Abstract
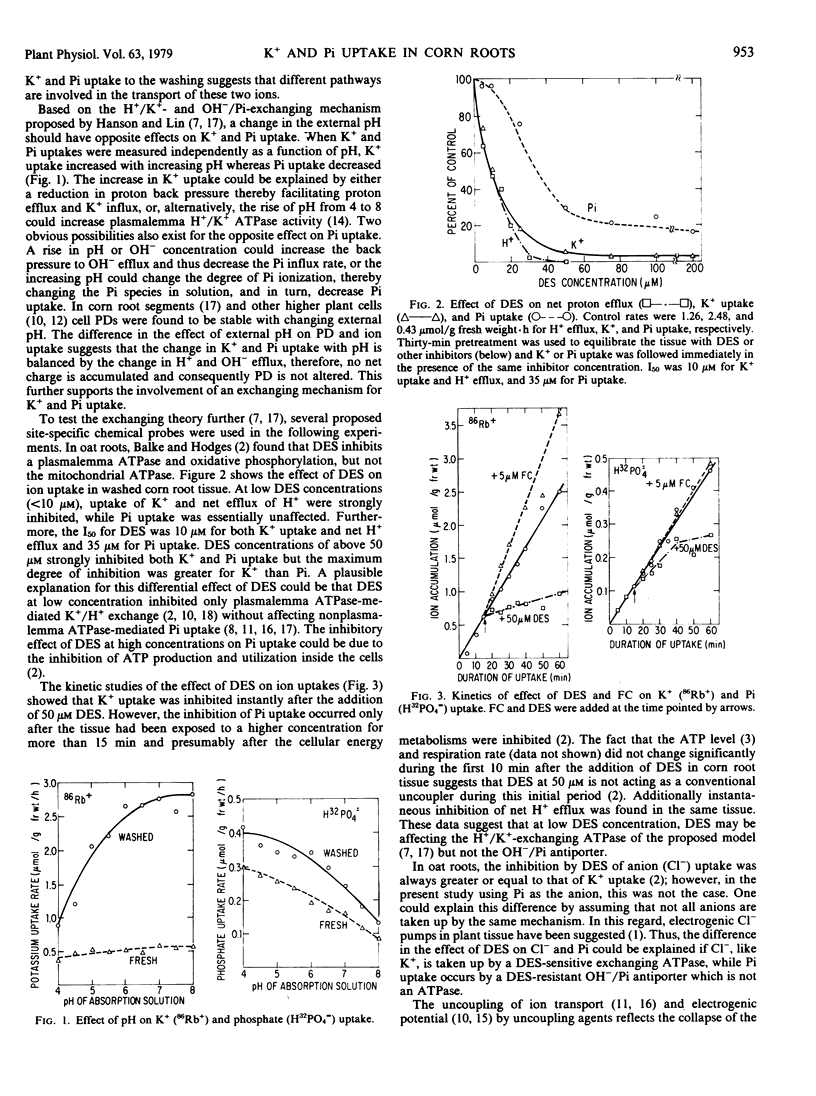
Evidence is presented that K+ uptake in corn root segments is coupled to an electrogenic H+/K+ -exchanging plasmalemma ATPase while phosphate uptake is coupled to an OH−/Pi antiporter. The plasmalemma ATPase inhibitor, diethylstilbestrol, or the stimulator, fusicoccin, altered K+ uptake directly and phosphate uptake indirectly. On the other hand, mersalyl, an OH−/Pi antiporter inhibitor, inhibited phosphate uptake instantly but only slightly affected K+ uptake. Collapse of the proton gradient across the membrane by (p-trifluoromethoxy) carbonyl cyanide phenylhydrazone resulted in immediate inhibition of K+ uptake but only later inhibited phosphate uptake. Changing the pH of the absorption solution had opposite effects on K+ and phosphate uptake. In addition, a 4-hour washing of corn root tissue induced a 5-fold increase in the rate of K+ uptake with little or no lag, but only a 2- to 3-fold increase in phosphate uptake with a 30- to 45-minute lag. Collectively these differences strongly support the coupling of an electrogenic H+/K+ -exchanging ATPase to an OH−/Pi antiporter in corn root tissue.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Day D. A., Hanson J. B. Effect of phosphate and uncouplers on substrate transport and oxidation by isolated corn mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1977 Feb;59(2):139–144. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick H., Nicholson R. L., Hodges T. K., Bauman L. F. Influence of Helminthosporium maydis, Race T, Toxin on Potassium Uptake in Maize Roots. Plant Physiol. 1976 Feb;57(2):171–174. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaquinta R. Phloem Loading of Sucrose: pH Dependence and Selectivity. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):750–755. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson J. B., Bertagnolli B. L., Shepherd W. D. Phosphate-induced Stimulation of Acceptorless Respiration in Corn Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1972 Sep;50(3):347–354. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.3.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hanson J. B. Induction and development of increased ion absorption in corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):430–435. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hodges T. K. Characterization of Plasma Membrane-associated Adenosine Triphosphase Activity of Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jul;52(1):6–12. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Hanson J. B. Cell potentials, cell resistance, and proton fluxes in corn root tissue: effects of dithioerythritol. Plant Physiol. 1976 Sep;58(3):276–282. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.3.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Hanson J. B. Increase in electrogenic membrane potential with washing of corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1974 Nov;54(5):799–801. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.5.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Hanson J. B. Phosphate absorption rates and adenosine 5'-triphosphate concentrations in corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):250–256. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrondo R. T., Smith R. C. Effect of removal of the root tip on the development of enhanced rb absorption by corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):607–611. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



