Abstract
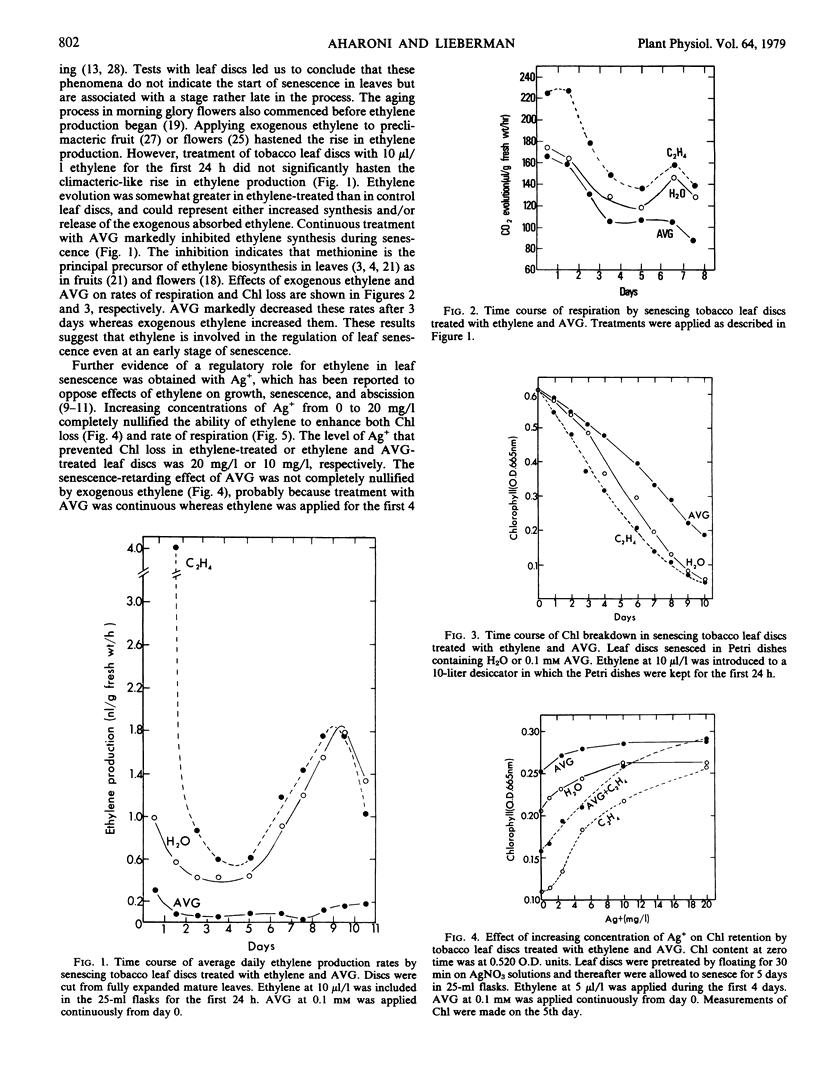
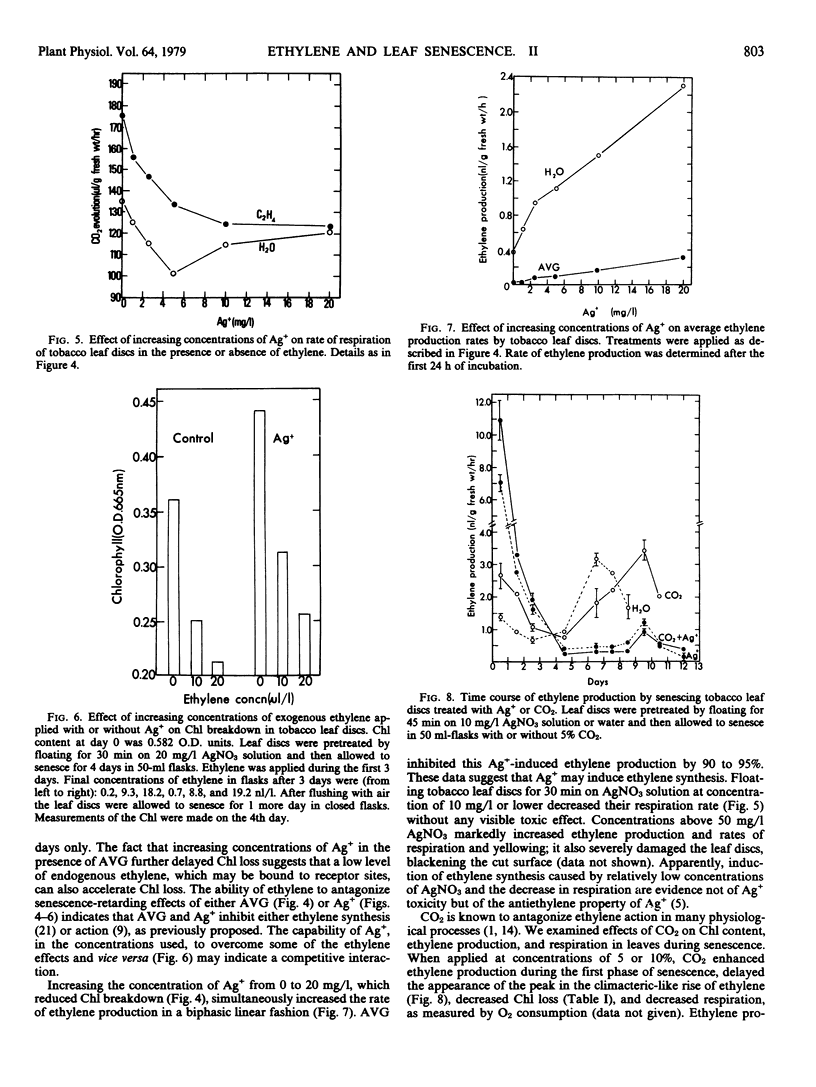
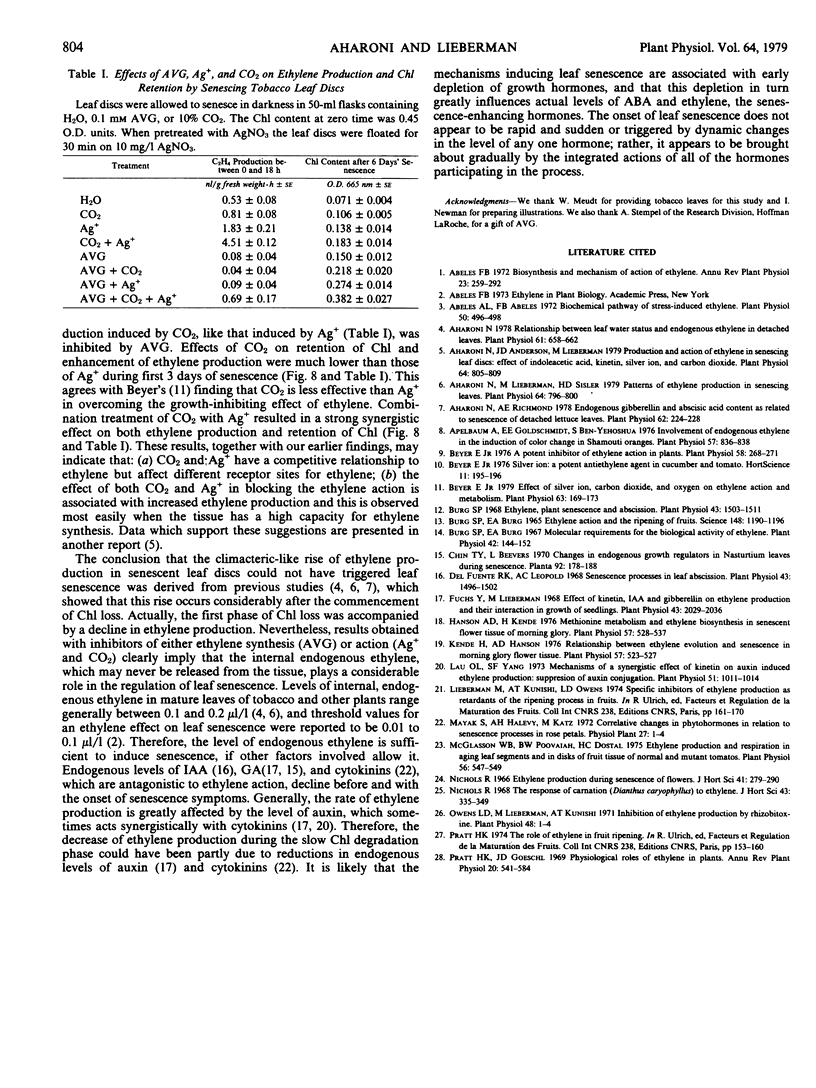
The regulatory role of ethylene in leaf senescence was studied with excised tobacco leaf discs which were allowed to senesce in darkness. Exogenous ethylene, applied during the first 24 hours of senescence, enhanced chlorophyll loss without accelerating the climacteric-like pattern of rise in both ethylene and CO2, which occurred in the advanced stage of leaf senescence. Rates of both ethylene and CO2 evolution increased in the ethylene-treated leaf discs, especially during the first 3 days of senescence. The rhizobitoxine analog, aminoethoxy vinyl glycine, markedly inhibited ethylene production and reduced respiration and chlorophyll loss. Pretreatment of leaf discs with Ag+ or enrichment of the atmosphere with 5 to 10% CO2 reduced chlorophyll loss, reduced rate of respiration, and delayed the climacteric-like rise in both ethylene and respiration. Ag+ was much more effective than CO2 in retarding leaf senescence. Despite their senescence-retarding effect, Ag+ and CO2, which are known to block ethylene action, stimulated ethylene production by the leaf discs during the first 3 days of the senescing period; Ag+ was more effective than CO2. The results suggest that although ethylene production decreases prior to the climacteric-like rise during the later stages of senescence, endogenous ethylene plays a considerable role throughout the senescence process, presumably by interacting with other hormones participating in leaf senescence.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles A. L. Biochemical Pathway of Stress-induced Ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1972 Oct;50(4):496–498. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.4.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aharoni N., Anderson J. D., Lieberman M. Production and action of ethylene in senescing leaf discs: effect of indoleacetic Acid, kinetin, silver ion, and carbon dioxide. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):805–809. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aharoni N. Endogenous gibberellin and abscisic Acid content as related to senescence of detached lettuce leaves. Plant Physiol. 1978 Aug;62(2):224–228. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.2.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aharoni N., Lieberman M. Patterns of ehtylene production in senescing leaves. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):796–800. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aharoni N. Relationship between Leaf Water Status and Endogenous Ethylene in Detached Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):658–662. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apelbaum A., Goldschmidt E. E., Ben-Yehoshua S. Involvement of endogenous ethylene in the induction of color change in shamouti oranges. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):836–838. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURG S. P., BURG E. A. ETHYLENE ACTION AND THE RIPENING OF FRUITS. Science. 1965 May 28;148(3674):1190–1196. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3674.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. M. A potent inhibitor of ethylene action in plants. Plant Physiol. 1976 Sep;58(3):268–271. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.3.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. M. Effect of silver ion, carbon dioxide, and oxygen on ethylene action and metabolism. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jan;63(1):169–173. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg S. P., Burg E. A. Molecular requirements for the biological activity of ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jan;42(1):144–152. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg S. P. Ethylene, plant senescence and abscission. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9 Pt B):1503–1511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dela Fuente R. K., Leopold A. C. Senescence processes in leaf abscission. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9 Pt B):1496–1502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs Y., Lieberman M. Effects of Kinetin, IAA, and Gibberellin on Ethylene Production, and Their Interactions in Growth of Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1968 Dec;43(12):2029–2036. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.12.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Kende H. Methionine metabolism and ethylene biosynthesis in senescent flower tissue of morning-glory. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):528–537. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kende H., Hanson A. D. Relationship between Ethylene Evolution and Senescence in Morning-Glory Flower Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):523–527. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau O. L., Yang S. F. Mechanism of a Synergistic Effect of Kinetin on Auxin-induced Ethylene Production: Suppression of Auxin Conjugation. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jun;51(6):1011–1014. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.6.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlasson W. B., Poovaiah B. W., Dostal H. C. Ethylene production and respiration in aging leaf segments and in disks of fruit tissue of normal and mutant tomatoes. Plant Physiol. 1975 Oct;56(4):547–549. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens L. D., Lieberman M., Kunishi A. Inhibition of ethylene production by rhizobitoxine. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jul;48(1):1–4. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


