Erratum
Following the publication of our article [1] in BMC Microbiology, it was brought to our attention that there was an error in Fig. 3: the panels showing BCBHV008 and 8325-4recUi supplemented with IPTG (2nd and 4th panels respectively) were identical. After checking the original files, we concluded that the images used to create the two panels came from the same files (corresponding to 8325-4recUi plus IPTG) and the original data for the control strain BCBHV008 plus IPTG had not been saved. Therefore we repeated the experiment described in Fig. 3. We achieved the same result, i.e. that BCBHV008 susceptibility to UV is not affected by the presence of IPTG, as expected given that this control strain does not encode any gene under the control of the Pspac IPTG inducible promoter. Hence, Fig. 3 should be replaced by the correct version below. This correction does not affect any of the results or the conclusions.
Fig. 3.
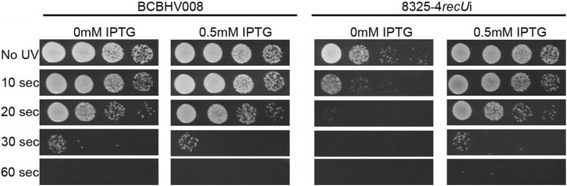
RecU depletion in 8325-4recUi strain leads to increased susceptibility to UV damage. Cultures of control strain BCBHV008 and recU inducible mutant 8325-4recUi showing serial dilutions from 10−2 (left) to 10−5 (right). 10 μl spots were placed on TSA agar, containing or not IPTG, and irradiated with a UV dose of 4 J/m2/s for 0, 10, 20, 30 and 60 s. Plates were then incubated overnight at 37 °C
Footnotes
The online version of the original article can be found under doi:10.1186/1471-2180-13-18
Reference
- 1.Pereira AR, Reed P, Veiga H, Pinho MG. The Holliday junction resolvase RecU is required for chromosome segregation and DNA damage repair in Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Microbiol. 2013;13:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


