Abstract
The evolution of tubercle bacilli parallels a route from environmental Mycobacterium kansasii, through intermediate “Mycobacterium canettii”, to the modern Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Cell envelope outer membrane lipids change systematically from hydrophilic lipooligosaccharides and phenolic glycolipids to hydrophobic phthiocerol dimycocerosates, di- and pentaacyl trehaloses and sulfoglycolipids. Such lipid changes point to a hydrophobic phenotype for M. tuberculosis sensu stricto. Using Congo Red staining and hexadecane-aqueous buffer partitioning, the hydrophobicity of rough morphology M. tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis strains was greater than smooth “M. canettii” and M. kansasii. Killed mycobacteria maintained differential hydrophobicity but defatted cells were similar, indicating that outer membrane lipids govern overall hydrophobicity. A rough M. tuberculosis H37Rv ΔpapA1 sulfoglycolipid-deficient mutant had significantly diminished Congo Red uptake though hexadecane-aqueous buffer partitioning was similar to H37Rv. An M. kansasii, ΔMKAN27435 partially lipooligosaccharide-deficient mutant absorbed marginally more Congo Red dye than the parent strain but was comparable in partition experiments. In evolving from ancestral mycobacteria, related to “M. canettii” and M. kansasii, modern M. tuberculosis probably became more hydrophobic by increasing the proportion of less polar lipids in the outer membrane. Importantly, such a change would enhance the capability for aerosol transmission, affecting virulence and pathogenicity.
Introduction
Coherent explanations are required for the development and upsurge in tuberculosis (TB) during the recent Holocene epoch. Developing evidence indicates an evolutionary pathway initiating from an environmental organism, possibly related to Mycobacterium kansasii, leading to an intermediate taxon similar to unusual smooth morphology tubercle bacilli, labelled “Mycobacterium canettii”1–4. Tuberculosis, due to “M. canettii”, is principally restricted to the Horn of Africa and its transmissibility is reduced in comparison with modern Mycobacterium tuberculosis 5–8. Detailed genomic scrutiny of “M. canettii” isolates revealed wide genetic diversity in comparison with modern members of the M. tuberculosis complex that are closely related5, 9–12.
Assuming a working hypothesis, involving an evolutionary progression from M. kansasii-like mycobacteria to M. tuberculosis via ancient relatives of “M. canettii”, it is possible to envisage a coherent developing pattern of mycobacterial outer membrane lipid changes (Fig. 1)2, 3. A strong phylogenetic link between M. kansasii and “M. canettii” is demonstrated by highly similar glycosyl phenolphthiocerol dimycocerosates, the so-called phenolic glycolipids (PGLs)1, 13. The main tetraglycosyl PGL of M. kansasii simply loses one or three sugars to produce the characteristic PGLs of “M. canettii”1–3, 13. A highly significant difference between M. kansasii and “M. canettii” resides in the so-called α-mycolic acids; subtle structural changes contribute to modified outer membrane physical properties2, 3. The phthiodiolone dimycocerosate waxes in M. kansasii are also replaced in “M. canettii” by a full set of dimycocerosates of the phthiocerol family (PDIMs). Distinct polar hydrophilic lipooligosaccharides (LOSs) are found in both M. kansasii and “M. canettii”, but only the latter express di- and pentaacyl trehaloses (DATs and PATs)6. On proceeding from “M. canettii” to M. tuberculosis sensu stricto, DATs, PATs, PDIMs are maintained, sulfoglycolipids (SGLs) are expressed, but PGLs and LOSs are deleted. The outcome of these changes is that M. tuberculosis sensu stricto has rather simplified mycobacterial outer membrane (MOM) free lipids, comprising only PDIMs, SGLs and DATs and PATs (Fig. 1).
Figure 1.
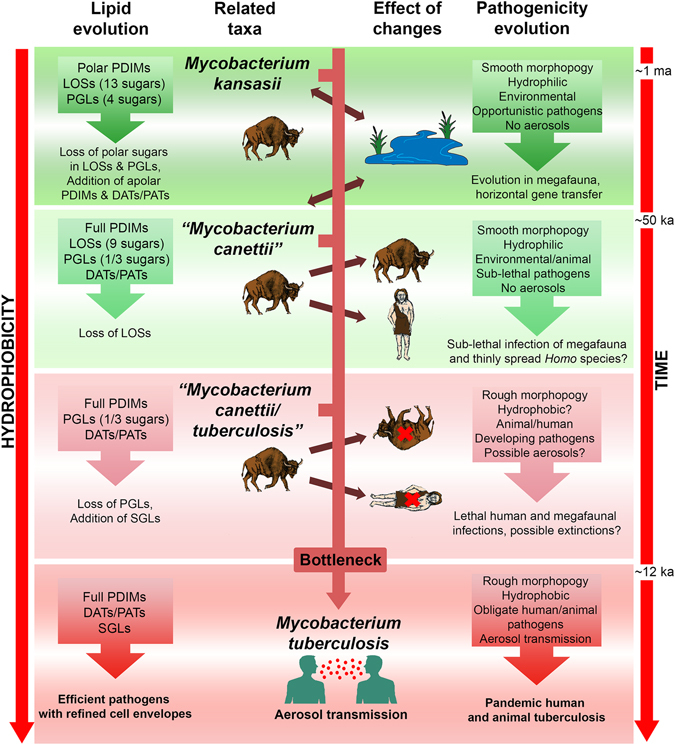
The importance of lipid composition and hydrophobicity in the evolution of tubercle bacilli. Abbreviations: PDIMs, phthiocerol dimycocerosates; LOSs, lipooligosaccharides, PGLs, glycosyl phenolphthiocerol dimycocerosates (phenolic glycolipids); DATs & PATs, di- & pentaacyl trehaloses; SGLs, sulfoglycolipids. Graded green and red backgrounds indicate environmental and mammalian pathogen associations, respectively. Evolution cannot take place directly from modern M. kansasii and “M. canettii”, which are shown as related taxa. The hypothetical transitional taxon, labelled “Mycobacterium canettii/tuberculosis”, possibly corresponds to the well-characterised So93R rough variant of “M. canettii”29. Increasing hydrophobicity, with time, applies to both lipid composition and whole cells.
It was realised that this selection of M. tuberculosis MOM free lipids (PDIMs, SGLs and DATs and PATs) was markedly apolar in comparison with those found in M. kansasii and “M. canettii” and this might result in relatively increased hydrophobicity of the cell surface3. Importantly, in other contexts, it has been demonstrated that aerosol transmissibility of non-tuberculous mycobacteria is enhanced by higher hydrophobicity14. Preliminary experiments3, 15, assessing Congo Red dye uptake16 and hexadecane/aqueous buffer partitioning17, did indeed show highly enhanced hydrophobicity of M. tuberculosis H37Rv.
The present study reinforces the evidence that mycobacterial strains with rough colony morphology, such as M. tuberculosis and M. bovis Ravenel, are significantly more hydrophobic than the representatives of smooth colony M. kansasii and “M. canettii”. Importantly, on removing the mycobacterial outer membrane lipids, the relative hydrophobicity of rough and smooth mycobacterial variants became marginal. In addition, available M. tuberculosis and M. kansasii mutants lacking SGLs and higher subclasses of LOSs, respectively18, 19, were used to investigate possible involvement of these lipids in cell-surface variation and hydrophobicity.
Results and Discussion
Lipid composition of test strains
The extractable free lipid compositions of the cultures examined are summarised in Table 1 and two-dimensional thin-layer chromatographic (2D TLC) patterns are displayed in Supplementary Figs S1–S3. Key confirmatory findings are the presence of the PDIM family in M. tuberculosis, M. bovis and “M. canettii”, with M. kansasii restricted to phthiodiolone dimycocerosates (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. S1). Small proportions of pentaacyl trehaloses (PATs) were detected in all except M. kansasii (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. S1). The expected phenolic glycolipids (PGLs) were only in M. bovis, “M. canettii” and M. kansasii and sulfoglycolipids (SGLs) were restricted to wild-type M. tuberculosis H37Rv and CDC1551, but obviously lacking in the ΔpapA1 mutant of H37Rv (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. S2). Diacyl trehaloses (DATs) were in all M. tuberculosis and “M. canettii” strains and lipooligosaccharides (LOSs) characterised “M. canettii” and M. kansasii, with a truncated range being detected in the ΔMKAN27435 mutant of the latter (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. S3). Consistent patterns of mycolic acid methyl esters were shown for defatted cells, remaining after the extraction of free lipids (Supplementary Fig. S4). The expected α-, methoxy- and ketomycolates varied in their proportions in line with a previous study20. Notably, gene knockouts did not change the general mycolic acid patterns found for M. tuberculosis H37Rv and M. kansasii (Supplementary Fig. S4).
Table 1.
Distribution of cell envelope lipids in test strains.
| PDIM | TAG | PAT | DAT | PGL(1) | PGL(>1) | SGL | LOS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. tuberculosis H37Rv | +++ | ++ | + | + | − | − | + | − |
| M. tuberculosis H37Rv ΔpapA1 | +++ | ++ | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| M. tb CDC1551 | +++ | ++ | + | + | − | − | + | − |
| M. bovis Ravenel | +++ | ++ | + | − | +* | − | − | − |
| “M. canettii” 140010060 | +++ | + | + | + | +* | +*** | − | ++ |
| “M. canettii” 140010061 | +++ | + | + | + | +* | +*** | − | ++ |
| M. kansasii Hauduroy | ++# | ++ | − | − | − | +**** | − | ++ |
| M. kansasii ΔMKAN27435 | ++# | ++ | − | − | − | +**** | − | + |
Abbreviations: PDIM, dimycocerosates of phthiocerol A, phthiocerol B and phthiodiolone (++#Indicates phthiodiolone); TAG, triacylglycerols; PAT & DAT, penta- and diacyl trehaloses; PGL(1), single sugar phenolic glycolipid (+*); PGL(>1), multiple sugar phenolic glycolipid (+*** & +****, 3 & 4 sugars); SGL, sulfoglycolipid; LOS, lipooligosaccharides.
Relative hydrophobicity of test strains
Two complementary methods were employed to determine the relative hydrophobicity of M. kansasii and members of the M. tuberculosis complex, including “M. canettii”. The Congo Red procedure involves an amphiphilic dye that associates with lipophilic regions of the mycobacterial cell envelope, providing a measure of overall hydrophobicity16, 21–23. An alternative approach partitions cells between a hexadecane organic phase and an aqueous buffer17, 21–24. In this study, Tween 80 was included in liquid culture to ensure uniform comparable growth and cell envelope lipid composition; it is likely that any loosely attached capsular material may have been removed25. Preliminary studies, using these procedures, have demonstrated that the rough colony morphology H37Rv type strain of M. tuberculosis is much more hydrophobic than the smooth colony morphology representatives of “M. canettii” and M. kansasii 3, 15.
Cultivation in the presence of Congo Red (Fig. 2) showed rough colonies for M. tuberculosis H37Rv, CDC1551 and M. bovis Ravenel, with clear dye uptake (Fig. 2a–d). The rough morphology of M. bovis Ravenel is characteristic of laboratory-adapted strains. The SGL-deficient ΔpapA1 mutant of M. tuberculosis H37Rv remained rough and absorbed dye uniformly (Fig. 2b). In contrast, smooth colonies of “M. canettii” and M. kansasii were poorly stained with Congo Red, as was the ΔMKAN27435 mutant that was partially deficient in LOS production (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. S3) but remained smooth (Fig. 2e–h). The quantitative results for the amount of Congo Red dye extracted are summarised in Fig. 3a and full numerical data are provided in Supplementary Table S1. The two M. tuberculosis strains absorbed the most dye, with CDC 1551 being the strongest. The H37Rv ΔpapA1mutant significantly took up less dye than the parent strain and M. bovis Ravenel had lower dye uptake than M. tuberculosis. As indicated previously3, 15, the two strains of “M. canettii” absorbed much less dye than the M. tuberculosis representatives. The dye absorbed by M. kansasii was reduced in comparison with the “M. canettii” strains, but the ΔMKAN27435 partially LOS-deficient mutant appeared to absorb more dye than the parent. The statistically significant reduced Congo Red uptake of the H37Rv ΔpapA1 mutant (Fig. 3a) could be correlated with loss of sulfoglycolipid (SGL) (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. S2), with its extremely hydrophobic phthioceranate and hydroxyphthioceranic fatty acids3. Conversely, diminished hydrophilic LOS content (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. S3) did not give a decisive increase in dye retention in M. kansasii ΔMKAN27435 (Fig. 3a).
Figure 2.
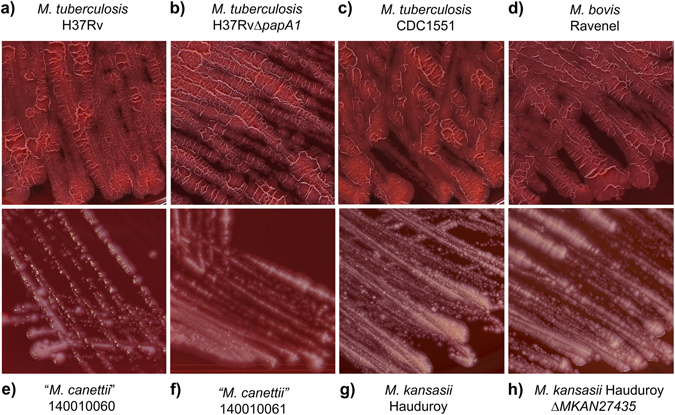
Staining of test strains with Congo Red dye on solid media. (a) M. tuberculosis H37Rv; (b) M. tuberculosis H37Rv ΔpapA1; (c) M. tuberculosis CDC1551; (d) M. bovis Ravenel; (e)“M. canettii” 140010060; (f) “M. canettii” 140010061; (g) M. kansasii Hauduroy; (h) M. kansasii Hauduroy ΔMKAN27435.
Figure 3.
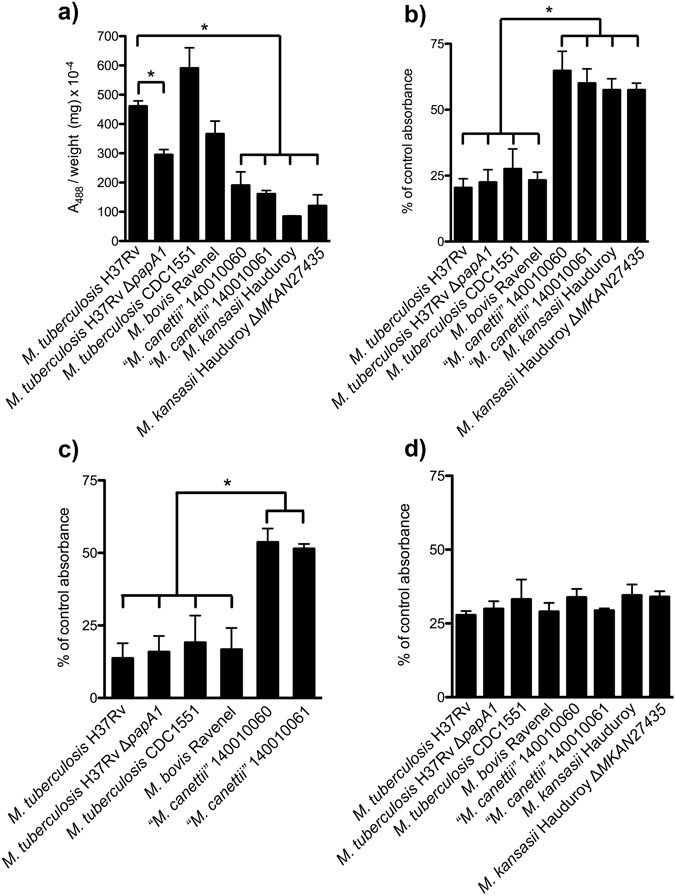
Quantitative assessment of relative mycobacterial hydrophobicity. (a) Quantification of Congo Red extracted from solid media growth. Hexadecane/aqueous buffer partitioning of: (b) Live cells, (c) Killed cells, (d) Defatted killed cells. Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of at least three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test (p < 0.01).
Partitioning of live cultures between hexadecane and aqueous buffer again revealed the presence of two clear categories (Fig. 3b). M. bovis Ravenel, the two M. tuberculosis strains and the ΔpapA1 mutant of H37Rv were significantly more hydrophobic in comparison with the “M. canettii” and M. kansasii strains, with the latter taxa having practically doubled affinities for the aqueous phase. Interestingly, M. tuberculosis CDC1551 was marginally less hydrophobic than M. tuberculosis H37Rv, the H37Rv ΔpapA1 mutant and M. bovis. The M. kansasii ΔMKAN27435 mutant was not distinguishable from its parent strain (Fig. 3b). The partitioning of representative killed cultures gave discriminatory results (Fig. 3c), paralleling those for live cells (Fig. 3b), but with reduced overall hydrophilicity. Partition analysis of delipidated cells (Fig. 3d) gave relatively uniform results, with comparable hydrophobicities. Numerical data for partitioning studies are included in Supplementary Table S2.
The Congo Red and hexadecane-aqueous buffer partitioning techniques showed encouraging correlations, but certain subtle differences were apparent. In the partitioning studies, M. tuberculosis CDC1551 was marginally more hydrophilic than M. tuberculosis H37Rv (Fig. 3b), in contrast to the results of the Congo Red dye uptake (Fig. 3a). A previous study also found that M. tuberculosis CDC1551 was more hydrophilic in partition experiments than M. tuberculosis H37Rv, but hydrophobic parity was achieved by introducing a second copy of the phoPR operon into CDC155126. Lipid profiles were not recorded in that study, but PhoPR is known to regulate cell envelope phenotypes, including synthesis of DATs, PATs and SGLs27. The ΔpapA1 mutant was only marginally more hydrophilic than the parent M. tuberculosis H37Rv in partition experiments (Fig. 3b), when it was significantly greater with Congo Red (Fig. 3a). M. bovis Ravenel was intermediate in partition experiments between the two representatives of M. tuberculosis. The diminished LOS content of the M. kansasii ΔMKAN27435 mutant, that remained smooth, had no significant effect on partitioning between the aqueous and organic phases; however, it should be noted that the polar PGL content was maintained in both cultures (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. S2). It appears that total loss of polar LOSs from smooth M. kansasii may be necessary to generate a rough variant, as shown previously28. A spontaneous mutant of smooth “M. canettii”, totally deficient in LOSs, was transformed to rough morphology even though it maintained the presence of polar PGLs29.
The differential hydrophobic properties of the rough and smooth strains, under study, are most clearly demonstrated by partitioning between hexadecane and aqueous buffer (Fig. 3b) rather than by Congo Red uptake on solid media (Fig. 3a). The partitioning experiment probably reflects the gross physical properties of the relatively homogeneous liquid-grown biomass. In contrast, the Congo Red staining involves more heterogeneous solid surface cultures that may include differentially responsive variations between individual cells. Overall uptake of Congo Red dye will represent the sum of many individual micro interactions in cells having subtle compositional differences.
Partitioning a selection of killed biomass (Fig. 3c) demonstrated that the effects, chronicled so far, reflect innate properties of the cells, independent of viability. The dead cells were somewhat more hydrophobic than the live equivalents but the relative hydrophobicities remained the same (Fig. 3b,c). Perhaps immobilisation of the envelope lipids resulted in some consolidation of the cell surface, this being particularly apparent for the ΔpapA1 mutant of M. tuberculosis H37Rv (Fig. 3c). Stripping away the extractable cell envelope lipids produced dead cell cores, all with comparable hydrophobicities (Fig. 3d). This is a good indication that variations in cell surface hydrophobicity are governed by free lipid composition, particularly those residing in the mycobacterial outer membrane. In the case of the H37Rv ΔpapA1 mutant, the dead cell core was of comparable hydrophobicity (Fig. 3d), suggesting that any perturbations affecting physical properties were limited to the outer membrane. It is notable that the ~25% hydrophilicity of the delipidated cells (Fig. 3d) is greater than that (<10%) recorded for killed M. tuberculosis and M. bovis Ravenel (Fig. 3c), signifying that key non-polar hydrophobic lipids have been sacrificed. Conversely, removal of relatively polar and hydrophilic lipids, such as LOSs and PGLs, will reduce the hydrophilicity of killed “M. canettii” from approximately 50% (Fig. 3c) to the common ~25% level of the delipidated cells (Fig. 3d). The overall uniform level of the relatively high hydrophobicity of the delipidated cells presumably is an expression of the presence of covalently-bound 70–90 carbon mycolic acids. Such mycolic acids assemble in a monolayer linked to arabinogalactan, with the distal portions interacting with a range of characteristic free lipids to create a coherent mycobacterial outer membrane3, 30. Released from the restraints of free lipid interactions, presumably all the mycolate distal hydrocarbon chains collapse to provide a relatively uniform hydrophobic external layer.
As previously noted3, the enhanced hydrophobicity of the representatives of M. tuberculosis sensu stricto appears to reside in the cell envelope free lipids (Fig. 1). The principal outer membrane free lipids of M. kansasii are a limited selection of relatively polar phenolic glycolipids (PGLs) and lipooligosaccharides (LOSs)2, 3, accompanied by a restricted phthiodiolone version of the phthiocerol dimycocerosate (PDIM) family (Table 1, Supplementary Figs S1–S3). The intermediate “M. canettii” taxon has an extended cocktail of outer mebrane free lipids, adding DATs, PATs and a full complement of the PDIM family, in addition to PGLs and LOSs. The loss of the ability to synthesise polar hydrophilic PGLs and LOSs, coupled with SGL production, gave the refined MOM free lipid composition characteristic of M. tuberculosis (Fig. 1)2, 3. Even though the trehalose-based SGLs include a polar sulfate functionality, the distinctive very long-chain phthioceranate and hydroxyphthioceranate fatty acid constituents possibly contribute to increased hydrophobicity of the outer membrane surface. From the point of view of the cell envelope lipophilic components, it is clear that M. kansasii and M. tuberculosis are adapted to their particular stable environments, but “M. canettii” may represent a transitory state suited to variable evolutionary situations2, 3. A major area of uncertainty is the role of triacylglycerols (TAGs) in the mycobacterial outer membrane. It was shown by selective extraction that substantial amounts of TAGs are apparently located in the outer membrane of Mycobacterium smegmatis 31, but the precise molecular structures remain to be delineated. Certain mycobacteria display substantial TAG-rich lipid bodies that are implicated in energy storage32.
Lipid composition and rough and smooth morphology of mycobacteria
A smooth to rough change in a scotochromogenic Mycobacterium correlated with loss of a glycopeptidolipid33 and this was confirmed in Mycobacterium intracellulare 34. Rough variants of smooth M. kansasii lacked polar lipooligosaccharides28 and correlation with a previous study35 indicated that smooth strains were more rapidly cleared from mice organs. A rough variant (So93R) of “M. canettii” did not revert to its smooth progenitor So93; it had lost the capacity to produce lipooligosaccharides (LOSs) and it was significantly more virulent in the Guinea pig29. The rough So93R variant retained the triglycosyl phenolic glycolipid PGL29. Knocking out the gene for the production of LOSs converts smooth “M. canettii” strains to rough variants12. A rough mutant of M. smegmatis lacking glycopeptidolipids, had increased cell hydrophobicity, clumped to form aggregates and was rapidly phagocytosised by human macrophages21. Surface glycopeptidolipids were found to inhibit human macrophage phagocytosis of M. smegmatis 36. A rough M. marinum mutant, lacking LOSs, was phagocytosed more efficiently37.
Hydrophobicity and the pathogenicity of Mycobacterium abscessus
Mycobacterium abscessus is emerging as an important cause of pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis patients38. It was found that smooth strains were cleared, but rough variants persisted and multiplied in a murine pulmonary infection model39. The smooth (390S) and rough (390R) colonies were moist and dry, respectively, correlating with hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity. Only the rough variants exhibited cording, drawing comparison with virulent M. tuberculosis 39. A follow-up study confirmed cording and proved that rough M. abscessus lacked glycopeptidolipids (GPLs)40. The same phenotypes were found for rough and smooth M. abscessus, including two of the same strains, 390R and 390S; another rough variant was hyper-lethal for mice41. The emergence of an isogenic rough variant of M. abscessus resulted in acute respiratory failure42. Rough variants of M. abscessus infected or colonized the airways of cystic fibrosis patients and some isolates were harboured for years43. In contrast, contaminants and wound isolates mainly exhibited smooth colony morphology43. Smooth M. abscessus was internalised by human monocytes but rough variants were not, as they formed serpentine cords44. The lack of GPLs could make rough strains cord together and be difficult to internalise44. Using the zebrafish model, rough M. abscessus formed cords that prevented phagocytosis, initiated abscess formation and rapid larval death45. A rough variant, deficient in GPL production/transport, produced cords in vitro 46. A comprehensive investigation of smooth-to-rough morphotype alterations implicated lipid changes in cellular interactions of clinically persistent M. abscessus 47. Rough morphology M. abscessus strains, from lung infections, correlated with shifts in lipid metabolism indicating triacylglycerol accumulation and some GPL loss48. Greater host inflammatory responses were seen for rough M. abscessus morphotypes in a murine model49. Expanding on previous cording studies50, 51, it was found that clumped rough M. abscessus variants had increased phagocytosis and damaged macrophages52.
Hydrophobicity and aerosol transmission
As pointed out previously3, 15, a very significant implication of enhanced mycobacterial hydrophobicity is that the propensity for aerosol transmission is facilitated. This principle has been established in extended investigations of members of the Mycobacterium avium family and other nontuberculous mycobacteria, where clear correlations were demonstrated between hydrophobicity and entry into aerosols from aqueous media14, 53, 54. The significance of the clearly enhanced hydrophobicity of M. tuberculosis is the implication that aerosol transmission would be encouraged3, 15. Similarly, it was noted3 that rough variants of M. abscessus, lacking polar glycopeptidolipids are likely to be more hydrophobic and aerosol transmissible than the smooth strains. As summarised above, the overall virulence of rough M. abscessus strains is apparently enhanced and it was also noted that isolates causing chronic airway colonisation/infection are usually rough43, 44, 48. In a comprehensive world-wide survey of M. abscessus infections, the possibility of aerosol transmission was raised but any link with rough-smooth variations was not addressed38. The degree of hydrophobicity and propensity for aerosol transmission of rough M. abscessus variants requires detailed investigation.
Evolutionary origins of pathogenic rough tubercle bacilli
It is important to consider when less virulent smooth tubercle bacilli evolved into rough pathogenic members of the current M. tuberculosis complex. Recent genomic extrapolations claimed that TB is not older than ~6 ka55, 56, but this simply points to the most recent common ancestor of the specimens investigated57, 58. Coalescent analyses of TB and human mitochondrial genome evolution predicted that TB co-emerged with Homo sapiens from Africa 70,000 years ago59, but linked co-evolution is not a necessary consequence of parallel evolution. A consensus concludes that tubercle bacilli have passed through a bottleneck, around 35–20 ka BP9–11, 60. Post-bottleneck, members of the M. tuberculosis complex arose through linear gene deletions61–66. Prior to the bottleneck, there is evidence for horizontal gene transfer in ancestral strains1, 67, 68.
TB has been diagnosed in a ~9 ka woman and child from Atlit-Yam in the Eastern Mediterranean69, 70 and a ~17 ka bison from Natural Trap Cave, Wyoming70, 71. Clear M. tuberculosis complex DNA sequences were amplified, supported by lipid biomarkers70. The oldest TB in H. sapiens was recorded in Syrian skeletons from 10.8–10.3 ka, DNA amplification being backed up by lipid biomarker profiles72. There is a lack of evidence for tuberculosis in H. sapiens, prior to the Holocene, probably due to low population densities73. However, diagnostic bone lesions indicate tuberculosis in Pleistocene megafauna, back to ~120 ka BP74, 75. Diverse microbial species in megafaunal oral cavities and digestive organs would be available to participate in evolutionary horizontal gene transfer67, 68. A feasible scenario (Fig. 1), for the emergence of all the modern biotypes of the M. tuberculosis complex through the bottleneck would involve a complex web of interactions between H. sapiens and Pleistocene animal reservoirs until the dramatically ameliorated climatic conditions at the beginning of the Holocene allowed humans to form settlements and promulgate communal tuberculosis.
Implications for mammalian extinctions in the Pleistocene
The accumulating evidence of TB lesions in a wide range of extinct Pleistocene megafauna74, 75 arouses suspicion that TB may have contributed to the extinction of particular classes of these animals (Fig. 1). Mammoths are exceptional, as they do not appear to have bone lesions, attributable to TB74, 75. As noted above, many of these megafauna may have survived to maturity with sub-lethal disease; an informative example is the 17 ka Natural Trap Cave mature bison71, 76 that was not killed by TB, as it suffered an obvious lethal accident. The possible involvement of bacterial disease in megafaunal extinctions has received less and less credence over the years, the only possibility deemed worthy of mention being unspecified “hyperdisease” contracted from man or other mammalian species77, 78. The hypothesis advanced here is a diametrically opposite scenario, with environmental bacteria slowly evolving into tubercle bacilli using megafaunal hosts2, 3, 15. Once hydrophobic tubercle bacilli became transmissible in aerosols, snorting bison and other megafauna would rapidly spread lethal disease within their own herds and greatly facilitate infection of other species. The fact that a number of megafaunal extinctions happened over a relatively short time favours the primary rapid intervention of a particular factor, such as virulent TB, rather than the more secondary gradual effects of environmental change and/or human interaction77, 78. Early cases of TB in H. sapiens in the so-called Fertile Crescent region69, 72 may correlate with naïve humans migrating out of Africa, at the conclusion of the Ice Ages, encountering contagious rough hydrophobic tubercle bacilli of megafaunal origin.
Conclusions
Enhanced hydrophobicity is an important characteristic of pathogenic members of the modern M. tuberculosis complex. The evolutionary transformation from hydrophilic environmental low-pathogenicity ancestors, related to M. kansasii and “M. canettii”, to hydrophobic virulent tubercle bacilli is particularly decisive (Fig. 1), but it is important to be aware of zoological and paleogeographic aspects. The oldest proven cases of TB in H. sapiens are so far restricted to ~11–9 ka in the early Holocene, but there is developing evidence for megafaunal TB in the late Pleistocene. It is plausible for environmental mycobacteria to have experienced the necessary horizontal gene transfer in evolving into intermediate tubercle bacilli, related to “M. canettii”, in the multiple intestinal tracts of Northern Hemisphere Pleistocene megafauna rather than in thinly-spread human hosts. The high diversity of the “M. canettii” taxon might indicate that its evolution was multi-centred over an extended period resulting in animals carrying “smooth” bacteria with low pathogenicity and transmissibility. The emergence of rough “M. canettii” hydrophobic variants, readily transmitted in aerosols, may well have contributed to the demise of Pleistocene megafauna and any associated mammals (Fig. 1). Modern humans, settling in the Eastern Mediterranean so-called Fertile Crescent, may have encountered bottleneck-refined virulent tubercle bacilli and initiated the modern human and animal TB pandemic.
The broad conclusions concerning the influence of hydrophobicity on the evolution of tubercle bacilli are summarised in Fig. 1. The scheme is essentially self-explanatory, as it mainly illustrates the major points discussed previously. The taxon, provisionally labelled “Mycobacterium canettii/tuberculosis”, represents a pivotal stage in TB evolution. The relatively low-pathogenicity smooth “M. canettii” strains do have many attributes of modern M. tuberculosis, but they may have co-existed with mammalian hosts without decimating populations. Prior to the bottleneck refinement, there may have been a variety of rough tubercle bacilli with developing potential for pathogenicity and rapid aerosol transmission. The hypothetical “Mycobacterium canettii/tuberculosis” taxon is simply a representative of bacteria in process of developing enhanced pathogenic traits; it possibly corresponds to the well-characterised So93R rough variant of “M. canettii”29.
The relentless pathogenic success of current mycobacterial pathogens is probably a direct consequence of the special hydrophobic properties of rough variants, more virulent than corresponding smooth strains. Aerosolisation of hydrophobic bacilli is favoured and such rough organisms are more difficult to clear in animals than smooth varieties. In addition to members of the M. tuberculosis complex and other slow-growing mycobacterial pathogens, these principles are very applicable to the important rapid-growing strains of M. abscessus that are a major problem for cystic fibrosis patients.
Methods
Bacterial strains and culture media
Mycobacterial strains included in this study were as follows: Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv, the SGL-deficient mutant M. tuberculosis H37Rv ΔpapA1 18, Mycobacterium tuberculosis CDC1551, Mycobacterium bovis Ravenel, “Mycobacterium canettii” CIPT 140010060 and 140010061 (Institute Pasteur, Paris)79, Mycobacterium kansasii Hauduroy (ATCC12478), and the partial LOS-deficient M. kansasii ΔMKAN27435 19. Homogenous static liquid cultures of mycobacterial strains were prepared aerobically in shallow flat flasks with filter caps to allow gas exchange. Growth at 37 °C in 7H9 liquid media, containing 10% v/v OADC, 0.2% v/v glycerol and 0.05% v/v Tween-80, was allowed to an optical density (OD) 600 nm of 0.8–1.0 followed by harvesting at 3000 g and washing with PUM buffer (22.2 g K2HPO4 3H2O, 7.26 g KH2PO4, 1.8 g urea, 0.2 g of MgSO4 7H2O and distilled water to 1 L; pH 7.1). Cell pellet material was divided and one half was killed by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 min. Solid media growth was on 7H10 agar plates containing 10% v/v OADC, 0.5% v/v glycerol and Congo Red at 100 µg/ml at 37 °C until bacterial colonies became clearly visible.
Lipid extraction and analysis
Apolar and polar fractions of free lipids were recovered from 150 mg wet autoclaved biomass, washed with PBS buffer, according to an established protocol80. Profiles of the lipid classes were recorded by a series of two-dimensional thin-layer chromatographic (TLC) systems (Supplementary Figs S1–S3), covering the whole range of lipid polarities80. Apolar fraction lipids were visualised by spraying with 5% w/v ethanolic molybdophosphoric acid and charring with a heat gun. Glycolipids in polar fractions were revealed by spraying with ethanolic α-naphthol-sulfuric acid80, followed by gentle charring with a heat gun; the same procedure was used to confirm the presence of glycolipids in apolar fractions. Mycolic acid methyl esters were released from lyophilised defatted cells, by alkaline methanolysis81. Cellular material (100 mg) was placed in a 10 ml PTFE capped glass tube and 0.5 % methanolic potassium hydroxide (2 ml) was added. The mixture was kept at 37 °C for 3 days. Cell residues were washed twice with methanol (2 ml) to remove all lipids, excepting methanol-insoluble mycolates. Mycolic acid methyl esters (MAMEs) were extracted from the residues with diethyl ether (3 × 1 ml). Samples were subjected to TLC, using silica gel plates (5725 silica gel 60F254, Merck), developing thrice in petroleum ether (60–80 °C)/diethyl ether (90:10). MAMEs were visualised by spraying with 5% w/v ethanolic molybdophosphoric acid, followed by charring with a heat gun (Supplementary Fig. S4). TLC plates were scanned using CanoScan LiDE 220 scanner and images were processed using Adobe Photoshop CC 2015 software.
Congo Red binding assay
Cells scraped from Congo Red plates were washed with distilled water until the supernatant was colourless and re-suspended in 3 ml of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). After mixing for 3 h at room temperature, cells were harvested by centrifugation (20 min at 3000 g) and the extraction step repeated twice. Pooled supernatants were dried under vacuum and re-dissolved in 1 ml of DMSO; Congo Red was spectrophotometrically measured at OD 488 nm. Congo Red binding index was defined as A488 of the DMSO extracts divided by the dry weight (mg) of the cell pellet. Results are expressed as mean ±SD of at least three independent experiments. Photographs of agar plates were taken with a Canon PowerShot G16 and Canon EOS 5D Mark III.
Hexadecane-aqueous buffer partitioning
Live exponentially growing cells from liquid culture were washed twice in PUM buffer and finally suspended to an OD of 0.7 at 600 nm. Aliquots (3 ml) were transferred to glass tubes and hexadecane (2.4 ml) added. After brief mixing, samples were incubated for 8 min at 37 °C and phase separation allowed at 22 °C for 15 min. Hydrophobicity index was defined as aqueous phase OD at 600 nm, expressed as a percentage of that of the bacterial suspension in PUM buffer alone. Results are expressed as mean ±SD of at least three independent experiments. The same procedure was applied to a selection of autoclaved cells and cell core material after extraction of lipids, as above.
Statistical analysis
The results were expressed as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. The student’s unpaired t-test (equal variance assumed) was used to evaluate differences between the samples. Two-tailed P-values below 0.01 were considered statistically significant. Graphic data were prepared with GraphPad Prism software.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
The present concepts originated in research funded by Leverhulme Trust Project Grant F/00094/BL (O.Y.-C.L., D.E.M., G.S.B.). G.S.B. acknowledges support in the form of a Personal Research Chair from Mr. James Bardrick and the UK Medical Research Council (grant MR/K012118/1) and Wellcome Trust (grant 081569/Z/06/Z).
Author Contributions
The study was conceived by D.E.M., M.R., A.B. and G.S.B. Experiments were conducted by M.J. and V.N. Scientific input was contributed by O.Y.-C.L., H.H.T.W., N.J.G. and M.R.B. The paper was written by D.E.M., M.J., M.R., N.J.G., A.B. and G.S.B.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at doi:10.1038/s41598-017-01501-0
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Veyrier FJ, Dufort A, Behr MA. The rise and fall of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis genome. Trends Microbiol. 2011;19:156–161. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2010.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Minnikin DE, et al. Ancient mycobacterial lipids: Key reference biomarkers in charting the evolution of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis. 2015;95(Suppl 1):S133–139. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Minnikin, D. E. et al. Pathophysiological implications of cell envelope structure in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and related taxa. In Tuberculosis - Expanding Knowledge (ed. Ribón, W.) 145–175 (InTech Open Access Publisher, Rijeka, 2015).
- 4.Wang J, et al. Insights on the emergence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the analysis of Mycobacterium kansasii. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015;7:856–870. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fabre M, et al. Molecular characteristics of ‘Mycobacterium canettii’ the smooth Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacilli. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010;10:1165–1173. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2010.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Koeck J-L, et al. Clinical characteristics of the smooth tubercle bacilli ‘Mycobacterium canettii’ infection suggest the existence of an environmental reservoir. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011;17:1013–1019. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Blouin Y, et al. Progenitor ‘Mycobacterium canettii’ clone responsible for lymph node tuberculosis epidemic, Djibouti. Emerging Infect. Dis. 2014;20:21–28. doi: 10.3201/eid2001.130652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Osman DA, Bouzid F, Canaan S, Drancourt M. Smooth tubercle bacilli: neglected opportunistic tropical pathogens. Front. Public Health. 2015;3:283. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2015.00283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Supply P, et al. Genomic analysis of smooth tubercle bacilli provides insights into ancestry and pathoadaptation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat. Genet. 2013;45:172–179. doi: 10.1038/ng.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bottai D, Supply P, Brosch R, Stinear TP. Mycobacterial pathogenomics and evolution. Microbiol. Spectrum. 2014;2(1):MGM2-0025–2013. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MGM2-0025-2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Boritsch EC, et al. A glimpse into the past and predictions for the future: the molecular evolution of the tuberculosis agent. Mol. Microbiol. 2014;93:835–852. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Boritsch EC, et al. Pks5-recombination-mediated surface remodelling in Mycobacterium tuberculosis emergence. Nat Microbiol. 2016;1:15019. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2015.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hartmann, S. & Minnikin, D. E. Mycobacterial phenolic glycolipids. In Surfactants in lipid chemistry: recent synthetic, physical, and biodegradative studies (ed. Tyman, J. H. P.) 135–158 (Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 1992).
- 14.Falkinham JO. Mycobacterial aerosols and respiratory disease. Emerging Infect. Dis. 2003;9:763–767. doi: 10.3201/eid0907.020415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Minnikin DE, et al. Les biomarqueurs lipidiques, fidèles témoins de l’évolution de la tuberculose [The lipid biomarkers, faithful witnesses to the evolution of tuberculosis] Biofutur. 2015;34(365):38–41. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cangelosi GA, Palermo CO, Laurent JP, Hamlin AM, Brabant WH. Colony morphotypes on Congo Red agar segregate along species and drug susceptibility lines in the Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex. Microbiology. 1999;145:1317–1324. doi: 10.1099/13500872-145-6-1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stokes RW, et al. The glycan-rich outer layer of the cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis acts as an antiphagocytic capsule limiting the association of the bacterium with macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2004;72:5676–5686. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5676-5686.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bhatt K, Gurcha SS, Bhatt A, Besra GS, Jacobs WR. Two polyketide-synthase-associated acyltransferases are required for sulfolipid biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microbiology. 2007;153:513–520. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2006/003103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nataraj V, et al. MKAN27435 is required for the biosynthesis of higher subclasses of lipooligosaccharides in Mycobacterium kansasii. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0122804. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Watanabe M, Aoyagi Y, Ridell M, Minnikin DE. Separation and characterization of individual mycolic acids in representative mycobacteria. Microbiology. 2001;147:1825–1837. doi: 10.1099/00221287-147-7-1825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Etienne G, et al. The impact of the absence of glycopeptidolipids on the ultrastructure, cell surface and cell wall properties, and phagocytosis of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Microbiology. 2002;148:3089–3100. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-10-3089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Etienne G, et al. The cell envelope structure and properties of Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155: is there a clue for the unique transformability of the strain? Microbiology. 2005;151:2075–2086. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27869-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Etienne G, et al. Identification of the polyketide synthase involved in the biosynthesis of the surface-exposed lipooligosaccharides in mycobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2009;191:2613–2621. doi: 10.1128/JB.01235-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rosenberg M, Gutnick D, Rosenberg E. Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: a simple method for measuring cell‐surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1980;9:29–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1980.tb05599.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Leisching, G., Pietersen, R.-D., Wiid, I. & Baker, B. Virulence, biochemistry, morphology and host-interacting properties of detergent-free cultured mycobacteria: an update. 100, 53–60 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 26.Schreuder LJ, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv has a single nucleotide polymorphism in PhoR which affects cell wall hydrophobicity and gene expression. Microbiology. 2015;161:765–773. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Broset E, Martín C, Gonzalo-Asensio J. Evolutionary landscape of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex from the viewpoint of PhoPR: implications for virulence regulation and application to vaccine development. MBio. 2015;6:e01289–15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01289-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Belisle JT, Brennan PJ. Chemical basis of rough and smooth variation in mycobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1989;171:3465–3470. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3465-3470.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.van Soolingen D, et al. A novel pathogenic taxon of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, Canetti: characterization of an exceptional isolate from Africa. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997;47:1236–1245. doi: 10.1099/00207713-47-4-1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Minnikin, D. E. Lipids: complex lipids, their chemistry, biosynthesis and role. In The Biology of Mycobacteria (eds. Ratledge, C. & Stanford, J. L.) 95–184 (Academic Press, 1982).
- 31.Bansal-Mutalik R, Nikaido H. Mycobacterial outer membrane is a lipid bilayer and the inner membrane is unusually rich in diacyl phosphatidylinositol dimannosides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:4958–4963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1403078111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Garton NJ, Christensen H, Minnikin DE, Adegbola RA, Barer MR. Intracellular lipophilic inclusions of mycobacteria in vitro and in sputum. Microbiology. 2002;148:2951–2958. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-10-2951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fregnan GB, Smith DW, Randall HM. A mutant of a scotochromogenic Mycobacterium detected by colony morphology and lipid studies. J. Bacteriol. 1962;83:828–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.828-836.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Barrow WW, Brennan PJ. Isolation in high frequency of rough variants of Mycobacterium intracellulare lacking C-mycoside glycopeptidolipid antigens. J. Bacteriol. 1982;150:381–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.381-384.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Collins FM, Cunningham DS. Systemic Mycobacterium kansasii infection and regulation of the alloantigenic response. Infect. Immun. 1981;32:614–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.614-624.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Villeneuve C, et al. Surface-exposed glycopeptidolipids of Mycobacterium smegmatis specifically inhibit the phagocytosis of mycobacteria by human macrophages. Identification of a novel family of glycopeptidolipids. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:51291–51300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306554200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Alibaud L, et al. Increased phagocytosis of Mycobacterium marinum mutants defective in lipooligosaccharide production: a structure-activity relationship study. J. Biol. Chem. 2014;289:215–228. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.525550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bryant JM, et al. Emergence and spread of a human-transmissible multidrug-resistant nontuberculous Mycobacterium. Science. 2016;354:751–757. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf8156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Byrd TF, Lyons CR. Preliminary characterization of a Mycobacterium abscessus mutant in human and murine models of infection. Infect. Immun. 1999;67:4700–4707. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.9.4700-4707.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Howard ST, et al. Spontaneous reversion of Mycobacterium abscessus from a smooth to a rough morphotype is associated with reduced expression of glycopeptidolipid and reacquisition of an invasive phenotype. Microbiology. 2006;152:1581–1590. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28625-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Catherinot E, et al. Hypervirulence of a rough variant of the Mycobacterium abscessus type strain. Infect. Immun. 2007;75:1055–1058. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00835-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Catherinot E, et al. Acute respiratory failure involving an R variant of Mycobacterium abscessus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009;47:271–274. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01478-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jönsson BE, et al. Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium abscessus, with focus on cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007;45:1497–1504. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02592-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jönsson B, Ridell M, Wold AE. Phagocytosis and cytokine response to rough and smooth colony variants of Mycobacterium abscessus by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. APMIS. 2013;121:45–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2012.02932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bernut A, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus cording prevents phagocytosis and promotes abscess formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:E943–E952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1321390111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bernut A, et al. Insights into the smooth-to-rough transitioning in Mycobacterium bolletii unravels a functional Tyr residue conserved in all mycobacterial MmpL family members. Mol. Microbiol. 2016;99:866–883. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pawlik A, et al. Identification and characterization of the genetic changes responsible for the characteristic smooth-to-rough morphotype alterations of clinically persistent Mycobacterium abscessus. Mol. Microbiol. 2013;90:612–629. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Park IK, et al. Clonal diversification and changes in lipid traits and colony morphology in Mycobacterium abscessus clinical isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015;53:3438–3447. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02015-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Caverly LJ, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus morphotype comparison in a murine model. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0117657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sánchez-Chardi A, et al. Demonstration of cord formation by rough Mycobacterium abscessus variants: implications for the clinical microbiology laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011;49:2293–2295. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02322-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Julián E, et al. Microscopic cords, a virulence-related characteristic of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, are also present in nonpathogenic mycobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2010;192:1751–1760. doi: 10.1128/JB.01485-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Brambilla C, et al. Mycobacteria clumping increase their capacity to damage macrophages. Front. Microbiol. 2016;7:1562. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Falkinham JO. Environmental sources of nontuberculous mycobacteria. Clin. Chest Med. 2015;36:35–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2014.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Parker BC, Ford MA, Gruft H, Falkinham JO. Epidemiology of infection by nontuberculous mycobacteria. IV. Preferential aerosolization of Mycobacterium intracellulare from natural waters. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1983;128:652–656. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.4.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bos KI, et al. Pre-Columbian mycobacterial genomes reveal seals as a source of New World human tuberculosis. Nature. 2014;514:494–497. doi: 10.1038/nature13591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kay GL, et al. Eighteenth-century genomes show that mixed infections were common at time of peak tuberculosis in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:6717. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Smith NH, Hewinson RG, Kremer K, Brosch R, Gordon SV. Myths and misconceptions: the origin and evolution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009;7:537–544. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Brites D, Gagneux S. Co-evolution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Homo sapiens. Immunol. Rev. 2015;264:6–24. doi: 10.1111/imr.12264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Comas I, et al. Out-of-Africa migration and Neolithic coexpansion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with modern humans. Nature Genetics. 2013;45:1176–1182. doi: 10.1038/ng.2744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sreevatsan S, et al. Restricted structural gene polymorphism in the complex indicates evolutionarily recent global dissemination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1997;94:9869–9874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.18.9869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Brosch R, et al. A new evolutionary scenario for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:3684–3689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052548299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Mostowy S, Cousins D, Brinkman J, Aranaz A, Behr MA. Genomic deletions suggest a phylogeny for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J. Infect. Dis. 2002;186:74–80. doi: 10.1086/341068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gutierrez MC, et al. Ancient origin and gene mosaicism of the progenitor of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 2005;1:e5. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0010005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Gordon SV, Bottai D, Simeone R, Stinear TP, Brosch R. Pathogenicity in the tubercle bacillus: molecular and evolutionary determinants. Bioessays. 2009;31:378–388. doi: 10.1002/bies.200800191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Djelouadji Z, Raoult D, Drancourt M. Palaeogenomics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: epidemic bursts with a degrading genome. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011;11:641–650. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Galagan JE. Genomic insights into tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014;15:307–320. doi: 10.1038/nrg3664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Jang J, Becq J, Gicquel B, Deschavanne P, Neyrolles O. Horizontally acquired genomic islands in the tubercle bacilli. Trends Microbiol. 2008;16:303–308. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2008.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Veyrier F, Pletzer D, Turenne C, Behr MA. Phylogenetic detection of horizontal gene transfer during the step-wise genesis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009;9:196. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hershkovitz I, et al. Detection and molecular characterization of 9000-year-old Mycobacterium tuberculosis from a Neolithic settlement in the Eastern Mediterranean. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e3426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Lee OY-C, et al. Lipid biomarkers provide evolutionary signposts for the oldest known cases of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis. 2015;95(Suppl 1):S127–132. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lee OY-C, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex lipid virulence factors preserved in the 17,000-year-old skeleton of an extinct bison, Bison antiquus. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e41923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Baker O, et al. Human tuberculosis predates domestication in ancient Syria. Tuberculosis. 2015;95(Suppl 1):S4–S12. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Stewart JR, Stringer CB. Human evolution out of Africa: the role of refugia and climate change. Science. 2012;335:1317–1321. doi: 10.1126/science.1215627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Rothschild BM, Laub R. Hyperdisease in the late Pleistocene: validation of an early 20th century hypothesis. Naturwissenschaften. 2006;93:557–564. doi: 10.1007/s00114-006-0144-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Rothschild BM, Martin LD. Did ice-age bovids spread tuberculosis? Naturwissenschaften. 2006;93:565–569. doi: 10.1007/s00114-006-0145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Rothschild BM, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex DNA from an extinct bison dated 17,000 years before the present. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001;33:305–311. doi: 10.1086/321886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Elias, S. A. & Schreve, D. C. Late Pleistocene megafaunal extinctions. In Encyclopedia of Quaternary Science, 2ndEdition (ed. Elias, S.) 700–712 (Elsevier, 2013).
- 78.Stuart AJ. Late Quaternary megafaunal extinctions on the continents: a short review. Geol. J. 2015;50:338–363. doi: 10.1002/gj.2633. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Minnikin DE, Ridell M, Bolton RC, Magnusson M. Recognition of novel glycolipid antigens from smooth variants of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1990;55:55–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb13835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Dobson, G. et al. Systematic analyses of complex mycobacterial lipids. In Chemical Methods in Bacterial Systematics (eds. Goodfellow, M. & Minnikin, D. E.) 237–265 (Academic Press, 1985).
- 81.Davidson LA, Draper P, Minnikin DE. Studies on the mycolic acids from the walls of Mycobacterium microti. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1982;128:823–828. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-4-823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


