Abstract
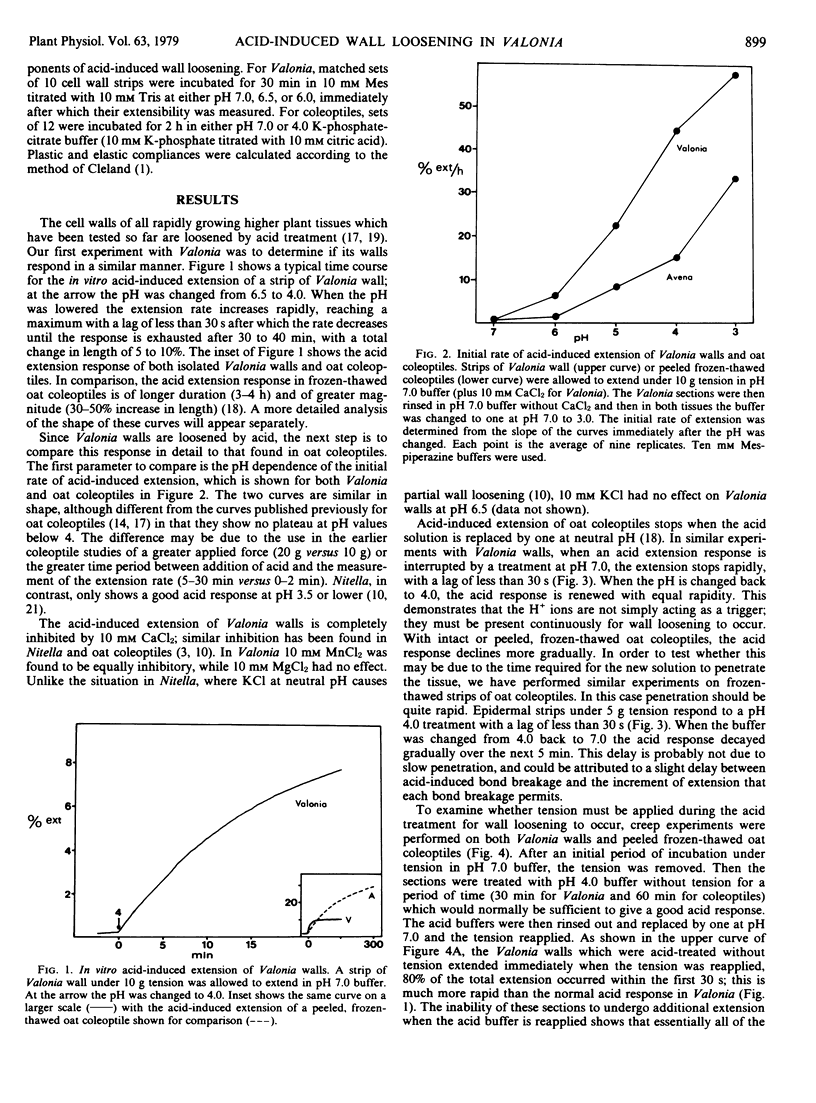
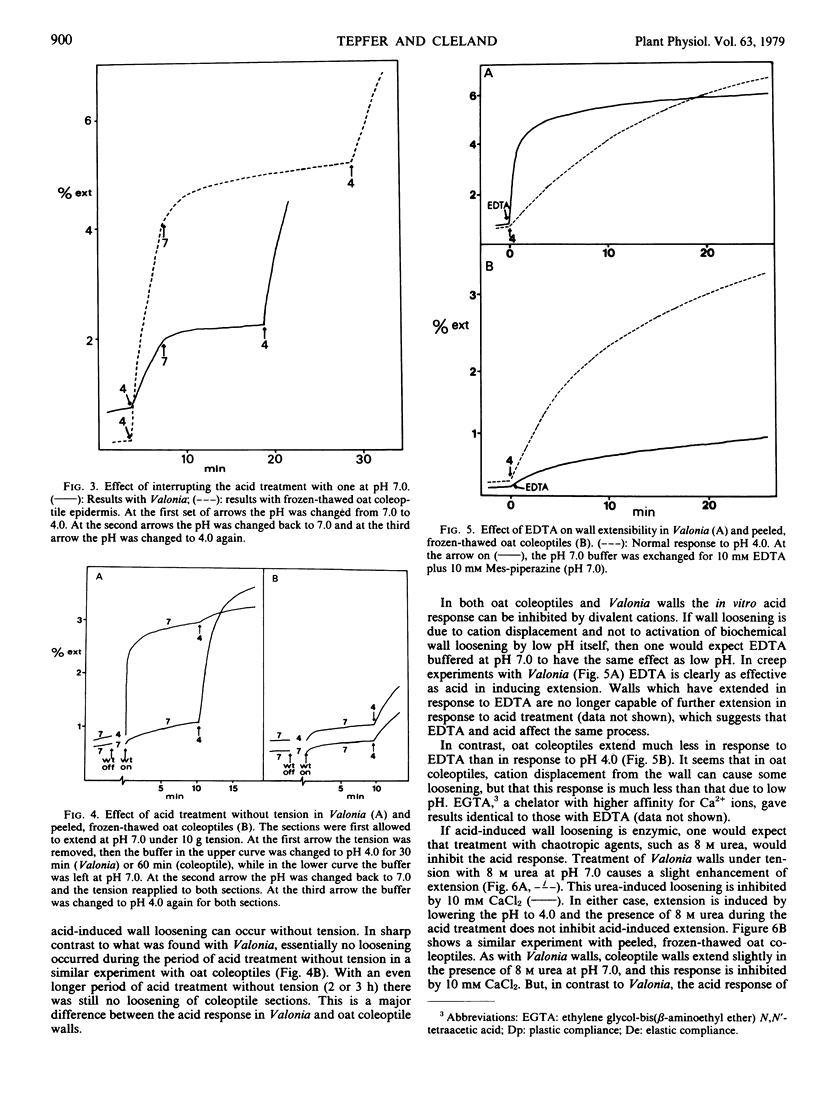
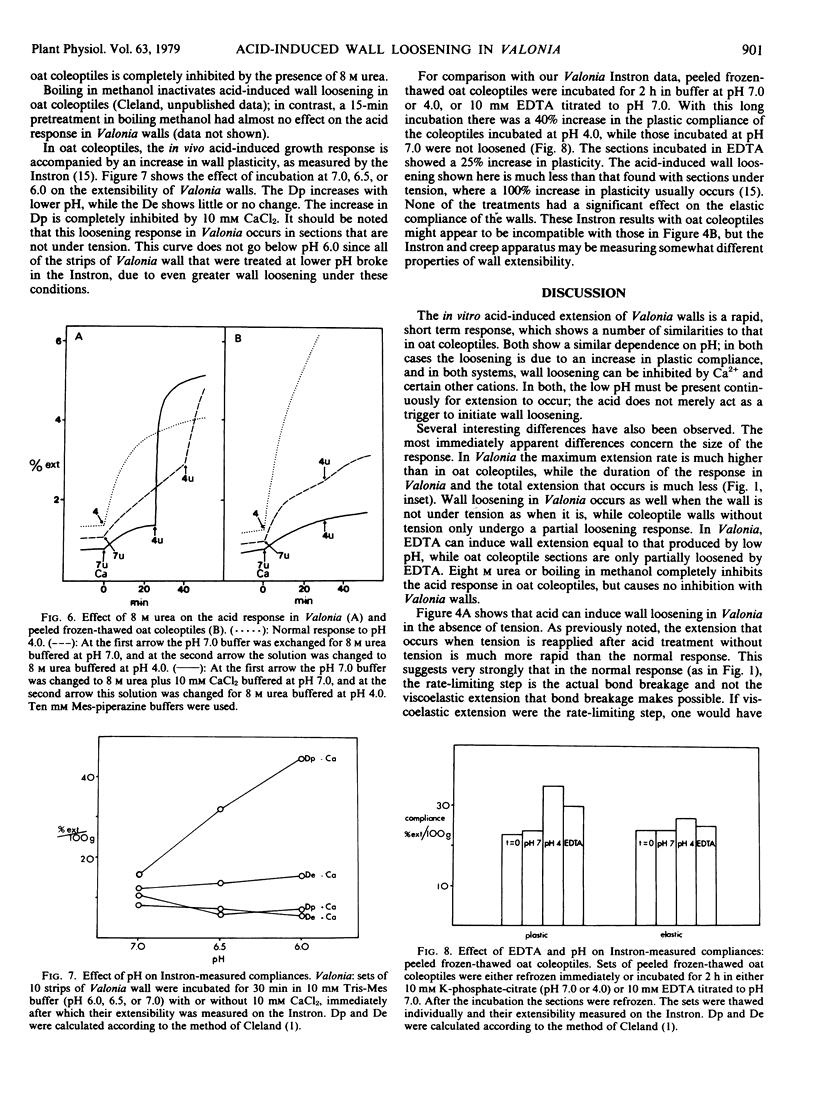
The acid-induced loosening of cell walls of Valonia ventricosa has been compared to that of frozen-thawed oat coleoptiles. The two acid extension responses are similar in regard to the shape of the pH response curve and the increase in plastic compliance induced by acid treatment. In both systems the acid response can be inhibited by Ca2+ and in both the removal of the protons leads to a rapid termination of wall loosening. The two responses differ in several significant ways, however. The acid-induced extension of Valonia walls is more rapid than that of coleoptile walls, but of smaller total magnitude. Acid-induced loosening can occur in Valonia without the wall being under tension, but not in coleoptiles. The acid-induced extension of Valonia walls is not inhibited by 8 molar urea, whereas the response in oat coleoptiles is completely inhibited by this treatment. Ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) can cause wall loosening in Valonia comparable to that produced by low pH, whereas in coleoptiles EDTA causes a much smaller response. These results with Valonia are consistent with a mechanism of acid-induced wall loosening in which a central role is played by the displacement of Ca2+ from the wall, while the larger part of acid-induced wall loosening in oat coleoptiles appears to be via a different mechanism.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleland R. E. Reevaluation of the Effect of Calcium Ions on Auxin-induced Elongation. Plant Physiol. 1977 Nov;60(5):709–712. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.5.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland R. Auxin-induced hydrogen ion excretion from Avena coleoptiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3092–3093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebard F. V., Amatangelo S. J., Dayanandan P., Kaufman P. B. Studies on acidification of media by Avena stem segments in the presence and absence of gibberellic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1976 Nov;58(5):670–674. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.5.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauss H., Glaser C. Carbohydrate-binding proteins from plant cell walls and their possible involvement in extension growth. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80867-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegstra K., Talmadge K. W., Bauer W. D., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: III. A Model of the Walls of Suspension-cultured Sycamore Cells Based on the Interconnections of the Macromolecular Components. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):188–197. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentze J., Raymond B., Cohen J. D., Rayle D. L. Auxin-induced H Secretion in Helianthus and Its Implications. Plant Physiol. 1977 Oct;60(4):509–512. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.4.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Métraux J. P., Taiz L. Cell wall extension in Nitella as influenced by acids and ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1565–1569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayle D. L., Cleland R. Control of plant cell enlargement by hydrogen ions. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1977;11:187–214. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60746-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayle D. L., Cleland R. Enhancement of wall loosening and elongation by Acid solutions. Plant Physiol. 1970 Aug;46(2):250–253. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.2.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayle D. L., Haughton P. M., Cleland R. An in vitro system that simulates plant cell extension growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1814–1817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa T., Bonner J. Mechanical Properties of the Avena Coleoptile As Related to Auxin and to Ionic Interactions. Plant Physiol. 1957 May;32(3):207–212. doi: 10.1104/pp.32.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



