Abstract
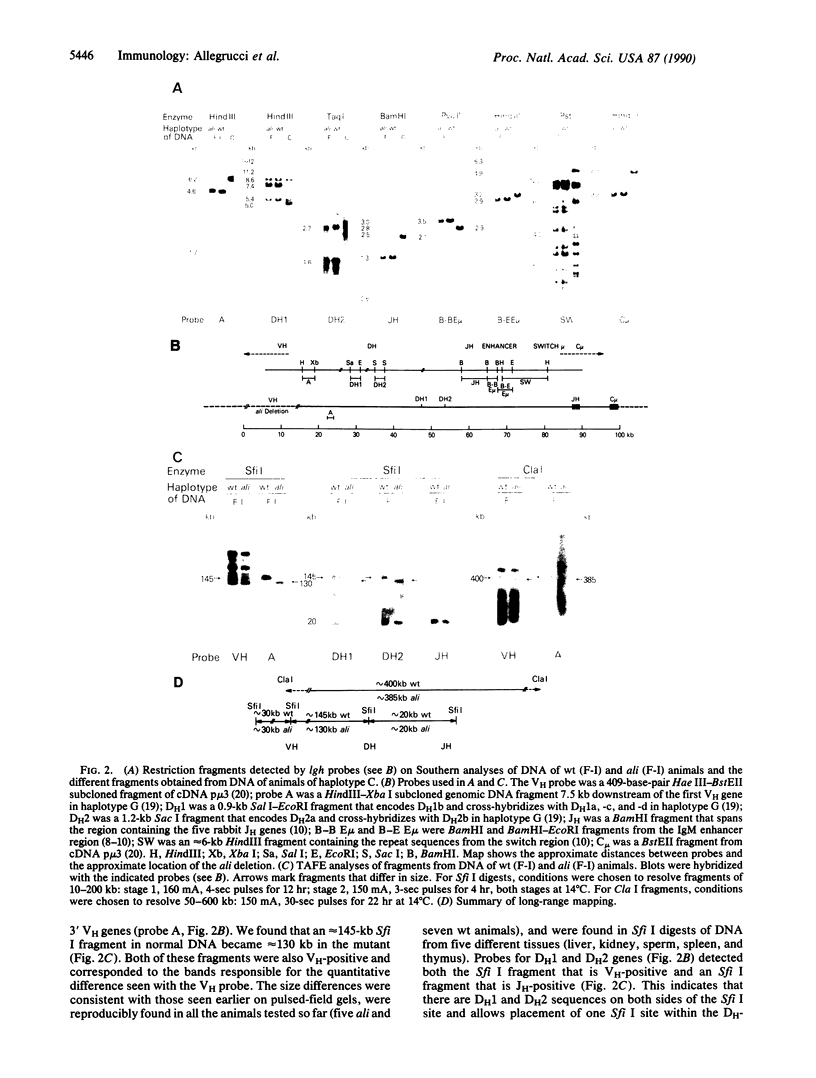
Rabbits of the Alicia strain have a mutation (ali) that segregates with the immunoglobulin heavy-chain (lgh) locus and has a cis effect upon the expression of heavy-chain variable-region (VH) genes encoding the a2 allotype. In heterozygous a1/ali or a3/ali rabbits, serum immunoglobulins are almost entirely the products of the normal a1 or a3 allele and only traces of a2 immunoglobulin are detectable. Adult homozygous ali/ali rabbits likewise have normal immunoglobulin levels resulting from increased production of a-negative immunoglobulins and some residual ability to produce the a2 allotype. By contrast, the majority of the immunoglobulins of wild-type a2 rabbits are a2-positive and only a small percentage are a-negative. Genomic DNAs from homozygous mutant and wild-type animals were indistinguishable by Southern analyses using a variety of restriction enzyme digests and lgh probes. However, when digests with infrequently cutting enzymes were analyzed by transverse alternating-field electrophoresis, the ali DNA fragments were 10-15 kilobases smaller than the wild type. These fragments hybridized to probes both for VH and for a region of DNA a few kilobases downstream of the VH genes nearest the joining region. We suggest that this relatively small deletion affects a segment containing 3' VH genes with important regulatory functions, the loss of which leads to the ali phenotype. These results, and the fact that the 3' VH genes rearrange early in B-cell development, indicate that the 3' end of the VH locus probably plays a key role in regulation of VH gene expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker R. S., Zhai S. K., Currier S. J., Knight K. L. Ig VH, DH, and JH germ-line gene segments linked by overlapping cosmid clones of rabbit DNA. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1351–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein K. E., Alexander C. B., Mage R. G. Germline VH genes in an a3 rabbit not typical of any one VHa allotype. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3480–3488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein K. E., Alexander C. B., Reddy E. P., Mage R. G. Complete sequence of a cloned cDNA encoding rabbit secreted mu-chain of VHa2 allotype: comparisons with VHa1 and membrane mu sequences. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):490–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Notkins A. L. CD5+ B lymphocytes, polyreactive antibodies and the human B-cell repertoire. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):364–368. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier S. J., Gallarda J. L., Knight K. L. Partial molecular genetic map of the rabbit VH chromosomal region. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1651–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Lembezat M. P., Coutinho A. Expression of antibody V-regions is genetically and developmentally controlled and modulated by the B lymphocyte environment. Int Immunol. 1989;1(4):342–354. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.4.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallarda J. L., Gleason K. S., Knight K. L. Organization of rabbit immunoglobulin genes. I. Structure and multiplicity of germ-line VH genes. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4222–4228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa K., Hardy R. R. Normal, autoimmune, and malignant CD5+ B cells: the Ly-1 B lineage? Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:197–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Toward a layered immune system. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):953–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90748-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelus A. S., Weiss S. Mutation affecting the expression of immunoglobulin variable regions in the rabbit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4883–4886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinfield R., Hardy R. R., Tarlinton D., Dangl J., Herzenberg L. A., Weigert M. Recombination between an expressed immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene and a germline variable gene segment in a Ly 1+ B-cell lymphoma. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):843–846. doi: 10.1038/322843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Becker R. S. Molecular basis of the allelic inheritance of rabbit immunoglobulin VH allotypes: implications for the generation of antibody diversity. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90344-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Burnett R. C., McNicholas J. M. Organization and polymorphism of rabbit immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1245–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Spieker-Polet H., Kazdin D. S., Oi V. T. Transgenic rabbits with lymphocytic leukemia induced by the c-myc oncogene fused with the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3130–3134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalor P. A., Herzenberg L. A., Adams S., Stall A. M. Feedback regulation of murine Ly-1 B cell development. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Mar;19(3):507–513. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalor P. A., Stall A. M., Adams S., Herzenberg L. A. Permanent alteration of the murine Ly-1 B repertoire due to selective depletion of Ly-1 B cells in neonatal animals. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Mar;19(3):501–506. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage R. G. Allotype suppression in rabbits: effects of anti-allotype antisera upon expression of immunoglobulin genes. Transplant Rev. 1975;27:84–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage R. G., Bernstein K. E., McCartney-Francis N., Alexander C. B., Young-Cooper G. O., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H. The structural and genetic basis for expression of normal and latent VHa allotypes of the rabbit. Mol Immunol. 1984 Nov;21(11):1067–1081. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage R. G., Dray S., Gilman-Sachs A., Hamers-Casterman C., Hamers R., Hanly W. C., Kindt T. J., Knight K. L., Mandy W. J., Naessens J. Rabbit heavy chain haplotypes--allotypic determinants expressed by VH-CH recombinants. Immunogenetics. 1982 Mar;15(3):287–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00364337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage R. G., Harindranath N., Hole N. J., Newman B., Perez R., Alexander C. B., Young-Cooper G. O. Genetic analyses of restriction fragment length polymorphisms using high molecular weight DNA from sperm or lymphocytes embedded in agarose. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 Sep-Oct;5(5):94–96. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage R. G., Newman B. A., Harindranath N., Bernstein K. E., Becker R. S., Knight K. L. Evolutionary conservation of splice sites in sterile C mu transcripts and of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) enhancer region sequences. Mol Immunol. 1989 Oct;26(10):1007–1010. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels N. Might gene conversion be the mechanism of somatic hypermutation of mammalian immunoglobulin genes? Trends Genet. 1989 Jan;5(1):4–8. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthyssens G., Rabbitts T. H. Structure and multiplicity of genes for the human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6561–6565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Laster S. M., Marzluff W. F., Roux K. H. Dynamic gene interactions in the evolution of rabbit VH genes: a four codon duplication and block homologies provide evidence for intergenic exchange. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):7041–7054. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M., Gehrmann P., Petrac E., Wiese P. A novel VH to VHDJH joining mechanism in heavy-chain-negative (null) pre-B cells results in heavy-chain production. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):840–842. doi: 10.1038/322840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud C. A., Dahan A., Anquez V., Weill J. C. Somatic hyperconversion diversifies the single Vh gene of the chicken with a high incidence in the D region. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90879-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Hillson J. L., Perlmutter R. M. Early restriction of the human antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):791–793. doi: 10.1126/science.3118465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Hillson J. L., Perlmutter R. M. Structure and evolution of mammalian VH families. Int Immunol. 1990;2(1):41–50. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J., Sims M. J., Krawinkel U. Regulation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and expression. Immunol Today. 1989 May;10(5):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90163-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutter A., Riblet R. Conservation of an immunoglobulin variable-region gene family indicates a specific, noncoding function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7460–7464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C., Tonegawa S. Diversity and joining segments of mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain genes are closely linked and in the same orientation: implications for the joining mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3030–3034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. E., Paige C. J. VH gene family utilization is regulated by a locus outside of the VH region. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1499–1504. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Desiderio S. V., Paskind M., Kearney J. F., Baltimore D., Alt F. W. Preferential utilization of the most JH-proximal VH gene segments in pre-B-cell lines. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):727–733. doi: 10.1038/311727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]