Abstract
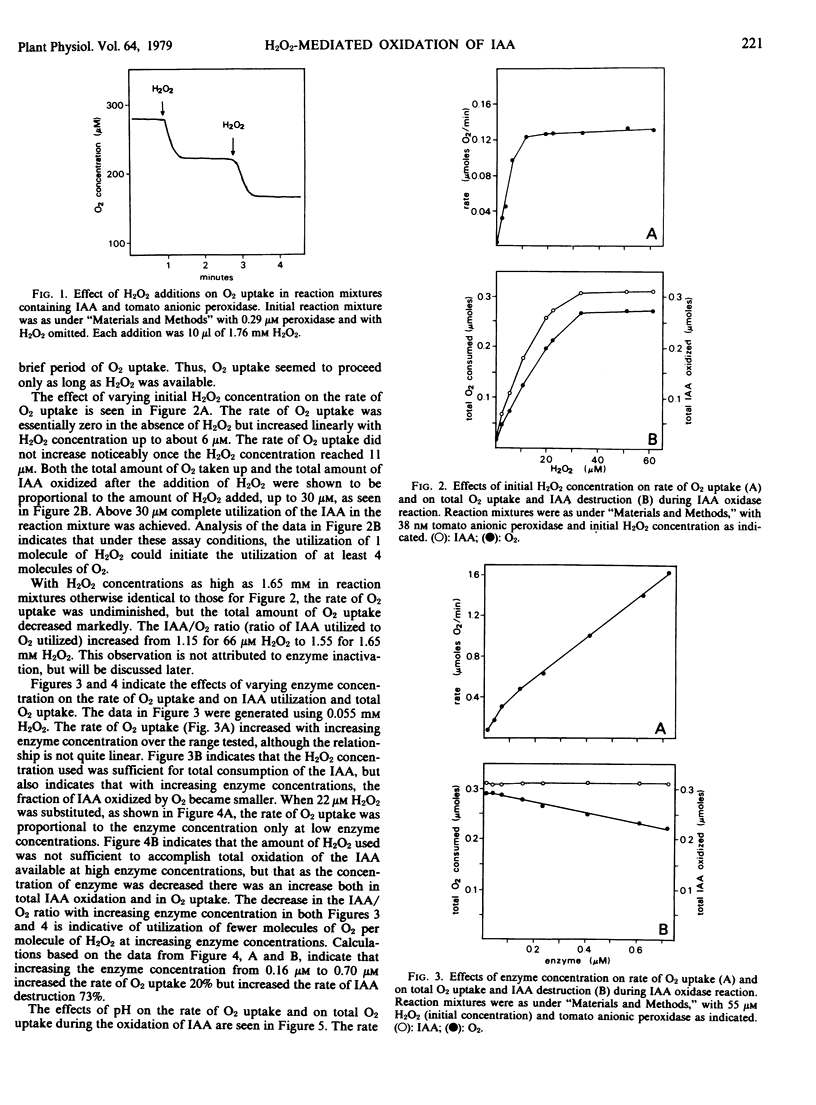
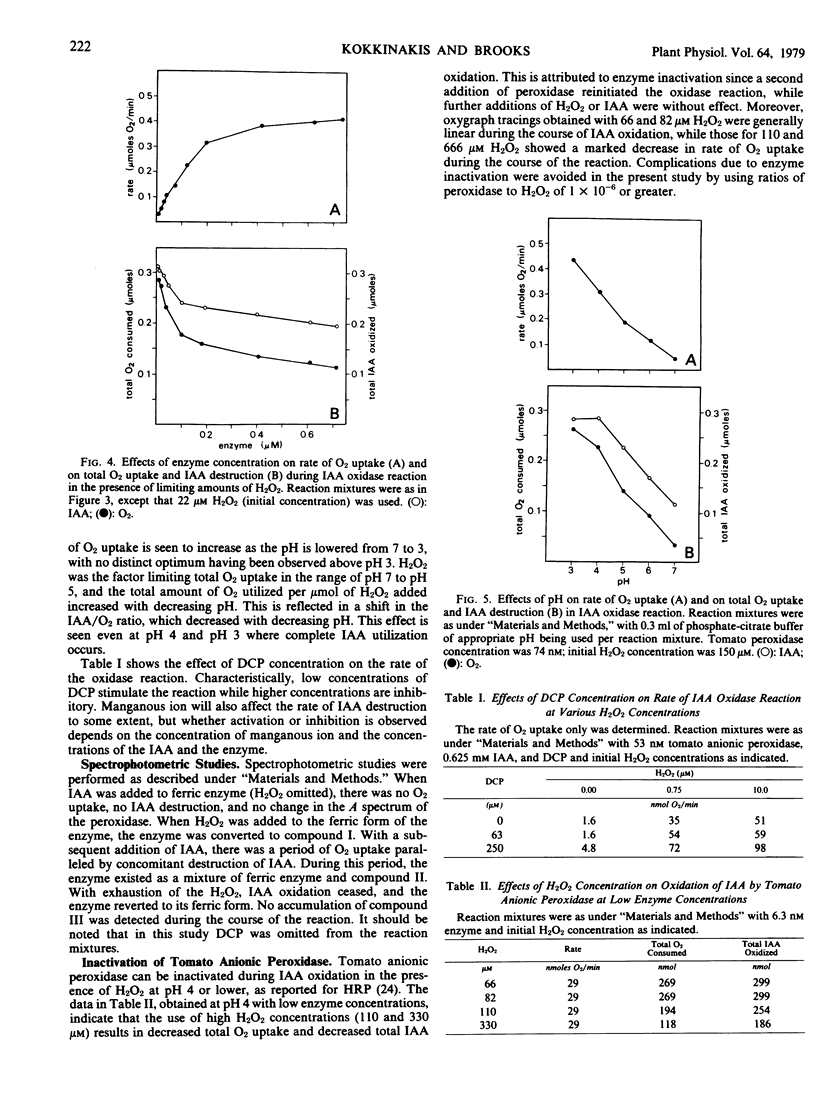
The oxidation of indole-3-acetic acid by anionic tomato peroxidase was found to be negligible unless reaction mixtures were supplemented with H2O2. The addition of H2O2 to reaction mixtures initiated a period of rapid indole-3-acetic acid oxidation and O2 uptake; this phase ended and O2 uptake fell to a low level when the H2O2 was exhausted. The stoichiometry of the reaction, which is highly dependent on enzyme concentration and pH, suggests that H2O2 initiates a sequence of reactions in which indole-3-acetic acid is oxidized.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpar E. K., Brooks D. M. Long-term results of ulnar to median nerve pedicle grafts. Hand. 1978 Feb;10(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/s0072-968x(78)80027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T., Frenkel C. Involvement of hydrogen peroxide in the regulation of senescence in pear. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):411–416. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degn H. Compound 3 kinetics and chemiluminescence in oscillatory oxidation reactions catalyzed by horseradish peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 24;180(2):271–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90114-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel C., Haard N. F. Initiation of Ripening in Bartlett Pear with an Antiauxin alpha(p-Chlorophenoxy)isobutyric Acid. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):380–384. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel C. Oxidative turnover of auxins in relation to the onset of ripening in bartlett pear. Plant Physiol. 1975 Mar;55(3):480–484. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.3.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALSTON A. W., BONNER J., BAKER R. S. Flavoprotein and peroxidase as components of the indoleacetic acid oxidase system of peas. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Feb;42(2):456–470. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINMAN R. L., LANG J. PEROXIDASE-CATALYZED OXIDATION OF INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1965 Jan;4:144–158. doi: 10.1021/bi00877a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENTEN R. H. The oxidation of indolyl-3-acetic acid by waxpod bean root sap and peroxidase systems. Biochem J. 1955 Jan;59(1):110–121. doi: 10.1042/bj0590110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokkinakis D. M., Brooks J. L. Tomato peroxidase: purification, characterization, and catalytic properties. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jan;63(1):93–99. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLACHLAN G. A., WAYGOOD E. R. Kinetics of the enzymically-catalyzed oxidation of indoleacetic acid. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1956 Nov;34(6):1233–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnicol P. K. Peroxidases of the Alaska pea (Pisum sativum L.). Enzymic properties and distribution within the plant. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Nov;117(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. T., Galston A. W. On the Nature of the Enzymatically Catalyzed Oxidation Products of Indoleacetic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1955 May;30(3):225–231. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.3.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY P. M. Destruction of indoleacetic acid. IV. Kinetics of enzymic oxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Feb;96:199–209. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90399-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY P. M., THIMANN K. V. The destruction of indoleacetic acid. I. Action of an enzyme from Omphalia flavida. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Sep;64(1):175–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL S. M., GALSTON A. W. Peroxide genesis in plant tissues and its relation to indoleacetic acid destruction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Jan;54(1):102–113. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stonier T., Yang H. M. Studies on Auxin Protectors: XI. Inhibition of Peroxidase-Catalyzed Oxidation of Glutathione by Auxin Protectors and o-Dihydroxyphenols. Plant Physiol. 1973 Feb;51(2):391–395. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingwa P. O., Young R. E. The Effect of Indole-3-acetic Acid and Other Growth Regulators on the Ripening of Avocado Fruits. Plant Physiol. 1975 May;55(5):937–940. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.5.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAZAKI I., PIETTE L. H. THE MECHANISM OF AEROBIC OXIDASE REACTION CATALYZED BY PEROXIDASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 3;77:47–64. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90468-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAZAKI I., SOUZU H. The mechanism of indoleacetic acid oxidase reaction catalyzed by turnip peroxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Feb;86:294–301. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90421-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOKOTA K., YAMAZAKI I. THE ACTIVITY OF THE HORSERADISH PEROXIDASE COMPOUND 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 4;18:48–53. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90880-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki H., Yamazaki I. The reaction between indole 3-acetic acid and horseradish peroxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


