Abstract
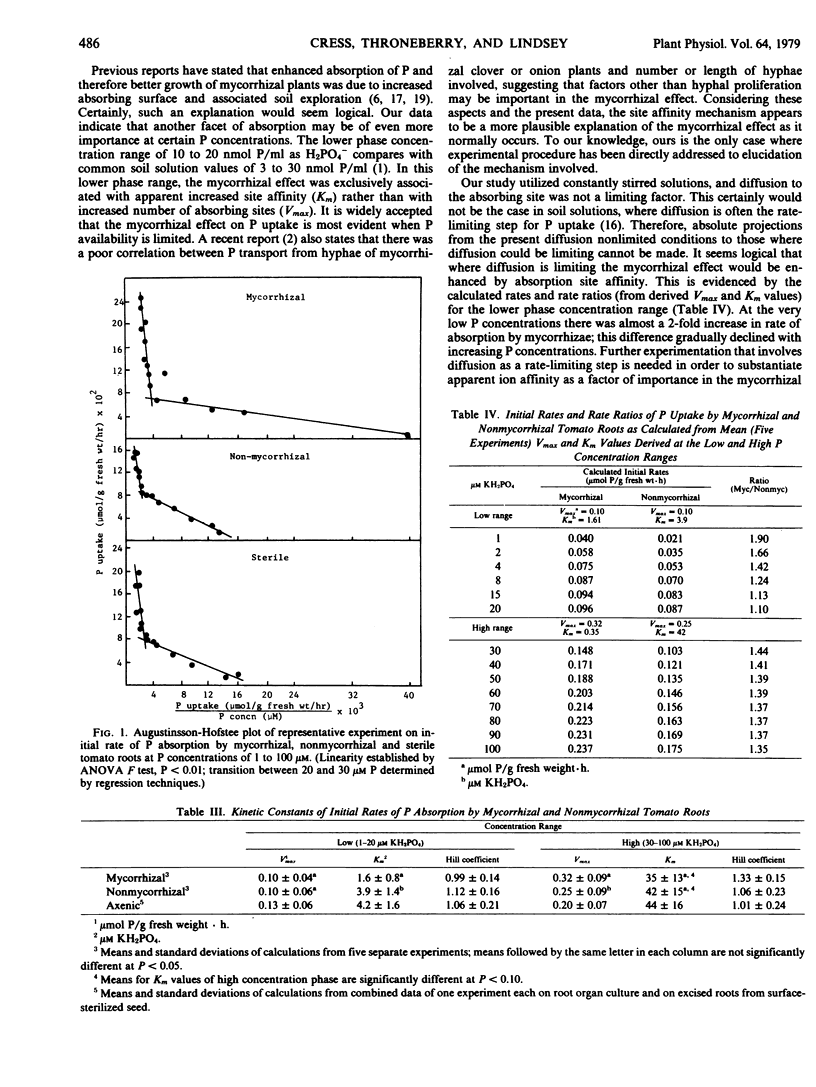
Kinetics of P absorption were investigated in mycorrhizal (Glomus fasciculatus) and nonmycorrhizal tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) roots to determine why increased ion absorption by mycorrhizae occurs. Initial rates of absorption of 32P were measured at 1 to 100 micromolar KH2PO4 (pH 4.6). Absorption rates of mycorrhizae were about twice those of control roots. Augustinsson-Hofstee analysis yielded two linear phases; Vmax and Km were calculated for each phase. In the low phase (1 to 20 micromolar), Vmax values for the mycorrhizal and nonmycorrhizal roots were each 0.10 micromoles P per gram fresh weight per hour while Km values were 1.6 and 3.9 micromolar KH2PO4, respectively. For the high phase (30 to 100 micromolar), Vmax values for mycorrhizal and nonmycorrhizal roots were 0.32 and 0.25 micromoles P per gram fresh weight per hour and Km values were 35 and 42 micromolar, respectively. These results indicate that at the lower phase concentrations, similar to those expected in most soil solutions, a major factor contributing to the increased uptake was an apparent greater affinity of the absorbing sites for H2PO4− (lower Km).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Sanders F. E., Tinker P. B. Mechanism of absorption of phosphate from soil by Endogone mycorrhizas. Nature. 1971 Sep 24;233(5317):278–279. doi: 10.1038/233278c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spears G., Sneyd J. G., Loten E. G. A method for deriving kinetic constants for two enzymes acting on the same substrate. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1149–1151. doi: 10.1042/bj1251149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Throneberry G. O. Phosphorus and zinc measurements in Kjeldahl digests. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90242-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


