Abstract
Given the important role that inhibitory kappa B (IκB) kinase β (IKKβ) plays in pancreatic cancer (PC) development and progression, inhibitors targeting IKKβ are believed to be increasingly popular as novel anti-PC therapies. Two synthetic molecules, named EF24 and EF31, exhibited favorable potential in terms of inhibition of both IKKβ activity and PC cell proliferation. Aiming to enhance their cellular efficacy and to analyze their structure–activity relationship, four series of EF24 and EF31 analogs were designed and synthesized. Through kinase activity and vitality screening of cancer cells, D6 displayed excellent inhibition of both IKKβ activity and PC cell proliferation. Additionally, multiple biological evaluations showed that D6 was directly bound to IKKβ and significantly suppressed the activation of the IKKβ/nuclear factor κB pathway induced by tumor necrosis factor-α, as well as effectively inducing cancer cell apoptosis. Moreover, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation analysis indicated that the dominant force between D6 and IKKβ comprised hydrophobic interactions. In conclusion, D6 may be a promising therapeutic agent for PC treatment and it also provides a structural lead for the design of novel IKKβ inhibitors.
Keywords: anti-pancreatic cancer activity, IκB kinase β, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation
Introduction
PC is currently one of the most devastating malignant neoplasms.1,2 According to statistics, it has been estimated that the number of new cases of Americans diagnosed with PC was 53,070 in 2016, and 41,780 people had died of this disease.3 The overall 5-year survival rate of PC patients is ~7%.3 For patients with advanced disease, this figure is worse, as low as 1%.4 Due to the highly nonspecific incipient symptoms, 80%–85% of patients diagnosed with PC already were in the advanced and metastatic stages and not suited for surgical resection.5 Thus, chemotherapy becomes the principal remedy for patients with advanced PC. As the only standard first-line therapy for advanced PC patients, GEM, a conventional cytotoxic drug, exerts favorable anticancer action by breaking down the deoxynucleotide metabolism of PC cells.6,7 However, the increasing occurrence of acquired resistance by PC cells and the nonselective cytotoxicity to normal cells led to the outcomes of GEM monotherapy being extremely poor.8–10 Currently, various combination therapeutic regimens have been assessed in clinical or preclinical practice in the hope of overcoming the intricate mechanism of resistance.11,12 Unfortunately, this approach is also more likely to increase the incidence of toxic effects, such as irreversible myelosuppression and gastrointestinal adverse reactions.13 Thus, development of new targeted therapies for PC is highly urgent and crucial. Of the proteins closely related to the formation and progress of PC, IKKβ is considered to be an important potential target.14,15
The IKK family consists of a series of four enzymes (IKKα, IKKβ, IKKγ, and IKKε).16 IKKβ is the predominant catalytic subunit mediating the classic IKK/NF-κB pathway, and it contains an N-terminal KD, a central ULD, and a C-terminal SDD structurally.17 Following extracellular stimulations (stress, cytokines, and free radicals), IKKβ KD becomes phosphorylated, resulting in the phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and separation of the IκB/NF-κB complex, allowing the release and translocation of NF-κB into the nucleus to regulate multiple key genes involved in cell oncogenesis, inflammation, and apoptosis.18–21 In recent years, numerous studies have documented that constitutive activation of NF-κB triggered by deregulation of IKKβ occurs in almost all PC specimens, as well as in various PC cell lines.14,22,23 For example, Ling et al24 noted that IKKβ-mediated NF-κB activation is highly required for development of PDAC, and pancreas-targeted IKKβ inactivation inhibited both NF-κB activation and PDAC tumorigenesis. Accumulating evidence suggests that aberrant IKKβ activity intensively contributes to pancreatic tumorigenesis by triggering the production of many antiapoptotic and proliferation-related molecules that NF-κB regulates, such as Bcl-xL, cIAP, cyclin D1, KU70, and KU80.25,26 Moreover, the IKKβ/NF-κB pathway is a versatile and complicated pathway that is widely associated with other pivotal signal proteins (Ras, MAPKs, GSK-3β, and Notch), which may activate IKKβ/NF-κB in a bypass manner and promote carcinogenesis as an accomplice.22,24,27 Wilson and Baldwin22 reported that GSK-3α/β upregulated the activity of IKKβ to promote the survival of PANC-1 and MiaPaCa-2 cells (two human PC cell lines). All these reports reveal that exploiting effective IKKβ inhibitors could be an advisable approach for the treatment of PC.
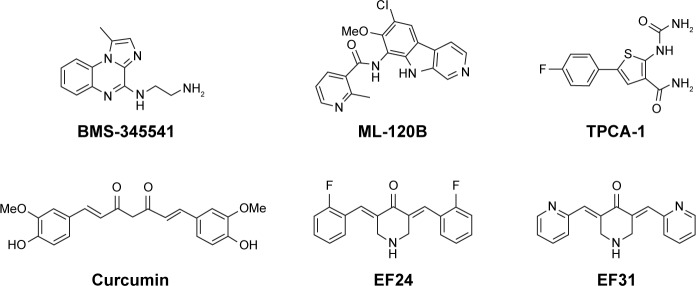
Given the important therapeutic potential of IKKβ inhibitors for treating PC, numerous selective IKKβ inhibitors have been discovered, including BMS-345541, ML-120B, and TPCA-1, the IC50 values of which were 300, 45, and 18 nM, respectively (Figure 1).28–30 Nonetheless, no small-molecule IKKβ inhibitor has been approved for clinical applications so far.31 Part of the reason for these inhibitors possessing excellent enzymatic inhibitory activity but failing in the preclinical trials is their poor metabolism and severe toxicity to normal cells. CUR, a well-known anticancer compound derived from turmeric, has become the research hotspot of natural products and drug candidates in recent years due to its inhibition of multiple targets highly related to cancer, such as IKKβ, STAT-3, and PKC, as well as its nontoxicity (Figure 1).32,33 However, the low biostability of CUR dramatically restrains its clinical application. By screening a large number of CUR analogs, two more stable and effective analogs of CUR, named as EF24 and EF31 (Figure 1), were discovered successively, the IC50 values of which against IKKβ were 1.9 and 1.92 μM, respectively.34,35 In addition, EF24 and EF31 also exhibited striking inhibition of PC cells.36,37 Although the favorable suppression effect of EF24 and EF31 against IKKβ and PC cells attracted much researcher interest, surprisingly, there is still no systematic medicinal chemistry research on EF24 and EF31 analogs.
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of some reported IKKβ inhibitors.
Abbreviation: IKKβ, inhibitory kappa B kinase β.
In this research, aiming to screen more potent anti-PC agents, and to build a valid pharmacophore model of EF24-and EF31-based inhibitors, four (A–D) series of analogs with EF24 and EF31 as the lead compounds were designed and synthesized. Through kinase activity screening and SPR analysis, D6 was found to be a direct inhibitor of IKKβ. Molecular docking and MD stimulation studies were performed to estimate the key interactions between D6 and IKKβ KD. Further, the biological evaluation results indicated that D6 has the potential to be developed as an anti-PC drug.
Materials and methods
General procedure for the synthesis of compounds
All chemical reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co., St Louis, MO, USA, Aladdin, or Alfa Aesar and used without purification. Silica gel (GF254) for TLC and column chromatography (200–300 mesh) was obtained from Aladdin. Melting points were determined on an uncorrected X4 microscopic melting point meter (Shanghai Instrument Physical Optics Instrument Co, Shanghai, China). 1H-NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker 500 MHz Avance DRX spectrometer (UC Davis NMR Facility, 4303 Tupper Hall, Davis, CA, USA). The chemical shifts are presented in terms of parts per million with tetramethylsilane as the internal reference. Data of ESI-MS in positive mode were recorded on a Waters TQ-S micro-mass spectrometer (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA). All the synthesized compounds have at least 95% purity as assessed by HPLC, which was performed on an Agilent 1200 device (Agilent Technologies Co. Ltd, Wang Jing Bei Road, Beijing, China) with a flow rate of 1 mL/min and a gradient of 50%–60% (v/v) MeOH in H2O using a diode array detector. A ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 column (4.6 ×150 mm, 5 μM; Agilent) was used. The spectral characterization information (NMR, MS, and HPLC data) and parts of representative original spectrums are displayed in the Supplementary materials.
Target compounds were obtained through a one-step Claisen-Schmidt condensation reaction taking 4-piperidone monohydrate hydrochloride and various substituted aromatic aldehydes as starting materials. The experimental procedure is summarized in brief. The corresponding benzaldehyde (4 mmol) and 4-piperidone monohydrate hydrochloride (2 mmol) were dissolved in a mixture of absolute ethanol (18 mL) and distilled water (2 mL). Aqueous NaOH (40%, 1 mL) was added dropwise with stirring in an ice water bath (0–4°C). The reaction temperature was gradually elevated to room temperature. After completion of the reaction as monitored by TLC (up to 4–24 h), distilled water (20 mL) was poured into it, resulting in the product being precipitated totally. After filtration, the residues were purified by column chromatography using appropriate ratio of PE/EA or DCM/MeOH as eluent.
Screening for IKKβ inhibition
The kinase activity of IKKβ was determined by mobility shift assay on a Caliper Life Sciences Labchip EZ Reader. The enzyme solution was prepared in a 1.25× kinase base buffer (62.5 mM HEPES, 0.001875% Brij-35, 12.5 mM MgCl2, and 2.5 mM DTT). Stop buffer (100 mM HEPES, 0.015% Brij-35, 0.2% coating reagent No 3, and 50 mM EDTA) was prepared. Then, 5 μL of the test compounds at 100 μM in 10% DMSO was diluted with 10 μL of 2.5× enzyme solution in a 384-well assay plate and incubated at room temperature for 10 min. Moreover, 10 mM EDTA was used as the low control. Then, 10 μL of peptide solution was added into each well. After incubation at 28°C for 1 h, 25 μL of stop buffer was added into the mixture to stop the reaction. Conversion data were then collected on the EZ reader automatically, and the percentage inhibition was calculated relative to blank wells (containing no enzyme and 1%, v/v, DMSO) and total wells (containing all reagents and 1%, v/v, DMSO). The conversion formula used is as follows:
| (1) |
“Max” stands for the DMSO control, “Min” stands for low control, and “conversion” means the average of three experimental values given by the EZ reader.
To determine the IC50 of the test compounds relative to kinase activity, ten gradient concentrations of the compounds (100, 33.330, 11.110, 3.700, 1.230, 0.410, 0.140, 0.046, 0.015, and 0.005 μM) were set up. The inhibition ratios for different concentrations were determined and calculated, and the concentration−inhibition rate curve was fit using the GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA).
SPR analysis
SPR experiments were performed on a ProteOn XPR36 Protein Interaction Array system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). All solutions used in the experiment were prepared with ultrapure water, filtered with a 0.22-μM membrane filter before use. IKKβ solution in PBST (5 mM, pH 7.4) at a concentration of 1 mg/mL was diluted to 30 μg/mL with sodium acetate buffer (pH 4.5). The chip was activated with EDC/NHS (10 μL/min for 600 s). Then, IKKβ was loaded (5 μL/min for 400 s) and immobilized covalently. Approximately 8,000 RU of IKKβ was immobilized on the chip. Any excess of unbound IKKβ was removed by flowing PBS solution (5 mM, pH 7.4, with 5%, w/v, DMSO). D6 was prepared as 20–100 μM solution in PBS solution (5 mM, pH 7.4, with 5%, w/v, DMSO), and injected (10 μL/min for 100 s). After each loading, data were collected and analyzed with the ProteOn manager software (Bio-Rad Laboratories).
Molecular docking
Molecular docking analysis was carried out by the latest version of AutoDock 4.2.6 package.38 AutoDock is a flexible docking program, which is based on the fundamental principle of LGA. The coordinates of human IKKβ (PDB ID: 4KIK) were downloaded from the PDB.39 In the preliminary step of the protein preparation, AutoDock4 atomic radii and Gasteiger partial charges were assigned to the protein and ligands. The scoring grid dimensions of 60×60×60 Å were assigned using the AutoGrid module with grid spacing of 0.375 Å. The docking parameters were as follows: 200 conformations were generated, which were clustered according to the RMSD tolerance of 1.5 Å, population size of 300, maximum number of evaluations 25,000,000, and other settings were set at the default parameters. A reasonable pose with best-predicted binding affinity of D6 was selected for detailed analysis and further studies.
MD simulation
Preparation of structures
The reasonable pose was used as the initial structure for MD simulations. Prior to MD simulations, the electrostatic potentials of D6 were computed by the HF/6-31G* level of theory in Gaussian09 program. Then the atomic partial charges were obtained by fitting the electrostatic potentials using the RESP fitting technique. The generation of the partial charges and the force field parameters for D6 was accomplished using the antechamber program in Assisted Model Building with Energy Refinement (AMBER; USA)-14 simulation package.40 In the MM optimizations, ff99SB force field and gaff force field were used for IKKβ and D6, respectively. The complex was solvated in a box of TIP3P water molecules with a 10 Å distance between the protein surface and the box boundary. Moreover, the counterions of Na+ were added to neutralize the systems.
Molecular minimizations and conventional MD simulations
Before the MD productive simulation, we carried out an equilibration protocol. The geometry of the system was minimized in two steps before MD simulation. First, the water molecules were refined through 2,500 steps of steepest descent, followed by 2,500 steps of conjugate gradient, keeping the protein fixed with harmonic restraints of 5.0 kcal mol−1 Å−2. Second, the complexes were relaxed by 5,000 cycles of minimization procedure (2,500 cycles of steepest descent and 2,500 cycles of conjugate gradient minimization). Then, the whole system was heated from 0 to 300K running 100 ps MD with position restraints at constant volume. Subsequent isothermal–isobaric ensemble (NPT)-MD was performed for 100 ps to adjust the solvent density with a time constant of 1.0 ps for pressure relaxation. Harmonic restraints with force constants of 1 kcal mol−1 Å−2 were applied to IKKβ and D6. An additional 100 ps of unconstrained NPT-MD at 300K with a time constant of 2.0 ps for pressure relaxation was performed to relax the system without constraints. Finally, the system was submitted to 60 ns MD simulation. During simulation, the pressure and temperature were maintained using the Langevin temperature scalings.41 SHAKE constraints were applied to all bonds involving hydrogen.42 In addition, periodic boundary conditions and electrostatic interactions were treated using the particle mesh Ewald algorithm with cutoff of 10 Å.43 Conformational snapshots were saved every 10 ps for further analysis.
MM/GBSA binding free energy calculations
The MM/GBSA method has been widely used for free energy calculation and to investigate the energy contributions of each residue to binding.32,45 The basic theory of the MM/GBSA approach is that the free energy of binding can be obtained through calculating only the end points of the thermodynamic cycle of ligand binding. The binding free energies (ΔGbind) were calculated based on the 200 snapshots evenly extracted from 50 ns to 60 ns according to the following equations:
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
In Equation (2), the free binding energy ΔGbind was calculated as a sum of the three terms in Equation (3). ΔEMM and ΔGsolv represent the MM interaction energy and solvation energy, respectively. TΔS represents the change of the conformational entropy upon ligand binding at temperature T. For Equation (4), ΔEMM can be decomposed into three components: intermolecular interaction energy (ΔEint), van der Waals energy (ΔEvdW), and electrostatic energy (ΔEele); for Equation (5), the value of the solute’s dielectric constant was used as the default (ε=1) for both the polar solvation energies (ΔGGB), and we used a value of 80 for the exterior dielectric constants. The nonpolar part (ΔGSA) was estimated by the LCPO method: ΔGSA=0.0072×ΔSASA.
Cell culture
Three pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines, PANC-1, MiaPaCa-2, and BxPC-3 (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA), were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Sigma-Aldrich Canada, Mississauga, ON, Canada) supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS standard (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and 10 mg/mL gentamicin (Gibco BRL, VWR, Mississauga, ON, Canada).
MTT cell proliferation assay
Three pancreatic cancer cell lines (5,000 cells per well) were seeded on a 96-well plate. After incubation overnight, cells were treated with different concentrations (0, 0.080, 0.400, 2.000, 10.000, and 50.000 μM) of the test compounds. After 72 h incubation, 25 μL of MTT (5 mg/mL; Sigma) was added to each well for 4 h at 37°C in the dark. Next, 150 μL of DMSO was added to each well to solubilize the MTT metabolic product and the absorbance was read at 490 nm.
Western blot analysis
PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells (treated with the test compound after 24 h starvation, and then stimulated with 1 ng/mL TNF-α for 30 min) were lysed in a lysis buffer for 15 min on ice. The cell lysates were centrifuged at 4°C to remove insoluble components. Protein (80 μg) from each sample was subjected to SDS-PAGE and transferred onto PVDF membranes (Bio-Rad Laboratories). After incubation with 5% skim milk in TBST for 1.5 h, the membranes were incubated with primary antibodies (pIKKβ, IκB, cleaved PARP, bcl-2, and GAPDH; Santa Cruz) at 4°C overnight and then with the horseradish peroxidase-labeled secondary antibody at room temperature for 1 h. The results were visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence reagents (Bio-Rad Laboratories), and the band densities were quantified using ImageJ analysis software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Hoechst staining
For qualitative measurement of apoptosis, PANC-1 cells were seeded in six-well plates and incubated with the test compounds for 12 h. Furthermore, cells were stained with Hoechst 33342 according to the protocol provided with the kit (Beyotime Biotech, Nantong, China). Micrographs of all groups were taken using a fluorescence microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) with a 200× objective lens.
Statistical analysis
The results are presented as mean values ± standard deviation. Student’s t-test and a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to analyze the differences between sets of data. Statistics were analyzed using GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad). A P-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant. All in vitro experiments were repeated at least three times.
Results
Chemistry
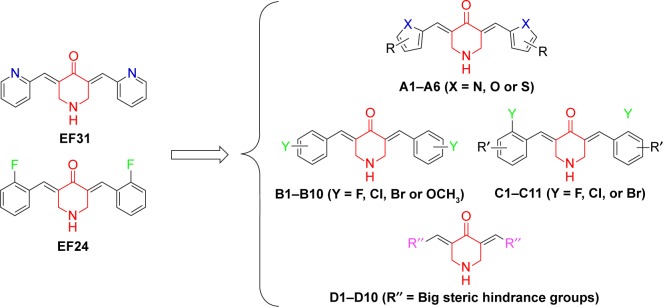
We observed that EF24 and EF31 shared the same 4-piperidone middle linker, which may have an important influence on their inhibitory effects. Hence, we designed four series of compounds with the framework of diarylidenepiperidin-4-one. The “A” series of compounds is obtained by changing the pyridine of EF31 into different five-membered heterocycles (Scheme 1). The strategy for “B” and “C” series of compounds was altering the 2-F phenyl of EF24 into other monosubstituted (B) or bis-substituted (C) phenyl groups. Considering that the EF24 and EF31 molecules were much smaller relative to the ATP-binding pocket of IKKβ, we hypothesized that introducing some big steric hindrance groups may effectively utilize the spare residues in the deep pocket to form more helpful interactions, which generated the “D” series of compounds.
Scheme 1.
The design of (A–D) series of derivatives of EF24 and EF31.
Through a classical Claisen-Schmidt condensation reaction, the A–D series compounds were synthesized (yield varied from 30% to 80%). The synthesis route is shown in Figure 2, and their molecular structures, which were confirmed by MS and proton NMR (1H-NMR) spectroscopy, are shown in Figure 3. As the purity is important to the structural character and also to the bioactivity, all the synthetic compounds were analyzed by HPLC to ensure that they were adequately pure for use in biological experiments (purity ≥95%).
Figure 2.
General synthesis route for the four series of compounds.
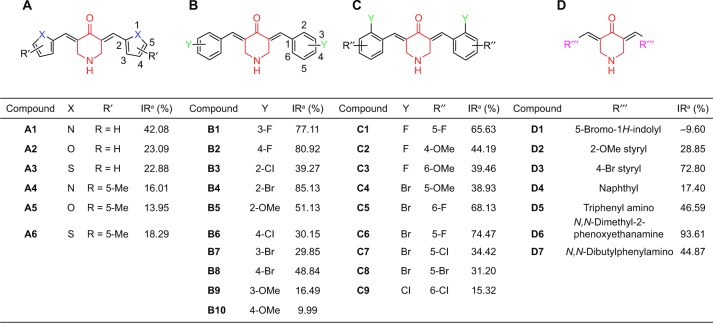
Figure 3.
Inhibition of IKKβ kinase by the (A–D) series of analogs of EF24 and EF31 at a concentration of 20 μM was screened through a Caliper mobility shift assay.
Note: IRa refers to the inhibitory ratio of the measured compounds at a concentration of 20 μM.
Abbreviations: IKKβ, inhibitory kappa B kinase β; IR, inhibitory ratio; Me, methyl; OMe, methoxy.
Screening for inhibition of IKKβ kinase activity and preliminary analysis of the structure–activity relationship
The four series of analogs of EF24 and EF31 were initially screened for inhibition of IKKβ kinase activity at a concentration of 20 μM by a mobility shift assay. As shown in Figure 3, compounds B1, B2, B4, C6, D3, and D6 exhibited considerable kinase inhibition (IR >70%). Based on our past experience, these six compounds with IR >70% were expected to be active inhibitors of IKKβ kinase. By determination of IC50, D6 showed the strongest IKKβ inhibition (IC50 =0.8 μM, Figure 3), while both the other compounds had lower values than EF31 and EF24.
According to the screening results, several preliminary points of structure–activity relationship can be summarized. First, altering the pyridine ring into five-membered heterocycles resulted in the original activity almost diminishing in the “A” series compounds, suggesting that the pyridinyl, or at least, the hexatomic ring of EF31 may be a pivotal moiety for the maintenance of its inhibitory conformation. In addition, in the “B” and “C” series compounds, the results showed that halogen-substituted analogs of EF24 indeed are more effective than the methoxyl-substituted ones, indicating that introducing an electron-withdrawing group may be more useful to enhance activity. In the last series, it is difficult to conclude the structure–activity relationship, which needs to be investigated after more compounds are synthesized.
Direct binding demonstration, molecular docking, and MD simulation of D6
SPR experiments were performed to evaluate the direct binding between D6 and IKKβ. As shown in Figure 4, the SPR response value was observed to increase gradually with elevated ZCL278 concentrations and a low equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) of 22.2 μM was obtained. Combined with its excellent kinase inhibition, it could be concluded that D6 was very likely to be a direct, high-affinity binding inhibitor of IKKβ.
Figure 4.
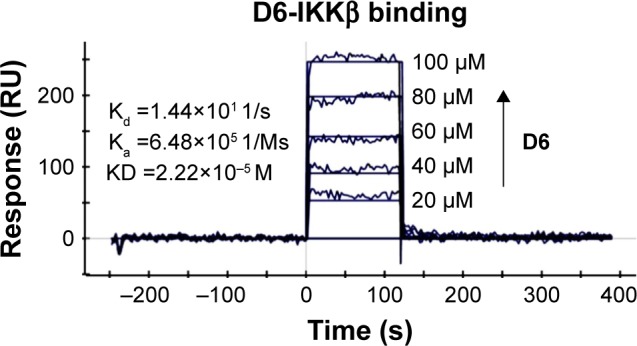
Direct-binding affinity between D6 and IKKβ demonstrated by SPR. Note: Ka, Kd, equilibrium dissociation constant.
Abbreviations: IKKβ, inhibitory kappa B kinase β; KD, kinase domain; RU, response units; SPR, surface plasmon resonance.
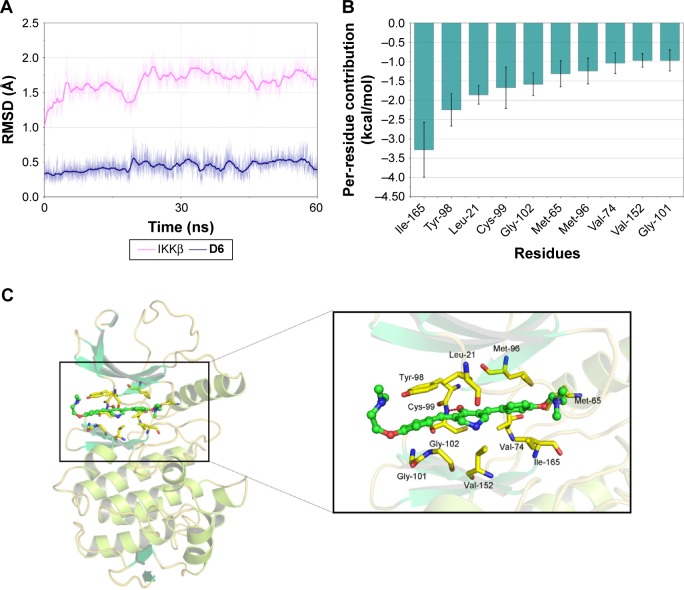
To further clarify the interactions between D6 and IKKβ KD, molecular docking and MD simulation studies of IKKβ/D6 were carried out. Initially, we docked D6 into the IKKβ KD based on a human IKKβ crystal structure for reference (PDB code: 4KIK). The optimum docking results were chosen as the initial structures for MD simulation. The detailed RMSD of the receptor in the IKKβ/D6 complex was converged after 20–30 ns in 60 ns MD simulations with the backbone RMSD of ~1.7 Å for IKKβ and ~0.4–0.5 Å for D6, suggesting that the IKKβ/D6 complex became sufficiently stable through 60 ns MD simulations (Figure 5A).
Figure 5.
Molecular docking and MD simulation analysis of binding of D6 to the activity cavity of IKKβ.
Notes: (A) Backbone RMSDs are shown as a function of time for IKKβ/D6 in 60 ns MD simulation. (B) Per-residue value of the top ten contributions to the binding effective energy of D6. Per-residue contributions were calculated by the MM-GBSA decomposition method. (C) Last snapshot of IKKβ/D6 in 60 ns MD simulation.
Abbreviations: IKKβ, inhibitory kappa B kinase β; MD, molecular dynamics; MM-GBSA, molecular mechanics/generalized Born surface area; RMSD, root-mean-square deviation.
To illuminate the roles of the individual residues in determining the interactions between IKKβ and D6, the MM/GBSA method was used to analyze the contributions of each residue. It can be observed that the most contributing residues are Ile-165, Tyr-98, Leu-21, Cys-99, Gly-102, Met-65, Met-96, Val-74, Val-152, and Gly-101 (Figure 5B). Except for Tyr-98, the other nine residues are hydrophobic amino acids. The MD simulation results (Figure 5C) intuitively exhibit that the backbone of D6 was interposed into a hydrophobic cleft developed by the above nine hydrophobic amino acids. The left phenyl ring of D6 formed p–p stacking with the benzene side chain of Tyr-98 to stabilize the binding conformation, and another phenyl ring generated hydrophobic contacts with the residues Met-96, Met-65, Ile-165, and Val-74. Moreover, the bilateral dimethylamino ethoxy long chain of D6 was oriented toward the outside solvent areas of the protein, which can be explained by the fact that the ligand and receptor underwent a conformational change to accommodate each other and reach the optimal binding mode (induced-fit phenomenon). To further validate our simulated result, the cocrystallization assay of IKKβ/D6 is still under way. In short, a critical hydrophobic interaction was clarified as the underlying mechanism of D6 and IKKβ KD interaction.
D6 suppresses the growth of PC cell lines
Numerous studies support the concept that the constitutive activation of the IKK/NF-κB pathway promotes growth and development in a number of different cancers, including PC.26,46 The antiproliferative effect of the four IKKβ kinase inhibitors (IKKβ IC50 <10 μM; B1, B2, B4, and D6) on the three PC cell lines was determined using the MTT assay. The PC cell lines were treated with varying concentrations of four inhibitors, their leads EF24 and EF31, or CUR for 72 h. Among all the compounds tested, D6 exhibited the greatest inhibitory activity in the PANC-1 and MiaPaCa-2 cell lines, the IC50 values being lower than those for EF24 and EF31 (Table 1). The growth inhibition by D6 in BxPC-3 was slightly weaker than that by EF31, but much better than that by EF24. This result denoted that D6 is a promising anti-PC agent in vitro.
Table 1.
Six compounds (B1, B2, B4, C6, D3, D6, and CUR) were selected for determining the IC50 values of IKKβ kinase activity, and the active compounds B1, B2, B4, and D6 (IKKβ IC50 <10 μM) were further measured for the antiproliferative effects in three PC cell lines (PANC-1, MiaPaCa-2, and BxPC-3) by the well-established MTT assay
| Compound | IC50 (µM)
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IKKβ | PANC-1 | MiaPaCa-2 | BxPC-3 | |
| B1 | 8.9±1.1 | 12.8±6.9 | 11.8±1.8 | 21.5±13.3 |
| B2 | 5.6±0.5 | 9.6±2.7 | 10.6±4.3 | 12.0±0.9 |
| B4 | 3.4±1.4 | 8.2±0.9 | 6.3±1.3 | 5.2±1.1 |
| C6 | 12.4±5.6 | NDa | NDa | NDa |
| D3 | >20 | NDa | NDa | NDa |
| D6 | 0.8±0.3 | 0.7±1.1 | 1.3±0.4 | 1.9±1.3 |
| EF31 | 1.92b | 1.7±1.8 | 5.0±0.5 | 2.1±0.9 |
| EF24 | 1.9b | 2.8±3.0 | 4.2±1.5 | 5.9±5.9 |
| CUR | 20.5±1.5 | 21.5±17.3 | 24.8±7.4 | 17.9±2.3 |
Notes: The test results at both enzyme and cell levels are shown. The lead compounds EF31, EF24, and CUR are used for comparison. 1.92a and 1.9a were the IC50 values of EF31 and EF24, respectively, against IKKβ.31,32 All data are presented as the mean value of three to five independent tests. NDa means not determined; 1.92b and 1.9b are the IC50 values in the previous reported reference. The bold values represent the favorable inhibitory activity of two most active derivatives of EF24 and EF31.
Abbreviations: CUR, curcumin; IC50, half-maximal inhibitory concentration; IKKβ, inhibitory kappa B kinase β; MTT, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; ND, not determined.
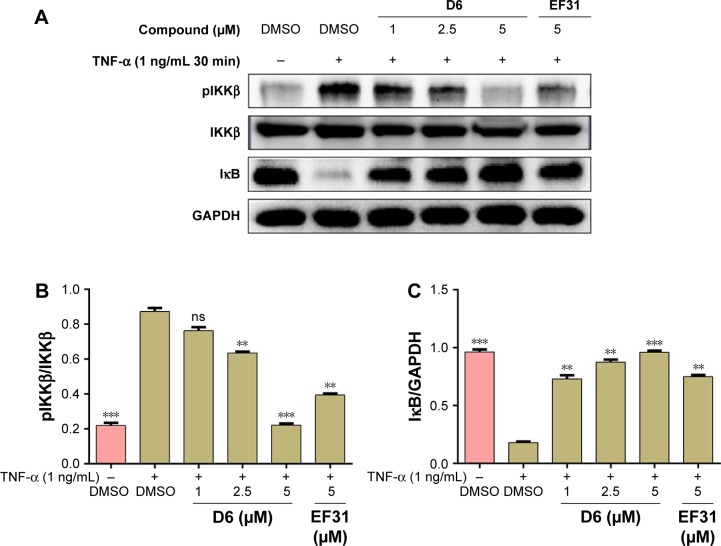
D6 inhibits the phosphorylation of IKKβ and the downstream signaling
TNF-α binding to TLR4 (the receptor of the NF-κB pathway present on the cell membrane) induces the phosphorylation of IKKβ, which leads to the downstream IκB/NF-κB complex getting detached and the subsequent degradation of IκB. IκB is a crucial inhibitory factor deciding whether the NF-κB target genes are activated or not. Thus, we determined the influence of D6 on the phosphorylation of IKKβ and the expression of intracellular IκB in PANC-1 cells by Western blot analysis. The results (Figure 6) showed that D6 significantly suppressed the TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of IKKβ and increased the level of IκB in a dose-dependent manner with a similar effect as for EF31.
Figure 6.
Compound D6 suppressed TNF-α induced phosphorylation of IKKβ and degradation of the downstream signal molecule IκB in a dose-dependent manner.
Notes: (A) PANC-1 cells were incubated with the compounds D6 (1, 2.5, and 5 μM), EF31 (5 μM), or DMSO. After stimulation with TNF-α (1 ng/mL) for 30 min, the protein levels of pIKKβ and IκB were detected by Western blotting with the corresponding total IKKβ protein or GAPDH as loading control. (B and C) The columns show the normalized optical density as a percentage of the control. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of three to four independent experiments. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; “ns” means no significance.
Abbreviations: DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IKKβ, inhibitory kappa B kinase β; pIKKβ, phosphorylated IKKβ; SEM, standard error of the mean; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
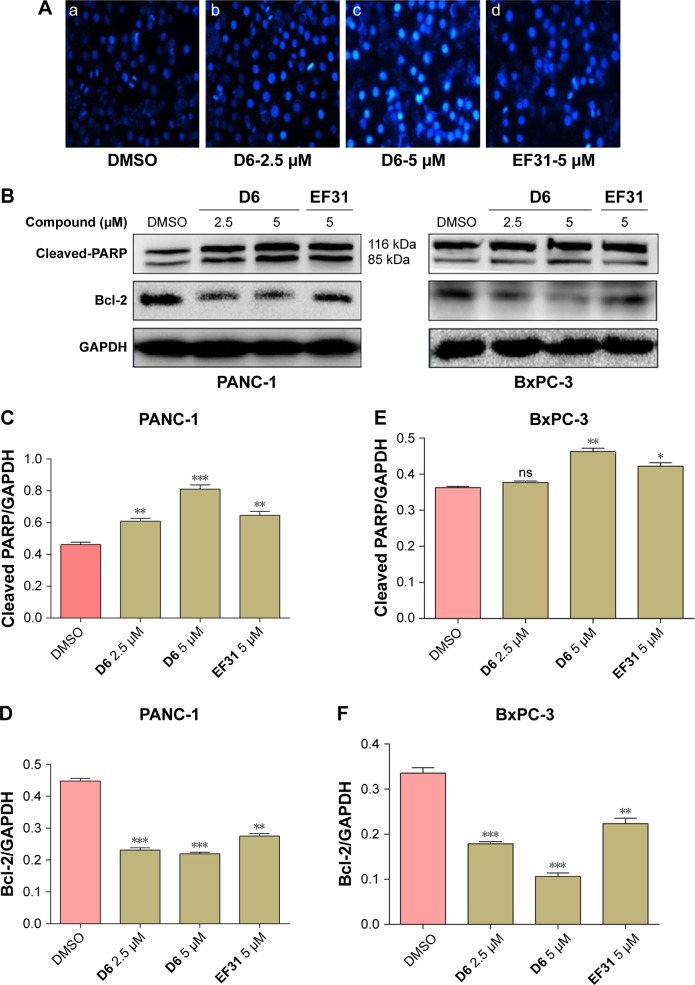
D6 induces apoptosis of PC cell lines
NF-κB, as a nuclear transcription factor, regulates the expression of many antiapoptotic genes. So, we further evaluated the apoptosis induction effect of D6. The morphological changes in the PC cell nuclei were determined by Hoechst staining, and the expression of apoptosis-related molecules (cleaved PARP and anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2) was detected by Western blot analysis. PANC-1 cells were treated with D6 (2.5 and 5 μM) or EF31 (5 μM) for 12 h. Hoechst staining showed chromatin condensation (strong blue fluorescence) and nucleus fragmentation (Figure 7A). For Western blot analysis, PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells were incubated with D6 (2.5 and 5 μM) or EF31 (5 μM). Results (Figure 7B–F) showed that the expression of cleaved PARP was increased and was accompanied by decreased expression of Bcl-2, both in a dose-dependent manner. These results indicated that D6 is an effective inducer of PC cell apoptosis.
Figure 7.
Compound D6 induced PC cell apoptosis.
Notes: (A) Hoechst staining was performed in PANC-1 cells cultured with (a) DMSO, (b and c) D6 (2.5 and 5 μM) or (d) EF31 (5 μM) for 12 h (200×). (B) Effects of D6 on the activation of PARP and inhibition of Bcl-2 in PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells. (C–F) The quantitative analysis of cleaved PARP and Bcl-2 band was performed using ImageJ image processing program. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments performed in triplicate: *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; “ns” means no significance.
Abbreviations: DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; SD, standard deviation.
Discussion
PC is a strong aggressive malignancy with poor prognosis.47 Despite massive efforts being taken to improve the clinical efficacy of chemotherapy, the outcomes of current remedies remain far from inadequate.48 GEM was approved by the FDA as the first-line chemotherapy drug for patients with locally advanced or metastatic PC. However, the acquired resistance to GEM chemotherapy treatment immensely restricted the clinical application of GEM.49 Accompanied with the rapid development of targeted therapy, an increasing number of molecular targets that are closely related to the tumorigenesis and progress of PC were discovered.48 Among these, IKKβ is considered to be a promising target.26 A number of investigations reported that constitutive NF-κB activity resulting from the enhanced IKKβ activity in PC cells led to their excessive proliferation and protection from cell death.15,26 Conversely, downregulation of IKKβ/NF-κB using small inhibitors or siRNA successfully suppressed the growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis of PC.15,50 Thus, the exploitation of IKKβ inhibitors as a novel therapeutic strategy against PC has attracted much attention in the past decades.
Several favorable selective IKKβ inhibitors were discovered through HTS of synthetic small molecules or by recognizing active natural products. Through HTS strategies, BMS-345541, ML-120B, and TPCA-1 (Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Millennium Pharmaceuticals and Glaxo-SmithKline Pharmaceuticals Ltd.) were screened and evaluated in rodent models for their antitumor effect. Nevertheless, the emergence of chronic toxicity of ML-120B and TPCA-1 in in vivo experiments greatly restricts the possibility of their further clinical application.21,51 Apart from the inhibitors identified by HTS, naturally sourced IKKβ inhibitors, such as curcumin, apigenin, genistein, and wedelolactone, are believed to be effective and of low toxicity in the treatment of PC.52–54 Of particular note is that a phase II clinical trial of curcumin in patients with advanced PC has been carried out (NCT00094445).55 But unfortunately, curcumin failed in the clinical test due to poor stability and bioavailability.
Herein, we started the analysis of two more potent and stable curcumin analogs, EF24 and EF31, and designed a series of derivatives of EF24 and EF31. The two major innovative points that can be concluded are as follows: 1) this study presents a systematic medicinal chemistry modification work based on the structural character of EF24 and EF31 for the first time; 2) by kinase screening and SPR assay, a novel IKKβ inhibitor, numbered as D6, displaying commendable efficiency both at the enzyme and cellular levels has been identified.
Our results (Table 1) demonstrated that D6 is a direct powerful IKKβ inhibitor with a desirable small IC50 value (0.8 μM) that is less than half the values of EF24 (1.90 μM) and EF31 (1.92 μM) and 25-fold less than that of curcumin (20.5 μM). However, except for D6, the other synthetic compounds showed relatively lower activity, as well as cellular inhibition, when compared with EF24 and EF31. To clarify the underlying reason for the difference, we performed molecular docking and MD simulation studies on the D6/IKKβ complex. The corresponding results (Figure 5) revealed that the bilateral 4-(dimethylamino)ethoxy substituents of D6 not only formed crucial interactions with the adjacent hydrophobic amino acid residues, but also prolonged its N,N-dimethylamino group into the outside solvent region. Comparing the bilateral substituents in the “C” series compounds with the 4-(dimethylamino)ethoxy group in D6, it is not difficult to find that the chance of developing reliable hydrophobic interaction between the bilateral substituents, as well as the interaction with the solvent region, was dramatically reduced. Therefore, based on the excellent activity of D6, which is far superior to that of the others, we speculated that introducing a long-chain hydrophobic moiety in the bilateral aromatic rings may effectively contribute to elevating the inhibitory activity of EF24- and EF31-based IKKβ inhibitors. In addition, if there is a hydrophilic group at the end of a long chain, it may lead to an unexpected increase in activity. It can be explained by the fact that almost all the FDA-approved kinase inhibitors possessed a hydrophilic motif oriented outward toward the solvent region.56 For example, gefitinib, erlotinib, and afatinib, the representative medicines of the EGFR inhibitors being used in current clinical practice, all possess a long chain in the 6- and/or 7-position extending toward the solvent, to increase the overall solubility of the molecule and stabilize the inhibitory conformation.56,57
In this study, our findings identified that D6 effectively suppresses the activation of the IKKβ/NF-κB pathway and the proliferation of PC cells (Table 1 and Figure 6). On the other hand, D6 could induce the apoptosis of PC cells by intensifying the expression of proapoptotic molecules and downregulating the relevant antiapoptotic proteins in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 7). In continuing research, other impacts of D6 on PC progress need to be evaluated, such as invasion, migration, and cell cycle, as well as the antitumor growth effect in vivo. However, all the existing evidence suggests that D6 should be considered to be an efficient IKKβ inhibitor for potential anti-PC therapy and a useful lead compound for further pharmaceutical development of novel IKKβ inhibitors.
Conclusion
With EF24 and EF31 as lead compounds, A–D series of derivatives were designed and synthesized. Among them, D6 was screened by kinase inhibition assay and identified as a direct-binding inhibitor of IKKβ KD by SPR. Molecular docking and MD simulation analyses demonstrated that the binding mode of IKKβ/D6 was most likely to be hydrophobic interactions. Moreover, biological assays of anti-PC efficacy of D6 indicated effective inhibition of proliferation, as well as the activation of IKKβ/NF-κB pathway, and induction of apoptosis of PC cells. Based on these findings, we conclude that D6 is a potential agent for treatment of PC. This work provides a reference for the rational discovery of novel IKKβ inhibitors.
Abbreviations
- ATCC
American Type Culture Collection
- CUR
curcumin
- DCM/MeOH
dichloromethane/methanol
- DMSO
dimethyl sulfoxide
- DTT
dithiothreitol
- EDC/NHS
1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide/N-hydroxysuccinimide
- EDTA
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- EGFR
epidermal growth factor receptor
- ESI-MS
electron-spray ionization mass spectrometry
- FBS
fetal bovine serum
- FDA
US Food and Drug Administration
- GAPDH
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GEM
gemcitabine
- GSA
surface area energy
- GSK-3α/β
glycogen synthase kinase-3α/β
- HEPES
[2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethanesulfonic acid]
- HPLC
high-performance liquid chromatography
- HTS
high-throughput screening
- IC50
half-maximal inhibitory concentration
- IκB
inhibitory kappa B
- IKKβ
IκB kinase β
- IR
inhibitory ratio
- KD
kinase domain
- Kd
equilibrium dissociation constant
- LCPO
linear combinations of pairwise overlaps
- LGA
Lamarckian genetic algorithm
- MD
molecular dynamics
- MM/GBSA
molecular mechanics/generalized Born surface area
- MS
mass spectrometry
- MTT
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- NF-κB
nuclear factor κB
- NMR
nuclear magnetic resonance
- PBST
phosphate buffered saline plus Tween 20
- PC
pancreatic cancer
- PDAC
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PDB
Protein Data Bank
- PE/EA
petroleum ether/ethyl acetate
- pIKKβ
phosphorylated IKKβ
- PKC
protein kinase C
- PVDF
polyvinylidene difluoride
- RMSD
root-mean-square deviation
- RU
response units
- SASA
solvent accessible surface area
- SDD
scaffold/dimerization domain
- SDS-PAGE
sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- siRNA
small interfering RNA
- SPR
surface plasmon resonance
- STAT-3
signal transducer and activator of transcription-3
- TBST
tris-buffered saline plus Tween 20
- TLC
thin layer chromatography
- TLR4
toll-like receptor 4
- TNF
tumor necrosis factor
- ULD
ubiquitin-like domain
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Makohon-Moore A, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA. Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics from an evolutionary perspective. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16(9):553–565. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(17):1605–1617. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0901557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(1):7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kamisawa T, Wood LD, Itoi T, Takaori K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2016;388(10039):73–85. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH, Goggins M. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2011;378(9791):607–620. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62307-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Colloca G, Venturino A, Guarneri D. Analysis of response-related and time-to-event endpoints in randomized trials of gemcitabine-based treatment versus gemcitabine alone as first-line treatment of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Clin Colorectal Canc. 2016;15(3):264–276. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2015.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Xiang X, Zhang L, Li J, et al. A phase II study of biweekly gemcitabine at fixed dose rate infusion plus S1 as first-line chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(4):S357. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ju HQ, Gocho T, Aguilar M, et al. Mechanisms of overcoming intrinsic resistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through the redox modulation. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14(3):788–798. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Weizman N, Krelin Y, Shabtay-Orbach A, et al. Macrophages mediate gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic adenocarcinoma by upregulating cytidine deaminase. Oncogene. 2014;33(29):3812–3819. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hill R, Rabb M, Madureira PA, et al. Gemcitabine-mediated tumour regression and p53-dependent gene expression: implications for colon and pancreatic cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e791. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hammel P, Huguet F, van Laethem JL, et al. Effect of chemoradiotherapy vs chemotherapy on survival in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer controlled after 4 months of gemcitabine with or without erlotinib the LAP07 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315(17):1844–1853. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.4324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Catenacci DVT, Junttila MR, Karrison T, et al. Randomized phase Ib/II study of gemcitabine plus placebo or vismodegib, a hedgehog pathway inhibitor, in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(36):4284–4292. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.8719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kobayashi S, Ueno M, Hara H, et al. Unexpected side effects of a high S-1 dose: subanalysis of a phase III trial comparing gemcitabine, S-1 and combinatorial treatments for advanced pancreatic cancer. Oncology. 2016;91(3):117–126. doi: 10.1159/000446989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Prabhu L, Mundade R, Korc M, Loehrer PJ, Lu T. Critical role of NF-kappa B in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 2014;5(22):10969–10975. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Radhakrishnan P, Bryant VC, Blowers EC, et al. Targeting the NF-kappa B and mTOR pathways with a quinoxaline urea analog that inhibits IKK beta for pancreas cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(8):2025–2035. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gamble C, McIntosh K, Scott R, et al. Inhibitory kappa B kinases as targets for pharmacological regulation. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;165(4):802–819. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xu G, Lo YC, Li Q, et al. Crystal structure of inhibitor of kappaB kinase beta. Nature. 2011;472(7343):325–330. doi: 10.1038/nature09853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wu HW, Wang GH, Wang ZW, et al. A negative feedback loop between miR-200b and the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway via IKBKB/IKK-beta in breast cancer cells. FEBS J. 2016;283(12):2259–2271. doi: 10.1111/febs.13543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sakamoto K, Hikiba Y, Nakagawa H, et al. Inhibitor of kappaB kinase beta regulates gastric carcinogenesis via interleukin-1alpha expression. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(1):226–238. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.03.047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Koppe C, Gautheron J, Vucur M, et al. A new molecular interaction between IKK alpha/beta and RIPK1 regulates biliary homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 2016;63(1 suppl):257a–258a. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Greten FR, Arkan MC, Bollrath J, et al. NF-kappa B is a negative regulator of IL-1 beta secretion as revealed by genetic and pharmacological inhibition of IKK beta. Cell. 2007;130(5):918–931. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wilson W, Baldwin AS. Maintenance of constitutive I kappa B kinase activity by glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha/beta in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68(19):8156–8163. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Weichert W, Boehm M, Gekeler V, et al. High expression of RelA/p65 is associated with activation of nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent signaling in pancreatic cancer and marks a patient population with poor prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2007;97(4):523–530. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ling J, Kang Y, Zhao R, et al. KrasG12D-induced IKK2/beta/NF-kappaB activation by IL-1alpha and p62 feedforward loops is required for development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;21(1):105–120. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Holcom B, Yip-Schneider M, Schmidt CM. The role of nuclear factor kappa B in pancreatic cancer and the clinical applications of targeted therapy. Pancreas. 2008;36(3):225–235. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31815b3207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Arkan MC, Greten FR. IKK- and NF-kappa B-mediated functions in carcinogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011;349:159–169. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maniati E, Bossard M, Cook N, et al. Crosstalk between the canonical NF-kappa B and Notch signaling pathways inhibits Ppar gamma expression and promotes pancreatic cancer progression in mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(12):4685–4699. doi: 10.1172/JCI45797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gaddipati S, Lu QX, Kasetti RB, et al. IKK2 inhibition using TPCA-1-loaded PLGA microparticles attenuates laser-induced chor-oidal neovascularization and macrophage recruitment. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0121185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Berger A, Quast SA, Plotz M, Kammermeier A, Eberle J. Sensitization of melanoma cells for TRAIL-induced apoptosis by BMS-345541 correlates with altered phosphorylation and activation of Bax. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e477. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Miles RR, Waxman I, Van Den Ven C, et al. Bortezomib (BTZ), IKK inhibitor ML120B, and combination therapy induce apoptosis, inhibit NF-kappa B activation, and decrease specific proteins in primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBL) Ann Oncol. 2011;22:133. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Huang JJ, Chu HX, Jiang ZY, et al. Recent advances in the structure-based and ligand-based design of IKK beta inhibitors as anti-inflammation and anti-cancer agents. Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(34):3893–3917. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666140815130205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Li L, Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S, Abbruzzese J, Kurzrock R. Nuclear factor-kappa B and I kappa B kinase are constitutively active in human pancreatic cells, and their down-regulation by curcumin (diferuloyl-methane) is associated with the suppression of proliferation and the induction of apoptosis. Cancer. 2004;101(10):2351–2362. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Aggarwal BB, Sung B. Pharmacological basis for the role of curcumin in chronic diseases: an age-old spice with modern targets. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009;30(2):85–94. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2008.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kasinski AL, Du YH, Thomas SL, et al. Inhibition of I kappa B kinase-nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway by 3,5-bis(2-flurobenzylidene) piperidin-4-one (EF24), a novel monoketone analog of curcumin. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;74(3):654–661. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.046201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Olivera A, Moore TW, Hu F, et al. Inhibition of the NF-kappa B signaling pathway by the curcumin analog, 3,5-Bis(2-pyridinylmethylidene)-4-piperidone (EF31): anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. Int Immunopharmacol. 2012;12(2):368–377. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lagisetty P, Subramaniam D, Sahoo K, Anant S, Awasthi V. Anticancer activity of an imageable curcuminoid 1-[2-Aminoethyl-(6-hydrazinopyridine-3-carbamidyl)-3,5-bis-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-4-piperidone (EFAH) Chem Biol Drug Des. 2012;79(2):194–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2011.01271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nagaraju GP, Zhu SJ, Wen J, et al. Novel synthetic curcumin analogues EF31 and UBS109 are potent DNA hypomethylating agents in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013;341(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, et al. AutoDock4 and AutoDock-Tools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem. 2009;30(16):2785–2791. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Liu SP, Misquitta YR, Olland A, et al. Crystal structure of a human I kappa B kinase beta asymmetric dimer. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(31):22758–22767. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.482596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang JM, Wang W, Kollman PA. Antechamber: an accessory software package for molecular mechanical calculations. Abstr Pap Am Chem Soc. 2001;222:U403. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Izaguirre JA, Catarello DP, Wozniak JM, Skeel RD. Langevin stabilization of molecular dynamics. J Chem Phys. 2001;114(5):2090–2098. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Krautler V, Van Gunsteren WF, Hunenberger PH. A fast SHAKE: algorithm to solve distance constraint equations for small molecules in molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem. 2001;22(5):501–508. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shan Y, Klepeis JL, Eastwood MP, Dror RO, Shaw DE. Gaussian split Ewald: a fast Ewald mesh method for molecular simulation. J Chem Phys. 2005;122(5):54101. doi: 10.1063/1.1839571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kuhn B, Gerber P, Schulz-Gasch T, Stahl M. Validation and use of the MM-PBSA approach for drug discovery. J Med Chem. 2005;48(12):4040–4048. doi: 10.1021/jm049081q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Miller BR, 3rd, McGee TD, Jr, Swails JM, Homeyer N, Gohlke H, Roitberg AE. MMPBSA.py: an efficient program for end-state free energy calculations. J Chem Theory Comput. 2012;8(9):3314–3321. doi: 10.1021/ct300418h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hoesel B, Schmid JA. The complexity of NF-kappa B signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:86. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wolfgang CL, Herman JM, Laheru DA, et al. Recent progress in pancreatic cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(5):318–348. doi: 10.3322/caac.21190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Singh D, Upadhyay G, Srivastava RK, Shankar S. Recent advances in pancreatic cancer: biology, treatment, and prevention. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1856(1):13–27. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2015.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Long J, Zhang YQ, Yu XJ, et al. Overcoming drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011;15(7):817–828. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2011.566216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Li YW, VandenBoom TG, Wang ZW, et al. miR-146a suppresses invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010;70(4):1486–1495. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Xia YF, Yeddula N, Leblanc M, et al. Reduced cell proliferation by IKK2 depletion in a mouse lung-cancer model. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(3):257–266. doi: 10.1038/ncb2428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wu DG, Yu P, Li JW, et al. Apigenin potentiates the growth inhibitory effects by IKK-beta-mediated NF-kappa B activation in pancreatic cancer cells. Toxicol Lett. 2014;224(1):157–164. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Leung CH, Chan DSH, Li YW, Fong WF, Ma DL. Hit identification of IKK beta natural product inhibitor. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013;14:3. doi: 10.1186/2050-6511-14-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Li YW, Ellis KL, Ali S, et al. Apoptosis-inducing effect of chemotherapeutic agents is potentiated by soy isoflavone genistein, a natural inhibitor of NF-kappa B in BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cell line. Pancreas. 2004;28(4):E90–E95. doi: 10.1097/00006676-200405000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Dhillon N, Aggarwal BB, Newman RA, et al. Phase II trial of cur-cumin in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(14):4491–4499. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wu P, Nielsen TE, Clausen MH. FDA-approved small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015;36(7):422–439. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2015.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhang JM, Yang PL, Gray NS. Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(1):28–39. doi: 10.1038/nrc2559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]