton's disease. J Neurosci. 2010;30:316–324. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4974-09.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Maddahi A, Chen Q, Edvinsson L. Enhanced cerebrovascular expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 via the MEK/ERK pathway during cerebral ischemia in the rat. BMC Neurosci. 2009;10:56. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-10-56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Ahnstedt H, Mostajeran M, Blixt FW, Warfvinge K, Ansar S, Krause DN, Edvinsson L. U0126 attenuates cerebral vasocon-striction and improves long-term neurologic outcome after stroke in female rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015;35:454–460. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Vikman P, Ansar S, Henriksson M, Stenman E, Edvinsson L. Cerebral ischemia induces transcription of inflammatory and extracellular-matrix-related genes in rat cerebral arteries. Exp Brain Res. 2007;183:499–510. doi: 10.1007/s00221-007-1062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Maddahi A, Kruse LS, Chen QW, Edvinsson L. The role of tumor necrosis factor-α and TNF-α receptors in cerebral arteries following cerebral ischemia in rat. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:107. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Zhang J, Xu X, Zhou D, Li H, You W, Wang Z, Chen G. Possible role of Raf-1 kinase in the development of cerebral vaso-spasm and early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;52:1527–1539. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8939-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Beg SA, Hansen-Schwartz JA, Vikman PJ, Xu CB, Edvinsson LI. ERK1/2 inhibition attenuates cerebral blood flow reduction and abolishes ET(B) and 5-HT(1B) receptor upregulation after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26:846–856. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Li J, Fan Y, Zhang YN, Sun DJ, Fu SB, Ma L, Jiang LH, Cui C, Ding HF, Yang J. The Raf-1 inhibitor GW5074 and the ERK1/2 pathway inhibitor U0126 ameliorate PC12 cells apoptosis induced by 6-hydroxydopamine. Pharmazie. 2012;67:718–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Bartolomé F, de Las Cuevas N, Muñoz U, Bermejo F, Martín-Requero A. Impaired apoptosis in lymphoblasts from Alzheimer's disease patients: cross-talk of Ca2+/calmodulin and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007;64:1437–1448. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7081-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Pei JJ, Gong CX, An WL, Winblad B, Cowburn RF, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K. Okadaic-acid-induced inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A produces activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2, MEK1/2, and p70 S6, similar to that in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:845–858. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63445-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Chong YH, Shin YJ, Lee EO, Kayed R, Glabe CG, Tenner AJ. ERK1/2 activation mediates Abeta oligomer-induced neurotoxicity via caspase-3 activation and tau cleavage in rat organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:20315–20325. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601016200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Andersen JM, Myhre O, Fonnum F. Discussion of the role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase-phospholipase A2 pathway in production of reactive oxygen species in Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Res. 2003;28:319–326. doi: 10.1023/A:1022389503105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Pan B, Zhong P, Sun D, Liu QS. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling in the ventral tegmental area mediates cocaine-induced synaptic plasticity and rewarding effects. J Neurosci. 2011;31:11244–11255. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1040-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]