Abstract
Background
A decrease in blood lactate levels (Lac) >10% during the first hours of resuscitation in sepsis is associated with better outcomes, but the mechanisms are unclear. Our objective was to investigate the relationship between the time course of Lac, inflammatory response, and mitochondrial respiration during experimental sepsis.
Methods
Original data from two previously published studies were reanalyzed. In cohort 1, pigs were randomized to be resuscitated for 48 h starting at 6, 12, and 24 h, respectively, after fecal peritonitis induction (n = 8 each). Animals were categorized according to the decrease in Lac during the first 6 h of resuscitation (early if ≥10% [Lac ≥10%] or late if <10% or increased [Lac <10%]), and systemic hemodynamics, inflammatory parameters, and mitochondrial function were compared between groups. In a second group of animals with fecal peritonitis and 24 h of resuscitation (n = 16, cohort 2), abdominal regional Lac exchange was measured, and animals were categorized according to the decrease in Lac as in cohort 1.
Results
Overall mortality was 20% (4 of 20) in the Lac ≥10% group and 60% (12 of 20) in the Lac <10% group (p = 0.022). In cohort 1, systemic hemodynamics were similar in the Lac ≥10% (n = 13) and Lac <10% (n = 11) groups. Plasma interleukin-6 levels increased during unresuscitated sepsis and decreased during resusciation in both groups, but they were lower at study end in the Lac ≥10% group (p = 0.047). Complexes I and II maximal (state 3) and resting (state 4) isolated brain mitochondrial respiration at study end was higher in the Lac ≥10% group than in the Lac <10% group, whereas hepatic, myocardial, and skeletal muscle mitochondrial respiration was similar in both groups. In cohort 2, mesenteric, total hepatic, and renal blood flow at study end was higher in the Lac ≥10% group (n = 7) than in the Lac <10% group (n = 9), despite similar cardiac output. Hepatic lactate influx and uptake in the Lac ≥10% group were approximately 1.5 and 3 times higher, respectively, than in the Lac <10% group (p = 0.066 for both).
Conclusions
A decrease in Lac >10% during early resuscitation (6 h) after abdominal sepsis is associated with lower levels of plasma interleukin-6 and improved brain but not hepatic or muscle mitochondrial respiration. Blood flow redistribution to abdominal organs in animals with early decrease in Lac concentrations increases the potential to both deliver and extract Lac.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13054-017-1691-4) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Sepsis, Septic shock, Lactate kinetics, Mitochondrial respiration, Resuscitation, Cytokines, Multiple organ failure
Background
Hyperlactatemia and lactic acidosis are widely accepted as strong predictors of multiple-organ dysfunction and death in different populations of critically ill patients [1–5]. Measurement of blood lactate (Lac) for the management of severe sepsis and septic shock has been strongly recommended since the first publication of the international sepsis guidelines [6, 7].
Although there are no single or direct interventions available to reverse hyperlactatemia, it has been proposed that Lac could be used as a guide during early resuscitation of patients with sepsis [8, 9]. It has been shown that a decrease in blood Lac levels >10% during the first 6 h of resuscitation is associated with reduced in-hospital mortality [10]. Interestingly, in another study, mortality was improved in the group with the goal of early Lac decrease despite the fact that achieved Lac values did not differ between the intervention and control groups [8].
In the last 2 decades, the assumption that high Lac levels represent a consequence of anaerobic metabolism has been challenged [11]. Other factors not related to insufficient tissue oxygen delivery may contribute to hyperlactatemia, such as impaired aerobic respiration, accelerated aerobic glycolysis, and reduced Lac uptake by the liver [12].
We recently demonstrated that treatment delay in fecal peritonitis increased inflammatory markers and Lac concentrations and was associated with impaired cerebral mitochondrial respiration at the end of the resuscitation period [13]. However, all these variables varied widely in individual animals [13]. In the present investigation, we hypothesized that animals with a greater decrease in blood Lac levels during the early resuscitation period would exhibit a less intense inflammatory response and preserve better mitochondrial respiration. To evaluate a possible contribution of gut and hepatic Lac handling to time course of blood Lac levels, we reanalyzed a second group of animals with fecal peritonitis where these measurements were available [14].
Methods
We used original data from two previously published studies [13, 14]. The studies were performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Experimental Animals and with the approval of the Animal Care Committee of the Canton of Bern, Switzerland.
The first study (cohort 1) was designed to address the impact of three different treatment delays (i.e., resuscitation initiated 6, 12, or 24 h after induction of fecal peritonitis) on disease severity, development of sepsis-associated organ dysfunction, and mitochondrial function [13]. In the second study (cohort 2), the impact of two different fluid resuscitation strategies (moderate-volume and high-volume expansion) on mortality, sepsis-associated organ dysfunction, and mitochondrial function in animals subjected to either fecal peritonitis or endotoxin infusion were evaluated [14]. For cohort 2, only data from animals challenged with fecal peritonitis were included. The full study protocols of the original studies can be found elsewhere [13, 14].
Cohort 1
Experimental protocol
Fecal peritonitis was induced by peritoneal instillation of 2 g/kg body weight of autologous feces dissolved in 200 ml of 5% glucose solution. Thirty minutes after surgery, baseline (BL) measurements were taken. Then animals (n = 8 per group) were randomized to a sham control group or one of three groups in which resuscitation was started 6, 12, or 24 h after peritonitis induction. The 48-h resuscitation period consisted of broad-spectrum antibiotics (piperacillin/tazobactam [Tazobac®; Savoy, Manimajra, India] 2.25 g intravenously) administered every 8 h, volume expansion (alternating bolus of 150 ml of Ringer’s lactate and 6% hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 [HES]), vasopressors, and inotropes wherever necessary to reach predefined hemodynamic goals [13].
Blood gas analyses
Blood samples were drawn from an indwelling carotid artery catheter for Lac measurement (in millimoles per liter) (GEM Premier 3000 analyzer; Instrumentation Laboratory, Bedford, MA, USA) at BL and every 6 h during the resuscitation period. Inflammatory markers (plasma interleukin-6 [IL-6], tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α], and C-reactive protein [CRP]) were measured in blood samples drawn from the carotid artery at BL, immediately before starting resuscitation maneuvers (BR), and at the end of the experiment as previously described [13].
Mitochondrial function and skeletal muscle adenosine triphosphate content
At BL, BR, and the end of the experiment, tissue samples were taken from the right quadriceps muscle to assess mitochondrial function and skeletal muscle adenosine triphosphate (ATP) content as previously reported [13]. Additional tissue samples were taken from the brain, liver (left lobe), and heart (left ventricle) at the end of the experiment [13]. In animals that died earlier, the final tissue samples were taken when the animals were still alive, were receiving the maximal norepinephrine dose (1000 μg/h), and when mean arterial blood pressure approached 30 mmHg [13].
Oxygen consumption by complexes I, II, and IV was measured using high-resolution respirometry (Oxygraph-2 k; Oroboros Instruments, Innsbruck, Austria) and was expressed as picomoles per second per milligram of mitochondrial protein. State 3 represents active respiration after addition of adenosine diphosphate (ADP), whereas state 4 represents respiration after depletion of ADP. The respiratory control ratio, an indicator of coupling between respiration and ATP phosphorylation, was calculated by dividing state 3 by state 4 respiration rates [13]. The time course of blood Lac levels was defined as change in blood Lac levels in percent during 6 h of resuscitation [15].
Cohort 2
Surgical preparation
With animals in supine position, a midline laparotomy was performed, and the abdominal cavity was exposed [14]. Catheters for pressure monitoring and blood sampling were inserted into the carotid, hepatic, and pulmonary arteries and into the jugular, hepatic, portal, mesenteric, splenic, and renal veins [14]. A large-bore catheter for fluid administration was inserted into the femoral vein. Ultrasound Doppler flow probes (Transonic® Systems Inc., Ithaca, NY, USA) were placed around the carotid, superior mesenteric, splenic, hepatic, celiac trunk, and renal arteries and around the portal vein. A drainage catheter was inserted into the urinary bladder. Finally, two large-bore drains were inserted into both flanks of the animals [14]. The surgical procedure was followed by a 12-h period of hemodynamic stabilization.
Experimental protocol
Fecal peritonitis was induced by peritoneal instillation through a peritoneal drainage tube of 1 g/kg body weight of autologous feces dissolved in 200 ml of 5% glucose solution [14]. The intraperitoneal drains were maintained clamped during the following 6 h. Before fecal peritonitis induction, animals were randomized to either moderate-volume (10 ml/kg/h Ringer’s lactate) or high-volume (15 ml/kg/h Ringer’s lactate + 5 ml/kg/h HES) (n = 8 each) fluid resuscitation for 24 h or until death, if earlier. Resuscitation started immediately after fecal peritonitis induction. Wherever necessary to reach a pulmonary arterial occlusion pressure >5 mmHg or urinary output >0.5 ml/kg/h, an additional fluid bolus (50 ml of HES) was given as long as stroke volume increased ≥10%. Vasopressors and inotropes were not used [14].
Blood measurements
Hemoglobin and oxygen saturation were analyzed at BL (before fecal peritonitis induction) and every 6 h thereafter (OSM3; Radiometer, Copenhagen, Denmark). At the same time, blood gases were measured and values corrected for temperature using a blood gas analyzer (ABL520; Radiometer), and arterial and venous blood Lac levels were measured with a Lac analyzer (YSI 2300 STAT PLUS; YSI Life Sciences, Yellow Springs, OH, USA) [14].
Calculations
In contrast to cohort 1, where resuscitation was delayed for 6–24 h, resuscitation in cohort 2 started immediately after fecal peritonitis was induced. Therefore, BL for Lac time-course analysis in cohort 2 was considered after 6 h of resuscitation, corresponding to the shortest resuscitation delay in cohort 1 and the time point of maximum Lac levels.
Systemic oxygen delivery and consumption were calculated according to standard formulas [16, 17]. Hepatic Lac influx (in micromoles per kilogram per minute) was calculated as follows: (portal venous Lac × portal vein blood flow) + (arterial Lac × hepatic arterial blood flow). Hepatic Lac efflux (in micromoles per kilogram per minute) was calculated as follows: hepatic venous Lac × (portal venous + hepatic arterial blood flow). Hepatic Lac uptake (in micromoles per kilogram per minute) was calculated as follows: hepatic Lac influx − hepatic Lac efflux. Other regional Lac exchanges (spleen, gut, kidney, and lung) were calculated as follows: regional Lac influx − regional Lac efflux. Whole-body venous efflux (in micromoles per kilogram per minute) was calculated as follows: cardiac output × mixed venous Lac concentration. Extrahepatic organ Lac efflux was calculated as follows: (cardiac output × mixed venous Lac concentration) − hepatic Lac efflux [17].
Statistical analysis
In each cohort, animals were classified according to their time course of blood Lac levels: early (≥10% Lac decrease, Lac ≥10%) vs. late (<10% Lac decrease or increase, Lac <10%). All data are presented as mean ± SD, or as median with IQR in cases of non-normal distribution (tested by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test).
Proportions between groups were compared with Fisher’s exact test. Survival analysis was performed using the Kaplan-Meier method, and the log-rank test was used for between-group comparisons. Continuous variables (administered treatments; fluid output and balance; brain, liver, and heart mitochondrial respiration) were compared between groups with an independent-samples t test or with the Mann-Whitney U test in cases of non-normal distribution.
Repeated measurements were assessed by analysis of variance using group as a between-subjects factor and time as a within-subjects factor. If a time × group interaction was detected, independent-samples t tests were performed at the end of the 6-h resuscitation period used for Lac kinetics and at the end of the experiment. In cases of non-normal distribution, time effects within each group were separately assessed by Friedman’s test followed by a Mann-Whitney U test at the end of the 6-h resuscitation period and at the end of the experiment for differences between groups. To account for testing twice, the significance level was reduced from 0.05 to 0.025 (Bonferroni correction). IBM SPSS Statistics version 21.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for statistical analyses, and Prism version 6.07 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA) was used for graph plotting.
Results
Cohort 1
Twenty-four domestic pigs of both sexes (mean ± SD weight 40.2 ± 3.8 kg) were analyzed. Of those, 13 of 24 (54.2%) had a decrease in blood Lac levels ≥10% (early or Lac ≥10% group) and 11 of 24 (45.8%) had a decrease in blood Lac levels <10% (late or Lac <10%) (Fig. 1). An additional.pdf file shows this in more detail (see Additional file 1: Table S1).
Fig. 1.
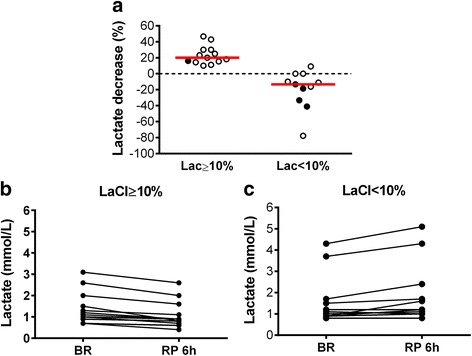
Time course of blood lactate (Lac) levels in cohort 1 animals. a Changes in blood Lac levels during the first 6 h of resuscitation accordingly to study group. b and c Individual arterial Lac levels before starting resuscitation maneuvers (BR) and after the first 6-h resuscitation period (RP 6 h) in the Lac ≥10% and Lac <10% groups. Filled circles in (a) represent animals that died during the 48-h resuscitation period. Red horizontal bars represent median values
Mortality
One of 13 animals (7.7%) in the Lac ≥10% group and 4 of 11 animals (36.4%) in the Lac <10% group died during the resuscitation period (p = 0.082) (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
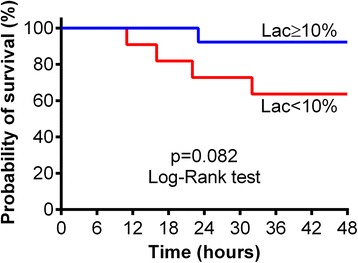
Kaplan-Meier curves for 48-h survival after the beginning of resuscitation in cohort 1
Administered treatments
Doses of administered propofol, midazolam, fentanyl, resuscitation fluids, norepinephrine, and dobutamine, as well as net fluid balance, did not differ between the Lac ≥10% and Lac <10% groups (Table 1).
Table 1.
Administered treatment, fluid output, and balance in cohort 1 study
| Parameters | Lac ≥10% | Lac <10% | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propofol, mg/kg/h | 5.7 (5.1–6.2) | 5.5 (4.9–5.9) | 0.459a |
| Fentanylb, μg/kg/h | 4.9 (4.5–5.7) | 5.2 (5.0–8.1) | 0.072a |
| Midazolam, mg/kg/h | 0.05 (0.04–0.06) | 0.06 (0.05–00.7) | 0.331a |
| Fluid bolusc,d, ml/kg/h | 0.80 (0.53–1.24) | 1.68 (0.50–2.82) | 0.186a |
| Ringer’s lactate | 0.45 (0.30–0.65) | 0.84 (0.28–1.75) | 0.186a |
| HES | 0.39 (0.23–0.58 | 0.84 (0.21–1.07) | 0.150a |
| Norepinephrine | |||
| n/Total n, % | 7/13 (53.8) | 8/11 (72.7) | 0.423e |
| Dose, μg/kg/minute | 0.02 (0.01–0.07) | 0.10 (0.06–0.22) | 0.054a |
| Dobutamine | |||
| n/Total n, % | 2/13 (15.4) | 5/11 (45.5) | 0.182e |
| Dose, μg/kg/minute | 1.89 (0.65–3.13) | 0.44 (0.33–0.58) | 0.190a |
| Total volume receivedf, ml/kg/h | 3.61 (3.49–4.11) | 4.12 (3.43–5.39) | 0.303a |
| Urine output, ml/kg/h | 1.00 (0.96–1.15) | 1.21 (0.99–1.36) | 0.134a |
| Gastric tube output, ml/kg/h | 0.22 (0.05–0.30) | 0.42 (0.22–0.71) | 0.036a |
| Final balanceg, ml/kg/h | 2.48 (2.15–2.75) | 2.45 (1.93–4.13) | 1.000a |
HES 6% Hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4, Lac Lactate
Values are median (IQR) or n/total n (%) when indicated
aMann-Whitney U test
bSum of basic fentanyl infusion with additional bolus
cSum of Ringer’s lactate and HES
dAdministered during resuscitation period
eFisher’s exact test
fSum of Ringer’s lactate basal infusion + 50% glucose basal infusion + Ringer’s lactate bolus + HES
gFinal balance = total volume received − (urine output + gastric tube output)
Hemodynamics and respiratory and acid-base parameters
Systemic and regional hemodynamics and oxygenation did not differ between the Lac ≥10% and Lac <10% groups (Table 2). Respiratory parameters (see Additional file 1: Table S2), as well as arterial blood gas analysis and hemoglobin levels (see Additional file 1: Table S3), were similar in both groups.
Table 2.
Hemodynamics and arterial lactate levels in cohort 1
| Parameters | Group | BL | BR | RP 6 h | End | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart rate, beats/minute | Lac ≥10% | 94 ± 20 | 160 ± 40 | 165 ± 26 | 132 ± 34 | 0.369a |
| Lac <10% | 97 ± 17 | 166 ± 30 | 161 ± 34 | 154 ± 33 | ||
| MAP, mmHg | Lac ≥10% | 85 ± 12 | 75 ± 11 | 82 ± 13 | 65 ± 10 | 0.113a |
| Lac <10% | 88 ± 13 | 77 ± 19 | 71 ± 12 | 56 ± 20 | ||
| MPAP, mmHg | Lac ≥10% | 14 ± 3 | 17 ± 3 | 17 ± 3 | 21 ± 5 | 0.594a |
| Lac <10% | 15 ± 6 | 17 ± 5 | 20 ± 6 | 22 ± 4 | ||
| CVP, mmHg | Lac ≥10% | 4 ± 1 | 3 ± 2 | 3 ± 2 | 7 ± 2 | 0.632a |
| Lac <10% | 5 ± 3 | 2 ± 2 | 3 ± 2 | 8 ± 4 | ||
| Cardiac output, ml/kg/minute | Lac ≥10% | 131 ± 14 | 106 ± 16 | 120 ± 20 | 151 ± 32 | 0.618a |
| Lac <10% | 132 ± 22 | 119 ± 33 | 122 ± 24 | 144 ± 46 | ||
| SVRI, mmHg, L/kg/minute | Lac ≥10% | 629 ± 112 | 696 ± 146 | 677 ± 154 | 393 ± 92 | 0.322a |
| Lac <10% | 654 ± 171 | 652 ± 164 | 575 ± 164 | 326 ± 73 | ||
| SvO2, % | Lac ≥10% | 55 ± 8 | 59 ± 11 | 64 ± 9 | 63 ± 12 | 0.264a |
| Lac <10% | 53 ± 9 | 57 ± 6 | 60 ± 6 | 52 ± 18 | ||
| DO2, ml/minute | Lac ≥10% | 625 ± 99 | 684 ± 116 | 739 ± 76 | 653 ± 151 | 0.796a |
| Lac <10% | 610 ± 148 | 702 ± 133 | 697 ± 156 | 609 ± 197 | ||
| VO2, ml/minute | Lac ≥10% | 273 ± 63 | 270 ± 86 | 249 ± 79 | 220 ± 81 | 0.987a |
| Lac <10% | 275 ± 61 | 281 ± 48 | 256 ± 60 | 234 ± 59 | ||
| O2ER | Lac ≥10% | 0.44 ± 0.08 | 0.40 ± 0.11 | 0.34 ± 0.10 | 0.34 ± 0.13 | 0.511a |
| Lac <10% | 0.46 ± 0.09 | 0.41 ± 0.05 | 0.37 ± 0.06 | 0.43 ± 0.18 | ||
| Fractional carotid artery blood flow, % | Lac ≥10% | 5.8 ± 1.9 | 4.7 ± 1.8 | 4.6 ± 1.5 | 4.4 ± 1.5 | 0.340a |
| Lac <10% | 5.8 ± 1.2 | 5.4 ± 1.3 | 5.6 ± 1.3 | 5.0 ± 2.0 | ||
| Fractional femoral artery blood flow, % | Lac ≥10% | 3.3 ± 1.1 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 0.499a |
| Lac <10% | 3.3 ± 0.8 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 2.2 ± 0.9 | 2.1 ± 0.8 | ||
| Arterial Lac, mmol/L | Lac ≥10% | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.7 | 1.1 ± 0.6 | 1.1 ± 0.7 | 0.124a |
| Lac <10% | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 1.2 | 1.9 ± 1.4 | 2.3 ± 2.5 |
Abbreviations: BL Baseline, BR Immediately before start resuscitation, RP Resuscitation period, End End of the experiment (at 48 h of resuscitation or before death if earlier), MAP Mean arterial blood pressure, MPAP Mean pulmonary arterial pressure, CVP Central venous pressure, SVRI Systemic vascular resistance index, SvO 2 Mixed venous oxygen saturation, DO 2 Oxygen delivery, VO 2 Oxygen consumption, O 2 ER Oxygen extraction ratio
Values represent mean ± SD
aTime × group interaction with repeated-measures analysis of variance including all time points
Inflammatory markers and skeletal muscle ATP
Plasma IL-6 levels increased during untreated sepsis and decreased during the resuscitation period in both groups, but they were lower at the end of the study in the Lac ≥10% group than in the Lac <10% group (p = 0.047) (Table 3). Plasma TNF-α levels, CRP, and skeletal muscle ATP content did not differ between groups (Table 3).
Table 3.
Inflammatory markers and skeletal muscle adenosine triphosphate content in cohort 1
| Parameters | Group | BL | BR | End | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6, pg/ml | Lac ≥10% | 0 (0–0) | 854 (481–990) | 45 (37–204) | 0.003a |
| Lac <10% | 16 (0–180) | 873 (531–1983) | 166 (128–310) | <0.001a | |
| 0.047b | |||||
| CRP, pg/ml | Lac ≥10% | 1.6 (0.6–2.9) | 10.7 (5.6–12.8) | 19.2 (9.9–39.8) | 0.139c |
| Lac <10% | 3.2 (1.8–5.7) | 16.7 (4.9–31.1) | 16.7 (13.5–33.3) | ||
| TNF-α, pg/ml | Lac ≥10% | 53 (38–55) | 119 (94–169) | 72 (47–88) | 0.579c |
| Lac <10% | 47 (37–67) | 178 (120–219) | 92 (57–144) | ||
| ATP content, μmol/g wet tissue weight | Lac ≥10% | 2.1 (1.2–2.3) | 2.3 (1.8–3.1) | 0.6 (0.4–0.9) | 0.081c |
| Lac <10% | 2.8 (1.8–4.5) | 3.3 (1.5–4.8) | 0.6 (0.3–0.7) |
Abbreviations: ATP Adenosine triphosphate, BL Baseline, BR Immediately before start resuscitation, End End of the experiment (at 48 h of resuscitation or before death if earlier), IL-6 Interleukin-6, CRP C-reactive protein, TNF-α Tumor necrosis factor-α
Values represent median (IQR)
aTime effect with Friedman’s test including all time points
bMann-Whitney U test at end of study
cTime × group interaction with repeated-measures analysis of variance including all time points
Mitochondrial respiration
Complexes I and II maximal (state 3) and resting (state 4) isolated brain mitochondrial respiration at the end of the experiment were higher in the Lac ≥10% group than in the Lac <10% group (Fig. 3 and Additional file 1: Table S4). Isolated skeletal muscle (see Additional file 1: Table S5), liver (see Additional file 1: Table S6), and heart (see Additional file 1: Table S7) mitochondrial respiration did not differ between the groups.
Fig. 3.
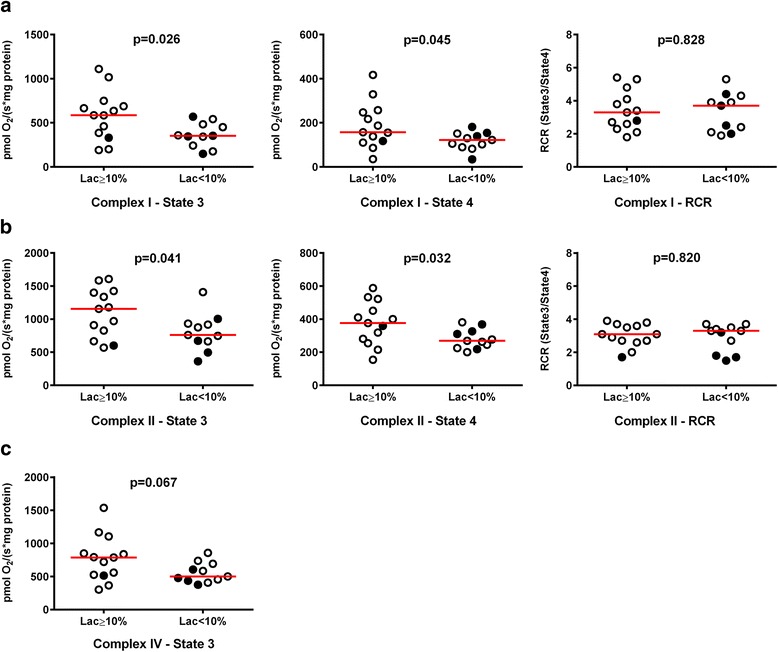
Isolated brain mitochondrial respiration in cohort 1 animals. Red horizontal bars represent median values. Black filled circles represent animals that died during the resuscitation period. p Values provided were calculated with an independent-samples t test or the Mann-Whitney U test. State 3 represents active respiration after addition of adenosine diphosphate (ADP), and state 4 represents the respiration after depletion of ADP. The respiratory control ratio (RCR) was calculated by dividing state 3 by state 4 respiration rates. a Complex I. b Complex II. c Complex – IV
Cohort 2
Sixteen domestic pigs of both sexes (mean ± SD weight 41.6 ± 2.7 kg) were included in the cohort 2 analysis. Of those, 7 of 16 (43.8%) exhibited a decrease in blood Lac levels ≥10% (early group), and 9 of 16 (56.2%) had a decrease in blood Lac levels <10% (late group) (see Additional file 1: Table S8 and Figure S1).
Mortality
Three of seven animals (42.9%) in the early (Lac ≥10%) group and eight of nine animals (88.9%) in the late (Lac <10%) group died during the resuscitation period (p = 0.006) (Additional file 1: Figure S2).
Hemodynamics
Systemic hemodynamics did not differ between the groups during the study period (see Additional file 1: Table S9).
Regional blood flow and Lac exchange
Superior mesenteric artery blood flow increased and renal artery blood flow decreased in both groups during the 24 h of resuscitation, but both flows were higher at the end in the Lac ≥10% group than in the Lac <10% group (Table 4). Similarly, total hepatic blood flow was higher in the Lac ≥10% group than in the Lac <10% group at the study end (Table 4). Fractional regional blood flows are presented in Additional file 1: Table S10.
Table 4.
Regional blood flow in cohort 2
| Parameters | Group | BL | 3 h | 6 h | 12 h | End | p value | Time × group p valuea | Time p valuea | Group p valuea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carotid artery | Lac ≥10% | 4.2 ± 0.9 | 3.8 ± 1.1 | 3.6 ± 0.5 | 3.2 ± 0.7 | 5.7 ± 2.6 | 0.030b | 0.077 | 0.458 | 0.078 |
| Lac <10% | 3.9 ± 0.9 | 4.1 ± 1.3 | 4.1 ± 1.4 | 5.0 ± 2.0 | 4.9 ± 1.6 | 0.457c | ||||
| 0.028c | ||||||||||
| Superior mesenteric artery | Lac ≥10% | 18.4 ± 8.0 | 17.7 ± 9.8 | 17.5 ± 6.6 | 18.8 ± 9.6 | 26.6 ± 11.0 | 0.010b | 0.858 | 0.179 | 0.807 |
| Lac <10% | 13.7 ± 2.9 | 15.7 ± 3.1 | 16.6 ± 3.4 | 18.2 ± 4.1 | 15.3 ± 7.6 | 0.028c | ||||
| Celiac trunk | Lac ≥10% | 9.2 ± 4.6 | 10.8 ± 3.4 | 9.8 ± 4.4 | 12.5 ± 3.9 | 11.8 ± 5.9 | 0.191b | 0.067 | 0.221 | 0.067 |
| Lac <10% | 8.8 ± 3.7 | 9.2 ± 4.1 | 9.9 ± 4.2 | 9.3 ± 5.0 | 7.0 ± 2.1 | |||||
| Hepatic artery | Lac ≥10% | 4.2 ± 3.7 | 5.2 ± 2.9 | 5.0 ± 3.0 | 6.3 ± 3.6 | 5.5 ± 2.6 | 0.232b | 0.100 | 0.149 | 0.142 |
| Lac <10% | 3.7 ± 1.8 | 3.0 ± 1.6 | 3.7 ± 1.8 | 3.6 ± 2.3 | 2.5 ± 0.9 | |||||
| Portal vein | Lac ≥10% | 20.5 ± 7.0 | 20.5 ± 11.5 | 19.2 ± 6.7 | 20.5 ± 8.4 | 27.4 ± 11.6 | 0.006b | 0.717 | 0.408 | 0.488 |
| Lac <10% | 19.3 ± 5.4 | 22.3 ± 5.6 | 21.8 ± 4.3 | 22.3 ± 6.0 | 17.3 ± 10.0 | 0.083c | ||||
| Total hepaticd | Lac ≥10% | 24.8 ± 8.2 | 25.7 ± 12.1 | 24.2 ± 8.0 | 26.8 ± 9.4 | 32.8 ± 13.0 | 0.006b | 0.371 | 0.224 | 0.965 |
| Lac <10% | 23.0 ± 5.4 | 25.3 ± 6.1 | 25.4 ± 4.7 | 25.9 ± 7.8 | 19.8 ± 10.1 | 0.040c | ||||
| Spleen artery | Lac ≥10% | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 1.0 | 1.2 ± 1.2 | 0.049b | 0.115 | 0.341 | 0.766 |
| Lac <10% | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 1.2 | 1.3 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 1.0 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.167c | ||||
| Renal artery | Lac ≥10% | 5.2 ± 1.9 | 5.1 ± 1.4 | 4.4 ± 1.0 | 5.0 ± 1.0 | 3.9 ± 1.3 | 0.036b | 0.059 | 0.409 | 0.782 |
| Lac <10% | 5.8 ± 2.0 | 5.4 ± 2.1 | 5.7 ± 2.9 | 4.3 ± 2.7 | 2.1 ± 1.4 | 0.018c |
BL baseline, End End of experiment after 24 h of randomization or before death, if earlier
Values represent mean ± SD. All flows are in milliliters per kilogram per minute
a p Values were calculated with repeated-measures analysis of variance including time points 6 h and 12 h for time × group interaction, time effect, and group effect
bTime × group interaction with repeated-measures analysis of variance including all time points
cIndependent-samples t test at end of study
dSum of hepatic artery and portal vein blood flows
Hepatic Lac delivery (hepatic Lac influx) and uptake in the Lac ≥10% group were approximately 1.5 and 3 times higher, respectively, than in the Lac <10% group at the end of the study, although statistical significance was not reached (p = 0.066 for both) (Table 5). Gut, spleen, kidney, and lung Lac uptake did not differ between groups (Table 5).
Table 5.
Lac influx, efflux, and uptake in cohort 2
| Parameters | Group | BL | 3 h | 6 h | 12 h | End | p value | Time × group p valuea | Time p valuea | Group p valuea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatic Lac uptake | Lac ≥10% | 10.3 (7.0 to 14.8) | 7.8 (5.5 to 15.7) | 10.6 (2.3 to 11.4) | 15.4 (8.0 to 17.3) | 23.0 (8.9 to 26.3) | 0.066b | 0.389 | 0.221 | 0.754 |
| Lac <10% | 12.1 (11.9 to 19.5) | 15.0 (10.2 to 22.5) | 11.4 (9.3 to 12.7) | 7.0 (3.5 to 22.3) | 7.5 (6.6 to 11.2) | |||||
| Hepatic Lac influx | Lac ≥10% | 24.8 (19.0 to 30.2) | 30.8 (18.8 to 57.8) | 23.9 (19.0 to 49.4) | 39.4 (13.6 to 47.1) | 32.6 (29.0 to 59.6) | 0.066c | |||
| Lac <10% | 27.1 (19.3 to 45.0) | 35.2 (16.5 to 56.5) | 25.5 (18.3 to 33.7) | 32.5 (17.5 to 45.2) | 20.3 (10.1 to 32.5) | 0.321c | ||||
| Hepatic Lac efflux | Lac ≥10% | 12.7 (8.1 to 26.3) | 15.0 (5.5 to 52.4) | 21.3 (7.7 to 35.9) | 26.0 (6.8 to 27.1) | 22.1 (10.1 to 30.3) | 0.645b | 0.576 | 0.036 | 0.560 |
| Lac <10% | 12.4 (9.1 to 23.7) | 14.7 (4.7 to 38.8) | 15.4 (8.1 to 20.9) | 19.9 (14.0 to 32.3) | 14.3 (3.5 to 21.6) | |||||
| Gut Lac uptake | Lac ≥10% | −2.6 (−2.9 to 0.3) | −2.2 (−2.8 to −2.1) | −1.7 (−3.9 to 0.3) | −2.4 (−6.8 to 0.5) | −3.8 (−9.9 to −0.6) | 0.942b | 0.440 | 0.779 | 0.299 |
| Lac <10% | −1.4 (−3.7 to 5.2) | −3.3 (−10.7 to 1.3) | −2.9 (−4.0 to −0.9) | −4.7 (−11.6 to −1.8) | −2.1 (−3.8 to −0.4) | |||||
| Spleen Lac uptake | Lac ≥10% | −0.2 (−0.7 to −0.2) | −0.2 (−0.6 to −0.1) | −0.2 (−1.1 to −0.1) | −0.1 (−0.9 to −0.1) | 0.0 (−0.4 to 0.2) | 0.185b | 0.465 | 0.347 | 0.911 |
| Lac <10% | −0.1 (−0.3 to 0.1) | −0.1 (−0.3 to 0.1) | −0.3 (−1.6 to −0.1) | −0.1 (−0.7 to 0.0) | −0.1 (−0.2 to 0.0) | |||||
| Kidney Lac uptake | Lac ≥10% | −0.4 (−1.0 to 0.0) | −1.0 (−1.9 to −0.7) | −0.4 (−2.3 to 0.2) | −0.5 (−2.5 to 1.1) | 0.3 (0.1 to 0.9) | 0.110b | 0.743 | 0.546 | 0.921 |
| Lac <10% | −0.1 (−0.8 to 2.5) | 0.4 (−2.0 to 1.7) | −0.6 (−2.1 to 0.2) | −0.2 (−0.7 to 0.4) | −0.4 (−1.0 to 0.3) | |||||
| Lung Lac uptake | Lac ≥10% | −2.0 (−8.3 to 5.4) | −1.1 (−5.9 to 1.6) | −4.4 (−19.8 to 2.7) | −5.4 (−11.9 to 4.3) | 0.0 (−5.4 to 108.3) | 0.622c | |||
| Lac <10% | 4.8 (−3.0 to 7.2) | −4.1 (−18.3 to 25.7) | −0.1 (−6.5 to 5.4) | −6.5 (−17.8 to 3.2) | −5.6 (−32.2 to 5.3) | 0.525c | ||||
| Whole-body venous Lac efflux | Lac ≥10% | 76.9 (61.6 to 116.3) | 84.0 (57.1 to 174.6) | 105.4 (93.8 to 162.8) | 119.7 (47.6 to 123.6) | 104.3 (79.7 to 131.9) | 0.635b | 0.144 | 0.253 | 0.692 |
| Lac <10% | 98.3 (59.2 to 38.6) | 107.3 (61.7 to 215.6) | 90.2 (76.1 to 109.1) | 104.3 (84.3 to 188.1) | 110.5 (69.4 to 327.1) | |||||
| Extrahepatic organ Lac efflux | Lac ≥10% | 69.6 (56.5 to 90.0) | 59.1 (39.1 to 137.2) | 97.0 (72.5 to 117.6) | 91.4 (40.2 to 102.4) | 82.0 (71.0 to 101.6) | 0.346b | 0.077 | 0.883 | 0.397 |
| Lac <10% | 66.3 (50.0 to 123.5) | 92.6 (53.3 to 176.8) | 74.8 (61.5 to 94.8) | 87.9 (66.8 to 154.6) | 102.9 (63.9 to 191.1) |
BL baseline, End End of experiment after 24 h of randomization or before death, if earlier, Lac Lactate
Values represent median (IQR). All Lac uptake and efflux values are in micromoles per kilogram per minute
a p Values were calculated with repeated-measures analysis of variance including time points 6 h and 12 h for time × group interaction, time effect, and group effect
bTime × group interaction was calculated with repeated-measures analysis of variance including all time points
cTime effect was calculated with Friedman’s test including all time points
Hepatic function and oxygen consumption
Serum alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, total bilirubin, and hepatic oxygen consumption did not differ between groups (see Additional file 1: Table S11).
Discussion
The main finding of the present study was that a decrease in blood Lac levels ≥10% during the first 6 h of resuscitation, regardless of the delay in starting resuscitation, was associated with lower levels of IL-6 and higher brain mitochondrial respiration after 48 h of resuscitation. The enhanced decrease in Lac levels (early group) was associated with higher absolute and relative (fraction of cardiac output) abdominal blood flows favoring higher hepatic Lac delivery and uptake.
Lac and inflammation have been linked recently in different contexts and diseases, including in cancer [18], asthma [19], and abdominal surgery [20]. During experimentally induced systemic inflammatory conditions (e.g., acute pancreatitis and acute hepatitis) Lac may downregulate Toll-like receptor 4, NLRP3 (NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 3) inflammasome, and concomitantly IL-1β [21]. Nguyen et al. divided 220 patients with sepsis into 4 different groups according to Lac kinetics and showed an inverse correlation between IL-1 receptor antagonist, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNF-α, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, high-mobility group box 1 protein, D-dimer, and caspase-3 concentrations and Lac clearance quartiles [22]. We do not have data to evaluate whether early decreases in blood Lac levels reduced the extent of inflammation or whether a less aggravated inflammatory response enhanced Lac handling. It is possible that pronounced inflammation directly or indirectly impedes the ability of mitochondria to use Lac as a crucial alternative source of energy [23, 24]. In a study of endotoxemic sheep, both esmolol and dexmedetomidine improved exogenous Lac clearance [23]. The study authors suggested that the anti-inflammatory properties of these two drugs may have contributed to this finding.
The importance of Lac as a mitochondrial substrate was reinforced with the Lac shuttle theory [24] and, very recently, with the demonstration that cytosolic Lac can be directly metabolized within mitochondria by an intrinsic nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase [25, 26]. Increased use of Lac by cerebral mitochondria in animals in our Lac ≥10% group could theoretically explain better mitochondrial respiration.
Whereas mitochondrial respiration was higher in brain biopsies of our Lac ≥10% group animals, it was not in biopsies of heart, liver, and skeletal muscle. On one hand, in sepsis, use of substrates and mitochondrial respiration efficiency vary between organs [27]. On the other hand, brain mitochondria may be especially vulnerable to toxic products released as a consequence of septic liver dysfunction [28]. For example, hyperammonemia can compromise energy metabolism by inhibition of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in cerebral isolated mitochondria [29, 30].
In our Lac ≥10% group, state 3 as well as state 4 respiration was slightly higher than in our Lac <10% group, indicating mild uncoupling of respiration due to proton leak. Mild uncoupling is not associated with decreasing ATP synthesis rates [31]. Proton leak across the mitochondrial inner membrane may be mediated by components of the mitochondrial inner membrane proteins, such as uncoupling proteins and adenine nucleotide translocase [32]. Mild uncoupling can be helpful in protecting against oxidative damage by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production [33, 34]. It has been shown that ROS can activate the transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) [35] and that activation of IL-6 gene expression occurs through NF-κB [36], which may explain higher levels of IL-6 in our Lac <10% group.
Numerically higher hepatic Lac uptake in the Lac ≥10% group of cohort 2 may indicate better-preserved liver function in this group. We cannot judge the effect of increased liver perfusion (and hence Lac delivery) on liver Lac uptake. In a short-term endotoxemic shock model in sheep, exogenous Lac clearance decreased despite maintained liver perfusion [37]. Nevertheless, the authors in that study did not address the relationship between (widely varying) liver perfusion and exogenous Lac clearance in their endotoxemic animals [37]. It has been shown that, in sepsis, the gut releases, among other substances, adrenomedullin, a potent vasodilatory peptide [38]. In our study, the other monitored organs did not play a major role in Lac uptake.
Our findings must be interpreted with caution, mainly regarding inadvertent attempts to establish cause-and-effect relationships, because this was a hypothesis-generating study. On one hand, the different design of the two analyzed studies is a limitation. On the other hand, mortality trend differences were consistent between the early (Lac ≥10%) and late (Lac <10%) groups when resuscitation followed immediately after the septic insult or was delayed. Thus, another limitation is that we did not measure Lac uptake of the brain and the heart, two organs where mitochondrial Lac use has been demonstrated previously [23, 24]. Furthermore, in vitro mitochondrial respiration may not directly reflect in vivo conditions in diseases where substrate availability may be altered. The association between Lac time course, inflammation, and brain mitochondrial function in a clinically relevant model of sepsis suggests that inflammation may modify brain mitochondrial respiration. To evaluate this further, changes in brain tissue inflammation and mitochondrial respiration should be studied.
Conclusions
A decrease in blood Lac level ≥10% is associated with lower levels of plasma IL-6 and better brain mitochondrial respiration during the first 6 h of resuscitation after experimental sepsis induced by fecal peritonitis. Increased liver Lac uptake may account at least partially for the differences.
Acknowledgements
We thank the research nurses, Olgica Beslac and Daniel Mettler, for their assistance during the experiments.
Funding
This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant 32003B-127619) and the Stiftung für die Forschung in Anästhesiologie und Intensivmedizin (Bern, Switzerland) (to SD and SMJ).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
TDC, AJP, and SMJ conceived of the study hypothesis and design. TDC, SB, MV, SD, and SMJ initiated and performed animal experiments. MV and SD performed mitochondria-related experiments. TDC, AJP, and SMJ analyzed and interpreted the data. TDC and AJP wrote the first manuscript draft. SB, MV, SD, JT, and SMJ critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript and assume responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
This study was performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Experimental Animals and with the approval of the Animal Care Committee of the Canton of Bern, Switzerland.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- ADP
Adenosine diphosphate
- ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
- BL
Baseline
- BR
Before starting resuscitation maneuvers
- CRP
C-reactive protein
- CVP
Central venous pressure
- DO2
Oxygen delivery
- END
End of the experiment
- HES
6% Hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4
- IL-6
Interleukin-6
- Lac
Lactate
- MAP
Mean arterial pressure
- MPAP
Mean pulmonary arterial pressure
- NF-κB
Nuclear factor-κB
- O2ER
Systemic oxygen extraction ratio
- RCR
Respiratory control ratio (state 3 respiration divided by state 4 respiration)
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- RP
Resuscitation period
- SvO2
Mixed venous oxygen saturation
- SVRI
Systemic vascular resistance index
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor α
- VO2
Oxygen consumption
Additional file
Composition of study groups in cohort 1. Table S2. Respiratory system variables in cohort 1. Table S3. Arterial blood gas analysis and arterial hemoglobin levels in cohort 1. Table S4. Isolated brain mitochondrial respiration in cohort 1. Table S5. Skeletal muscle-dependent mitochondrial respiration in cohort 1. Table S6. Isolated liver mitochondrial respiration in cohort 1. Table S7. Isolated heart mitochondrial respiration in cohort 1. Table S8. Composition of study groups in cohort 2. Table S9. Systemic hemodynamics and arterial lactate levels in cohort 2. Table S10. Fractional regional blood flow in cohort 2. Table S11. Liver tests and hepatic oxygen consumption in cohort 2. Figure S1. Time course of blood lactate levels in cohort 2. Figure S2. Kaplan-Meier curves for 24-h survival after randomization in cohort 2. (DOC 389 kb)
Footnotes
The work reported was performed in the Experimental Surgery Unit of the University of Bern.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13054-017-1691-4) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Thiago Domingos Corrêa, Phone: +55 11 21510603, Email: thiago.correa@einstein.br.
Adriano José Pereira, Email: Adriano.Pereira2@einstein.br.
Sebastian Brandt, Email: Sebastian.Brandt@uksh.de.
Madhusudanarao Vuda, Email: umadhu999@gmail.com.
Siamak Djafarzadeh, Email: Siamak.Djafarzadeh@insel.ch.
Jukka Takala, Email: Jukka.Takala@insel.ch.
Stephan Mathias Jakob, Email: Stephan.Jakob@insel.ch.
References
- 1.Bakker J, Gris P, Coffernils M, Kahn RJ, Vincent JL. Serial blood lactate levels can predict the development of multiple organ failure following septic shock. Am J Surg. 1996;171:221–6. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(97)89552-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blow O, Magliore L, Claridge JA, Butler K, Young JS. The golden hour and the silver day: detection and correction of occult hypoperfusion within 24 hours improves outcome from major trauma. J Trauma. 1999;47:964–9. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199911000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jeng JC, Jablonski K, Bridgeman A, Jordan MH. Serum lactate, not base deficit, rapidly predicts survival after major burns. Burns. 2002;28:161–6. doi: 10.1016/S0305-4179(01)00098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Meregalli A, Oliveira RP, Friedman G. Occult hypoperfusion is associated with increased mortality in hemodynamically stable, high-risk, surgical patients. Crit Care. 2004;8:R60–5. doi: 10.1186/cc2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Filho RR, Rocha LL, Corrêa TD, Pessoa CM, Colombo G, Assuncao MS. Blood lactate levels cutoff and mortality prediction in sepsis—time for a reappraisal? A retrospective cohort study. Shock. 2016;46:480–5. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dellinger RP, Carlet JM, Masur H, Gerlach H, Calandra T, Cohen J, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30:536–55. doi: 10.1007/s00134-004-2398-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:580–637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jansen TC, van Bommel J, Schoonderbeek FJ, Sleeswijk Visser SJ, van der Klooster JM, Lima AP, et al. Early lactate-guided therapy in intensive care unit patients: a multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182:752–61. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200912-1918OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jones AE, Shapiro NI, Trzeciak S, Arnold RC, Claremont HA, Kline JA. Lactate clearance vs central venous oxygen saturation as goals of early sepsis therapy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2010;303:739–46. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nguyen HB, Rivers EP, Knoblich BP, Jacobsen G, Muzzin A, Ressler JA, et al. Early lactate clearance is associated with improved outcome in severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:1637–42. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000132904.35713.A7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.James JH, Luchette FA, McCarter FD, Fischer JE. Lactate is an unreliable indicator of tissue hypoxia in injury or sepsis. Lancet. 1999;354:505–8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)91132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Garcia-Alvarez M, Marik P, Bellomo R. Sepsis-associated hyperlactatemia. Crit Care. 2014;18:503. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0503-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Correa TD, Vuda M, Blaser AR, Takala J, Djafarzadeh S, Dunser MW, et al. Effect of treatment delay on disease severity and need for resuscitation in porcine fecal peritonitis. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:2841–9. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31825b916b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brandt S, Regueira T, Bracht H, Porta F, Djafarzadeh S, Takala J, et al. Effect of fluid resuscitation on mortality and organ function in experimental sepsis models. Crit Care. 2009;13:R186. doi: 10.1186/cc8179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Puskarich MA, Trzeciak S, Shapiro NI, Albers AB, Heffner AC, Kline JA, et al. Whole blood lactate kinetics in patients undergoing quantitative resuscitation for severe sepsis and septic shock. Chest. 2013;143:1548–53. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-0878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Regueira T, Djafarzadeh S, Brandt S, Gorrasi J, Borotto E, Porta F, et al. Oxygen transport and mitochondrial function in porcine septic shock, cardiogenic shock, and hypoxaemia. Acta Anaesth Scand. 2012;56:846–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2012.02706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gorrasi J, Eleftheriadis A, Takala J, Brandt S, Djafarzadeh S, Bruegger LE, et al. Different contribution of splanchnic organs to hyperlactatemia in fecal peritonitis and cardiac tamponade. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:251084. doi: 10.1155/2013/251084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wei L, Zhou Y, Yao J, Qiao C, Ni T, Guo R, et al. Lactate promotes PGE2 synthesis and gluconeogenesis in monocytes to benefit the growth of inflammation-associated colorectal tumor. Oncotarget. 2015;6:16198–214. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ostroukhova M, Goplen N, Karim MZ, Michalec L, Guo L, Liang Q, et al. The role of low-level lactate production in airway inflammation in asthma. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012;302:L300–7. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00221.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ravishankaran P, Shah AM, Bhat R. Correlation of interleukin-6, serum lactate, and C-reactive protein to inflammation, complication, and outcome during the surgical course of patients with acute abdomen. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011;31:685–90. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hoque R, Farooq A, Ghani A, Gorelick F, Mehal WZ. Lactate reduces liver and pancreatic injury in Toll-like receptor- and inflammasome-mediated inflammation via GPR81-mediated suppression of innate immunity. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:1763–74. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.03.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nguyen HB, Loomba M, Yang JJ, Jacobsen G, Shah K, Otero RM, et al. Early lactate clearance is associated with biomarkers of inflammation, coagulation, apoptosis, organ dysfunction and mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock. J Inflamm (Lond) 2010;7:6. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-7-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hernandez G, Tapia P, Alegria L, Soto D, Luengo C, Gomez J, et al. Effects of dexmedetomidine and esmolol on systemic hemodynamics and exogenous lactate clearance in early experimental septic shock. Crit Care. 2016;20:234. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1419-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brooks GA. Lactate shuttles in nature. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002;30:258–64. doi: 10.1042/bst0300258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.De Bari L, Atlante A, Valenti D, Passarella S. Partial reconstruction of in vitro gluconeogenesis arising from mitochondrial L-lactate uptake/metabolism and oxaloacetate export via novel L-lactate translocators. Biochem J. 2004;380:231–42. doi: 10.1042/bj20031981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chen YJ, Mahieu NG, Huang X, Singh M, Crawford PA, Johnson SL, et al. Lactate metabolism is associated with mammalian mitochondria. Nat Chem Biol. 2016;12:937–43. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ling B, Peng F, Alcorn J, Lohmann K, Bandy B, Zello GA. D-Lactate altered mitochondrial energy production in rat brain and heart but not liver. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2012;9:6. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-9-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ott P, Vilstrup H. Cerebral effects of ammonia in liver disease: current hypotheses. Metab Brain Dis. 2014;29:901–11. doi: 10.1007/s11011-014-9494-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lai JC, Cooper AJ. Brain α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: kinetic properties, regional distribution, and effects of inhibitors. J Neurochem. 1986;47:1376–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cooper AJ, Plum F. Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia. Physiol Rev. 1987;67:440–519. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.2.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tejerina S, De Pauw A, Vankoningsloo S, Houbion A, Renard P, De Longueville F, et al. Mild mitochondrial uncoupling induces 3 T3-L1 adipocyte de-differentiation by a PPARγ-independent mechanism, whereas TNFα-induced de-differentiation is PPARγ dependent. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:145–55. doi: 10.1242/jcs.027508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ruiz-Ramírez A, López-Acosta O, Barrios-Maya MA, El-Hafidi M. Cell death and heart failure in obesity: role of uncoupling proteins. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:9340654. doi: 10.1155/2016/9340654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Divakaruni AS, Brand MD. The regulation and physiology of mitochondrial proton leak. Physiology (Bethesda) 2011;26:192–205. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00046.2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shabalina IG, Nedergaard J. Mitochondrial (‘mild’) uncoupling and ROS production: physiologically relevant or not? Biochem Soc Trans. 2011;39:1305–9. doi: 10.1042/BST0391305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gloire G, Legrand-Poels S, Piette J. NF-κB activation by reactive oxygen species: fifteen years later. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:1493–505. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Libermann TA, Baltimore D. Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-κB transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:2327–34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.10.5.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tapia P, Soto D, Bruhn A, Alegria L, Jarufe N, Luengo C, et al. Impairment of exogenous lactate clearance in experimental hyperdynamic septic shock is not related to total liver hypoperfusion. Crit Care. 2015;19:188. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0928-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhou M, Chaudry IH, Wang P. The small intestine is an important source of adrenomedullin release during polymicrobial sepsis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001;281:R654–60. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.2001.281.2.R654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.


