Abstract
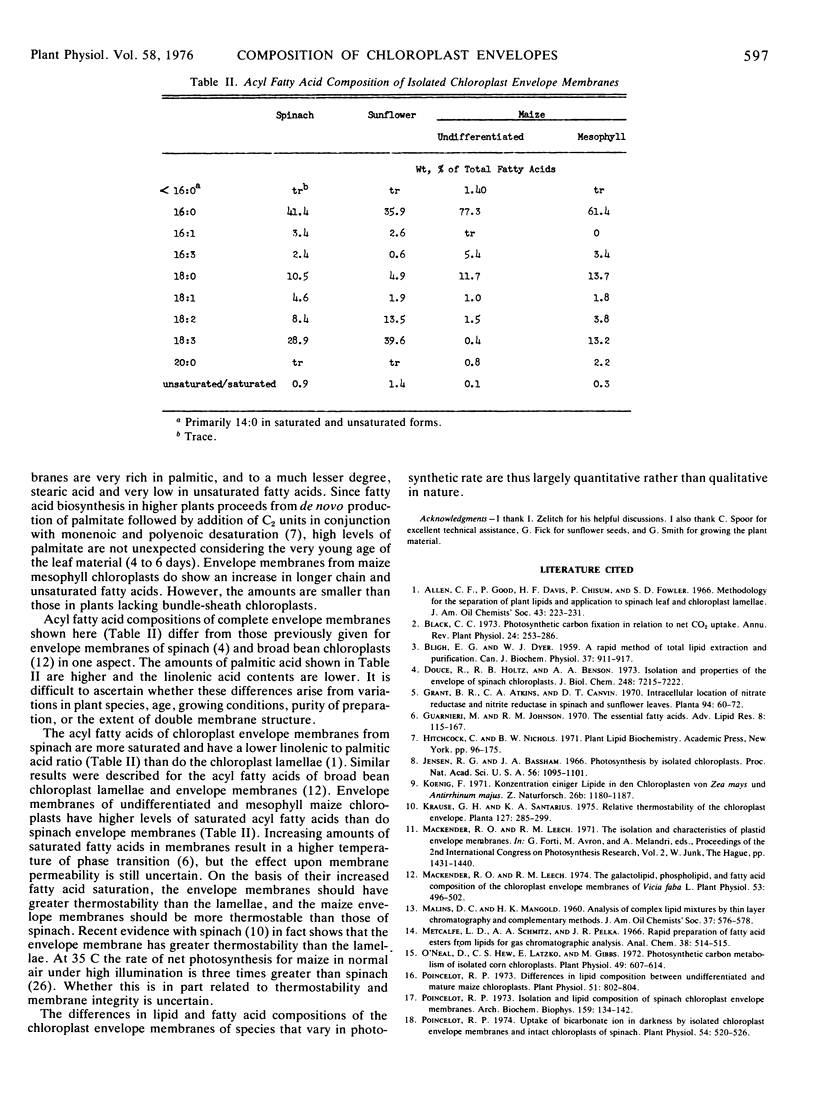
Lipid and fatty acid compositions were determined for chloroplast envelope membranes isolated from spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.), sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.), and maize (Zea mays L.) leaves. The lipid composition was similar in sunflower, spinach, and undifferentiated maize chloroplast envelope membranes and different in maize mesophyll chloroplast envelope membranes. The predominant lipid constituents in all envelope membranes were monogalactosyldiglyceride (27 to 46%), digalactosyldiglyceride (18 to 33%), and phosphatidylcholine (7 to 30%). The fatty acid composition was also similar in sunflower and spinach chloroplast envelope membranes in comparison to those from maize. The major acyl fatty acids of the chloroplast envelope membrane were palmitic (C16:0, 41 and 36%) and linolenic (C18:3, 29 and 40%) acids for spinach and sunflower; palmitic (77%) and stearic (C18:0, 12%) acids for young maize; and palmitic (61%), stearic (14%), and linolenic (13%) acids for mature maize. The differences in lipid and acyl fatty acid compositions among these plants which vary in their rates of net photosynthesis were largely quantitative rather than qualitative.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douce R., Holtz R. B., Benson A. A. Isolation and properties of the envelope of spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7215–7222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarnieri M., Johnson R. M. The essential fatty acids. Adv Lipid Res. 1970;8:115–174. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024908-4.50010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. G., Bassham J. A. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1095–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackender R. O., Leech R. M. The Galactolipid, Phospholipid, and Fatty Acid Composition of the Chloroplast Envelope Membranes of Vicia faba. L. Plant Physiol. 1974 Mar;53(3):496–502. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.3.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'neal D., Hew C. S., Latzko E., Gibbs M. Photosynthetic carbon metabolism of isolated corn chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1972 Apr;49(4):607–614. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poincelot R. P. Differences in Lipid Composition between Undifferentiated and Mature Maize Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1973 Apr;51(4):802–804. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.4.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poincelot R. P. Isolation and lipid composition of spinach chloroplast envelope membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90437-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poincelot R. P. Uptake of bicarbonate ion in darkness by isolated chloroplast envelope membranes and intact chloroplasts of spinach. Plant Physiol. 1974 Oct;54(4):520–526. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.4.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racusen D. Distribution of Protein-bound Hexosamine in Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):53–54. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo K. C., Anderson J. M., Boardman N. K., Downton W. J., Osmond C. B., Thorne S. W. Deficient Photosystem II in Agranal Bundle Sheath Chloroplasts of C(4) Plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):18–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


