Abstract
We assessed the frequency and clinicopathologic significance of 19 genes currently identified as significantly mutated in myeloid neoplasms, RUNX1, ASXL1, TET2, CEBPA, IDH1, IDH2, DNMT3A, FLT3, NPM1, TP53, NRAS, EZH2, CBL, U2AF1, SF3B1, SRSF2, JAK2, CSF3R, and SETBP1, across 93 cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) using capture target enrichment and next-generation sequencing. Of these cases, 79% showed at least one nonsynonymous mutation, and cases of AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities showed a lower frequency of mutations versus AML with myelodysplasia-related changes (P<0.001). Mutational analysis further demonstrated that TP53 mutations are associated with complex karyotype AML, whereas ASXL1 and U2AF1 mutations are associated with AML with myelodysplasia-related changes. Furthermore, U2AF1 mutations were specifically associated with trilineage morphologic dysplasia. Univariate analysis demonstrated that U2AF1 and TP53 mutations are associated with absence of clinical remission, poor overall survival (OS), and poor disease-free survival (DFS; P<0.0001), whereas TET2 and ASXL1 mutations are associated with poor OS (P<0.03). In multivariate analysis, U2AF1 and TP53 mutations retained independent prognostic significance in OS and DFS, respectively. Our results demonstrate unique relationships between mutations in AML, clinicopathologic prognosis, subtype categorization, and morphologic dysplasia.
Myeloid neoplasms are a diverse group of diseases that include acute myeloid leukemia (AML), myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms (MDS/MPN).1 Among these neoplasms, AML is the most common.2-4 Currently, morphology, immunophenotype, cytogenetic studies, clinical history, and molecular analyses play integral roles in the subclassification of AML.5-7 Although particular structural rearrangements in chromosomes, such as t(15;17)(q24;q21); PML-RARA, are known to confer specific pathologic, prognostic, and therapeutic properties, the roles and significance of specific point and insertion/deletion (indel) mutations in most genes are less understood in AML.
However, in recent years, several large whole genome and exome studies have been published that detail the general mutational landscape seen in different myeloid diseases; interestingly, many mutations observed in AML are shared across other subtypes of myeloid neoplasms.8-21 For instance, mutations in TET2 and ASXL1 are found in all types of myeloid neoplasms, whereas RUNX1 mutations are seen predominantly in AML, MDS, and MDS/MPN, but are rarer in MPNs. Other gene mutations such as those seen in NPM1 and FLT3 appear relatively exclusive to AML. Given the partially overlapping spectrum of mutations present in these diverse diseases, we sought to determine the clinicopathologic associations of specific variant mutations in AML by using targeted next-generation sequencing.
We designed a panel of 19 genes that are commonly mutated in myeloid neoplasms and assessed their frequency in a well-defined cohort of AML patients and the relevance of these gene mutations in diagnosis and prognosis. Our results identify specific frequencies and patterns of mutations in AML, and novel associations of mutations in the genes TP53, U2AF1, ASXL1, and TET2 with AML subtype, morphology, and prognosis.
Materials and methods
Patient Cohort
A total of 93 AML patients, 4 pediatric, with diagnostic specimens available for genetic analysis were selected. Clinical, hemogram, flow cytometry, immunophenotypic, morphologic, cytogenetic, and prior molecular data were reviewed. Cases were diagnosed according to the 2008 World Health Organization criteria and all cases were re-reviewed by RSO and DAA. Data on clinical follow-up were obtained from electronic medical records. All patients were treated with standard therapies according to National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines with the majority undergoing induction with cytarabine and danorubicin or idarubicin, and consolidation with cytarabine; a subset of patients transitioned to stem cell transplantation, but were censored at the time of transplant.22 No patients on clinical trials were included. Cytogenetic risk stratification was performed using the Medical Research Council criteria,6,23 and this study was approved by Stanford University’s institutional review board.
Next-Generation Sequencing
Genomic DNA was isolated from frozen blood or bone marrow aspirate samples using DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and as previously described;24 in four cases, genomic DNA was isolated from Wright Giemsa-stained slides for repeat validation with similar results to frozen or fresh tissue. 125 ng of total genomic DNA was used and quantified using the Qubit DNA BR assay (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). A Haloplex (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) target enrichment panel of 45 selected exons in 19 genes (RUNX1, ASXL1, TET2, CEBPA, IDH1, IDH2, DNMT3A, FLT3, NPM1, TP53, NRAS, EZH2, CBL, U2AF1, SF3B1, SRSF2, JAK2, CSF3R, and SETBP1) was designed using SureDesign (Agilent Technologies) (Supplementary Data). Haloplex target enrichment DNA libraries were prepared according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Agilent Technologies). Samples were sequenced on a MiSeq sequencer using the MiSeq Reagent Kit v2 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
NGS Data Analysis
Sequence data alignment and variant calling were performed using Agilent’s SureCall V2.0.82 (Agilent Technologies) that incorporates BWA, BWA-MEM, SAMtools, and SNPPET (Agilent Technologies) for alignment, variant calling, and annotation (Supplementary Data). Human genome build 19 (hg19) was used as the reference. FLT3–ITD mutations were identified with a FLT3 PCR and capillary electrophoresis assay as previously described.25,26 All variants identified by NGS were confirmed by Sanger sequencing of individual mutations (Supplementary Data).
Sanger Sequencing of TP53
Genomic DNA was isolated from samples using Qiagen DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Sanger sequencing was performed on an ABI 3500 sequencer and sequences were analyzed using ABI Sequencing Analysis 5.1 software as previously described. Four primer sets were used: TP53-Set1-F 5′-AAGGCGCACTGGCCTCATCTT-3′ and TP53-Set1-R 5′-TGGAGTCTTCCAGTGTGATGATG-3′; TP53-Set2-F 5′-CATGAGCGCTGCTCAGATAG-3′ and TP53-Set2-5′-AGTTGCAAACCAGACCTCAG-3′; TP53-Set3-F 5′-TCTGTCTCCTTCCTCTTCCTAC-3′ and TP53-Set3-R 5′-CTGCTCACCATCGCTATCTG-3′; TP53-Set4-F 5′-CCTGATTTCCTTACTGCCTCTT-3′ and TP53-Set4-R 5′-TCTTGTCCTGCTTGCTTACC-3′.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SAS (SAS, Cary, NC, USA), STATA (Statcorp, College Station, TX, USA), Prism 6 (Graphpad, La Jolla, CA, USA), and/or XLSTAT (XLSTAT, Belmont, MA, USA). Fisher’s exact test, ANOVA, Student’s t-test, Kaplan–Meier methods, log-rank test, and univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard models were performed as previously described.26,27 Variables included in multivariate analysis were age, sex, % blasts, 2008 WHO AML subtype, multilineage dysplasia, cytogenetic risk group, and mutational status of genes in our 19-gene panel. Mutational data were modeled using Gene-E (Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA, USA).28
Results
Patient Cohort
A total of 93 patients were entered into this study. Median age was 55 years, with a range of 5–79 years, and the subjects included 45 males and 48 females (Table 1). Most cases consisted of AML with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MRC; 39% of patients) and AML-not otherwise specified (AML-NOS; 33%) with fewer AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities (AML-RGA; 18%) or therapy-related AMLs (AML-T; 10%).
Table 1.
Patient cohort
| Clinical data | Values |
|---|---|
| Median age, years (range) | 55 (5–79) |
| Male:female | 45:48 |
| Median bone marrow blasts, % (range) | 62 (5–98) |
| Median white blood cells, 109/l (range) | 10.35 (1.1–210) |
| Median hemoglobin, g/dl (range) | 8.8 (3.37–14.4) |
| Median platelets, 109/l (range) | 52 (2–422) |
| Median disease-free survival, days (range) | 121 (6–1298) |
| Median overall survival, days (range) | 221 (6–1298) |
| WHO classification | |
| AML with myelodysplasia-related changes | 36 |
| Prior history of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) | 12 |
| MDS-related cytogenetic abnormality | 14 |
| Multilineage dysplasia | 34 |
| AML, not otherwise specified | 31 |
| AML with minimal differentiation | 1 |
| AML without maturation | 10 |
| AML with maturation | 4 |
| Acute myelomonocytic leukemia | 2 |
| Acute monoblastic/monocytic leukemia | 12 |
| Acute erythroid leukemia | 2 |
| AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities | 17 |
| AML with t(8;21)(q22;q22);(RUNX1-RUNX1T1) | 5 |
| AML with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22);(CBFB-MYH11) | 4 |
| AML with t(15;17)(q24;q21);(PML-RARA) | 7 |
| AML with inv(3)(q21q26.2); (RPN-EVI1) | 1 |
| Provisional entity: AML with mutated NPM1a | 11 |
| Provisional entity: AML with mutated CEBPAa | 5 |
| AML, therapy related | 9 |
| Cytogenetic risk groups, no. | |
| Favorable | 18 |
| Intermediate | 54 |
| Unfavorable | 21 |
| FLT3 mutation status | |
| FLT3 ITD | 14 |
| FLT3 D835 | 3 |
The provisional entities were classified in other relevant categories.
AML-RGA Shows Fewer Missense Mutations than Other AML Subtypes, Whereas AML-MRC Has a Higher Mutational Frequency and Burden
We assessed the frequency and relationship of mutations in subtypes of AML including AML-MRC, AML-NOS, AML-RGA, and AML-T using unsupervised hierarchical gene cluster analysis (Figure 1). Such analysis demonstrated that the majority of AML-RGA did not show mutations in our panel of genes compared with other subtypes of AMLs (P<0.001; Figure 1). In addition, patients with AML-MRC showed an increased burden and higher frequency of mutations (average 2.03 mutations/patient) compared with AML-NOS (average 1.71 mutations/patient), AML-RGA (average 0.375 mutations/patient), and AML-T (average 1.44 mutations/ patient) (Figure 1). In assessing the relationship of these mutations to cytogenetic risk categories, mutations in our panel of 19 genes were more frequently observed in AML with intermediate- and high-risk cytogenetics vs cases with low-risk cytogenetics (P = 0.04; Figure 2).
Figure 1.
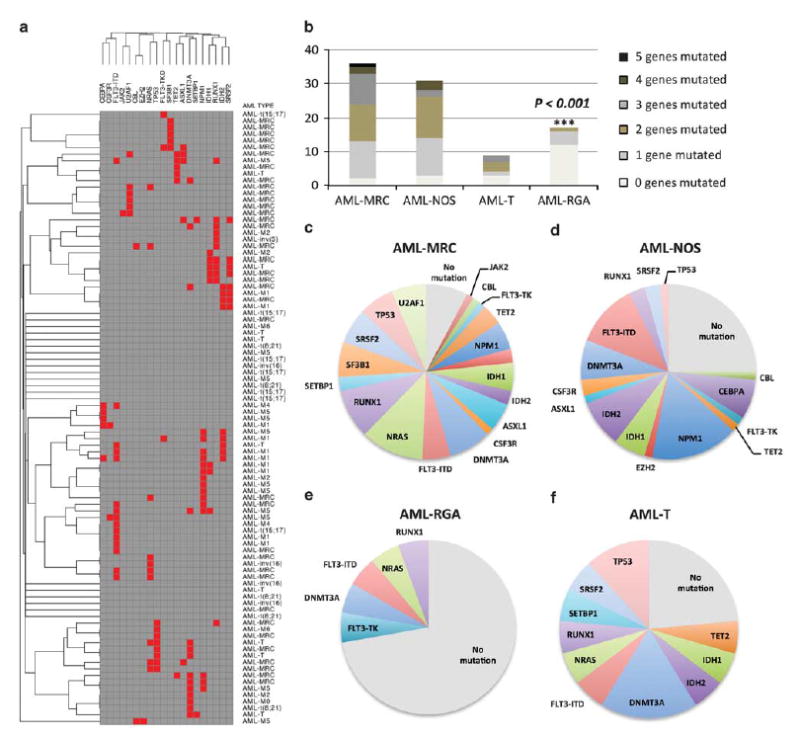
Mutational patterns in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). (a) Unsupervised gene cluster analysis of 19 genes (RUNX1, ASXL1, TET2, CEBPA, IDH1, IDH2, DNMT3A, FLT3, NPM1, TP53, NRAS, EZH2, CBL, U2AF1, SF3B1, SRSF2, JAK2, CSF3R, and SETBP1) in association with AML subtypes. (b) Overall mutational burden and frequency in AML with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MRC), AML-not otherwise specified (AML-NOS), AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities (AML-RGA), and therapy-related AML (AML-T). Comparison demonstrates that AML-MRC shows increased frequency of mutations and higher number of genes mutated, whereas AML-RGA shows fewer mutations. (c–e) The mutational distribution of 19 genes in AML subtypes; depicted are the frequency in each subtype.
Figure 2.
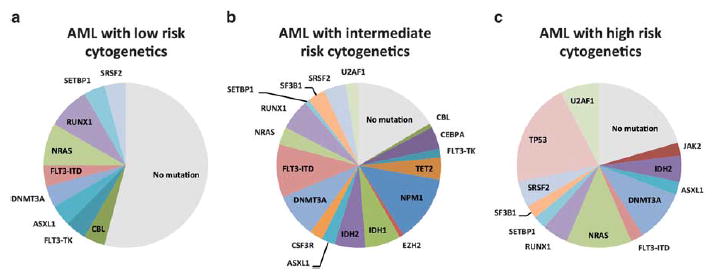
Frequency of mutations in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) by cytogenetic risk stratification. (a) AML with low-risk cytogenetics, (b) AML with intermediate-risk cytogenetics, and (c) AML with high-risk cytogenetics.
TP53 Mutations are Associated with AML with Complex Karyotype Whereas ASXL1 and U2AF1 Mutations are Associated with AML-MRC
Further analysis of the association of individual mutations with AML subtypes demonstrated that TP53 mutations were not only associated with AML with high-risk cytogenetics, but specifically cases with a complex karyotype (P<0.001). Of 15 cases with a complex karyotype, 8 cases demonstrated TP53 mutations (53%), whereas of the remaining 78 AML cases without a complex karyotype, none contained a TP53 mutation. To verify this cytogenetic relationship with TP53, we sequenced an additional 21 cases of AML with complex karyotype by Sanger sequencing; of these, 12 cases demonstrated TP53 mutations (57%) (Figure 3). In addition, we found that mutations in TP53 were frequently seen in association with chromosome 17p deletions (del(17p)): of 20 total cases with TP53 mutations, 11 were seen in association with del(17p) (55%); 2 cases without chromosome 17p deletions contained two independent TP53 mutations.
Figure 3.
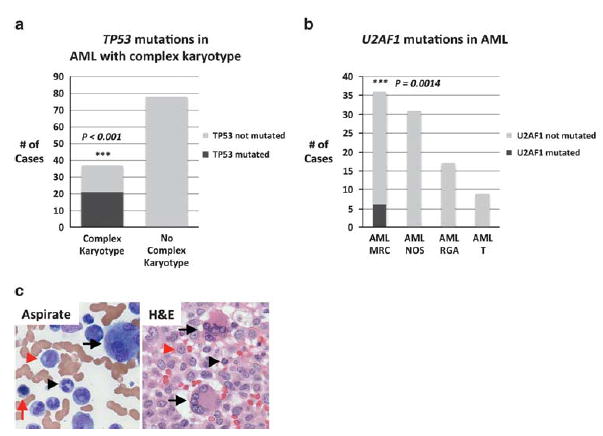
TP53 mutations are associated with complex karyotype, whereas U2AF1 mutations are associated with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with myelodysplasia-related changes (MRC) and trilineage dysplasia. (a) Cases of AML with complex karyotype vs cases without complex karyotype. Black bars indicate cases with TP53 mutated, whereas gray bars indicate cases without TP53 mutated. Complex karyotype cases include an additional 21 cases studied for TP53 mutations by Sanger sequencing. (b) Cases of AML by WHO subtype including AML-MRC, AML-not otherwise specified (AML-NOS), AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities (AML-RGA), and therapy-related AML (AML-T). The black bar indicates cases with U2AF1 mutated, and gray bars indicate cases without U2AF1 mutated. (c) An example of an AML with U2AF1 mutated that shows profound trilineage dysplasia including megakaryocytes with separate nuclear lobes (black arrows), hypogranular neutrophils (black arrowhead), and erythroids with nuclear membrane irregularities (red arrow). Blasts are identified by red arrowheads.
Our analysis additionally identified a unique relationship of U2AF1 mutations with AML-MRC. Of the 6 cases with U2AF1 mutations, all were associated with AML-MRC (P = 0.0014). Two of the four patients had a history of a MDS. Interestingly, all six cases showed profound trilineage morphologic dysplasia (erythroid, myeloid, and megakaryocytic). This relationship between U2AF1 mutations with trilineage dysplasia was statistically significant as only 22 of the 36 cases of AML-MRC showed triline-age morphologic dysplasia (P = 0.038; Figure 3c). We additionally found an association of ASXL1 mutations with AML-MRC (P = 0.013), with 4 of 5 cases associated with AML-MRC and 1 with AML-NOS. However, unlike mutations in U2AF1, a correlation with trilineage dysplasia was not present (P>0.5).
We additionally assessed intermutational relationships. Analyses demonstrated that IDH1 mutations were frequently associated with RUNX1 mutations (4 of 8 cases) whereas IDH2 mutations were frequently associated with SRSF2 mutations (4 of 9) (Figure 1).
Mutations in TP53, U2AF1, ASXL1, and TET2 are Associated with Poor Prognosis
We next assessed the prognostic significance of mutations in these 19 genes in AML with regard to clinical remission, overall survival (OS), and disease-free survival (DFS). In univariate analysis, point mutations and indels in TP53 were associated with poorer OS and DFS (P<0.0001), as shown in Figure 4. However, as TP53 mutations were intimately associated with AMLs with a complex karyotype, we wanted to determine whether such mutations conferred prognostic significance within this cytogenetic group. Our analysis additionally showed that among cases of AML with complex karyotype, mutations in TP53 retained prognostic significance in DFS (P = 0.013) and showed a trend toward worse OS (P = 0.153; Figure 5).
Figure 4.
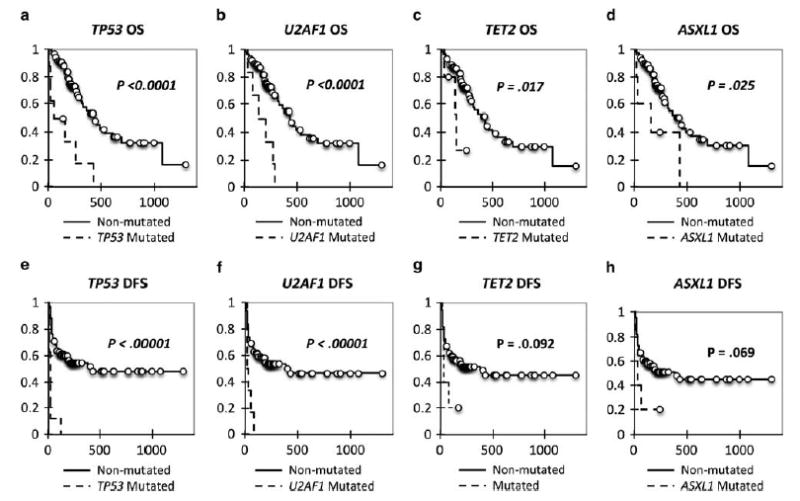
Kaplan–Meier curves for TP53, U2AF1, and TET2. (a) Overall survival (OS) Kaplan–Meier curve for TP53. (b) OS Kaplan–Meier curve for U2AF1. (c) OS Kaplan–Meier curve for TET2. (d) OS Kaplan–Meier curve for ASXL1. (e) Disease-free survival (DFS) Kaplan–Meier curve for TP53. (f) DFS Kaplan–Meier curve for U2AF1. (g) DFS Kaplan–Meier curve for TET2. (h) DFS Kaplan–Meier curve for ASXL1.
Figure 5.
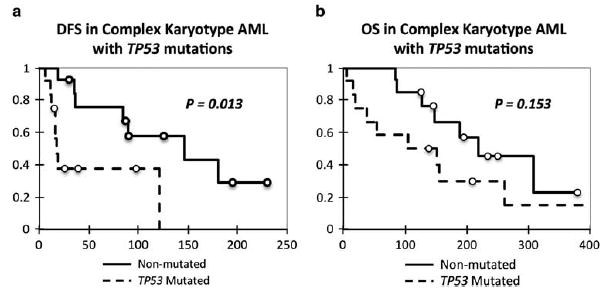
Prognostic significance of TP53 mutations in cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with complex karyotype. (a) Kaplan–Meier curve of disease-free survival (DSF) in AML with complex karyotype with relation to TP53 mutations. (b) Kaplan–Meier curve of overall survival (OS) in AML with complex karyotype with relation to TP53 mutations. Cases included those sequenced by next-generation sequencing and TP53 Sanger sequencing.
In univariate analysis, mutations in U2AF1 were additionally associated with poor OS and DFS (P<0.0001), and for both TP53 and U2AF1, mutations in these genes were associated with absence of clinical remission (P<0.03; Figure 4). In addition, mutations in TET2 and ASXL1 showed prognostic significance with regard to poor OS (P = 0.017 and P = 0.025, respectively) but not clinical remission (P>0.2) or DFS (P = 0.092 and P = 0.069) (Figure 4).
In multivariate analysis, U2AF1 and TP53 mutations retained prognostic significance as markers of poor prognosis in OS and DFS respectively with hazard ratios of 3.989 and 4.455 respectively, although other mutations were not significant in OS or DFS (Table 2). Age, complex karyotype, and the subcategory AML-MRC also retained prognostic significance (Table 2). Mutations in other genes including ASXL1 and TET2 were not significant in multivariate analysis.
Table 2.
Multivariate Cox proportional hazard model
| Variable | P-value | Hazard ratio | Hazard ratio lower bound (95%) | Hazard ratio upper bound (95%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall survival | ||||
| Age | 0.002 | 1.032 | 1.012 | 1.053 |
| U2AF1 mutation | 0.002 | 3.989 | 1.643 | 9.687 |
| Complex karyotype | <0.0001 | 4.604 | 2.118 | 10.006 |
| Disease-free survival | ||||
| Age | 0.001 | 1.037 | 1.016 | 1.059 |
| TP53 mutation | <0.0001 | 10.571 | 4.455 | 25.079 |
| AML-MRC | <0.0001 | 3.621 | 1.972 | 6.651 |
Abbreviation: AML-MRC, acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes.
Discussion
Our work demonstrates the significance of mutations in TP53, U2AF1, and TET2 in AML. It is not surprising that mutations in TP53 are associated with poor prognosis, as TP53 is a well-defined tumor suppressor and known to play a critical role in tumorigenesis, cell survival, and proliferation in many solid tumors and other hematopoietic neoplasms.29,30 Indeed, our findings are in line with those of Rucker et al31 and Kihara et al32 who also found TP53 mutations to be associated with poor prognosis in AML; furthermore, such mutations have also been found to be associated with a complex karyotype.31 However, our work extends the work of earlier studies by demonstrating an independent prognostic significance for mutations in TP53 in AML in a multivariate model that includes clinical features, cytogenetics, and 18 other genes commonly mutated in myeloid neoplasms, and importantly the current WHO subclassification of AML. Indeed, even within the subcategory of AML with complex karyotype, mutations in TP53 may show prognostic significance with regard to DFS (P = 0.013) and a trend toward worse OS (P = 0.153).
Why TP53 mutations are linked with complex karyotype is still unclear, and raises the question as to whether these mutations promote and instigate increasing cytogenetic instability, or whether these mutations are secondary mutations only appearing after chromosomal instability has occurred. In our series, a subset of cases of AML with complex karyotype do not have TP53 mutations, whereas all TP53-mutated AMLs are observed in complex karyotypes, arguing that the complex karyotypic changes generally precede mutation of TP53. Indeed, we additionally found that most mutations in TP53 are associated with del(17p), suggesting that chromosome instability, and specifically deletion of chromosome 17p, may precede mutations in TP53 (two-hit hypothesis). However, further work is needed to assess these possibilities.
Recently, Graubert et al33 identified mutations in U2AF1 as a poor prognostic indicator in MDS; other groups have studied the relationship between U2AF1 with prognosis in AML with conflicting results.13,34 Using a carefully annotated and well-defined cohort of AML patients, we identify a clear link between U2AF1 mutations and poor prognosis in AML in univariate analysis. In some sense, it might not be surprising that mutations in U2AF1 should be associated with poor prognosis in AML. As U2AF1 mutations are seen in MDS, and given that AMLs transformed from MDS have poorer survival, a logical progression of thought could be that AMLs with U2AF1 mutations arise from MDS. However, of the six AMLs with U2AF1 mutations, only two in our series had a reported history of a MDS. Furthermore, we demonstrated an independent prognostic relationship between U2AF1 mutations and poor survival in multivariate analysis. As such, the poor survival outcome of patients with mutations in U2AF1 does not appear to be associated with a prior history of a MDS.
Importantly, we found a novel and clear relationship between U2AF1 mutations and the subgroup AML-MRC. In some sense, as mutations in U2AF1 were all associated with AML-MRC, it is not surprising that such cases showed background dysplasia. However, what is surprising is the degree of profound dysplasia associated with U2AF1 mutations that affected all three hematopoietic lineages (erythroid, myeloid, and megakaryocytic; P = 0.038). From a mechanistic and biological viewpoint, how mutations in U2AF1 lead to such profound multilineage dysplasia is not clear. Given the function of U2AF1 as a splicing factor, and ubiquitous expression in tissues,35 one possibility is that mutations in U2AF1 are acquired in a primitive stem cell that has the capacity to give rise to dysplastic cells in all three lineages in the bone marrow, and as U2AF1 is expressed continuously in these developing hematopoietic cells, alterations in its normal function are manifest morphologically. Further studies to assess molecular signaling pathways are needed.
With regard to other genes, similar to Patel et al36 and other groups,37,38 TET2 and ASXL1 were also found to be important in prognostication in univariate analysis of OS, although in multivariate analysis, mutations in these genes lost importance as independent variables. Interestingly, both ASXL1 and TET2 are involved in epigenetic regulation of DNA. ASXL1 is a nuclear protein that interacts with polycomb complex proteins ultimately to affect methylation and ubiquitination of histones.39-42 Gene mutations in ASXL1 have been identified in all major subtypes of myeloid neoplasms, and hematopoietic-specific deletion results in a phenotype similar to a MDS.43,44 Like ASXL1, TET2 is involved in epigenetic modulation of DNA through conversion of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC).45 Similar to ASXL1, a causal and direct link to myeloid neoplasms has been identified through mutational studies in animal models where loss of function of TET2 has been shown to result in myeloid neoplasms.46 Given the in vivo mutational studies on ASXL1 and TET2 in murine models, mutations in these genes might be viewed as driver mutations; however, further work is necessary to fully evaluate this possibility.
Finally, our results also demonstrated that patients within the AML subtype AML-RGA exhibit fewer mutations in our panel of 19 genes, whereas those with AML-MRC had a higher frequency, as well as overall increased mutational burden. These results are not entirely surprising as many of the translocations that define the recurrent genetic subtypes of AMLs are believed to be core driver genetic changes; indeed, some of these findings have been reported previously by The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network.21 However, the link between AML-MRC with increased mutational frequency and burden has not previously been described. Further research into biochemical signaling pathways will be needed to understand how phenotypic manifestations are related to many of these gene mutations.
A refined mutational landscape of AML is rapidly taking form, and here our work sharpens our understanding of the prognostic, genetic, and phenotypic associations and significance of 19 genes critical in AML.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Anniek De Witte and Ashutosh for their support. We thank JK Ohgami for her expertise and advice.
Footnotes
Disclosure/conflict of interest
Dr Robert Ohgami has been a consultant for Agilent Technologies. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Modern Pathology website (http://www.nature.com/modpathol)
References
- 1.Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114:937–951. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-209262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Visser O, Trama A, Maynadie M, et al. RARECARE Working Group. Incidence, survival and prevalence of myeloid malignancies in Europe. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:3257–3266. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.05.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sant M, Allemani C, Tereanu C, et al. HAEMACARE Working Group. Incidence of hematologic malignancies in Europe by morphologic subtype: results of the HAEMACARE project. Blood. 2010;116:3724–3734. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-282632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Deschler B, Lubbert M. Acute myeloid leukemia: epidemiology and etiology. Cancer. 2006;107:2099–2107. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2008. p. 439. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, et al. National Cancer Research Institute Adult Leukaemia Working Group. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the united kingdom medical research council trials. Blood. 2010;116:354–365. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-254441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dohner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, et al. European LeukemiaNet. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: Recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2010;115:453–474. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-235358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shen Y, Zhu YM, Fan X, et al. Gene mutation patterns and their prognostic impact in a cohort of 1185 patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2011;118:5593–5603. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-343988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Welch JS, Ley TJ, Link DC, et al. The origin and evolution of mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell. 2012;150:264–278. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rocquain J, Carbuccia N, Trouplin V, et al. Combined mutations of ASXL1, CBL, FLT3, IDH1, IDH2, JAK2, KRAS, NPM1, NRAS, RUNX1, TET2 and WT1 genes in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemias. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:401. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-401. 2407-10-401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ley TJ, Ding L, Walter MJ, et al. DNMT3A mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2424–2433. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1005143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yan XJ, Xu J, Gu ZH, et al. Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DNA methyltransferase gene DNMT3A in acute monocytic leukemia. Nat Genet. 2011;43:309–315. doi: 10.1038/ng.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Thol F, Kade S, Schlarmann C, et al. Frequency and prognostic impact of mutations in SRSF2, U2AF1, and ZRSR2 in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2012;119:3578–3584. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-399337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cross NC. Genetic and epigenetic complexity in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011;2011:208–214. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2011.1.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tefferi A, Jimma T, Sulai NH, et al. IDH mutations in primary myelofibrosis predict leukemic transformation and shortened survival: clinical evidence for leukemogenic collaboration with JAK2V617F. Leukemia. 2012;26:475–480. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Brecqueville M, Rey J, Bertucci F, et al. Mutation analysis of ASXL1, CBL, DNMT3A, IDH1, IDH2, JAK2, MPL, NF1, SF3B1, SUZ12, and TET2 in myelo-proliferative neoplasms. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2012;51:743–755. doi: 10.1002/gcc.21960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fernandez-Mercado M, Yip BH, Pellagatti A, et al. Mutation patterns of 16 genes in primary and secondary acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with normal cytogenetics. PLoS One. 2012;7:e42334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kohlmann A, Grossmann V, Klein HU, et al. Next-generation sequencing technology reveals a characteristic pattern of molecular mutations in 72.8% of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia by detecting frequent alterations in TET2, CBL, RAS, and RUNX1. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3858–3865. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Malcovati L, et al. Chronic Myeloid Disorders Working Group of the International Cancer Genome Consortium. Clinical and biological implications of driver mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2013;122:3616–3627. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-08-518886. quiz 3699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen TC, Hou HA, Chou WC, et al. Dynamics of ASXL1 mutation and other associated genetic alterations during disease progression in patients with primary myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood Cancer J. 2014;4:e177. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2013.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2059–2074. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1301689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.National comprehensive cancer network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: acute myeloid leukemia. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/aml.pdf.
- 23.Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, et al. The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1,612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The Medical Research Council Adult and Children’s Leukaemia Working Parties. Blood. 1998;92:2322–2333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ohgami RS, Ohgami JK, Pereira IT, et al. Refining the diagnosis of T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia by combining distinct patterns of antigen expression with T-cell clonality studies. Leukemia. 2011;25:1439–1443. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Spencer DH, Abel HJ, Lockwood CM, et al. Detection of FLT3 internal tandem duplication in targeted, short-read-length, next-generation sequencing data. J Mol Diagn. 2013;15:81–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2012.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ohgami RS, Ma L, Ren L, et al. DNA methylation analysis of ALOX12 and GSTM1 in acute myeloid leukaemia identifies prognostically significant groups. Br J Haematol. 2012;159:182–190. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Weinberg OK, Ohgami RS, Ma L, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia with monosomal karyotype: morphologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular findings. Am J Clin Pathol. 2014;142:190–195. doi: 10.1309/AJCPMLO84JDNVLNK. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Reich M, Liefeld T, Gould J, et al. GenePattern 2.0. Nat Genet. 2006;38:500–501. doi: 10.1038/ng0506-500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Stiewe T. The p53 family in differentiation and tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:165–168. doi: 10.1038/nrc2072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Muller PA, Vousden KH. P53 mutations in cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15:2–8. doi: 10.1038/ncb2641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rucker FG, Schlenk RF, Bullinger L, et al. TP53 alterations in acute myeloid leukemia with complex karyotype correlate with specific copy number alterations, monosomal karyotype, and dismal outcome. Blood. 2012;119:2114–2121. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-08-375758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kihara R, Nagata Y, Kiyoi H, et al. Comprehensive analysis of genetic alterations and their prognostic impacts in adult acute myeloid leukemia patients. Leukemia. 2014;28:1586–1595. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Graubert TA, Shen D, Ding L, et al. Recurrent mutations in the U2AF1 splicing factor in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat Genet. 2011;44:53–57. doi: 10.1038/ng.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Qian J, Yao DM, Lin J, et al. U2AF1 mutations in Chinese patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. PLoS One. 2012;7:e45760. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yoshida K, Ogawa S. Splicing factor mutations and cancer. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014;5:445–459. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Patel JP, Gonen M, Figueroa ME, et al. Prognostic relevance of integrated genetic profiling in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1079–1089. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1112304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chou WC, Chou SC, Liu CY, et al. TET2 mutation is an unfavorable prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia patients with intermediate-risk cytogenetics. Blood. 2011;118:3803–3810. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-339747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gelsi-Boyer V, Brecqueville M, Devillier R, et al. Mutations in ASXL1 are associated with poor prognosis across the spectrum of malignant myeloid diseases. J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5:8722–5-12. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-5-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schuettengruber B, Chourrout D, Vervoort M, et al. Genome regulation by polycomb and trithorax proteins. Cell. 2007;128:735–745. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Schwartz YB, Kahn TG, Stenberg P, et al. Alternative epigenetic chromatin states of polycomb target genes. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1000805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schwartz YB, Pirrotta V. Polycomb silencing mechanisms and the management of genomic programmes. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:9–22. doi: 10.1038/nrg1981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Muller J, Verrijzer P. Biochemical mechanisms of gene regulation by polycomb group protein complexes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009;19:150–158. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Abdel-Wahab O, Gao J, Adli M, et al. Deletion of Asxl1 results in myelodysplasia and severe developmental defects in vivo. J Exp Med. 2013;210:2641–2659. doi: 10.1084/jem.20131141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Fisher CL, Pineault N, Brookes C, et al. Loss-of-function additional sex combs like 1 mutations disrupt hematopoiesis but do not cause severe myelodysplasia or leukemia. Blood. 2010;115:38–46. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-230698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wrighton KH. Chromatin: TET2 keeps histones sweet. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:64–65. doi: 10.1038/nrm3511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Li Z, Cai X, Cai CL, et al. Deletion of Tet2 in mice leads to dysregulated hematopoietic stem cells and subsequent development of myeloid malignancies. Blood. 2011;118:4509–4518. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-325241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


