Abstract
Natural antisense transcripts (NATs) as one of the most diverse classes of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), have been demonstrated involved in fundamental biological processes in human. Here, we reported that human prohibitin gene pseudogene 1 (PHBP1) was upregulated in ESCC, and increased PHBP1 expression in ESCC was associated with clinical advanced stage. Functional experiments showed that PHBP1 knockdown inhibited ESCC cells proliferation, colony formation and xenograft tumor growth in vitro and in vivo by causing cell-cycle arrest at the G1-G0 phase. Mechanisms analysis revealed that PHBP1 transcript as an antisense transcript of PHB is partially complementary to PHB mRNA and formed an RNA-RNA hybrid with PHB, consequently inducing an increase of PHB expression at both the mRNA and protein levels. Furthermore, PHBP1 expression is strongly correlated with PHB expression in ESCC tissues. Collectively, this study elucidates an important role of PHBP1 in promoting ESCC partly via increasing PHB expression.
Keywords: natural antisense transcript (NAT), long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
INTRODUCTION
In the past decades, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), as the most common type of esophageal cancer, has been one of the most leading causes of cancer-related death worldwide [1, 2]. According recent statistical data, incidence and mortality rate of ESCC is increasing rapidly occurring in China and the incidence of ESCC is around three times more common in men than in women [3, 4]. Though the improvements in the treatment of ESCC have been achieved by radiochemotherapy and surgical resection, its prognosis remains disappointed [5–7]. Therefore, fully understanding the genetic and molecular mechanism of ESCC development and progression is urgent for us to develop potential diagnostic and treatment approaches on ESCC.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) represent a diverse type of long RNA molecules lacking protein-coding capacity, with a length of larger than 200 nucleotides [8, 9]. A plenty of evidence has proved that lncRNAs play essential roles in fundamental biological processes, such as cell growth, differentiation, immune response and cancer biology [10–19]. Recently, one group of lncRNAs is the natural antisense transcripts (NATs), accounting for about 50-70% of lncRNAs, transcribed from the opposite DNA strand of their endogenous sense counterpart's protein-coding genes and non-protein-coding genes [20, 21]. For many years, the well-defined transcriptional units are initially overlooked due to low levels of expression, and unknown functions. However, recently, antisense lncRNAs (aslncRNAs) have garnered increased attention due to their highly locus-specific effects. Several studies have revealed the critical roles of aslncRNAs in various pathophysiological processes, particularly in multiple diseases and cancers [22–25]. One major emerging theme is centered on the effects of aslncRNAs exerting in cis on their neighboring genes or in trans on other distant genes through transcriptional or post-transcriptional regulation [26, 27].
Human prohibitin gene (PHB) pseudogene 1 (PHBP1) which located on chromosome 6q25, was identified to be processed pseudogene. The DNA sequence of PHBP1 shared the high level of the nucleotide sequence identity (91.3%) with its cognate gene PHB [28]. Data from different groups have examined the functional role of PHB in human cellular senescence and carcinogenesis [29–32]. Recent findings from Han et al. and Zhong et al. have demonstrated that change in the expression of PHB1 was linked to human pancreatic carcinoma and that PHB could be used as an early biomarker or a treatment target for pancreatic carcinoma. However, the exact biological functions of PHBP1 remain unknowns. We investigated the expression level of PHBP1 in human ESCC tissues and its association with clinicopathological characteristics. Furthermore, we further analyzed its biological functions and precise molecular mechanisms on its cognate gene PHB underlying ESCC pathogenesis.
RESULTS
Overexpression of PHBP1 in human ESCC tissues
In order to analyze the expression levels of PHBP1and PHBin ESCC, we performed qRT-PCR on 63 paired ESCC samples and noncancerous samples, and found that levels of PHBP1expression was unregulated in 76% (48 of 63), ESCC tissues as compared with that noncancerous samples (P<0.01, Figure 1A). Next, we evaluated the correlation between expression levels of PHBP1and clinicopathological features of ESCC patients. Remarkably, as showed in Table 1, a significant association between PHBP1 expression with TNM stage, and patients with high PHBP1 expression level was significantly correlated with advanced TNM stage in ESCC tissues (Figure 1B).
Figure 1. The expression patterns of PHBP1 in ESCC tissues and cell lines.
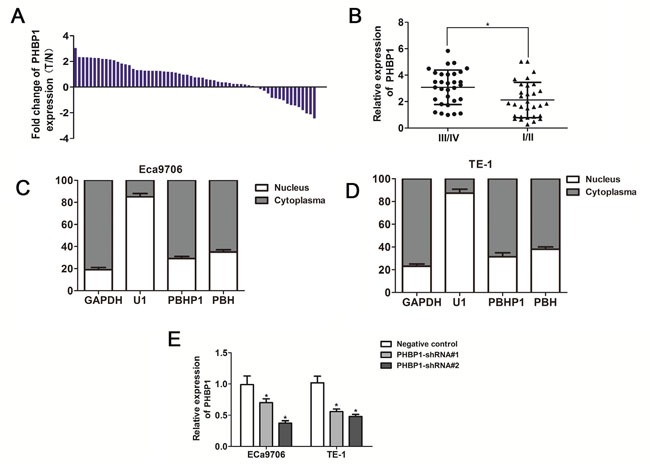
(A) PHBP1 expression in ESCC tissues and adjacent noncancerous tissues. The expression of PHBP1was measured by qRT-PCR. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (B) Patients with a higher PHBP1 expression have an advanced stage compared to a lower PHBP1 expression. Subcellular location of PHBP1 and PHB in Eca9706 (C) and TE-1 (D) cell lines. GAPDH and RNU1 were used as control of cytoplasm and nucleus, respectively. (E) The effectiveness of PHBP1 knockdown in ECa9706 and TE-1 cells induced by PHBP1-shRNAs (shRNA1# and shRNA2#). Relative levels of PHBP1 RNA expression in ESCC cells were measured by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) obtained from three independent experiments data; *P<0.05, compared with negative control.
Table 1. Relationship between PHBP1 and clinicopathological parameters in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients.
| Characteristics | Expression of PHBP1 | Pvaluea | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-PHBP1 group | High-PHBP1 group | ||
| Gender | |||
| <65 | 18 | 22 | |
| ≥65 | 13 | 9 | 0.268 |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 20 | 16 | |
| Female | 11 | 15 | 0.305 |
| Family history of cancer | |||
| Yes | 2 | 3 | |
| No | 29 | 28 | 0.640 |
| TNM stages | |||
| I+II | 17 | 6 | |
| III+IV | 14 | 25 | 0.003 |
| Pathological type | |||
| Highly differentiated | 11 | 13 | |
| Moderately differentiated | 13 | 13 | |
| Low differentiated | 7 | 5 | 0.493 |
Furthermore, subcellular location assay revealed that more than 70% PHBP1 RNA is predominantly located in cytoplasm of Eca9706 and TE-1 cell lines (Figure 1C and 1D; P<0.001 for both Eca9706 and TE-1 cells), and small nuclear RNA U6 and GAPDH utilized as control of nucleus and cytoplasm were mostly located in nucleus and cytoplasm, respectively.
ShRNA-mediated knockdown of PHBP1 inhibits ESCC cells proliferation and colony formation in vitro
We developed a downexpression of PHBP1 model in ESCC cells using lentiviral transduction to test whether PHBP1 was functionally involved in ESCC tumorigenesis. The inhibition of PHBP1 in ECa9706 and TE-1 cells induced by PHBP1-shRNAs (shRNA1# and shRNA2#) was confirmed by qRT-PCR with the scramble shRNA served as the negative control. Because of their effectiveness, we utilized PHBP1-shRNA2# transfected cells as the stable cells with knockdown of PHBP1 (Figure 1E). CCK-8 assays and colony formation assays were used to detect the impact of PHBP1 knockdown on proliferation of the ESCC cell lines. ECa9706 and TE-1 cells with the stable knockdown of PHBP1 lead to a significantly decreased cell growth by more than 42% and 47% relative to negative control at day 4 in both cell lines, respectively (P<0.05 in ECa9706 and P<0.05 in TE-1; Figure 2A and 2B). Similarly, the capacity of stable knockdown of PHBP1 to form colonies was reduced by 52% in ECa9706 cell and 61% in TE-1 cells (P=0.002 in ECa9706 and P=0.001 in TE-1; Figure 2C).
Figure 2. ShRNA-mediated knockdown of PHBP1 inhibits ESCC cells proliferation and tumor formation of ESCC cells.
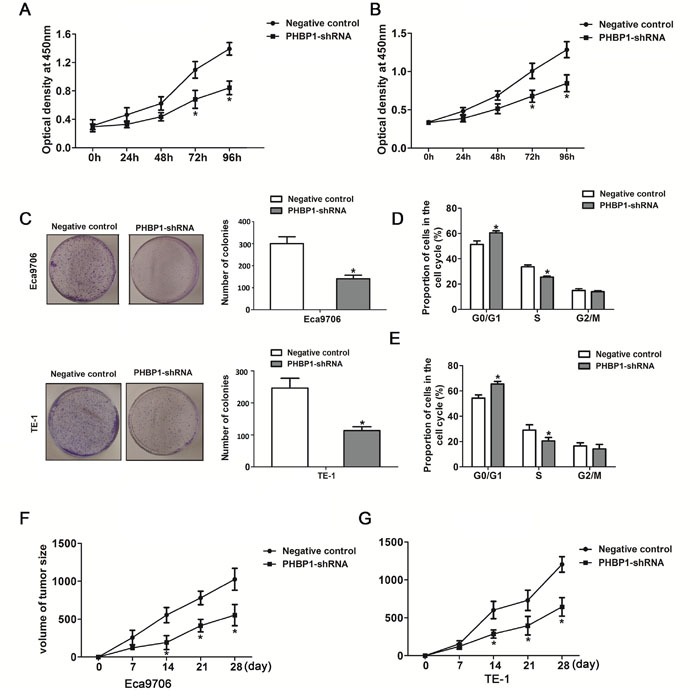
Knockdown of PHBP1 in Eca9706 cells (A) and TE-1 cells (B) markedly reduced cell proliferation. Significant proliferation inhibition was observed after 3 days incubation (P<0.05). (C) Knockdown of PHBP1 show significant inhibitory effects on the colony formation of ESCC cell lines. The percentage of Eca9706 cells (D) and TE-1 cells (E) with stable knockdown of PHBP1 in S phase was significantly decreased, compared to negative control. (F and G) Tumor growth in nude mice subcutaneously injected into flanks with PHBP1-shRNA or negative control. Data are presented as means± SDs (n=8/group). The values was present as means ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed using One-way ANOVA or two-tailed Student's t-test, *P<0.05, compared with negative control.
Knockdown of PHBP1 significantly induced cell-cycle arrest at the G1-G0 phase in ESCC cells
To further evaluate whether the functional consequences of downregulation of PHBP1 was induced by cell cycle, flow cytometry assay was performed. Compared to the negative controls, inhibition of PHBP1 led to a significant accumulation of cells at G0/G1-phase (60.49%± 1.62% vs 51.36% ± 2.84% in ECa9706 and 65.47%± 2.00% vs 54.35% ± 2.60% in TE-1; Figure 2D) and a markedly decrease of cells in S-phase (25.56%± 0.84% vs 33.65% ± 1.52% in ECa9706 and 20.41% ± 2.78% vs 29.12%± 2.14% in TE-1; Figure 2E). Taken together, the results imply that PHBP1 may inhibited ESCC cell proliferation by preventing cell-cycle progression through S-phase.
Inhibition of PHBP1 leads to reduced tumor growth in nude mice
An animal experiment was further used to confirm the effect of PHBP1 on tumorigenesis in vivo. ESCC cells with stable expression of PHBP1-shRNA or negative control was subcutaneously injected into the nude mices, respectively. The tumor was measured every 3 days. As showed in Figure 2F and 2G, during 4 weeks follow up measurement, the initiation and growth of tumor formed in mices with the inhibition of PHBP1 cells were significantly slower than that tumor formed in mices with negative control cells (P<0.05 for both Eca9706 and TE-1 cells).
Coordinated expression of PHBP1 and PHB in ESCC cell lines
Considering the special complementarily sequence of the PHBP1 gene and its cognate gene PHB at the nucleotide level, it attracted our attention to sought to elucidate the effect of PHBP1 on its cognate coding gene RNA. We first delineated PHBP1 and PHB expression patterns in ESCC cells with stable expression of PHBP1-shRNA. The result showed that PHB mRNA and protein levels were reduced in ECa9706 cells, after knockdown PHBP1 expression by PHBP1-shRNA. The expression patterns of PHBP1 and PHB was confirmed in TE-1 cells with stable expression of PHBP1-shRNA (Figure 3A). Based above data, we further examined the location of PHB following cell fractionation, and the results showed that PHB is mostly localized in cytoplasma (>65 %), similar to the subcellular location of PHBP1 (Figure 1C and 1D).
Figure 3. The regulatory effect of PHBP1 on PHB expression.
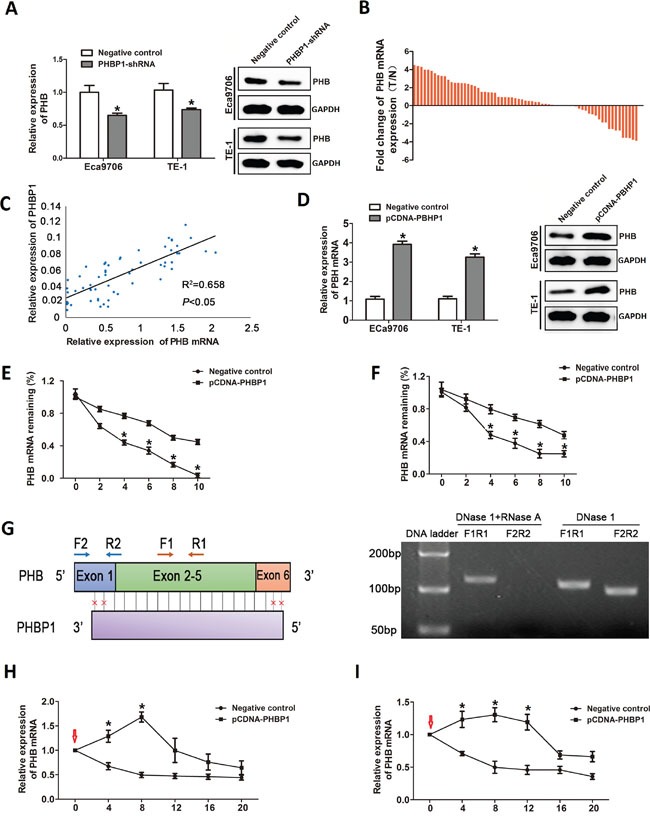
(A) The PHB mRNA levels (left) and protein levels (right) in both Eca9706 and TE-1 cells after PHBP1 knockdown by qRT-PCR analysis and western blot analysis. (B) The expression of PHB was measured by qRT-PCR in ESCC tissues and adjacent noncancerous tissues and normalized to GAPDH. Statistical differences between groups were performed using the two-tailed Student's t-test (P<0.05). (C) PHBP1 and PHB expression levels were positively correlated in ESCC tissues (R2= 0.658, P<0.05 by Pearson correlation test). (D) The PHB mRNA levels (left) and protein levels (right) in both Eca9706 and TE-1 cells transfected with pCDNA-PHBP1 or negative control. The PHB mRNA half-life by incubating Eca9706 cells (E) and TE-1 (F) transfected with pCDNA-PHBP1 or negative control with actinomycin D using qRT-PCR. (G) PHBP1transcript overlaps with 90% nucleotides of PHB mRNA indicated by vertical black lines (left). The blocks with colors indicate exons; Primer sites (F1: forward primer 1 and R1: reverse primer 1) in PHB mRNA represents the non-overlapping region between PHBP1 and PHB transcripts, and primer sites (F2: forward primer 2 and R2: reverse primer 2) indicates the overlapping region between PHBP1 and PHB transcripts. RT-PCR data depicted the detection of PHBP1 formed RNA duplex with PHB mRNA that protected PHB mRNA from RNase degradation (right) which digested the single-stranded RNA. PCR products were amplified using F1R1 and F2R2. The stability of PHB mRNA was examined by incubating Eca9706 cells (H) and TE-1 (I) transfected PHBP1 after 24h with α-amanitin (30mM) for 4, 8,12,16 and 24h compared with cells transfected with an empty vector; the red arrows indicated the time of α-amanitin added into the medium. Data are presented as mean±SD based on at least three independent experiments. *P<0.05, compared with negative control. Statistical analyses were performed using One-way ANOVA or two-tailed Student's t-test.
Expression patterns of PHB mRNA in ESCC tissue samples
Moreover, we also detected the expression levels of PHB in the same cohort of 63 ESCC tissue sample as described above. Similarly, PHB mRNA expression levels was significantly higher in 80% (36 of 41) tumor tissues than in noncancerous samples (P<0.05, Figure 3B). Interestingly, we found a similar concordant expression pattern of PHBP1 and PHB mRNA levels in the same samples, and PHBP1 levels and PHB mRNA levels were positively correlated in ESCC tissues (R2= 0.658, P<0.05; Figure 3C). These results implied that PHBP1 may activate PHB expression at both the RNA and protein levels.
The RNA stability of PHB was increased by PHBP1
We measured the PHB mRNA half-life by incubating cells with actinomycin D using qRT-PCR. The results showed that the transcript level and protein level of PHB was significantly increased in ESCC cells with PHBP1 overexpressed, compared with the controls (Figure 3D). Furthermore, the half-life of PHB mRNA was prolonged from 2.5 to 8h in ECa9706 cells and from 4 to 9h in TE-1 cells after actinomycin D treatment than in control cells (Figure 3E and 3F). These results imply that PHBP1 could increase PHB mRNA stability.
PHBP1 controls PHB mRNA stability by PHBP1/PHB duplex formation
Currently, as reported in several studies, numerous AS lncRNAs strongly co-expressed with their cognate mRNAs through forming duplex complexes, which is protected from ribonuclease resistant [33]. In addition, because of the perfectly complementary regions between the 90% nucleotides for PHBP1 and PHB mRNA (Figure 3G), we determined RNase protection assay (RPA) to explore whether PHBP1 could upregulates PHB transcription through forming a ribonuclease-resistant PHBP1/PHB protective duplex. As shown in Figure 3G, RT-PCR data using primers F1R1 (F1: forward primer 2 and R1: reverse primer 1) located the overlapping region between PHBP1 and PHB transcripts depicted the detection of PHBP1 formed RNA duplex with PHB mRNA that protected PHB mRNA from RNase A degradation. We further used the transcriptional inhibitor, α-amanitin to investigate the effect of PHBP1 on the stabilization or augmentation of PHB expression. Subsequent RT-PCR data revealed that PHB stability in ECa9706 and TE-1 cells overexpressing PHBP1 was increased after treated with α-amanitin (30mM) at 0h compared with cells transfected with an empty vector (Figure 3H and 3I), while RNA polymerase II expression was downregulated. Taken together, these data infer a role for PHBP1 in the stabilization of PHB expression by PHBP1 RNA/PHB mRNA heteroduplex formation of their perfectly complementary regions.
DISCUSSION
PHB gene, is a member of evolutionarily conserved family of membrane proteins, which plays essential roles in the regulation of human various pathophysiological processes and various cancers [34–36]. The role and the prognostic significance of PHB expression patterns suggest that it could be as a potential biomarker in human diseases, including particularly human cancers. PHBP1, which is transcribed in antisense orientation with respect to PHB and shared the high level of the nucleotide sequence identity with its cognate gene PHB. However, to date, the expressions and functions of PHBP1 in ESCC physiological functions remain obscure.
In this study, we investigated PHBP1 and PHB expression in an independent cohort of ESCC tissues and normal tissues. We found that the expression of PHBP1 and PHB were both higher in ESCC tissues, and PHBP1 expression was positively correlated with PHB in ESCC tissues. Clinical analysis showed that ESCC patients with higher PHBP1 expression tend to have advanced TNM stage. These findings indicate the abnormal expression of PHBP1 is linked to ESCC carcinogenesis.
aslncRNAs as one class of important heterogeneous lncRNAs transcribed in the opposite indirection with respect to one protein coding gene [37, 38]. They are defined as being complementary to one or more messenger RNA molecules [39]. Mounting lines of evidence have demonstrated that aslncRNAs have played essential regulatory roles in various biological processes [40, 41]. A growing studies also supports their importance in carcinogenesis and cancer development. So far, it is widely studied that aslncRNAs can activate or inhibit the expression of complementary coding genes at chromatin, transcriptional and post- transcriptional levels [42–45]. One example including promotion of the aggressive behaviors of colorectal carcinoma cells by FEZF1 antisense RNA1 (FEZF1-AS1), showed that FEZF1-AS1 could increase its corresponding cognate gene mRNA FEZF1 through regulating the transcription or mRNA stability of FEZF1 [26]. In this study, we investigated the biological functions of PHBP1 on ESCC tumorigenesis and the regulation mechanisms on its cognate gene PHB. Based on our results, we found that PHBP1 could activate its corresponding sense gene PHB. Mechanistically, actinomycin D assay provided evidences that PHBP1 prolonged PHB mRNA half-life. In addition, RPA further confirmed that PHBP1 could interact with PHB mRNA forming RNA duplex compound to induce PHB transcription and translation. Furthermore, subcellular location assay may provide clues regarding the possible molecular mechanism of PHBP1 exerting its biological function in cytoplasm as PHBP1 was predominantly located in cytoplasm of ESCC cell lines, similar to PHB. Both in vitro and in vivo data showed that the silence of PHBP1 induced cell cycle arrest at the G0–G1 phase and significantly inhibited proliferation and tumor growth of ESCC cells. Taken together, the effects of PHBP1 in aggressive phenotypes of ESCC, at least in part, dependent on the induction of PHB.
In summary, we provided a better understanding of the biology of ESCC carcinogenesis by PHBP1. We investigate that the PHBP1 was significantly upregulated in ESCC tissues and increased expression of PHBP1 might play a promotion role in ESCC carcinogenesis by binding to PHB mRNA forming RNA duplex, consequently inducing PHB mRNA stability and transcription. All of these findings illustrate the important roles of PHBP1 in ESCC carcinogenesis and the potential role of PHBP1 as a novel biomarker for ESCC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture
The human embryonic kidney cells 293T and the human ESCC cell lines (ECa9706 and TE-1) were purchased from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China), cultured in DMEM or RPMI 1640 medium with 10% fetal bovine serum (HyClone, Logan, USA), respectively. These cells were maintained at 37 °C in a humidified chamber with 5% CO2.
Animals’ model
4–6 weeks old female nude mices (20-25g/each) were obtained from Chinese Academy of Science Shanghai Experimental Animal Center and were maintained with food and water ad libitum. Protocol for animal experimentation was carried out in strict accordance with the laboratory animal care guidelines of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health.
Tissue preparation
63 paired ESCC tissues and adjacent normal tissues were collected from patients who were diagnosed with ESCC at Cancer Hospital, Peking Union Medical College and used in the investigation of clinicopathological and functional role of PHBP1. None of these subjects have received any treatment of ESCC, such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy before surgical resection preoperative. A comprehensive set of clinicopathological data were recorded, including age, gender, size of primary tumor, tumor differentiation and TNM stage. The clinical characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The stage of disease was determined according to the TNM classification system. The ages of all the patients ranged from 29 to 83 years, with a median age of 65 years and each patient signed the informed consent before donating the tissue specimens. And the study was also approved by the ethics committee of Cancer Hospital, Peking Union Medical College.
RNA isolation and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). For qRT-PCR, RNA (1μg) was used for cDNA synthesis by using a Reverse transcription kit (Takara, Dalian, China) according to the manufacturer's instructions. qRT-PCR analyses were carried out with SYBR Premix Ex Taq (Takara, Dalian China) in the ABI 7500 RT-PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA). Thermocycling parameters: 95°C for 20s followed by 45 cycles of 95°C for 10s and 60°C for 30s. The data was converted to fold change normalized to the expression level of GAPDH, which served as an endogenous control. For PHB mRNA stability analysis by qRT-PCR, 18s ribosomal RNA, a product of RNA polymerase I, was used as an internal control.
Subcellular fractionation
The procedure of nuclear and cytosolic fractions from ESCC cells were performed based on the manufacturer's instructions using the PARIS Kit (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The resulting supernatants and pellets were collected for the cytosolic fraction and nuclear fraction, respectively. Subsequently, the RNAs of cellular compartments were sequentially extracted and expression of PHBP1 or PHB was quantified by qRT-PCR.
Vector preparation and transfection of ESCC cells
The lentiviral vector PLVX containing PHBP1-shRNA (1# and 2#) or scrambled control sequence were synthesized by GenPharma (Shanghai, China) and were then packaged with pPACKH1 Lentivector Packaging Plasmid mix (System Biosciences) into 293T cells. Typically, ECa9706 cells and TE-1 cells were seeded at six-well plates for lentiviral transduction. Infected ESCC cells were selected by G418 to gain ESCC cells with stable knockdown of PHBP1. QRT-PCR was used to quantify the knockdown efficiency of PHBP1.
Western blotting analysis
The western blotting analysis procedures were performed as described as follows. Briefly, Total proteins extracted from transfected cells were subjected to the 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and then transfer to the nitrate cellulose (NC) membranes. The membrane was probed with specific antibody PHB overnight at 4°C, which were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc (CST). GAPDH antibody was used as control.
Actinomycin D assay
To detect the effect of PHBP1 on the stability of PHB mRNA, the PHBP1 transcript was synthesized and then subcloned into a pCNDA-3.1 vector (Invitrogen, Shanghai, China). For the Actinomycin D assay, the ESCC cells were planted in six-well plate before transfection. When ESCC cells were about 70% confluent, the pCDNA-PHBP1 or empty vector was transfected into ESCC cells using Lipofectamine 2000 reagent. After 24h, the transfected ESCC cells were cultured with Actinomycin D (Sigma) which was used to suppress transcription. After 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10h treatment, the cells were harvested and extracted total RNA to detect the half-life of PHB induced by PHBP1. The final concentration of actinomycin D was used at 5μg/ml.
RNase protection assay
Considering the overlapping region of the PHBP1 and its cognate transcript PHB, we performed RNase protection assay to test whether PHBP1 can form the RNA duplex with its cognate sense RNA, Briefly, total RNAs from ESCC cells transfected pCDNA-PHBP1 or empty vector were extracted and treated with the RNase A+T cocktail (Ambion) which digested the single-stranded RNA with increasing amounts. The remaining RNA duplexes were subjected to RT-PCR to detect PHBP1 and PHB employing two sets of primers to target the overlapping and non-overlapping part of PHBP1 and PHB transcripts.
Cell proliferation assays
For cell viability analyses, ECa9706 and TE-1 cells with stable knockdown of PHBP1 were plated in a 96-well plate at 2000 cells per well, maintained in RPMI1640 containing 10% FBS for 1, 2, 3 and 4 days. CCK-8 kit (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan) were conducted to measure the absorbance of the cells at OD 450nm every 24h, according to the manufacturer's instruction. The relative Cell viability rate was normalized with the value at day 0. All experiments were performed in triplicate. For colony formation assay, the indicated stable cells are seeded out in appropriate numbers in 60mm plates to form colonies. After two weeks, cell colonies are fixed with methanol, stained with 0.5% crystal violet and were counted normalized with the controls.
Cell cycle analysis
For cell cycle analysis, the indicated ESCC cells with stable overexpressed of PHBP1 were harvested and fixed with 70% ethanol. After the cells were stained with propidium iodide (Life Tecnologies) following the protocol, DNA content of the cells in G0/G1, S, and G2/M phase were qualified on FACS Calibur Flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences).
Xenograft experiment
For the in vivo tumor growth assay, a total of 100μL with 6×106 suspended ECa9706-shRNA-PHBP1, TE-1-shRNA-PHBP1 or shRNA-NC cells were injected into either side of the posterior flank of 5 weeks old BALB/c nude mices. Seven days after injection, the volumes of the subcutaneous tumor were measured every 3 days using the equation Volume=length×width2×0.5.
Statistical analyses
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois, USA). All cell biology assays performed in at least three independent experiments. Two-tailed Student's t-test or One-way ANOVA was used to assess the differences between variables among the groups. Pearson correlation test was performed to evaluate the association between the level of PHBP1 expression and PHB expression level. The data of experiments were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). P<0.05 was noted as statistical significance.
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 2013;381:400–412. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60643-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rustgi AK, El-Serag HB. Esophageal carcinoma. The New England journal of medicine. 2014;371:2499–2509. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1314530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhang J, Jiang Y, Wu C, Cai S, Wang R, Zhen Y, Chen S, Zhao K, Huang Y, Luketich J, Chen H. Comparison of clinicopathologic features and survival between eastern and western population with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of thoracic disease. 2015;7:1780–1786. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.10.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chuang WY, Chang YS, Chao YK, Yeh CJ, Liu YH, Tseng CK, Chang HK, Wan YL, Hsueh C. High sex determining region Y-box 2 (SOX2) expression correlates with absence of nodal metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. International journal of clinical and experimental pathology. 2015;8:9248–9255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhang W, Liu X, Xiao Z, Wang L, Zhang H, Chen D, Zhou Z, Feng Q, Hui Z, Liang J, Yin W, He J. Efficacy of intensity-modulated radiotherapy for resected thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Thoracic cancer. 2015;6:597–604. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kikuchi O, Ohashi S, Nakai Y, Nakagawa S, Matsuoka K, Kobunai T, Takechi T, Amanuma Y, Yoshioka M, Ida T, Yamamoto Y, Okuno Y, Miyamoto S, et al. Novel 5-fluorouracil-resistant human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells with dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase overexpression. American journal of cancer research. 2015;5:2431–2440. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. International journal of cancer. 2015;136:E359–386. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Birney E, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Dutta A, Guigo R, Gingeras TR, Margulies EH, Weng Z, Snyder M, Dermitzakis ET, Thurman RE, Kuehn MS, Taylor CM, Neph S, et al. Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature. 2007;447:799–816. doi: 10.1038/nature05874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Costa FF. Non-coding RNAs: Meet thy masters. Bioessays. 2010;32:599–608. doi: 10.1002/bies.200900112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brown CJ, Ballabio A, Rupert JL, Lafreniere RG, Grompe M, Tonlorenzi R, Willard HF. A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 1991;349:38–44. doi: 10.1038/349038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee JT, Davidow LS, Warshawsky D. Tsix, a gene antisense to Xist at the X-inactivation centre. Nat Genet. 1999;21:400–404. doi: 10.1038/7734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brannan CI, Dees EC, Ingram RS, Tilghman SM. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:28–36. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sotomaru Y, Katsuzawa Y, Hatada I, Obata Y, Sasaki H, Kono T. Unregulated expression of the imprinted genes H19 and Igf2r in mouse uniparental fetuses. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:12474–12478. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109212200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL, Xu X, Brugmann SA, Goodnough LH, Helms JA, Farnham PJ, Segal E, Chang HY. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2007;129:1311–1323. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang KC, Chang HY. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2011;43:904–914. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nagano T, Fraser P. No-nonsense functions for long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2011;145:178–181. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Clark MB, Mattick JS. Long noncoding RNAs in cell biology. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011;22:366–376. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen ZH, Hu HK, Zhang CR, Lu CY, Bao Y, Cai Z, Zou YX, Hu GH, Jiang L. Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA FOXD3 antisense RNA 1 (FOXD3-AS1) inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in malignant glioma cells. American journal of translational research. 2016;8:4106–4119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wu H, Zheng J, Deng J, Hu M, You Y, Li N, Li W, Lu J, Zhou Y. A genetic polymorphism in lincRNA-uc003opf.1 is associated with susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese populations. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:2908–2917. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Boopathi PA, Subudhi AK, Garg S, Middha S, Acharya J, Pakalapati D, Saxena V, Aiyaz M, Chand B, Mugasimangalam RC, Kochar SK, Sirohi P, Kochar DK, Das A. Dataset of natural antisense transcripts in P. vivax clinical isolates derived using custom designed strand-specific microarray. Genomics data. 2014;2:199–201. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2014.06.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Khorkova O, Myers AJ, Hsiao J, Wahlestedt C. Natural antisense transcripts. Human molecular genetics. 2014;23:R54–63. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rosikiewicz W, Makalowska I. Biological functions of natural antisense transcripts. Acta biochimica Polonica. 2016;63:665–673. doi: 10.18388/abp.2016_1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wight M, Werner A. The functions of natural antisense transcripts. Essays in biochemistry. 2013;54:91–101. doi: 10.1042/bse0540091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Su WY, Li JT, Cui Y, Hong J, Du W, Wang YC, Lin YW, Xiong H, Wang JL, Kong X, Gao QY, Wei LP, Fang JY. Bidirectional regulation between WDR83 and its natural antisense transcript DHPS in gastric cancer. Cell research. 2012;22:1374–1389. doi: 10.1038/cr.2012.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kohno K, Chiba M, Murata S, Pak S, Nagai K, Yamamoto M, Yanagisawa K, Kobayashi A, Yasue H, Ohkohchi N. Identification of natural antisense transcripts involved in human colorectal cancer development. International journal of oncology. 2010;37:1425–1432. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chen N, Guo D, Xu Q, Yang M, Wang D, Peng M, Ding Y, Wang S, Zhou J. Long non-coding RNA FEZF1-AS1 facilitates cell proliferation and migration in colorectal carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7:11271–11283. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhu XT, Yuan JH, Zhu TT, Li YY, Cheng XY. Long noncoding RNA GPC3-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via epigenetically activating GPC3. The FEBS journal. 2016;283:3739–3754. doi: 10.1111/febs.13839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sato T, Sakamoto T, Takita K, Saito H, Okui K, Nakamura Y. The human prohibitin (PHB) gene family and its somatic mutations in human tumors. Genomics. 1993;17:762–764. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhong N, Cui Y, Zhou X, Li T, Han J. Identification of prohibitin 1 as a potential prognostic biomarker in human pancreatic carcinoma using modified aqueous two-phase partition system combined with 2D-MALDI-TOF-TOF-MS/MS. Tumour biology. 2015;36:1221–1231. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2742-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Du MD, He KY, Qin G, Chen J, Li JY. Adriamycin resistance-associated prohibitin gene inhibits proliferation of human osteosarcoma MG63 cells by interacting with oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Oncology letters. 2016;12:1994–2000. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Salameh A, Daquinag AC, Staquicini DI, An Z, Hajjar KA, Pasqualini R, Arap W, Kolonin MG. Prohibitin/annexin 2 interaction regulates fatty acid transport in adipose tissue. JCI insight. 2016. p. 1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Wang Y, Liao H, Zheng HC, Li L, Jia L, Zhang Z, Zheng W. Effect of luteinizing hormone-induced prohibitin and matrix metalloproteinases on ovarian epithelial tumor cell proliferation. American journal of cancer research. 2015;5:114–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Michael DR, Phillips AO, Krupa A, Martin J, Redman JE, Altaher A, Neville RD, Webber J, Kim MY, Bowen T. The human hyaluronan synthase 2 (HAS2) gene and its natural antisense RNA exhibit coordinated expression in the renal proximal tubular epithelial cell. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2011;286:19523–19532. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.233916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sato T, Saito H, Swensen J, Olifant A, Wood C, Danner D, Sakamoto T, Takita K, Kasumi F, Miki Y, et al. The human prohibitin gene located on chromosome 17q21 is mutated in sporadic breast cancer. Cancer research. 1992;52:1643–1646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mishra S, Murphy LC, Nyomba BL, Murphy LJ. Prohibitin: a potential target for new therapeutics. Trends in molecular medicine. 2005;11:192–197. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2005.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chen D, Chen F, Lu X, Yang X, Xu Z, Pan J, Huang Y, Lin H, Chi P. Identification of prohibitin as a potential biomarker for colorectal carcinoma based on proteomics technology. International journal of oncology. 2010;37:355–365. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mahmoudi S, Henriksson S, Corcoran M, Mendez-Vidal C, Wiman KG, Farnebo M. Wrap53, a Natural p53 Antisense Transcript Required for p53 Induction upon DNA Damage. Molecular cell. 2016;64:1009. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.11.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.He Y, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE, Papadopoulos N, Kinzler KW. The antisense transcriptomes of human cells. Science. 2008;322:1855–1857. doi: 10.1126/science.1163853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Werner A, Carlile M, Swan D. What do natural antisense transcripts regulate? RNA biology. 2009;6:43–48. doi: 10.4161/rna.6.1.7568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Stojic L, Niemczyk M, Orjalo A, Ito Y, Ruijter AE, Uribe-Lewis S, Joseph N, Weston S, Menon S, Odom DT, Rinn J, Gergely F, Murrell A. Transcriptional silencing of long noncoding RNA GNG12-AS1 uncouples its transcriptional and product-related functions. Nature communications. 2016;7:10406. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chan J, Atianand M, Jiang Z, Carpenter S, Aiello D, Elling R, Fitzgerald KA, Caffrey DR. Cutting Edge: A Natural Antisense Transcript, AS-IL1alpha, Controls Inducible Transcription of the Proinflammatory Cytokine IL-1alpha. Journal of immunology. 2015;195:1359–1363. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Vigetti D, Deleonibus S, Moretto P, Bowen T, Fischer JW, Grandoch M, Oberhuber A, Love DC, Hanover JA, Cinquetti R, Karousou E, Viola M, D’Angelo ML, et al. Natural antisense transcript for hyaluronan synthase 2 (HAS2-AS1) induces transcription of HAS2 via protein O-GlcNAcylation. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2014;289:28816–28826. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.597401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhu XT, Yuan JH, Zhu TT, Li YY, Cheng XY. Long noncoding RNA glypican 3 (GPC3) antisense transcript 1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via epigenetically activating GPC3. The FEBS journal. 2016;283:3739–3754. doi: 10.1111/febs.13839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Matsui K, Nishizawa M, Ozaki T, Kimura T, Hashimoto I, Yamada M, Kaibori M, Kamiyama Y, Ito S, Okumura T. Natural antisense transcript stabilizes inducible nitric oxide synthase messenger RNA in rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2008;47:686–697. doi: 10.1002/hep.22036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang GQ, Wang Y, Xiong Y, Chen XC, Ma ML, Cai R, Gao Y, Sun YM, Yang GS, Pang WJ. Sirt1 AS lncRNA interacts with its mRNA to inhibit muscle formation by attenuating function of miR-34a. Scientific reports. 2016;6:21865. doi: 10.1038/srep21865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


