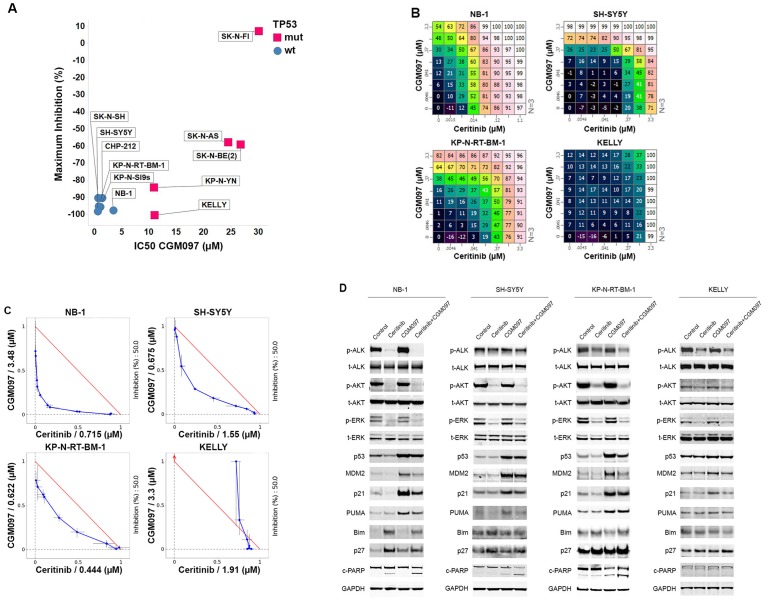
Figure 2. Combination of ceritinib with CGM097 leads to increased antitumor activity in TP53 wild-type neuroblastoma cell lines harboring ALK aberrations.
(A) Sensitivity of a panel of TP53 wild-type and mutant neuroblastoma cell lines to CGM097 treatment for 72 hr. Maximum percentages of inhibition are on the y-axis, and IC50 values are on the x-axis. (B) Growth effects of combining ceritinib and CGM097 in ALK-amplified or ALK mutant neuroblastoma cells. In each grid, the effects correspond to increasing doses of CGM097 on the y-axis and increasing doses of ceritinib on the x-axis. All remaining points on the grid display the results of the combination of the two inhibitors that correspond to the single-agent concentrations denoted on the two axes. Values are displayed as percentage of inhibition based on comparisons made with the Day 3 untreated controls. (C) Isobologram analysis of the data in (B). Doses of CGM097 are on the y-axis, and ceritinib on the x-axis. The red straight line in each panel defines all the pairs of doses of ceritinib and CGM097 that lead to 50% of proliferation inhibition from simple additivity. The points on the blue curve represent the actual doses of ceritinib and CGM097, when combined, to achieve 50% of inhibition. The blue curves of the TP53 wild-type cell lines bow under the red lines, indicating the combination of ceritinib and CGM097 is synergistic. (D) Enhanced apoptosis as evidenced by increased levels of cleaved PARP in TP53 wild-type neuroblastoma cells with ALK amplification or mutation when treated with ceritinib in combination with CGM097. Cells were incubated with DMSO, 1 µM ceritinib, 2 µM CGM097 and 1 µM ceritinib plus 2 µM CGM097 for 16 hr.