Abstract
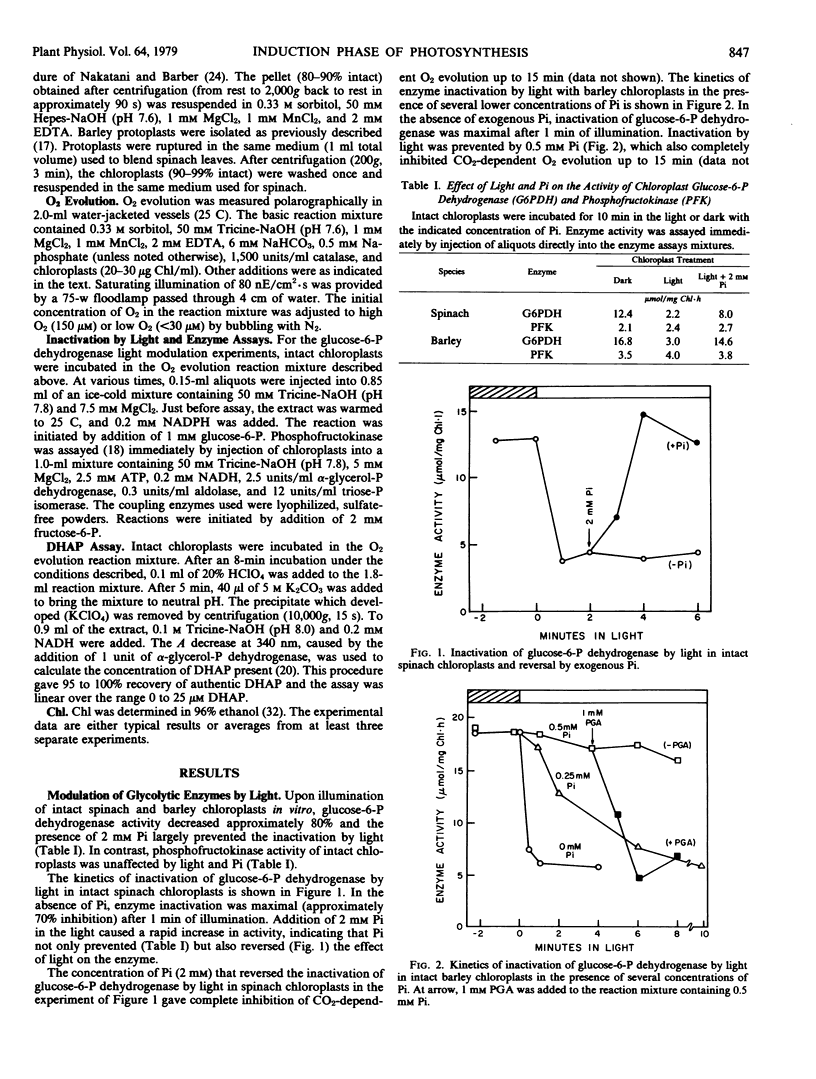
High concentrations of orthophosphate (Pi) inhibited CO2-dependent O2 evolution and prevented the inactivation of glucose-6-P dehydrogenase by light in intact spinach and barley chloroplasts. Addition of glycerate-3-P to chloroplasts inhibited by Pi in the light, induced O2 evolution and caused rapid inactivation of glucose-6-P dehydrogenase. The activity of phosphofructokinase detected in chloroplast preparations was not affected by light or by Pi.
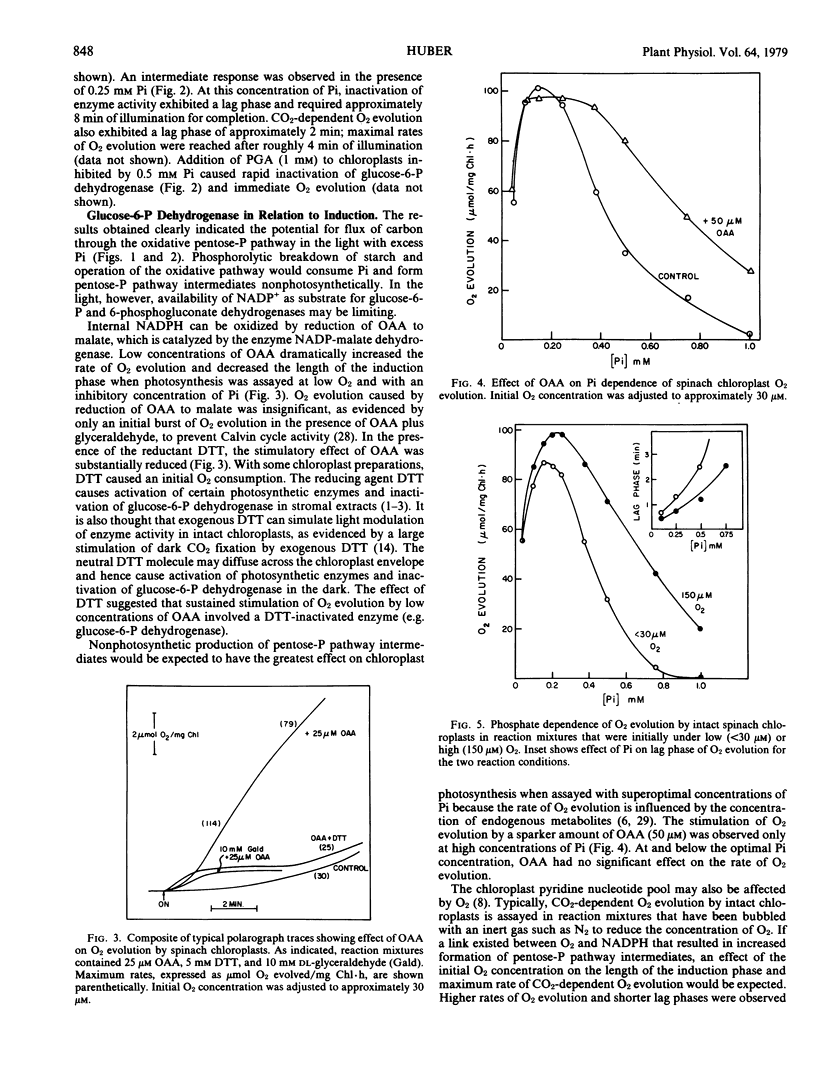
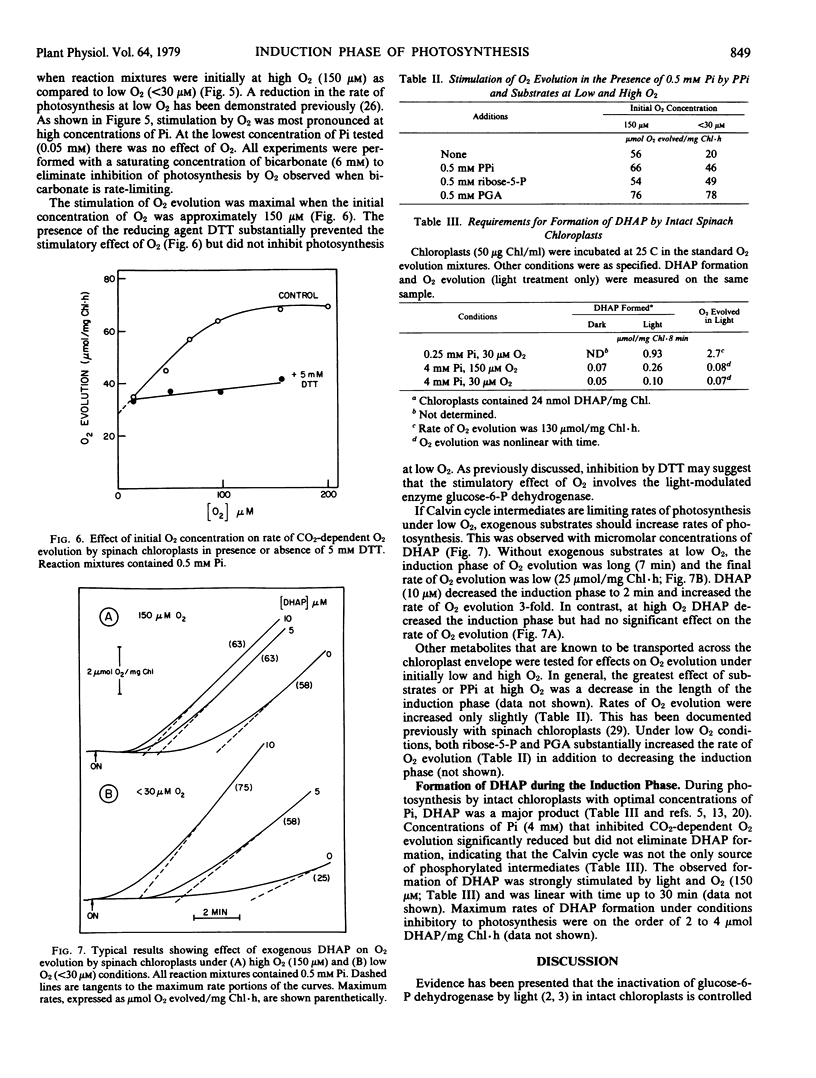
Dihydroxyacetone-P was a major product of chloroplast photosynthesis when optimum concentrations of Pi were used. Chloroplasts continued to form dihydroxyacetone-P at a slow rate in the presence of Pi at concentrations (2 to 4 millimolar) that gave complete inhibition of CO2-dependent O2 evolution. Formation of dihydroxyacetone-P in the presence of 4 millimolar Pi was stimulated by light and either O2 (150 micromolar) or sparker amounts of oxaloacetate.
Conditions that favored dihydroxyacetone-P formation (high O2 or low O2 plus oxaloacetate) increased the optimum Pi concentration for CO2-dependent O2 evolution and stimulated O2 evolution at high concentrations of Pi. The stimulation of O2 evolution at superoptimal concentrations of Pi by O2 or oxaloacetate was prevented by dithiothreitol.
The results suggested that formation of pentose-P pathway intermediates via the oxidative pentose-P pathway may be limited by availability of NADP in the light but may occur at significant rates and thereby contribute to termination of the induction phase of O2 evolution.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. E., Avron M. Light Modulation of Enzyme Activity in Chloroplasts: Generation of Membrane-bound Vicinal-Dithiol Groups by Photosynthetic Electron Transport. Plant Physiol. 1976 Feb;57(2):209–213. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E., Nehrlich S. C., Champigny M. L. Light modulation of enzyme activity: activation of the light effect mediators by reduction and modulation of enzyme activity by thiol-disulfide exchange. Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):601–605. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E., Ng T. C., Park K. E. Inactivation of pea leaf chloroplastic and cytoplasmic glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenases by light and dithiothreitol. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jun;53(6):835–839. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auclair C., Torrès M., Hakim J. Involvement of hydroxyl radical in NAD(P)H oxidation and associated oxygen reduction by the granule fraction of human blood polymorphonuclears. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 28;81(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberger E. S., Ehrlich B. A., Gibbs M. The glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and glycerate 3-phosphate shuttle and carbon dioxide assimilation in intact spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jun;55(6):1023–1030. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.6.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn W., Baldry C. W., Walker D. A. Some effects of inorganic phosphate on O2 evolution by isolated chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;143(3):614–624. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn W., Walker D. A., Baldry C. W. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Reversal of orthophosphate inhibition by Calvin-cycle intermediates. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(1):89–95. doi: 10.1042/bj1070089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egneus H., Heber U., Matthiesen U., Kirk M. Reduction of oxygen by the electron transport chain of chloroplasts during assimilation of carbon dioxide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 11;408(3):252–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliege R., Flügge U. I., Werdan K., Heldt H. W. Specific transport of inorganic phosphate, 3-phosphoglycerate and triosephosphates across the inner membrane of the envelope in spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 10;502(2):232–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt H. W., Chon C. J., Maronde D. Role of orthophosphate and other factors in the regulation of starch formation in leaves and isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jun;59(6):1146–1155. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.6.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt W. H., Werdan K., Milovancev M., Geller G. Alkalization of the chloroplast stroma caused by light-dependent proton flux into the thylakoid space. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 31;314(2):224–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. C. Effect of pH on chloroplast photosynthesis. Inhibition of O2 evolution by inorganic phosphate and magnesium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 11;545(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachru R. B., Anderson L. E. Inactivation of pea leaf phosphofructokinase by light and dithiothreitol. Plant Physiol. 1975 Feb;55(2):199–202. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly G. J., Latzko E. Chloroplast phosphofructokinase: I. Proof of phosphofructokinase activity in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1977 Aug;60(2):290–294. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lendzian K., Bassham J. A. Regulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in spinach chloroplasts by ribulose 1,5-diphosphate and NADPH/NADP+ ratios. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 11;396(2):260–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Preiss J. Amylopectin degradation in pea chloroplast extracts. Plant Physiol. 1978 Feb;61(2):218–220. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M., Walker D. A. The reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate by reconstituted chloroplasts and by chloroplast extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 19;368(3):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani H. Y., Barber J. An improved method for isolating chloroplasts retaining their outer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 14;461(3):500–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R., Jr, Heldt H. W. Light-dependent changes of the Mg2+ concentration in the stroma in relation to the Mg2+ dependency of CO2 fixation in intact chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 6;449(3):434–436. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slovacek R. E., Hind G. Influence of antimycin a and uncouplers on anaerobic photosynthesis in isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1977 Oct;60(4):538–542. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.4.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steup M., Peavey D. G., Gibbs M. The regulation of starch metabolism by inorganic phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1554–1561. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. M., Walker D. A. Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Inhibition by DL-glyceraldehyde of carbon dioxide assimilation. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1147–1157. doi: 10.1042/bj1281147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdan K., Heldt H. W., Milovancev M. The role of pH in the regulation of carbon fixation in the chloroplast stroma. Studies on CO2 fixation in the light and dark. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 11;396(2):276–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildner G. F. The regulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in chloroplasts. Z Naturforsch C. 1975 Nov-Dec;30(6):756–760. doi: 10.1515/znc-1975-11-1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



