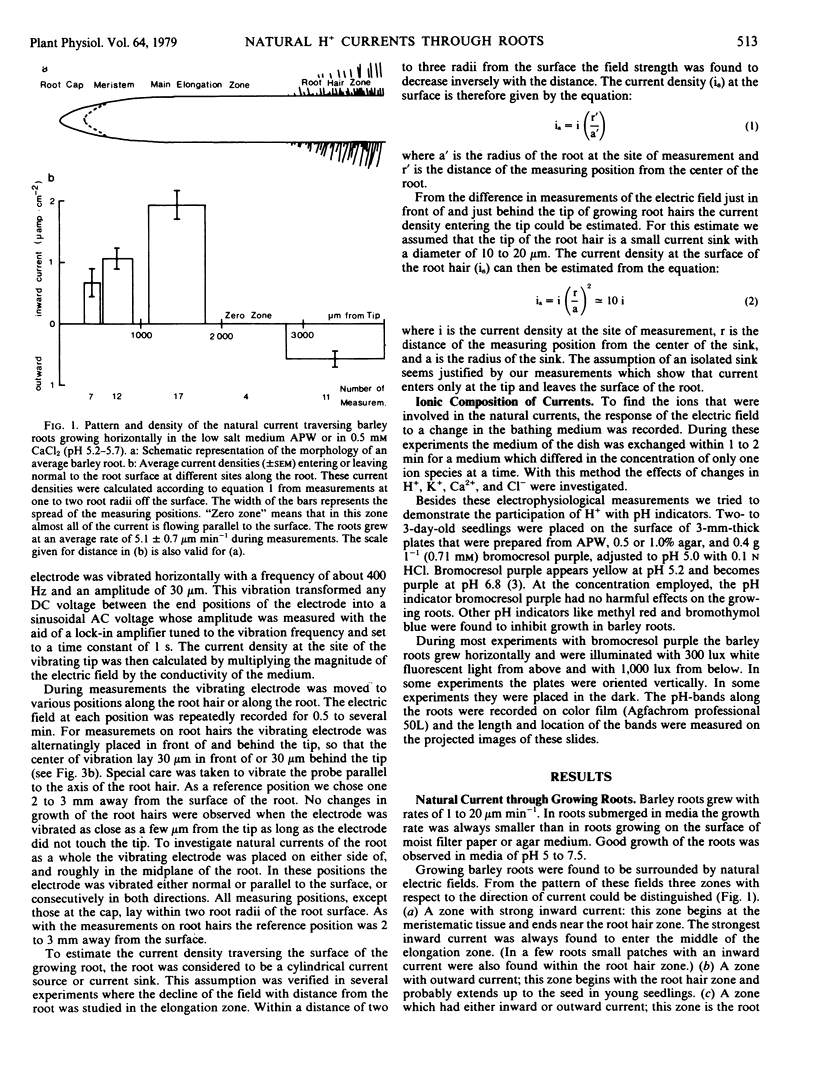
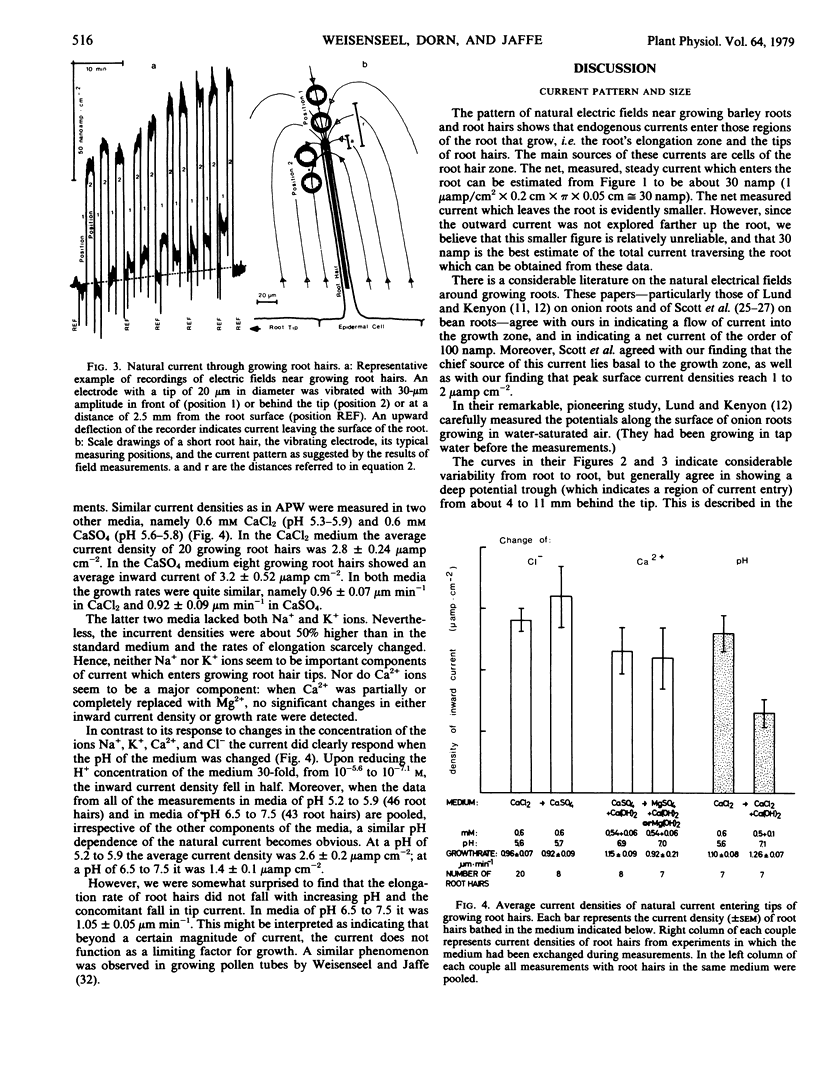
Abstract
With the aid of an extracellular vibrating electrode, natural electric fields were detected and measured in the medium near growing roots and root hairs of barley seedlings. An exploration of these fields indicates that both the root as a whole, as well as individual root hairs, drive large steady currents through themselves. Current consistently enters both the main elongation zone of the root as well as the growing tips of elongating root hairs; it leaves the surface of the root beneath the root hairs. These currents enter with a density of about 2 microamperes per square centimeter, leave with a density of about 0.5 to 1 microampere per square centimeter, and total about 30 nanoamperes.
Responses of the natural fields to changes in the ionic composition of the medium as well as observations of the pH pattern in the medium near the roots (made with bromocresol purple) together indicate that much of the current consists of hydrogen ions. Altogether, H+ ions seem to leak into growing cells or cell parts and to be pumped out of nongrowing ones.
Full text
PDF
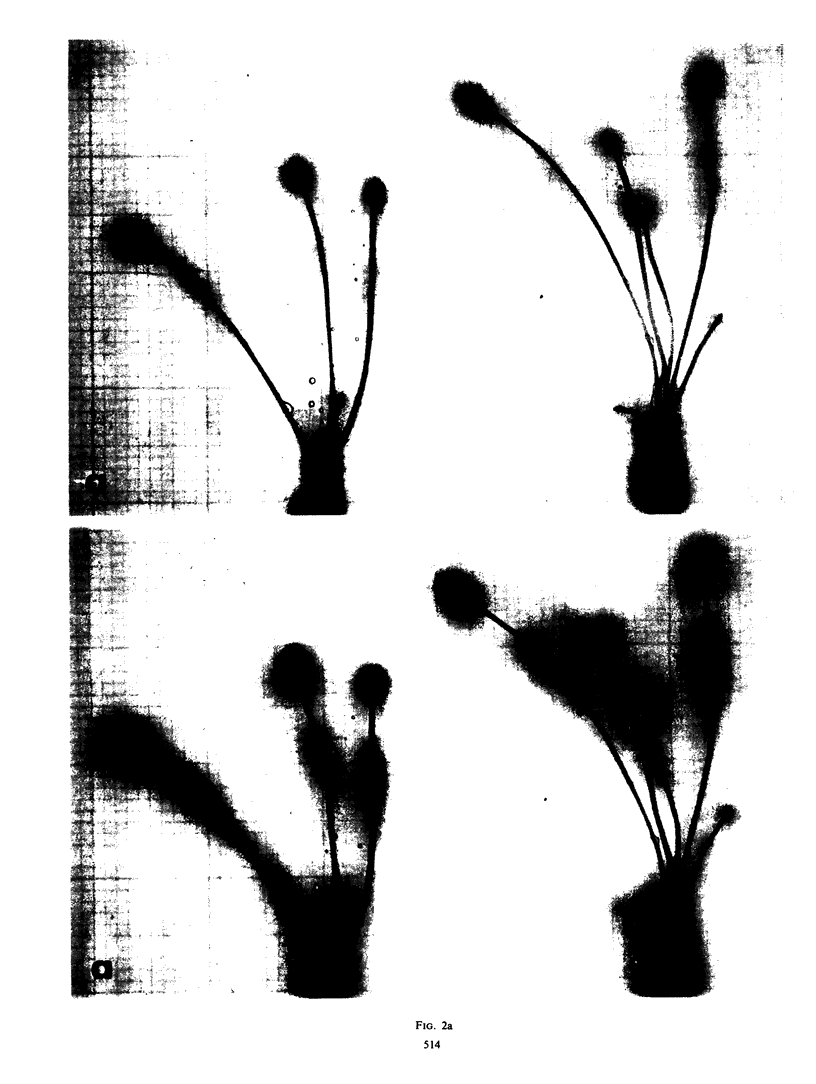




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jaffe L. A., Weisenseel M. H., Jaffe L. F. Calcium accumulations within the growing tips of pollen tubes. J Cell Biol. 1975 Nov;67(2PT1):488–492. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L. F., Nuccitelli R. An ultrasensitive vibrating probe for measuring steady extracellular currents. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):614–628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L. F., Nuccitelli R. Electrical controls of development. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:445–476. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentze J., Raymond B., Cohen J. D., Rayle D. L. Auxin-induced H Secretion in Helianthus and Its Implications. Plant Physiol. 1977 Oct;60(4):509–512. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.4.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz S. M., Higinbotham N. Transmembrane electropotential in barley roots as related to cell type, cell location, and cutting and aging effects. Plant Physiol. 1976 Feb;57(2):123–128. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.2.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuccitelli R., Jaffe L. F. Spontaneous current pulses through developing fucoid eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4855–4859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuccitelli R. Oöplasmic segregation and secretion in the Pelvetia egg is accompanied by a membrane-generated electrical current. Dev Biol. 1978 Jan;62(1):13–33. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman M. G. Active H Efflux from Cells of Low-salt Barley Roots during Salt Accumulation. Plant Physiol. 1970 Jun;45(6):787–790. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.6.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman M. G. Adaptation of barley roots to low oxygen supply and its relation to potassium and sodium uptake. Plant Physiol. 1969 Sep;44(9):1233–1240. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.9.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson K. R., Jaffe L. F. Polarizing fucoid eggs drive a calcium current through themselves. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1167318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenseel M. H., Nuccitelli R., Jaffe L. F. Large electrical currents traverse growing pollen tubes. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):556–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]