Abstract
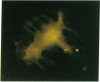
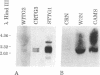
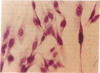
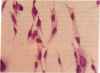
We have identified human cultured cell lines that are useful for studying angiotensinogen gene expression and its regulation in the central nervous system. A model cell system of human central nervous system origin expressing angiotensinogen has not previously been available. Expression of angiotensinogen has not previously been available, Expression noninduced human astrocytes, since astrocytic cell lines derived from human glioblastomas or nonneoplastic human brain tissue invariably produced angiotensinogen mRNA. In situ hybridization histochemistry revealed that angiotensinogen mRNA production was not limited to a subpopulation of astrocytes because greater than 99% of cells in these cultures contained angiotensinogen mRNA. These cell lines will be useful in studies of the molecular mechanisms controlling angiotensin synthesis and the role of biologically active angiotensin in the human brain by allowing us to examine regulation of expression of the renin-angiotensin system in human astrocyte cultures.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barna B. P., Chou S. M., Jacobs B., Ransohoff R. M., Hahn J. F., Bay J. W. Enhanced DNA synthesis of human glial cells exposed to human leukocyte products. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Dec;10(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(85)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Dahl D. Astrocyte-specific protein and neuroglial differentiation. An immunofluorescence study with antibodies to the glial fibrillary acidic protein. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Jan 1;153(1):27–38. doi: 10.1002/cne.901530104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block C. H., Santos R. A., Brosnihan K. B., Ferrario C. M. Immunocytochemical localization of angiotensin-(1-7) in the rat forebrain. Peptides. 1988 Nov-Dec;9(6):1395–1401. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham C. E., Hawelu-Johnson C. L., Frank B. M., Lynch K. R. Molecular cloning of rat renin cDNA and its gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5605–5609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clauser E., Gaillard I., Wei L., Corvol P. Regulation of angiotensinogen gene. Am J Hypertens. 1989 May;2(5 Pt 1):403–410. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.5.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschepper C. F., Bouhnik J., Ganong W. F. Colocalization of angiotensinogen and glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes in rat brain. Brain Res. 1986 May 21;374(1):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagami T., Clemens D. L., Hirose S., Okamura T., Naruse K., Takii Y., Yokosawa H. Brain renin. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1982;4(4-5):607–622. doi: 10.3109/10641968209061602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Primary structure of human preangiotensinogen deduced from the cloned cDNA sequence. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3603–3609. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Norenberg M. D. Astrocytes. Sci Am. 1989 Apr;260(4):66-72, 74, 76. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0489-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Rassoli A., Raizada M. K. Angiotensinogen gene expression in neuronal and glial cells in primary cultures of rat brain. J Neurosci Res. 1988 Mar;19(3):287–290. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490190302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind R. W., Swanson L. W., Ganten D. Organization of angiotensin II immunoreactive cells and fibers in the rat central nervous system. An immunohistochemical study. Neuroendocrinology. 1985 Jan;40(1):2–24. doi: 10.1159/000124046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. R., Hawelu-Johnson C. L., Guyenet P. G. Localization of brain angiotensinogen mRNA by hybridization histochemistry. Brain Res. 1987 Jul;388(2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(87)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milsted A., Silver B. J., Cox R. P., Nilson J. H. Coordinate regulation of the messenger ribonucleic acids encoding the alpha- and beta-subunits of human chorionic gonadotropin in HeLa cells and butyrate-resistant variants. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):2033–2039. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-2033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilson J. H., Nejedlik M. T., Virgin J. B., Crowder M. E., Nett T. M. Expression of alpha subunit and luteinizing hormone beta genes in the ovine anterior pituitary. Estradiol suppresses accumulation of mRNAS for both alpha subunit and luteinizing hormone beta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12087–12090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raizada M. K. Localization of insulin-like immunoreactivity in the neurons from primary cultures of rat brain. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Feb;143(2):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raizada M. K., Stenstrom B., Phillips M. I., Sumners C. Angiotensin II in neuronal cultures from brains of normotensive and hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 1):C115–C119. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.247.1.C115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soubrier F., Alhenc-Gelas F., Hubert C., Allegrini J., John M., Tregear G., Corvol P. Two putative active centers in human angiotensin I-converting enzyme revealed by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9386–9390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stornetta R. L., Hawelu-Johnson C. L., Guyenet P. G., Lynch K. R. Astrocytes synthesize angiotensinogen in brain. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1444–1446. doi: 10.1126/science.3201232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumners C., Raizada M. K. Catecholamine-angiotensin II receptor interaction in primary cultures of rat brain. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):C502–C509. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.5.C502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. G., Sernia C. Immunocytochemical localization of angiotensinogen in the rat brain. Neuroscience. 1988 Apr;25(1):319–341. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Mezey E., Siegel R. E. Vasopressin and oxytocin mRNAs in adrenalectomized and Brattleboro rats: analysis by quantitative in situ hybridization histochemistry. Brain Res. 1986 Dec;387(3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]