Abstract
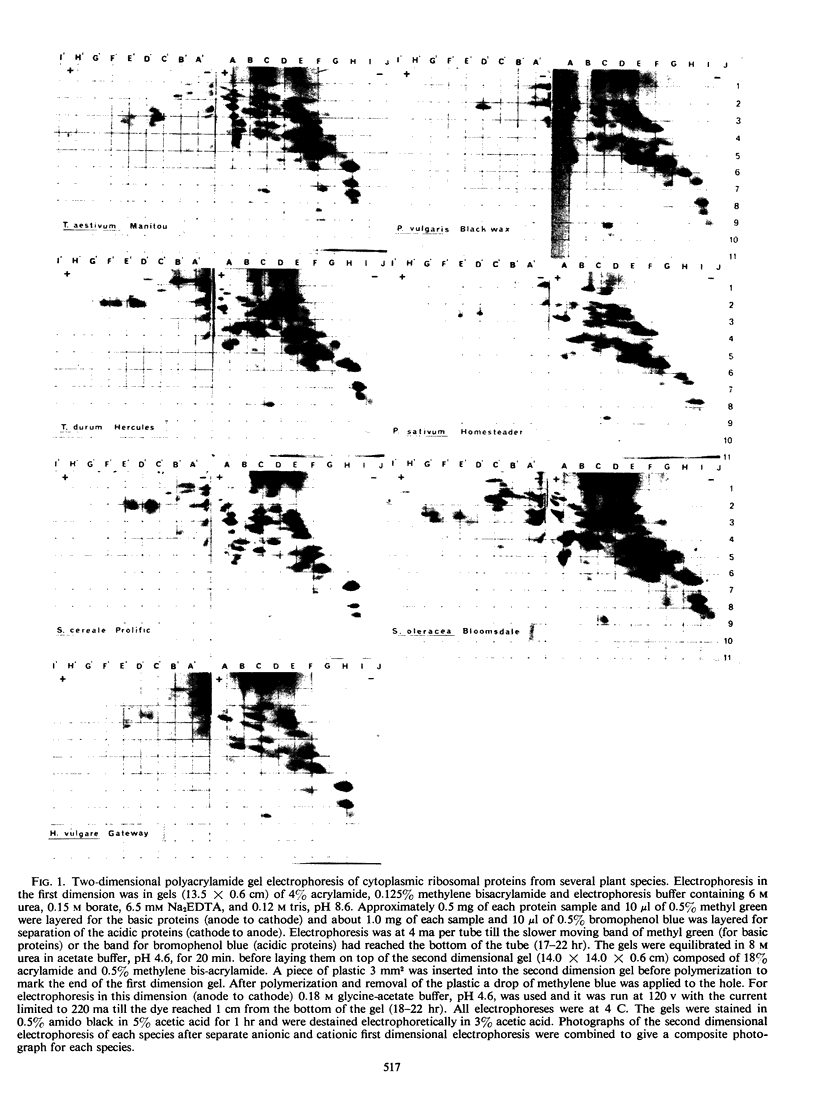
The electrophoretic mobilities of the cytoplasmic ribosomal proteins of several species of plants were compared using two-dimensional electrophoresis. The total number of proteins as well as the number of acidic and basic proteins in individual species varied markedly. Of the species examined, Triticum aestivum had the highest number of basic cytoplasmic ribosomal proteins and Hordeum vulgare had less than half as many. However, marked similarities were noted in the electrophoretic mobilities of many of the proteins, especially for wheat, rye, and barley and for peas and beans. There was a statistically significant positive correlation between the numbers of basic proteins in the species and their chromosome number.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biswas S., Mandal R. K., Biswas B. B. Ribosomal proteins and ribonucleic acids from chloroplasts. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Jan;54(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh-Van-Tan, Delaunay J., Schapira G. Eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Two-dimensional electrophoretic studies. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 15;17(1):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda H. G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. V. Comparison of protein patterns of 70S and 80S ribosomes from various plants by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Mol Gen Genet. 1968;103(3):238–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00273693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. L., Nagabhushan N., Tucker E. B., Zalik S. Dissociation reassociation and phenylalanine incorporation by chloroplast and cytoplasmic wheat-leaf ribosomes. Can J Biochem. 1973 May;51(5):686–693. doi: 10.1139/o73-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XII. Number of proteins in small and large ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli as determined by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1276–1282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins: VI. Preparative polyacrylamide del electrophoresis as applied to the isolation of ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):132–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyttleton J. W. Protein constituents of plant ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 22;154(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odintsova M. S., Yurina N. P. Proteins of chloroplast and cytoplasmic ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1969 Mar 28;40(3):503–506. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherton C. C., Wool I. G. Determination of the number of proteins in liver ribosomes and ribosomal subunits by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4460–4467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos A. C., Bogorad L. Proteins of cytoplasmic, chloroplast, and mitochondrial ribosomes of some plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 28;228(2):492–502. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welfle H., Stahl J., Bielka H. Studies on proteins of animal ribosomes. 8. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of ribosomal proteins of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 28;243(3):416–419. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]