Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus MRSA strains belonging to the clonal complex 398 (CC398) are highly prevalent in livestock and companion animals but may also cause serious infections in humans. CC398 strains in livestock usually do not possess well-known virulence factors that can be frequently found in other MRSA sequence types (ST). Since many staphylococcal virulence genes are residing on the genomes of temperate phages, the question arises why livestock-associated (LA-) CC398 strains are only rarely infected by those phages. We isolated and characterized four temperate phages (P240, P282, P630 and P1105) containing genes of the immune evasion cluster (IEC) and/or for the Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL). Sequence analysis of the phage genomes showed that they are closely related to known phages and that the DNA region encoding lysis proteins, virulence factors and the integrase exhibits numerous DNA repeats which may facilitate genomic rearrangements. All phages lysed and lysogenized LA-CC398 strains. Integration of IEC phage P282 was detected at ten sites of the hosts’ chromosome. The prophages were stably inherited in LA-CC398 and enterotoxin A, staphylokinase and PVL toxin were produced. The data demonstrate that lysogenic conversion of LA-CC398 strains by virulence-associated phages may occur and that new pathotypes may emerge by this mechanism.
Introduction
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (S.) aureus (MRSA) is an important human pathogen not only in health care systems but also in community settings1. In the last decade, MRSA has also emerged in livestock2. The predominant MRSA lineage detected in animals in Europe and USA is of clonal complex (CC) 398 comprising a heterogeneous group of strains with currently 43 sequence types (ST) and a variety of spa types3. Staphylococcus aureus CC398 strains cluster into two distinct phylogenetic clades, a livestock clade and a basal human clade4. Livestock-associated (LA-) CC398 strains may cause diseases in both humans and animals, e.g. wound infections and bacteremia5, foot joint infections in turkeys6 and bovine mastitis7, 8. CC398 strains are often multiresistant to several classes of antimicrobial agents but they usually lack well-known virulence genes9, of which a significant number is located on mobile genetic elements, e.g. temperate phages10. However, there are distinct differences between LA- and human-adapted CC398 strains. Whereas strains belonging to the human clade frequently harbor ΦSa3, a ß-hemolysin (hlb) converting integrase (int) group 3 prophage that carries the human-specific immune evasion cluster IEC11, this prophage is usually absent in LA-CC398 strains. IEC encodes several immune modulating proteins which counteract innate immunity. The most common proteins are the staphylokinase (SAK), staphylococcal complement inhibitor (SCIN) and chemotaxis inhibitory protein (CHIPS), but some IEC clusters also contain genes for staphylococcal enterotoxins like enterotoxin A (SEA) or enterotoxin P (SEP)12. SEA belongs to the classical staphylococcal enterotoxins and exhibits emetic and superantigenic activity13. Enterotoxin-producing S. aureus is one of the leading causes of foodborne poisoning14 but the strains are often methicillin-sensitive. The bi-component exotoxin Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL) encoded by int group 2 phages is common in community-acquired (CA-) MRSA15, but has only occasionally been found in CC39816. Its contribution to the virulence of MRSA is not fully understood, though it destroys polymorphonuclear granulocytes by forming pores, which leads to lysis of the cells17. It is still unclear why virulence gene containing phages have to date only rarely been detected in LA-MRSA CC398 strains. One reason could be an insusceptibility of LA-CC398 strains to those phages. The strains may lack a receptor for phage adsorption or a suitable integration site within their chromosome. They could also possess defence systems that can degrade phage DNA. Van der Mee-Marquet et al.18 studied a ß-hemolysin-converting ΦSa3 phage in a LA-MRSA CC398 strain and found that the prophage was not stable and needed a helper phage for infection. This finding suggests that LA-MRSA CC398 strains might not be suitable hosts for virulence gene-containing phages. On the other hand, many LA-CC398 strains are lysogenic and harbor one or even several prophages19, 20. Most of the identified prophages belong to the int groups 2 and 6, but known virulence genes have not been detected on their genomes. Nevertheless, the fact that such prophages occur in LA-CC398 strains indicates that basic requirements for a phage infection are fulfilled.
In this work, we isolated and characterized four temperate S. aureus phages containing a different composition of virulence genes and analysed their genomes. Bioinformatic analysis revealed repetitive DNA sequences on the genomes probably associated with recombinational events. All phages were able to infect and to lysogenize LA-CC398 strains. We determined multiple integration sites of the ΦSa3 phage P282 within the S. aureus chromosome and show that the phage-encoded virulence factors are expressed in LA-CC398, which may increase the virulence of these strains in vivo.
Results
Isolation of the virulence gene-carrying S. aureus phages P240, P282, P630 and P1105
To identify virulence gene-containing phages in S. aureus that should be used in subsequent experiments with LA-MRSA CC398, a large number of strains belonging to various MLST types was analysed by microarrays for the presence of virulence genes known to be located on the genomes of temperate phages10. Four strains (10S00630, 11S00282, 11S01105 and 13-ST00240) isolated from human clinical samples and from poultry harbored genes of the IEC cluster and/or encoded PVL (Table 1). To examine whether active prophages reside in these strains, mitomycin C induction was performed. In all prepared lysates the respective virulence genes were detected by PCR (data not shown). To identify suitable hosts for phage propagation, the lysates were spotted on a set of LA-MRSA CC398 strains. For each lysate at least one susceptible indicator strain was found. As it was uncertain how many prophages had been induced in each strain, single plaques were analysed by PCR targeting the respective virulence genes, which resulted in the isolation of four phages containing a different composition of these genes (Table 1). Using multiplex-PCR (see Materials and Methods) the int group of the phages was determined. Two phages (P240 and P1105) belong to int group 2. Both phages possess pvl genes, but P1105 additionally carries the enterotoxin A gene sea. Phage P282 is a member of int group 3 (ΦSa3) and contains three IEC genes (chp, sak, scn) whereas int group 6 phage P630 carries the virulence gene sea. All phages are members of the Siphoviridae family. Though, while P282, P630 and P1105 possess an isometric head, the head of P240 is prolate (Fig. 1).
Table 1.
Origin and some characteristics of the virulence gene containing phages used in this study.
| Strain | Isolated from | Spa type | MLST type | Phage | Integrase type | Virulence genes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10S00630 | MRSA | turkey, nasal swab | t002 | ST1791 | P630 | Sa6 | sea |
| 11S00282 | MRSA | chicken, meat | t899 | ST398 | P282 | Sa3 | chp, sak, scn |
| 11S01105 | MRSA | human, abscess | t657 | ST772 | P1105 | Sa2 | lukF-PVL, lukS-PVL, sea |
| 13-ST00240 | MSSA | human, wound swab | t034 | ST398 | P240 | Sa2 | lukF-PVL, lukS-PVL |
Figure 1.
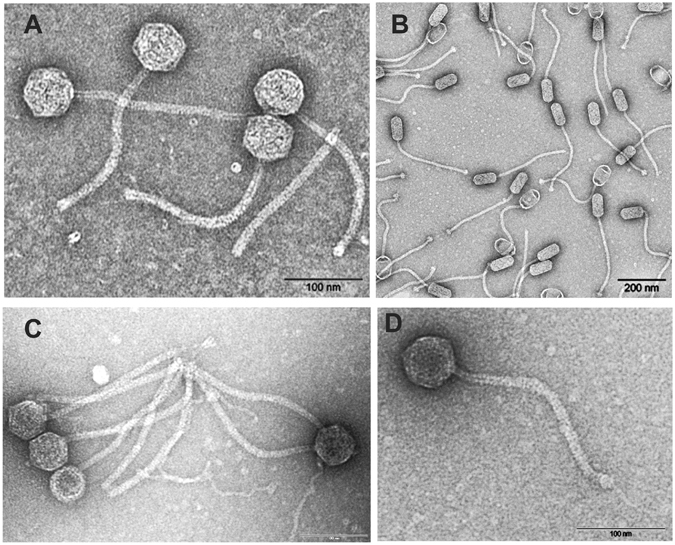
Electron micrographs of the phages P1105 (A), P240 (B), P630 (C) and P282 (D).
Sequence analyses of the phages disclosed repetitive DNA sequences probably involved in genomic rearrangements
We determined the sequences of the four phages and aligned their genomes using the start codon of the terminase small subunit gene as starting point. The phages P282, P630 and P1105 have similar genome sizes between 40.5 kb and 42.5 kb, the genome of P240 is a little larger (46 kb). All phages showed significant homologies to previously described S. aureus phages (Supplementary Material Table S2). Int 2 phage P240 is a typical member of the prolate-headed group 2 of Sfi21-like PVL phages like phiSLT21, which is 99% identical over 72% of the genome. According to the current taxonomy of staphylococcal phages, this group belongs to the genus “3alikevirus”22. The closest relatives of int 3 phage P282 are other ΦSa3 phages, e.g. phiNM323 that is 98% identical over 69% of the genome. Int 6 phage P630 is similarly related to ΦSa3 phages, the strongest overall homologies, however, exist to group 3 PVL phage phi7247PVL24. Finally int group 2 phage P1105 isolated from a ST772 strain is nearly identical (99% identical over 99% of the genome) to the ST772 phages ΦIND772PVL and phiSa119 isolated in India and Italy25, 26, both encoding PVL and enterotoxin A. As shown in Figure S1 the isometric-headed phages P282, P630 and P1105 are much more closely related to each other than to P240 and can be allocated to the genus “77likevirus”22, the type phage of which is phage 7727. Particularly the left arm of the genomes up to the holin gene, which mainly encodes proteins for DNA packaging and virion assembly are very similar. The large terminase subunits of the three phages are even identical and differ by only one amino acid from the terminase of phage 77. Though, only little homologies exist to terminases of other members of the genus “77likevirus”, e.g. phiPVL108, which is a group 1 Sfi21-like cos-site PVL phage28. We therefore analysed restriction digests of phage P282 and P240 by standard procedures (heating and cooling, analysis of ligated DNA). While 3′-overhangs of ten nucleotides (GGCGGGGGCC) were easily detectable in the P240 genome, which is in accordance with other group 2 Sfi21-like PVL phages29, 30 we did not identify any cos-site in P282. Treatment of P282 DNA with Bal31 prior to digestion with restriction endonucleases resulted in a degradation of all restriction fragments (data not shown). We therefore speculate that the P282 genome is circularly permuted. A sequence (5′-CAGATTTATCTC-3′) very similar to the P22 consensus pac-site (5′-AAGATTTATCTG-3′) exists on the P282 genome, albeit far away from the gene for the small terminase subunit. Nevertheless, our data rather suggest headful packaging of P282 DNA than packaging of molecules with cohesive ends. Hence, the genus “77likevirus” may be comprised of both cos- and pac-site phages.
As with the terminase, structural proteins (major capsid protein, tail protein) of P282, P630 and P1105 are highly homologous to each other and to structural proteins of phage 77, while the corresponding proteins of group 1 (e.g. phiPVL108) and group 2 (e.g. phiSLT) PVL phages significantly diverge. Thus, DNA packaging and virus assembly obviously occur in a similar way in P282, P630 and P1105. It is recalled that these phages possess different virulence and integrase genes. On the other hand, P240, which contains PVL genes like P1105 and belongs to the same int group is only distantly related to the other phages.
Compared to the left arm, the right arm of the phage genomes is much more diverse. It mainly contains genes coding for lysis proteins, virulence factors, the integrase, repressors and replication proteins (Fig. 2A). This DNA region is apparently prone to rearrangements leading to new compositions of genes. El Haddad and Moineau31 studied a deletion mutant of PVL phage LH1 and identified a heptanucleotide direct repeat (5′-TTTTACA-3′) and a palindrome (5′-ATTTAGTACNNNGTACTAAAT-3′) that possibly caused the deletion of pvl and int genes. The palindrome is also present in other staphylococcal siphophages where it is situated adjacent to int and might have an important regulatory function32. We analysed the P630 and P1105 genome in detail since these two phages possess uncommon combinations of genes, namely pvl/sea (P1105) and sea/int 6 (P630). Altogether, 14 copies of the LH1 direct repeat were identified on the genomes of these phages. In P630 one direct repeat overlaps the start codon of the group 6 int gene. Moreover, the palindromic sequence mentioned above was found 60 bp upstream of the direct repeat. Thus, sea phage P630 may have acquired the int 6 gene by recombination with another phage.
Figure 2.
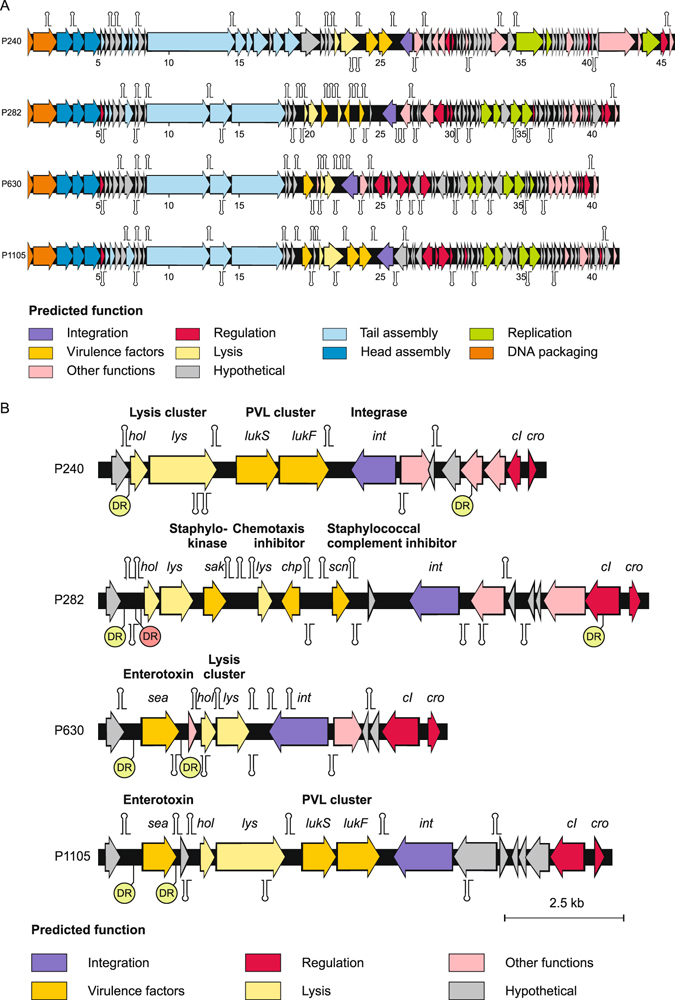
Genetic maps of P240, P282, P630 and P1105. (A) Whole genome comparison. Putative genes are coloured according to the predicted functions of their products. The position of putative Rho-independent transcription terminators are indicated. (B) Arrangement of virulence genes and genes for cell lysis, the integrase and repressors proteins. The positions of perfect (green) and imperfect (red) direct repeats are indicated.
In P630 and P1105, the sea enterotoxin A gene is located to the left of the holin gene (Fig. 2B). In both phages, sea is flanked by a direct repeat (5′-CTTTTTATTTTG-3′). This sequence occurs in many phages where it is similarly located upstream of the holin gene and may play a role in recombination events. The comparison of P1105 with ΦSa3 phage phiNM3 and group 2 PVL phages (LH1, P240) showed that the left arm of the P1105 genome up to position 20,775 is closely related to phiNM3 while upstream sequences share significant homology with the PVL phages (Fig. S2). The analysis of the transition point revealed the sequence 5′-CTTTTTATTTTG-3′ in all four genomes. Moreover, at this position the consensus sequence is expanded by further identical nucleotides creating an inverted repeat, which may form a stem-loop structure (Fig. 3). The same sequence was found in other phages (e.g. 77, phi108PVL, phi7247PVL) where it links sequences that are homologous respectively non-homologous to P1105. We also analysed the ends of a homologous DNA stretch in P630 and phi7247PVL and found the consensus sequence to be located there. Van der Mee-Marquet et al.18 reported on the recombination of the ΦSa3 prophage StauST398-4pro with a defective ΦMR11 related helper prophage (StauST398-5pro) resulting in a phage (StauST398-1) that had lost part of the IEC cluster. Our analyses showed that both prophages, which share only little overall DNA homology, contain the extended consensus sequence (the first nucleotide C is missing in the helper prophage) upstream of the holin gene, close to the recombination site. These all are clear signs that the identified sequences are involved in both the aquisitition of new genes and the recombination of whole phage genomes.
Figure 3.
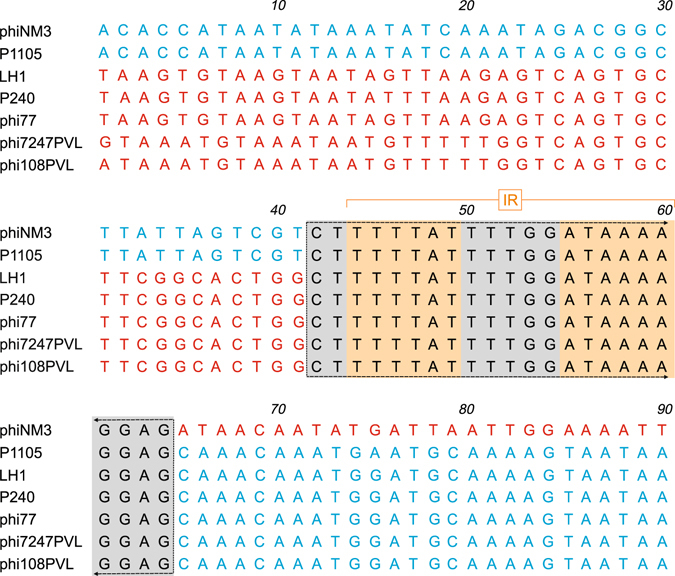
The transition point between homologous and non-homologous DNA segments of P1105 and other phages reveals striking consistency. The inverted repeat present in all phage genomes is shown in orange and grey. It separates sequences, which are identical in P1105 and phiNM3 from sequences that are identical in P1105 and the other phages. Homologous sequences are depicted in blue.
A large number of LA-MRSA CC398 strains exhibit sensitivity to the virulence gene-containing phages
In this study we first determined the range of MRSA CC398 strains which is susceptible to the four phages. Seventy-two MRSA CC398 strains representing 44 spa types mainly isolated from different stages of the swine, cattle and poultry food chain were tested (Supplementary Material, Table S1). Lytic activity was observed with all phages (Table 2). Phage P282 lysed 44% of the strains. The other phages infected a lower number of strains. Some strains were lysed by all phages. We did not detect any specificity for certain spa types since eighteen spa types were infected by at least one phage. In the next step the potential of the phages to lysogenize LA-MRSA CC398 strains was investigated. Susceptible strains were infected with the phages and subsequently analysed with respect to their prophage content. All phages were able to lysogenize LA-MRSA CC398. Prophages were detected in the lysogens by PCR using primers targeting the respective int and virulence genes. Moreover, upon mitomycin C treatment, the virulence gene-containing phages were released from the lysogenized MRSA CC398 strains proved by plaque assays and electron microscopy. As two of the indicator strains (10S01355 and 13-ST00030) do not possess an inherent prophage, only the phages P240, P282 or P630 (Fig. 1) were visible in lysates of the lysogenized derivatives. By contrast, indicator strain 10S00170 possesses an own int group 6 prophage. All particles released from this strain exhibited an elongated head while lysates of its derivative lysogenized by P1105 showed two different phage particles, one with an elongated and one with an isometric head (data not shown).
Table 2.
Lytic activity of the phages on livestock-associated CC398 strains.
| P1105 | P240 | P630 | P282 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origin of the strains | ||||
| cattle (dust sample, n = 1) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| cattle (nasal swab, n = 10) | 3 | 5 | 1 | 8 |
| cattle (carcass, n = 8) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| chicken (dust sample, n = 1) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| chicken (skin swab, n = 1) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| chicken (meat, n = 2) | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| swine (dust sample, n = 5) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| swine (boot swab, n = 1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| swine (nasal swab, n = 16) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| swine (meat, n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| swine (organs, n = 1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| turkey (dust sample, n = 7) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| turkey (skin swab, n = 7) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| turkey (tracheal swab, n = 1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| turkey (meat, n = 5) | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| minced meat (n = 2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| rabbit (organs, n = 1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| spa types | ||||
| t011 (n = 5) | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| t034 (n = 10) | 1 | 0 | 3 | 6 |
| t108 (n = 2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| t899 (n = 1) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| t1456 (n = 1) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| t2346 (n = 14) | 4 | 7 | 1 | 10 |
| Others (n = 39*) | 2 | 6 | 6 | 11 |
| Total numbers (n = 72) | 7 | 17 | 10 | 31 |
The numbers of sensitive strains and the numbers of tested strains (in parentheses) are given. *Detailed information on suceptible spa types is given in Supplemental Material Table S1.
ΦSa3 phage P282 integrates at numerous sites of the CC398 chromosome
ß-hemolysin converting phages are widespread in S. aureus but have only rarely been found in LA-MRSA CC398 strains, the reason for this finding has not been elucidated yet. We therefore studied the lysogenic properties of P282 in more detail. As lysogenization might be hampered by the presence of endogenous phages, we first determined the prophage content of 32 MRSA CC398 strains that were susceptible to P282 lytic infection. The multiplex PCR analysis targeting the int genes of the phages revealed that 21 strains contained one or more prophages (Table 3). Most common were the int groups 2 and 6, but groups 1, 7 and 9 were also identified. One t899 strain (09S02250) contained a ΦSa3 prophage and this was the only LA-MRSA CC398 strain which harbored phage-associated virulence genes (chp, sak). Integration of ΦSa3 phages may also be impeded by a mutated or missing integration site. For that reason, part of the ß-hemolysin gene of the MRSA CC398 strains was amplified by PCR and sequenced. Compared to the published attB site for ΦSa3 phages (5′-TGTATCCAAACTGG-3′33), all strains revealed two nucleotide exchanges (5′-TGTATCCGAATTGG-3′). To determine whether the endogenous prophages or the nucleotide variations within attB may affect lysogenization, all strains were infected with P282 and subsequently analysed. Fourteen out of 32 LA-MRSA CC398 strains (44%) were lysogenized by P282 (Table 3). There was no correlation detectable between lysogenization and the presence of inherent prophages. We then determined the integrity of the lysogens’ ß-hemolysin gene by PCR using primers flanking the attB site (see Methods). Between one and five lysogenic colonies of each strain were examined. All colonies of nine strains exhibited an uninterrupted ß-hemolysin gene (Table 3). By contrast, in none of four lysogenic colonies of another strain, a PCR product was detected. Finally, three strains showed only a very weak PCR product. The data indicate that phage P282 may integrate within or outside the ß-hemolysin gene. To determine the alternative P282 integration sites in the S. aureus chromosome, DNAs of twelve lysogenic colonies isolated from seven strains were subjected to an outward PCR using several restriction endonucleases (EcoRI, HindIII and XbaI) and primers deduced from the phage integrase gene, followed by sequencing of the amplicons. Altogether, nine alternative integration sites were identified in the strains, which were verified by a control PCR using an int primer and a primer deduced from the respective staphylococcal sequence. All phage integrations occurred within genes, most of them encoding metabolic enzymes (Table 4). Four strains revealed two integration sites, while only one site each was detected in the remaining three strains. The sites exhibited identity or strong similarities (maximal two nucleotide exchanges) to the reported attB site for ΦSa3 phages. Thus several attB related sites exist in LA-MRSA CC398 strains. This was confirmed by analysis of published CC398 whole genome sequences (NC_017333.1, NC_01808.1, NC_017673.1), in which up to three related sites were detected in each strain. At these sites, however, prophages were not identified.
Table 3.
Lysogenization of livestock-associated CC398 strains by P282.
| Strain | spa type | Origin | Endogenous prophages (int group) | Number of P282 lysogenic colonies | Integrase groups of lysogens | hlb intact in P282 lysogenic derivate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 07S00067 | t5675 | swine (nasal swab) | − | − | − | n.d. |
| 07S00107 | t2346 | swine (nasal swab) | Sa2 | 2 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 08S00699 | t2997 | swine (dust sample) | Sa1, (Sa5), Sa6 | − | − | n.d. |
| 09S00826 | t5524 | chicken (meat) | Sa2 | − | − | n.d. |
| 09S01005 | t2346 | cattle (nasal swab) | − | − | − | n.d. |
| 09S01007 | t2346 | cattle (nasal swab) | − | − | − | n.d. |
| 09S01009 | t2346 | cattle (nasal swab) | − | − | − | n.d. |
| 09S01382 | t034 | turkey (meat) | Sa2 | − | − | n.d. |
| 09S01404 | t5902 | turkey (meat) | Sa6 | − | − | n.d. |
| 09S02250 | t899 | turkey (skin swab) | Sa3 | − | − | n.d. |
| 09S02482 | t6574 | turkey (meat) | Sa2 | 3 | Sa2, Sa3 | + |
| 10S00170 | t034 | turkey (meat) | Sa6, Sa7 | 5 | Sa6, Sa3 | + |
| 10S01355 | t034 | swine (nasal swab) | − | 2 | Sa3 | + |
| 11S00742 | t4677 | swine (nasal swab) | Sa6, (Sa7) | − | − | n.d. |
| 11S01169 | t2346 | cattle (nasal swab) | − | − | − | n.d. |
| 11S01203 | t1580 | chicken (skin swab) | Sa2, Sa6 | 5 | Sa2, Sa6, Sa3 | + |
| 11S01539 | t1255 | swine (dust sample) | − | 1 | Sa3 | + |
| 12S00070 | t2582 | chicken (skin swab) | Sa6 | 1 | Sa6, Sa3 | + |
| 12S00148 | t2123 | cattle (dust sample) | Sa1, Sa2 | 1 | Sa1, Sa2, Sa3 | (+) |
| 12S00502 | t2576 | turkey (dust sample) | Sa2 | − | − | n.d. |
| 12S00563 | t2346 | cattle (nasal swab) | − | − | − | n.d. |
| 12S01090 | t2346 | cattle (nasal swab) | − | − | − | n.d. |
| 12S01091 | t2346 | cattle (nasal swab) | − | − | − | n.d. |
| 13-ST00013 | t034 | minced meat | Sa6 | 4 | Sa6, Sa3 | − |
| 13-ST00015 | t034 | turkey (dust sample) | Sa1, Sa6 | 2 | Sa1, Sa6, Sa3 | + |
| 13-ST00024 | t011 | cattle (nasal swab) | Sa2 | − | − | n.d. |
| 13-ST00029 | t034 | cattle (nasal swab) | Sa6 | 2 | Sa6, Sa3 | + |
| 13-ST00030 | t2346 | cattle (nasal swab) | − | − | − | n.d. |
| 13-ST00043 | t034 | swine (nasal swab) | Sa1, Sa6 | − | − | n.d. |
| 13-ST00054 | t011 | turkey (dust sample) | Sa1, Sa2 | 1 | Sa1, Sa2, Sa3 | (+) |
| 13-ST00090 | t034 | turkey (skin swab) | Sa2, Sa6, Sa9 | 5 | Sa2, Sa6, Sa9, Sa3 | + |
| 13-ST00207 | t1456 | cattle (nasal swab) | Sa2 | 3 | Sa2, Sa3 | (+)/− |
On the left side all strains lysed by the phage are listed. Int groups of prophages residing in the strains are stated. The right side shows numbers of isolated colonies containing P282, their prophage content (int groups) and data on the integration of the phage within hlb. (+), weak PCR product; n.d., not determined.
Table 4.
Alternative integration sites of phage P282 in livestock-associated CC398 strains.
| Lysogenic isolate | S. aureus strain | Attachment site attB* | Integration site (gene) | Reference genome | Accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sa-L35 | 10-355 | TGTATCCAAACTGG | General stress protein (AUC50_04635) | RIVM3897 | CP013621 |
| Sa-L36 | 10-355 | TGTATCCAAACTGG | Integrase | Sa54 | KT253891 |
| Sa-L48 | 10-170 | TGTATCCTTACTGT | Nucleoside permease (AUC50_03495) | RIVM3897 | CP013621 |
| Sa-L49 | 10-170 | TGTATCCAATCTGG | General stress protein (AUC50_04635) | RIVM3897 | CP013621 |
| Sa-L54 | 12-070 | TGTATCCAAACTGG | Cytochrome D ubiquinol oxidase subunit I (AUC50_05470) | RIVM3897 | CP013621 |
| Sa-L56 | 13-090 | TGTATCCAAACTGA | Hypothetical protein (AUC50_10740) | RIVM3897 | CP013621 |
| Sa-L57 | 13-090 | TGTATCCAAACTGA | GMP synthetase (AUC50_02200) | RIVM3897 | CP013621 |
| Sa-L67 | 13-015 | TGTATCCAAACTGG | Hypothetical protein (SAMI_1999) | S. aureus | AP017320 |
| Sa-L68 | 13-015 | TGTATCCAAGCTGG | Gamma-aminobutyrate permease (AUC50_08995) | RIVM3897 | CP013621 |
| Sa-L66 | 13-029 | TGTATCCAAACTGG | Gamma-aminobutyrate permease (AUC50_08995) | RIVM3897 | CP013621 |
| Sa-L65 | 13-029 | TGTATCCAAACTGG | Gamma-aminobutyrate permease (AUC50_08995) | RIVM3897 | CP013621 |
| Sa-L46 | 11-1203 | TGTATCCATACTGG | Alanine racemase (A7327_11665) | 08–02300 | CP015646 |
| attB within hlb P282 attP | TGTATCCGAATTGG TGTATCCGAATTGG |
*Nucleotides diverging from the published attB integration site for ΦSa3 phages (Coleman et al.33) are indicated.
The prophages are stably inherited in MRSA CC398 and their virulence genes are expressed
Previous experiments demonstrated that LA-MRSA CC398 strains can be lysed and lysogenized by virulence gene-containing phages. As prophages might be easily lost, we determined their stability in vitro. The lysogenized MRSA CC398 isolates were cultivated in 5 ml LB broth over a period of 15 days by daily inoculation (5 µl) of fresh medium. Every five days, 50 µl aliquots of the cultures were taken and analysed by PCR for the presence of the virulence genes of the prophages. Until the end of the experiment the prophages were detected in all cultures. This does of course not mean that the respective virulence genes are expressed in the MRSA CC398 lysogens. We therefore studied the production of the enterotoxin A, PVL toxin and staphylokinase in the natural hosts of the phages, in LA-MRSA CC398 indicator strains and in the lysogenic derivatives of these strains using a qualitative multiplex antibody microarray34. As shown in Table 5 the respective virulence factors were not synthesized in the phage indicator strains, but in both the natural hosts of the phages and in the lysogenized MRSA CC398 derivatives. The detection limits for PVL, SEA and SAK using this assay are 0.5 ng/ml, 0.01 ng/ml and 0.05 ng/ml, respectively34. Therefore, the proteins of the investigated strains were produced at least in these quantities. This clearly demonstrates that lysogenization of LA-MRSA CC398 by those phages is accompanied by the production of new virulence factors.
Table 5.
Virulence factors produced in the original phage host strains, CC398 strains and their lysogenized derivatives.
| Strain | PVL1 | SEA | SAK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11S00282 | donor | − | − | + |
| 10S01355 | recipient | − | − | − |
| 1355[P282] | lysogenized | − | − | + |
| 11S01105 | donor | + | + | − |
| 10S00170 | recipient | − | − | − |
| 170[P1105] | lysogenized | + | + | − |
| 13-ST00240 | donor | + | − | + |
| 13-ST00030 | recipient | − | − | − |
| 30[P240] | lysogenized | + | − | − |
| 10S00630 | donor | n.d. | +2 | n.d. |
| 10S01355 | recipient | − | − | − |
| 1355[P630] | lysogenized | n.d. | +2 | n.d. |
1lukF-PV/lukS-PV.
2Enterotoxin production of these strains was tested with the VIDAS SET 2 kit (bioMérieux, Nürtingen, Germany).
Discussion
Temperate phages play an important role in the virulence of S. aureus and in the emergence of new pathotypes. While prophages containing virulence genes are present in many MRSA strains, they have only rarely been detected in the clonal complex CC398 associated with livestock. The underlying reasons for this finding remain largely unclear. For a ß-hemolysin-converting ΦSa3 phage it has been reported that the phage was not stable in a LA-MRSA CC398 strain18. In addition, the ΦSa3 prophage was defective and required a helper phage for infection. McCarthy et al.35 investigated horizontal gene transfer of phages and plasmids in pigs and did not find any lysogenization of a LA-MRSA CC398 strain by a ΦSa3 phage residing in a human-specific isolate. These data raise the question whether LA-MRSA CC398 strains are suitable hosts for virulence gene-containing phages. To answer this question, we studied infection of LA-MRSA CC398 strains by four temperate phages possessing different combinations of virulence genes. Two phages (P240 and P1105) recovered from human isolates carry genes for the PVL toxin. P1105 additionally contains a sea gene for the enterotoxin A. The occurrence of pvl and sea on the same phage genome is rather uncommon and this combination of virulence genes has to date only been identified in phages isolated in the Far East and in Italy25, 26. Notably, all yet described phages harboring pvl and sea were isolated from ST772 MRSA strains. In contrast, the natural host of PVL phage P240 is a human MRSA CC398 isolate. Both P240 and P1105 are members of int group 2 but the phages exhibit only partial homologies. On the other hand, P1105 is closely related to the phages P282 and P630 carrying the genes chp, sak, scn and sea, respectively. While IEC genes are widespread in ΦSa3 phages like P282 that occasionally exist in LA-MRSA CC398 strains, sea is usually not found in int group 6 to which P630 belongs11. The content of virulence genes and the relationship of the isolated phages indicate that gene exchange between S. aureus phages also occurs across borders of integrase groups. This particularly applies to the DNA region harboring genes for cell lysis, virulence factors and phage integration but probably also to further-upstream sequences. Here, numerous repetitive DNA sequences are located, which are probably implicated in genomic rearrangements. Indeed, recombination between an int 2 and an int 6 phage has already been detected in pigs35.
Plaque assays with the virulence gene-carrying phages clearly showed that a significant number of LA-MRSA CC398 strains are susceptible to these phages. Interestingly, also lysogenic strains containing prophages belonging to the int groups 2 and 6 were lysed by P240 and P630, respectively. This shows that LA-MRSA CC398 strains do not lack phage receptors or possess defence systems that could prevent infection. Moreover, endogenous prophages, at least those of the int groups 2 and 6 obviously do not confer immunity against phages of the same int group indicating that the affiliation to a certain int group does not coincide with the specificity of the respective prophage repressor. Thus, also phages belonging to the same int group can encounter and recombine in S. aureus which may result in new combinations of virulence genes.
All isolated phages were able to lysogenize LA-MRSA CC398 and we did not find any indication for an instability of the prophages. Moreover, no helper phage was needed for lysogenization. However, our experiments were performed in vitro and the situation might be different in livestock. It might e.g. be possible that in animals an intact ß-hemolysin gene is required for efficient colonization. Studies with equine and porcine erythrocytes did not support this assumption36. Compared to the published 14 bp attB attachment site for ΦSa3 phages37, all analysed LA-MRSA CC398 strains exhibited two nucleotide exchanges in hlb but this alteration did not prevent lysogenization, since integration of P282 within this gene was observed. Furthermore, some LA-MRSA CC398 strains used in our study contain additional integration sites for this phage that are very similar or even identical to the published sequence. Hence, lysogenization by a ΦSa3 phage is not necessarily accompanied by the loss of ß-hemolysin activity. Atypical integration sites for ΦSa3 phages have yet only been reported for disease-related S. aureus isolates38. They differ from the integration sites that we identified in LA-MRSA CC398 strains.
The other phages of this study are members of the int groups 2 and 6. Prophages belonging to these groups are frequently present in LA-MRSA CC398 strains19. As shown above they do not protect the host against lytic infection by phages of the same group but they might alleviate the potential of new phages to lysogenize the bacteria because the integration site on the chromosome is already occupied. This fact may explain the rare occurrence of PVL phages belonging to int group 2 in LA-MRSA CC398 strains. On the other hand, integration of an int group 2 phage at a novel site has recently been reported for a human-specific MRSA CC398 isolate35, but corresponding data on livestock-associated strains are lacking. It is still obscure, why virulence gene-containing phages are not common in LA-MRSA CC398. Our results suggest that the natural conditions for lysogenization are fulfilled. Moreover, positive lysogenic conversion of the lysogenized strains was observed. Whether the newly acquired virulence factors are beneficial for MRSA CC398 strains in animals has still to be elucidated. In this study many different CC398 spa types were lysed by the phages, most of them are only infrequently found in livestock. By contrast, only some of the predominant t011 and t034 strains were infected. This might be a reason for the rare occurrence of phage encoded virulence factors in livestock. However, it would be naïve to believe that temperate phages do not have the potential to enhance the virulence of those strains. It is probably only a matter of time before livestock-associated strains with new virulence properties may emerge. Indeed, a new subpopulation of CC398 strains isolated from infected animals has recently been described39. The strains contained various virulence genes detected by high-density DNA microarray experiments. It is yet not known whether the virulence factors are encoded by prophages, which obtained the respective genes by recombination. It is also not clear what else differentiates these isolates from strains colonizing asymptomatic pigs. Nonetheless, the finding suggests that virulence genes may be spread by phages in CC398 populations resulting in new and possibly more virulent pathotypes posing an inceased risk to human health.
Methods
Staphylococcus aureus strains
All strains used in this study were selected from the strain collection of the National Reference Laboratory for Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci incl. Staphylococcus aureus at the Federal Institute for Risk Assessment. The strains 11S01105 (original no. 040-07765) and 13-ST00240 (original no. 11-02211) were provided by Robin Köck (University Hospital Münster, Institute of Medical Microbiology, Münster, Germany) and Wolfgang Witte (Robert Koch Institute, Wernigerode, Germany), respectively. MRSA CC398 strains used for the host range determination of the phages are listed in Supplementary Material Table S1. Bacteria were cultivated in lysogeny broth (LB) at 37 °C according to standard procedures (Sambrook and Russel, 2001).
Microarrays
DNA microarrays were performed using the StaphyType kit (Alere Technologies GmbH, Jena, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. It covers 333 target sequences including species specific controls, relevant virulence- and resistance genes as well as SCCmec-, agr group- and capsule typing markers.
Antibody microarrays for the detection of enterotoxin A, staphylokinase and PVL were performed by Alere Technologies GmbH (Jena, Germany) as described by Stieber et al.34.
Isolation, propagation and purification of the phages
Phages were released from S. aureus strains by mitomycin C induction (2.5 µg/ml). Lysates were centrifuged at 8,000 × g for 15 min and the supernatants were passed through 0.45 µm and 0.2 µm membrane filters (VWR International GmbH, Darmstadt). Lytic activity of the phages was tested by spotting 1:10 dilution series of each lysate onto a lawn of MRSA CC398 indicator strains. Phages were isolated by twofold recovery of single plaques. High titres of phages were achieved by harvesting overlay agar with confluent lysis. The agar was resuspended in SM buffer (100 mM NaCl, 8 mM MgSO4 7H2O, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7, 5) and stirred for several hours at room temperature. Thereafter, agar and cell debris were removed by centrifugation and filtration as described above. Phages were concentrated by ultracentrifugation and purified using CsCl step gradients (1,35–1,65 g/cm2). To determine phage titers, the softagar overlay method was applied40.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Phages were applied to pioloform-carbon-coated, 400-mesh copper grids (Plano GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany), for 7 min. Thereafter, grids were fixed with 2.5% aqueous glutaraldehyde solution (w/v) for 1 min, stained with 2% aqueous uranyl acetate solution (w/v) for 1 min and examined by transmission electron microscopy using a JEM-1010 (JOEL, Japan) at 80 kV accelerated voltage.
Determination of the phage host range
Lytic activity assays were used to determine the host range of the phages. 5 ml of prewarmed LB softagar (0.6%) were mixed with 100 µl of the indicator strain and poured onto a LB agar plate. Following this 10 µl aliquots of 1:10 serial dilutions of each lysate were spotted onto the overlay agar and the plates were incubated overnight at 37 °C. Phage activity was tested on 72 MRSA CC398 strains (Supplementary Table S1).
Lysogenisation experiments
Isolation of lysogenized MRSA CC398 strains was achieved by removing some softagar from a lysis zone on agar plates (see above). The material was suspended in 500 µl SM buffer and 50–100 µl were plated on LB agar plates and incubated overnight at 37 °C. Colonies were picked and investigated by PCR for the presence of phage encoded virulence genes.
PCR analyses
Bacterial DNA was extracted by thermal lysis. A 1 µl loop of culture material was suspended in 45 µl TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA) and 5 µl lysostaphin (0.1 mg/µl). After incubation for 45 min at 37 °C, the sample was heated at 95 °C for 10 min and cooled by adding 200 µl TE buffer.
For the detection of virulence genes, the following primers were used: (sak-F, 5′-GTAAGTGCATCAAGTTCATTCG-3′; sak-R, 5′-GCTCTGATAAATCTGGGACAAC-3′; scn-F, 5′-AATGGCTCTTCTTCGCTTTC-3′; scn-R, 5′-TGCTACTTTATTCCTTACGGC-3′; chp-F, 5′-GTTTTTTAACGGCAGGAATCAG-3′; chp-R, 5′-TTTCTATCTTCAGCAAGTGGTG-3′), (hlb1B, 5′-GTTGCAACACTTGCATTAGCA-3′; hlb2, 5′-TGTGTACCGATAACGTGAAC-3′); (pvl-F, 5′-TTGAAATGTTGTACTTAGAACC-3′; pvl-R, 5′-TAGGTAAAATGTCTGGACATG-3′). Primers used for the detection of the enterotoxin A gene sea and phage integrase genes have previously been described by Johnson et al.41, Goerke et al.11 and Kahankova et al.42. PCR was performed using 2x MyTaq HS Mix (Bioline, Luckenwalde, Germany) with a final volume of 25 µl containing 10 µl MyTaq HS Mix, 1 µM of forward and reverse primer, 1 µl DNA (10 ng) and dH2O.
For the determination of the attB site of ΦSa3 phage P282 within hlb, PCR products of the β-hemolysin gene were purified using the Invisorb Spin DNA Extraction Kit (Stratec Molecular, Berlin, Germany) and sequenced (Eurofins Genomics, Ebersberg, Germany).
Determination of alternative phage P282 integration sites
For the determination of the chromosomal integration sites (attB) of P282, genomic DNA (gDNA) of various lysogens was isolated using the DNA mini preparation kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). DNAs were digested with the restriction endonucleases Eco32I, HindIII, and XbaI according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (Thermo, St. Leon Roth, Germany). Following digestion, restriction fragments were treated with T4 ligase (Thermo) and used as template for PCR. Outward primers deduced from the 5′- and 3′-coding region of the P282 int gene were used under the following conditions: Initial PCR activation and template denaturation at 96 °C for 120 s followed by 35 cycles including denaturation phase at 96 °C for 15 s, annealing at 55 °C for 5 min and elongation for 210 s at 72 °C. In addition, a final elongation step at 72 °C for 1 min was included, before the amplicons were purified (QIAquick PCR purification kit, Qiagen) and sequenced according to Sanger (Eurofins Genomics,). The obtained nucleotide sequences of the amplicons were compared with whole genome sequences of S. aureus strains of the GenBank database (National Center for Biotechnology Information).
Extraction of phage DNA, sequencing and bioinformatics analyses
Phage DNA was extracted by incubating CsCl-purified phage particles (400 μl) in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 1 mM EDTA, 0.5% SDS supplemented with 2 μl Proteinase K (20 mg/ml) at 56 °C for 2 h, followed by ethanol precipitation40.
Sequencing of the phages P282 and P630 was performed using the PacBio RS system by GATC Biotech (Konstanz, Germany). De novo genome assemblies of raw reads (P282: 37,713; P630: 39,145) of one SMRT cell (run modus: 1 × 180 min movie) were obtained by SMRT analysis (version 2.3.0) software (Pacific Biosciences, USA) resulting in a sequence coverage of >100-fold per consensus base for both phage genomes. HGAP3-assembling resulted in a single sequence contig of 41,960 bp and 40,448 bp for phage P282 and P630, respectively.
To determine the P240 and P1105 genomic sequences, EcoRI and HindIII restriction fragments of the phages were inserted into the linearized vector pIV243. Escherichia coli strain GeneHogs (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, USA) was electroporated with aliquots of the respective ligation mixtures. Transformants were selected on LB agar supplemented with neomycin (100 µg/ml), X-Gal and IPTG40. Following isolation of recombinant plasmids (Plasmid Mini Two Kit, Stratec, Berlin, Germany) inserts were sequenced (Eurofins Genomics) using vector primers43. Based on the strong homologies to known phages, the whole genomic sequences of P240 and P1105 were determined by PCR and direct sequencing of phage DNA using primers deduced from the phages SMSAP5 (NC_019513.1) and PhiIND772PVL25.
Sequence analysis and alignments were carried out using Accelrys Gene (version 2.5, Accelrys Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). ORF analyses were carried out using MyRAST44. Similarity and identity values were determined at the NCBI homepage using different BLAST algorithms30. Transcription terminators were identified using Arnold45.
Nucleotide sequence accession number
The complete nucleotide sequence of the phage genomes were submitted to GenBank under the accession numbers KT809368 (P282), KT809369 (P630), KT878766 (P1105) and KY056620 (P240)P240.
Originality-Significance Statement
In this work the potential of temperate phages to increase the virulence of livestock-associated MRSA CC398 strains has been elucidated. We demonstrate that many CC398 strains can be lysogenized by virulence gene containing phages, that lysogeny is stable and that the respective virulence factors are synthesized. In addition, we show that integration of a ΦSa3 phage may occur at numerous sites on the CC398 chromosome.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
This work has been partly carried out within the framework of the project “MedVet-Staph” funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Science (BMBF), research grant: 01KI1014C. Further support was given by the Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (Internal BfR grants 44-001 and 1322-652). The authors would like to thank Robin Köck and Wolfgang Witte for providing S. aureus strains.
Author Contributions
B.K., J.A.H. and S.H. designed the study. M.K., M.L.H., N.S., M.D.T., C.J., B.K. and A.F. were responsible for extensive microbiological and molecular analyses. J.A.H., C.J. and S.H. performed bioinformatic analyses. Electron microscopy was executed by J.R., B.K., J.A.H. and S.H. drafted the manuscript and all authors approved its final version.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at doi:10.1038/s41598-017-02175-4
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Mediavilla JR, Chen L, Mathema B, Kreiswirth BN. Global epidemiology of community-associated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012;15:588–595. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2012.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wendlandt S, Schwarz S, Silley P. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a food-borne pathogen? Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2013;4:117–139. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-030212-182653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Butaye P, Argudín MA, Smith TC. Livestock-associated MRSA and its current evolution. Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 2016;3:19–31. doi: 10.1007/s40588-016-0031-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stegger M, et al. Rapid differentiation between livestock-associated and livestock-independent Staphylococcus aureus CC398 clades. PloS one. 2013;8:e79645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Becker K, Ballhausen B, Kahl BC, Köck R. The clinical impact of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus of the clonal complex 398 for humans. Vet Microbiol. 2015;200:33–38. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Argudin MA, et al. Genotyping and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from diseased turkeys. Avian Pathol. 2013;42:572–580. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2013.854308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Silva NC, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus of lineage ST398 as cause of mastitis in cows. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2014;59:665–669. doi: 10.1111/lam.12329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Spohr M, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in three dairy herds in southwest Germany. Zoonoses Public Health. 2011;58:252–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1863-2378.2010.01344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Argudin MA, et al. Virulence and resistance determinants of German Staphylococcus aureus ST398 isolates from nonhuman sources. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77:3052–3060. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02260-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Alibayov B, Baba-Moussa L, Sina H, Zdenkova K, Demnerova K. Staphylococcus aureus mobile genetic elements. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41:5005–5018. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3367-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Goerke C, et al. Diversity of prophages in dominant Staphylococcus aureus clonal lineages. J Bacteriol. 2009;191:3462–3468. doi: 10.1128/JB.01804-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.van Wamel WJ, Rooijakkers SH, Ruyken M, van Kessel KP, van Strijp JA. The innate immune modulators staphylococcal complement inhibitor and chemotaxis inhibitory protein of Staphylococcus aureus are located on beta-hemolysin-converting bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:1310–1315. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.4.1310-1315.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Balaban N, Rasooly A. Staphylococcal enterotoxins. Int J Food Microbiol. 2000;61:1–10. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1605(00)00377-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.European Food Safety Authority The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2014. EFSA Journal. 2015;13:4329. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kraushaar B, Fetsch A. First description of PVL-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in wild boar meat. Int J Food Microbiol. 2014;186:68–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Koyama H, et al. A fatal infection caused by sequence type 398 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying the Panton-Valentine leukocidin gene: A case report in Japan. J Infect Chemother. 2015;21:541–543. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2015.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Watkins RR, David MZ, Salata RA. Current concepts on the virulence mechanisms of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 2012;61:1179–1193. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.043513-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Van der Mee-Marquet N, et al. Analysis of prophages harbored by the human-adapted subpopulation of Staphylococcus aureus CC398. Infection, genetics and evolution: journal of molecular epidemiology and evolutionary genetics in infectious diseases. 2013;18:299–308. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McCarthy AJ, et al. The Distribution of Mobile Genetic Elements (MGEs) in MRSA CC398 Is Associated with Both Host and Country. Genome Biol Evol. 2011;3:1164–1174. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evr092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Price LB, et al. Staphylococcus aureus CC398: host adaptation and emergence of methicillin resistance in livestock. mBio. 2012;3:e00305–e00311. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00305-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Narita S, et al. Phage conversion of Panton-Valentine leukocidin in Staphylococcus aureus: molecular analysis of a PVL-converting phage, phiSLT. Gene. 2001;268:195–206. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00390-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gutierrez D, et al. Three proposed new bacteriophage genera of staphylococcal phages: “3alikevirus”, “77likevirus” and “Phietalikevirus”. Archives of virology. 2014;159:389–398. doi: 10.1007/s00705-013-1833-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bae T, Baba T, Hiramatsu K, Schneewind O. Prophages of Staphylococcus aureus Newman and their contribution to virulence. Mol Microbiol. 2006;62:1035–1047. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang M, et al. Identification of the third type of PVL phage in ST59 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2011;323:20–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Prabhakara S, et al. Genome sequencing unveils a novel sea enterotoxin-carrying PVL phage in Staphylococcus aureus ST772 from India. PloS one. 2013;8:e60013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sanchini A, et al. Typing of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-encoding phages carried by methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Italy. Clinical microbiology and infection: the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 2014;20:O840–O846. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kwan T, Liu J, Dubow M, Gros P, Pelletier J. The complete genomes and proteomes of 27 Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:5174–5179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501140102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ma XX, Ito T, Chongtrakool P, Hiramatsu K. Predominance of clones carrying Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated in Japanese hospitals from 1979 to 1985. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:4515–4527. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00985-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Canchaya C, Proux C, Fournous G, Bruttin A, Brüssow H. Prophage genomics. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003;67:238–276. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.2.238-276.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Johnson M, et al. NCBI BLAST: a better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:W5–9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.El Haddad L, Moineau S. Characterization of a novel Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL)-encoding staphylococcal phage and its naturally PVL-lacking variant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013;79:2828–2832. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03852-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Iandolo JJ, et al. Comparative analysis of the genomes of the temperate bacteriophages phi 11, phi 12 and phi 13 of Staphylococcus aureus 8325. Gene. 2002;289:109–118. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(02)00481-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Coleman D, et al. Insertional inactivation of the Staphylococcus aureus beta-toxin by bacteriophage phi 13 occurs by site- and orientation-specific integration of the phi 13 genome. Mol Microbiol. 1991;5:933–939. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stieber B, Monecke S, Müller E, Büchler J, Ehricht R. Direct, specific and rapid detection of staphylococcal proteins and exotoxins using a multiplex antibody microarray. PloS one. 2015;10:e0143246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McCarthy AJ, et al. Extensive horizontal gene transfer during Staphylococcus aureus co-colonization in vivo. Genome Biol Evol. 2014;6:2697–2708. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jung P, et al. Impact of bacteriophage Saint3 carriage on the immune evasion capacity and hemolytic potential of Staphylococcus aureus CC398. Vet Microbiol. 2016;200:46–51. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Carroll JD, Cafferkey MT, Coleman DC. Serotype F double- and triple-converting phage insertionally inactivate the Staphylococcus aureus beta-toxin determinant by a common molecular mechanism. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993;106:147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Goerke C, Wirtz C, Fluckiger U, Wolz C. Extensive phage dynamics in Staphylococcus aureus contributes to adaptation to the human host during infection. Mol Microbiol. 2006;61:1673–1685. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Van der Mee-Marquet NL, et al. Emergence of a novel subpopulation of CC398 Staphylococcus aureus infecting animals is a serious hazard for humans. Front Microbiol. 2014;5:652. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sambrook, J. & Russel, D. W. (New York, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2001).
- 41.Johnson WM, et al. Detection of genes for enterotoxins, exfoliative toxins, and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 in Staphylococcus aureus by the polymerase chain-reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1991;29:426–430. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.426-430.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kahankova J, et al. Multilocus PCR typing strategy for differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus siphoviruses reflecting their modular genome structure. Environ Microbiol. 2010;12:2527–2538. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Strauch E, Voigt I, Broll H, Appel B. Use of a plasmid of a Yersinia enterocolitica biogroup 1A strain for the construction of cloning vectors. J Biotechnol. 2000;79:63–72. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1656(00)00216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Aziz RK, et al. The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Naville M, Ghuillot-Gaudeffroy A, Marchais A, Gautheret D. ARNold: a web tool for the prediction of Rho-independent transcription terminators. RNA Biol. 2011;8:11–13. doi: 10.4161/rna.8.1.13346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


