Abstract
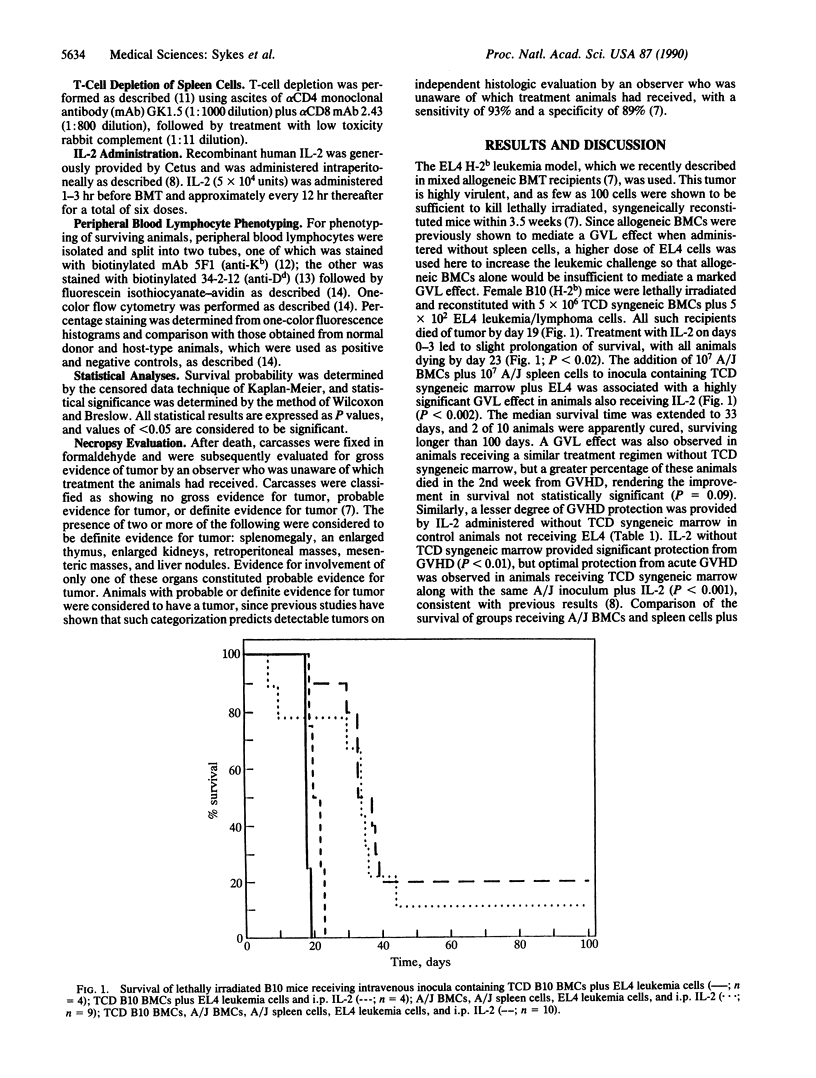
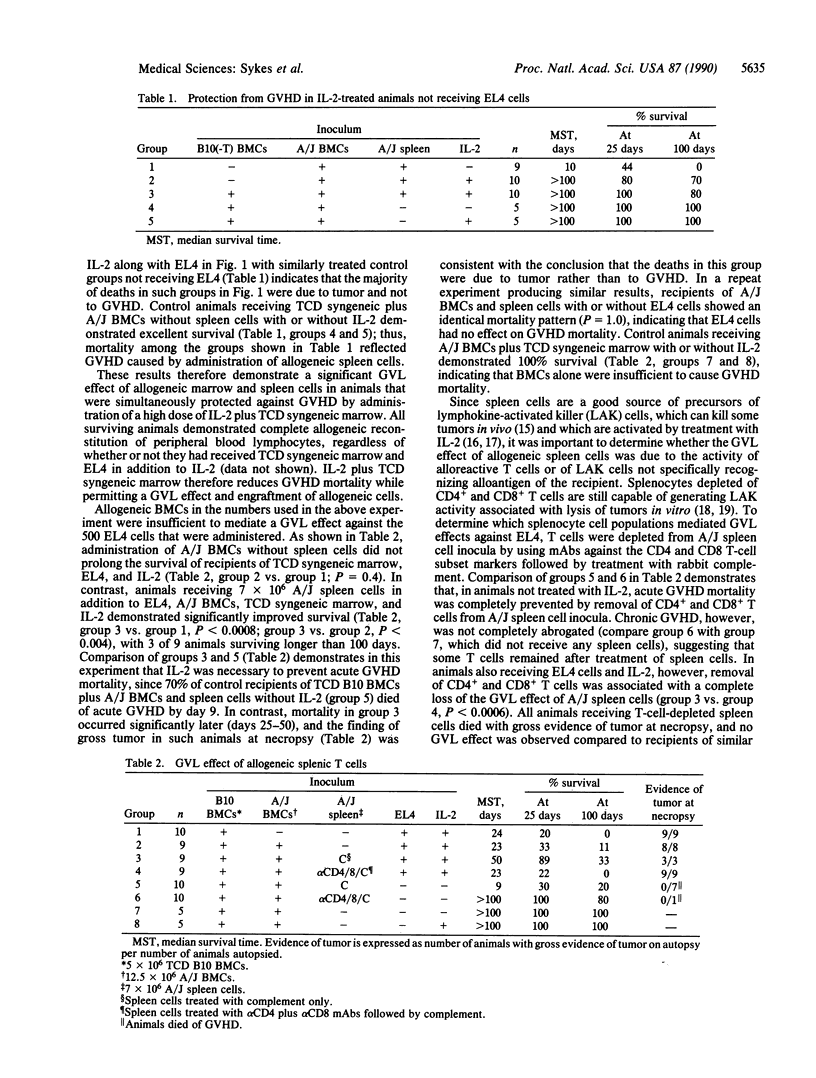
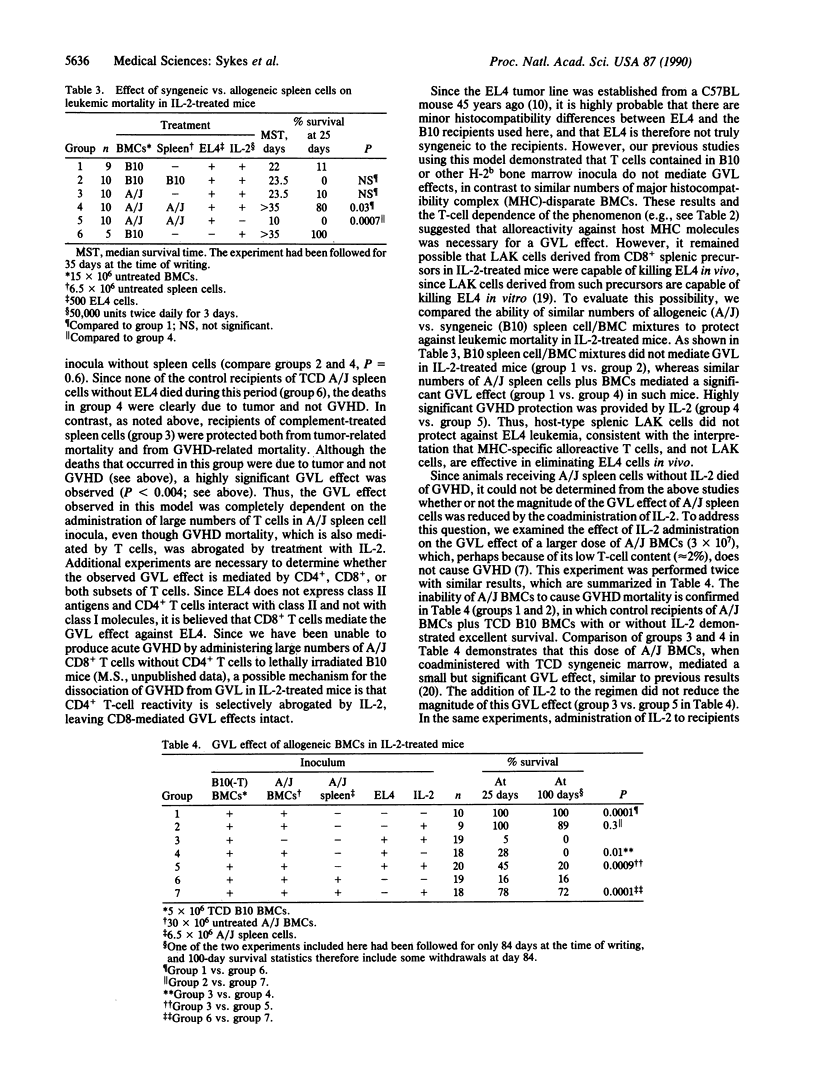
We have recently demonstrated that interleukin 2 (IL-2), when administered in high doses for several days beginning on the day of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT), markedly diminishes graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) mortality in lethally irradiated mice. An optimal anti-GVHD effect was attained by coadministering T-cell-depleted (TCD) syngeneic marrow. We demonstrate here that the full graft-versus-leukemia effect of allogeneic T lymphocytes is obtained even when GVHD is markedly diminished by the coadministration of IL-2 and TCD syngeneic marrow. This methodology represents an approach to the treatment of leukemia in which the beneficial effects of allogeneic T cells can be exploited while their major deleterious effect, GVHD, is avoided. These results may thus have an impact on the clinical use of BMT for the treatment of hematologic malignancies.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson T. D., Hayes T. J., Gately M. K., Bontempo J. M., Stern L. L., Truitt G. A. Toxicity of human recombinant interleukin-2 in the mouse is mediated by interleukin-activated lymphocytes. Separation of efficacy and toxicity by selective lymphocyte subset depletion. Lab Invest. 1988 Nov;59(5):598–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. E., Hyatt C. L., Rosenberg S. A. Systemic administration of recombinant human interleukin-2 in mice. J Biol Response Mod. 1984 Oct;3(5):561–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clift R. A., Storb R. Histoincompatible bone marrow transplants in humans. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:43–64. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORER P. A. Studies in antibody response of mice to tumour inoculation. Br J Cancer. 1950 Dec;4(4):372–379. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1950.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hank J. A., Kohler P. C., Weil-Hillman G., Rosenthal N., Moore K. H., Storer B., Minkoff D., Bradshaw J., Bechhofer R., Sondel P. M. In vivo induction of the lymphokine-activated killer phenomenon: interleukin 2-dependent human non-major histocompatibility complex-restricted cytotoxicity generated in vivo during administration of human recombinant interleukin 2. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1965–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ildstad S. T., Wren S. M., Bluestone J. A., Barbieri S. A., Sachs D. H. Characterization of mixed allogeneic chimeras. Immunocompetence, in vitro reactivity, and genetic specificity of tolerance. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):231–244. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ildstad S. T., Wren S. M., Bluestone J. A., Barbieri S. A., Stephany D., Sachs D. H. Effect of selective T cell depletion of host and/or donor bone marrow on lymphopoietic repopulation, tolerance, and graft-vs-host disease in mixed allogeneic chimeras (B10 + B10.D2----B10). J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):28–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalland T., Belfrage H., Bhiladvala P., Hedlund G. Analysis of the murine lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell phenomenon: dissection of effectors and progenitors into NK- and T-like cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3640–3645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay N. E., Oken M. M., Mazza J. J., Bradley E. C. Evidence for tumor reduction in refractory or relapsed B-CLL patients with infusional interleukin-2. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1988;30(5-6):475–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keever C. A., Small T. N., Flomenberg N., Heller G., Pekle K., Black P., Pecora A., Gillio A., Kernan N. A., O'Reilly R. J. Immune reconstitution following bone marrow transplantation: comparison of recipients of T-cell depleted marrow with recipients of conventional marrow grafts. Blood. 1989 Apr;73(5):1340–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernan N. A., Flomenberg N., Dupont B., O'Reilly R. J. Graft rejection in recipients of T-cell-depleted HLA-nonidentical marrow transplants for leukemia. Identification of host-derived antidonor allocytotoxic T lymphocytes. Transplantation. 1987 Jun;43(6):842–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFor A. T., Eisenthal A., Rosenberg S. A. Heterogeneity of lymphokine-activated killer cells induced by IL-2. Separate lymphoid subpopulations lyse tumor, allogeneic blasts, and modified syngeneic blasts. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):4062–4069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. J., Hansen J. A., Torok-Storb B., Durnam D., Przepiorka D., O'Quigley J., Sanders J., Sullivan K. M., Witherspoon R. P., Deeg H. J. Graft failure in patients receiving T cell-depleted HLA-identical allogeneic marrow transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1988 Sep;3(5):445–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N. M., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse major histocompatibility complex antigens. Transplantation. 1982 Sep;34(3):113–120. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198209000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Yang J. C., Aebersold P. M., Linehan W. M., Seipp C. A., White D. E. Experience with the use of high-dose interleukin-2 in the treatment of 652 cancer patients. Ann Surg. 1989 Oct;210(4):474–485. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198910000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Mulé J. J., Spiess P. J., Reichert C. M., Schwarz S. L. Regression of established pulmonary metastases and subcutaneous tumor mediated by the systemic administration of high-dose recombinant interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1169–1188. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Randolph C. P. Monoclonal anti-H-2Kb antibodies detect serological differences between H-2Kb mutants. Immunogenetics. 1981;12(1-2):183–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01561661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavin S., Eckerstein A., Weiss L. Adoptive immunotherapy in conjunction with bone marrow transplantation--amplification of natural host defence mechanisms against cancer by recombinant IL-2. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1988;7(3):180–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. M., Weiden P. L., Storb R., Witherspoon R. P., Fefer A., Fisher L., Buckner C. D., Anasetti C., Appelbaum F. R., Badger C. Influence of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease on relapse and survival after bone marrow transplantation from HLA-identical siblings as treatment of acute and chronic leukemia. Blood. 1989 May 1;73(6):1720–1728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes M., Bukhari Z., Sachs D. H. Graft-versus-leukemia effect using mixed allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1989 Sep;4(5):465–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes M., Chester C. H., Sundt T. M., Romick M. L., Hoyles K. A., Sachs D. H. Effects of T cell depletion in radiation bone marrow chimeras. III. Characterization of allogeneic bone marrow cell populations that increase allogeneic chimerism independently of graft-vs-host disease in mixed marrow recipients. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3503–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes M., Romick M. L., Hoyles K. A., Sachs D. H. In vivo administration of interleukin 2 plus T cell-depleted syngeneic marrow prevents graft-versus-host disease mortality and permits alloengraftment. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):645–658. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes M., Sachs D. H. Genetic analysis of the anti-leukemic effect of mixed allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1989 Feb;21(1 Pt 3):3022–3024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes M., Sheard M., Sachs D. H. Effects of T cell depletion in radiation bone marrow chimeras. I. Evidence for a donor cell population which increases allogeneic chimerism but which lacks the potential to produce GVHD. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2282–2288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiden P. L., Sullivan K. M., Flournoy N., Storb R., Thomas E. D. Antileukemic effect of chronic graft-versus-host disease: contribution to improved survival after allogeneic marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 18;304(25):1529–1533. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106183042507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


