Abstract
MicroRNA-370 (miR-370) has been observed to act as a tumor suppressor through the targeting of different proteins in a variety of tumors. Our previous study indicated that miR-370 was able to target forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) to inhibit cell growth and metastasis in human osteosarcoma cells. In this study, we reported that FOXM1 interacted with β-catenin in vitro and in vivo. Similar to FOXM1, critical components of the Wnt signaling pathway, including β-catenin, c-Myc, and Cyclin D1, were also highly expressed in different human osteosarcoma cells lines. Pharmacological inhibition of FOXM1 or β-catenin but not of c-Myc was associated with the increased expression of miR-370. Ectopic expression of miR-370 inhibited the downstream signaling of β-catenin. Moreover, osteosarcoma cells treated with 5-AZA-2'-deoxycytidine (AZA), a DNA methylation inhibitor, exhibited increased levels of miR-370 and decreased levels of β-catenin downstream targets, which resulted in inhibition of cell proliferation and colony formation ability. In conclusion, our results supported a model in which the DNA methylation-mediated down-regulation of miR-370 reduced its inhibitory effect on FOXM1, thereby promoting FOXM1-β-catenin interaction and activating the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells.
Keywords: miR-370, methylation, FOXM1, Wnt/β-Catenin, c-Myc and Cyclin D1.
Introduction
Osteosarcoma is a solid tumor and often occurs in children and young adults 1. In recent years, a number of microRNAs (a class of non- coding RNAs containing ∼22 nucleotides) such as miR-17-5p 2, miR-26a-5p 3, miR-34a 4, miR-135b 5, miR-150 6, and miR-203 4, have been reported to play important roles in contributing to the pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. According to their function and expression levels in osteosarcoma clinical samples and osteosarcoma cell lines, these miRNAs can be divided into two groups: oncogenic miRNAs and anti-oncogenic miRNAs 7-9. For instance, miR-34a and miR-203 are significantly decreased and act as tumor suppressors in osteosarcoma cell lines 4, while miR-135b and miR-150 are overexpressed in osteosarcoma patient samples and act as oncogenic miRNAs 5, 6. However, despite our extensive knowledge of their dysregulation, little is known about the mechanisms that control the expression of these miRNAs in osteosarcoma cells. One possibility is that DNA methylation may be involved in this process, and a number of studies have clearly demonstrated that DNA methylation is capable of regulating the expression of miRNAs in different types of cancer 10-12. For instance, several tumor-suppressive miRNAs, such as miR-33b, miR-124a and miR-127, can be modified by DNA methylation, which results in their down-regulation in different cancers 13-15.
The forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) is a member of FOX family and functions as a transcription factor to regulate the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation and differentiation, cell cycle progression, DNA damage repair, as well as apoptosis 16-18. In recent years, elevated expression of FOXM1 has been frequently found in a variety of cancers such as liver 19, prostate 20, breast 21, lung 22, pancreas 23, and osteosarcoma 24, suggesting its important role in tumorigenesis. Several miRNAs, including miR-370 and miR-802, are known to directly target the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of FOXM1, thereby repressing its expression 24, 25. In addition, FOXM1 is also involved in several important signaling pathways such as the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and interacts with critical members of these pathways, thereby contributing to signal transduction, rather than acting as a transcription factor 26-28. For instance, FOXM1 has been shown to interact with β-catenin, and promote β-catenin nuclear localization 28. When the FOXM1-β-catenin complex enters the nucleus, it further forms a transcriptional complex with T-cell factor (TCF) or lymphoid enhancer factor (LEF) to activate the expression of Wnt target genes such as c-Myc and Cyclin D1 28. Most recently, FOXM1 was found to be phosphorylated by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) at serine 474, and this phosphorylation could induce its ubiquitination mediated by F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 (FBXW7) 29. Activation of Wnt signaling inhibits FOXM1 phosphorylation, which results in the deubiquitination and accumulation of FOXM1 through the interaction with Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 5 (USP5), a deubiquitinating enzyme 29.
While studying miRNA expression in osteosarcoma cell, we noted that miR-370 was dramatically down-regulated 24, and it was able to directly target FOXM1 to regulate osteosarcoma cell growth and metastasis 24. Despite considerable interest in FOXM1 and miR-370, two critical issues are still unclear: one regards the underlying mechanism of miR-370 down-regulation; the other refers to the absence of downstream targets of FOXM1 in osteosarcoma cells. To solve these two questions, we first tried to identify the proteins that interact with FOXM1 in osteosarcoma cells through immunoprecipitation (IP) assays and liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis. In our primary LC-MS/MS results we found an important candidate protein: β-catenin. We then determined the interaction between FOXM1 and β-catenin with in vitro and in vivo assays, and found the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in osteosarcoma cells. Further analysis indicated that DNA methylation caused down-regulation of miR-370, and demethylation treatment with AZA was able to repress the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Taken together, our findings reveal the mechanism underlying miR-370 down-regulation in osteosarcoma cells and provide insight into regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through FOXM1 in human osteosarcoma cells.
Materials and Methods
Cell lines and cell culture
All cell lines used in this study were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, USA). Cells were grown in DMEM medium (Gibco, USA) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS (Gibco, USA) and 100 U/ml of penicillin-streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), then incubated at 37°C with 5% CO2. In addition, cells were analyzed with the MycoAlert™ Mycoplasma Detection Kit (Lonza, Switzerland) every two months, to detect the potential mycoplasma contamination.
Cell transfection
For plasmids and miR-370 mimics transfections, cells were first seeded in 6-well plates and incubated for 18 h, then transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, USA) and a suspension with 100 ng of plasmid or 50 nM of miR-370 mimics (RiboBio, China) following the manufacturer's protocol. Cells were then incubated in 0.5 ml DMEM medium with 10% FBS at 37°C for 48 h.
For shRNA knockdown of FOXM1 and β-catenin, their corresponding MISSION® shRNA Lentiviral Transduction Particles including shFOXM1 (TRCN0000273939) and shβ-catenin (TRCN0000350477) were purchased from Sigma (USA). The pLKO.1 vector was used as negative control. Briefly, the lentiviral particles were used to infect the cells following standard procedures. The virus-infected cells were then selected with puromycin (1 μg/ml) for 48 h and then subjected to the required experiments.
Immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry analysis
Immunoprecipitation procedures were performed at 4°C. Briefly, cells transfected with the pCDNA3-Flag-HA-FOXM1 or pCDNA3-Flag-HA plasmids were lysed with Pierce IP lysis buffer (ThermoFisher Scientific, USA) supplemented with 1 x cocktail protease inhibitor (Roche, USA). Lysates were then sonicated for 1 min and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag magnetic beads (Sigma, USA) for 4 h. The supernatant was discarded and the beads were washed five times with lysis buffer, and then incubated with the Flag peptide (Sigma, USA) for 2 h at room temperature. The eluted complex was subjected to SDS-PAGE separation and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R 250 (Invitrogen, USA). The entire gel was diced into small pieces (∼ 1 mm), followed by digestion with trypsin and to analysis via liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The resulting spectra data were blasted in the NCBI database using the MASCOT Distiller (2.3.2.0) software to generate peak lists.
Western blot analysis
Cells were lysed in 50 μl radio immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer. Equal amounts of total cell lysates were boiled in SDS-sample buffer and later separated by SDS-PAGE at 100 V for 3 h. Proteins on the gel were transferred to a PVDF membrane at 100 V for 1.5 h at 4°C and the membrane was blocked with 5% milk in 1 x TBST (Tris-buffered saline, 0.1% Tween 20) buffer at room temperature for 1 h. Blots were subsequently incubated with a primary antibody and a peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody. After washing five times with TBST, blots were incubated with enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) detection reagent, and imaged with the ChemiDoc MP (Bio-Rad, USA). The primary antibodies used for the blots were anti-GAPDH (Sigma, USA), anti-Flag (Sigma, USA), anti-HA (Sigma, USA), anti-β-catenin (Sigma, USA), anti-FOXM1 (Abcam, USA), anti-c-Myc (Sigma, USA) and anti-Cyclin D1 (Sigma, USA).
Yeast two-hybrid assay
Y2H was performed as previously described 30. The yeast strain AH109 expressing the pGADT7-FOXM1 plasmid (prey) was transformed with the plasmid pGBKT7-β-catenin (bait). Transformed yeast cells were selected on synthetic complete medium lacking Trp and Leu (SC-T/L). Cells containing the empty prey or bait vectors were transformed with pGBKT7-β-catenin or pGADT7-FOXM1, respectively, as negative controls. Interaction was determined on synthetic complete medium lacking Trp, Leu, and His (SC-T/L/H).
Mammalian two-hybrid (M2H) assay
The M2H assay was performed as previously described 31. Briefly, pBIND-β-catenin, pACT-FOXM1 and pGL4.31-luciferease reporter plasmids were combined in the same molar ratio (1:1:1) and transfected into U2OS cells. After 48 h, the cells were lysed in a buffer containing 0.1 M potassium phosphate (pH 7.8), 2 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 1% Triton X-100, and the luciferase activity was measured using the Luminoskan Ascent luinometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). The luciferase activity was calculated against the pGL4.31-luciferase basal control and normalized against the Renilla luciferase activity.
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from cultured cells using TRIZOL (Invitrogen, USA) following the manufacturer's instructions. cDNA was synthesized using the Verso cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). The resulting cDNAs were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) using the specific primers listed in Table-1. All experiments were replicated three times, and the individual gene expression was determined using the 2-ΔCt method by normalizing to β-Actin, an internal control as previously described 32.
Table 1.
Primers used for qRT-PCR
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| FOXM1 | 5'-AGCTGAAGGGTGGGAACAAC-3' | 5'-ACCCACCTTCTGGCAGTCTCT-3' |
| β-catenin | 5'-AGCCACAGCTCCTCTGACAG -3' | 5'-TCTCCCTGGGCACCAATATCA-3' |
| c-Myc | 5'-CTTGAACAGCTACGGAACTC -3' | 5'-GAGGCAGTTTACATTATGGC-3' |
| CCND1 | 5'-TGAAGCCAGCTCACAGTGCT -3' | 5'-AGCCAGGATGGTTGAGGTAA-3' |
| β-Actin | 5'-AGAGCTACGAGCTGCCTGAC-3' | 5'-AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG-3' |
Quantitative analysis of miR-370 expression was performed as previously described 4. Briefly, total mRNA was extracted from cells using the miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, MD, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The resulting mRNA was applied to generate cDNAs using TaqMan MicroRNA Reverse Transcription kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). The expression of miR-370 was then measured by qRT-PCR using a TaqMan MicroRNA Assay kit (assay ID: 478848, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) according to the manufacturer's protocols. The standard qRT-PCR program was performed on the Bio-rad CFX96 real-time PCR System (Bio-Rad, USA) and RNU6B was chosen as an internal control to normalize miR-370 expression using the 2-ΔCt method. All reactions were conducted in triplicate.
Cell proliferation and colony formation assays
For the cell proliferation assays, cells expressing low levels of FOXM1 or β-catenin by shRNA knockdown or cells treated with or without AZA were seeded onto 96-well plates for 0 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, 96 h or 120 h. Next, cell viability was determined at 490 nm using an MTT kit (Roche, USA) following the manufacturer's instructions. All of the experiments were performed in quadruplicates.
For the colony formation assays, the cells used in proliferation assay were diluted and seeded at approximately 1000 cells per well, followed by continuous culture with DMEM medium for 14 days with a change every 3 days. The cell colonies were fixed for 5 min with 3.7% paraformaldehyde (PFA), and then stained for 30 min with 0.05% crystal violet, and washed five times with ddH2O to remove the excess dye.
Quantitative methylation-specific PCR (qMSP)
Genomic DNA samples were modified by sodium bisulfite using the EpiTect Bisulfite Kit (Qiagen, USA) according to the manufacturer's protocols. The resulting DNA was applied to analysis on the Bio-rad CFX96 real-time PCR System (Bio-rad, USA) using KAPA SYBR FAST qPCR Kits (Kapa Biosystems, USA) with standard PCR program. GAPDH was used as an internal control to normalize expression of CpG Island 1 and 2 using the 2-ΔCt method. All reactions were conducted in triplicate. Primers used in qMSP were listed in Table-2.
Table 2.
Primers used for qMSP
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Island 1 | 5'-TGTGTGGGAGGTTAGAAAAATT-3' | 5'-AATACTAAACCAAAAAACAAACCC-3' |
| Island 2 | 5'-ATATGTTCGAATAATTTTTTGTTC-3' | 5'-TAACTTCTCTATCTTATACCCCGAC-3' |
| GAPDH | 5'- CGCTTTCTTTCCTTTCGC-3' | 5'- TGCCCATTCATTTCCTTCC-3' |
Statistical analysis
Data from each group were independently obtained from three replicates. Statistical analyses of data were performed using a two-sided Student's t test. Significance was set at P < 0.05.
Results
FOXM1 interacts with β-catenin in human osteosarcoma cells
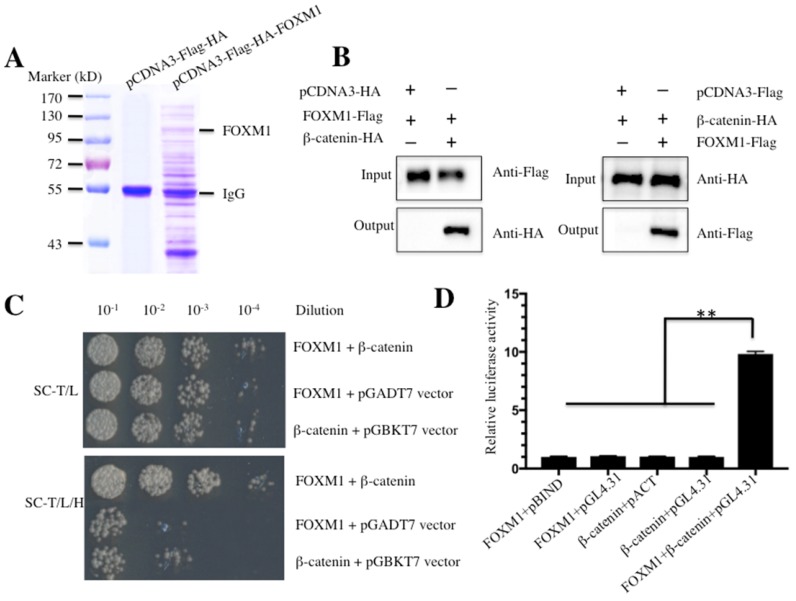
Given the important role of FOXM1 in a wide variety of cancers, including the osteosarcoma cells that we investigated, we sought to identify proteins that interacted with FOXM1 and to investigate the involvement of FOXM1 in different signaling pathways. Accordingly, we constructed the vector pCDNA3-Flag-HA-FOXM1 encoding for a two epitopes-tagged FOXM1. U2OS cells transfected with pCDNA3-Flag-HA-FOXM1 or empty vector (pCDNA3-Flag-HA) were harvested and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis. To minimize unspecific binding, we used a two-step approach to purify the FOXM1-associated complex. In brief, a Flag-tag affinity procedure was first used to purify Flag-HA-FOXM1-containing complexes. After the Flag epitope was cleaved off, an HA-tag affinity procedure to purify HA-FOXM1-containing complexes was used. After this two-step purification, FOXM1-containing complexes were enriched and subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis (Figure 1A). Fortunately, we identified a total number of 85 proteins in our primary list; the most abundant 10 proteins are listed in Table-3. Among the identified proteins, we found β-catenin, a critical protein involved in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway; this result strongly suggested that β-catenin might interact with FOXM1 in human osteosarcoma cells. To confirm these interactions, different approaches including Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), Y2H and M2H assays were used. For the Co-IP assay, U2OS cells expressing HA-tagged β-catenin (pCDNA3-HA-β-catenin), Flag-tagged FOXM1 (pCDNA3-Flag-FOXM1) or the empty vectors (pCDNA3-HA or pCDNA3-Flag) were lysed and immunoprecipitated with either anti-HA agarose or anti-Flag agarose. The results indicated that FOXM1 was immunoprecipitated with β-catenin but not with the empty vector (Figure 1B). For the Y2H assay, FOXM1 was co-transformed with β-catenin into yeast cells to determine if they could directly bind to each other. As expected, the results indicated that FOXM1 directly bound β-catenin (Figure 1C). Moreover, the M2H assay, a system to study protein interactions with luciferase reporters, was also used to evaluate the interaction between FOXM1 and β-catenin. As illustrated in Figure 1D, FOXM1 showed nearly 10-fold increase in its interacting activity with pBIND-β-catenin compared with the control groups. Taken together, these in vitro and in vivo assays clearly demonstrated that β-catenin directly bound FOXM1 in human osteosarcoma cells.
Figure 1.
FOXM1 directly binds to β-Catenin in vitro and in vivo. (A) Immunoprecipitation of the Flag-HA-FOXM1-associated complexes. U2OS cells transfected with pCDNA3-Flag-HA-FOXM1 or pCDNA3-Flag-HA were harvested and subjected to IP analysis by using a two-step approach with anti-Flag-agarose and anti-HA-agarose. The IP protein complexes were subjected to SDS-PAGE separation and staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R 250. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of FOXM1 and β-Catenin in U2OS cells. Cells co-transfected with pCDNA3-FOXM1-Flag and pCDNA3-β-Catenin-HA, or pCDNA3-FOXM1-Flag and pCDNA3-HA (left panel), or pCDNA3-Flag and pCDNA3-β-Catenin-HA (right panel) were co-immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag agarose (left panel) or anti-HA-agarose (right panel). The pull-down products were analyzed via immunoblots with anti-HA and anti-Flag antibodies, respectively. (C) FOXM1 directly bound β-Catenin in yeast. The pGBKT7-FOXM1 plasmid was co-transformed with the plasmid pGADT7-β-Catenin or pGADT7 empty vector into the yeast strain AH109. The resulted yeast colonies were dotted on media minus Trp and Leu (top panel) or minus Trp, Leu, and His (bottom panel) to determine their growth. Serial decimal dilutions were indicated. (D) The interaction of FOXM1 and β-Catenin enhanced the luciferase activity in a M2H assay. Luciferase assay in U2OS cells transfected with pACT-FOXM1 and pBIND, or pACT-FOXM1 and pGL4.31, or pBIND-β-Catenin and pACT, or pBIND-β-Catenin and pGL4.31, or pACT-FOXM1, pBIND-β-Catenin and pGL4.31 were subjected to lucifeare activity assay, which was normalized against the activity of Renilla luciferase. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. **P<0.001.
Table 3.
FOXM1-associated proteins in human osteosarcoma cells
| Accession Number | Protein ID | Symbol | Molecular Weight | MASCOT Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q09028 | Retinoblastoma binding protein 4 | RBBP4 | 48 kDa | 627 |
| P30304 | Cell division cycle 25A | CDC25A | 59 kDa | 569 |
| Q13309 | S-Phase Kinase-associated protein 2 | SKP2 | 48 kDa | 503 |
| O09472 | E1A binding protein P300 | EP300 | 264 kDa | 454 |
| P35222 | Catenin beta 1 | CTNNB | 85 kDa | 409 |
| Q6 MZP7 | Protein Lin-54 homolog | Lin-54 | 79 kDa | 320 |
| P41182 | B-Cell CLL/Lymphoma 6 | BCL6 | 79 kDa | 266 |
| P24941 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 2 | CDK2 | 34 kDa | 194 |
| P06493 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 | CDK1 | 34 kDa | 113 |
| Q12968 | Nuclear factor of activated T-Cells 3 | NFATC3 | 116 kDa | 82 |
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is activated in human osteosarcoma cells
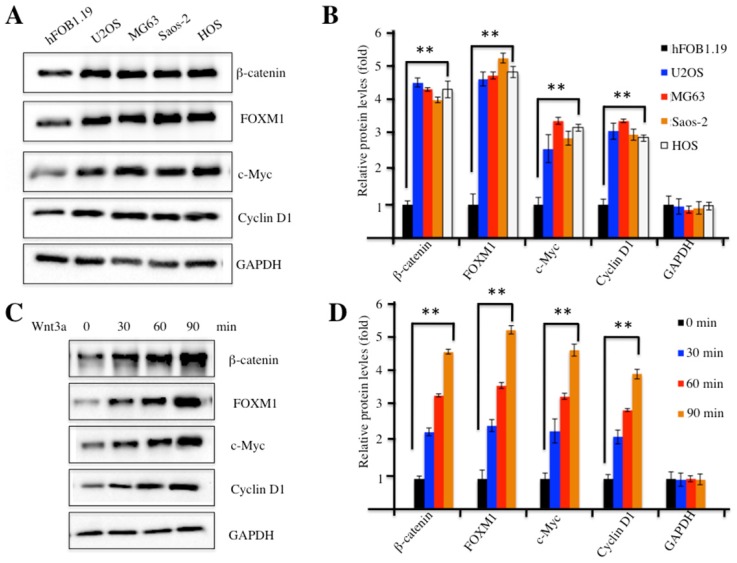
Our previous study indicated that FOXM1 was overexpressed in human osteosarcoma cells 24. To investigate whether FOXM1 overexpression could recruit more β-catenin, we examined β-catenin protein levels in four human osteosarcoma cell lines, including U2OS, MG63, Saos-2 and HOS cells. Our results indicated that β-catenin was also up-regulated in all four cell lines compared to hFOB1.19 control cells (Figure 2A). In addition, we also examined protein levels of c-Myc and Cyclin D1, two critical downstream targets of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Interestingly, similar to FOXM1 and β-catenin, c-Myc and Cyclin D1 were also elevated in these osteosarcoma cell lines (Figures 2A and 2B), implying the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Because treatment with Wnt3a can stabilize β-catenin and activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, we examined the β-catenin protein levels upon Wnt3a stimulation in U2OS cells. As expected, the amount of β-catenin increased substantially, upon Wnt3a treatment, in a time-dependent manner (Figures 2C and 2D). Similarly, the other three proteins, including FOXM1, c-Myc and Cyclin D1 also showed up-regulated expression after Wnt3a treatment (Figures 2C and 2D). These results indicated that the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway was activated in human osteosarcoma cells.
Figure 2.
The Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway was activated in human osteosarcoma cells. (A) Elevated protein levels of members of the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway. Protein levels of FOXM1, β-Catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 and GAPDH in hFOB1.19, U2OS, MG63, Saos-2 and HOS cells were determined by western blot. (B) Statistical analysis of the protein levels in (A). (C) Wnt3a treatment increased the levels of proteins of the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway. Protein levels of β-Catenin, FOXM1, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 and GAPDH in U2OS cells upon the treatment of Wnt3a (20 ng/ml) for 0, 30, 60 and 90 min, were determined by western blot. (D) Statistical analysis of the protein levels in (C). Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. **P<0.001.
Studies on the localization of the interaction between FOXM1 and β-catenin have shown that their interaction occurred in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus 28. Importantly, signaling activation with Wnt3a treatment increased the translocation of FOXM1 and β-catenin to the nucleus in 293T cells. To evaluate the location of their interaction, and whether the activation of the Wnt signaling pathway was able to affect the translocation of FOXM1 and β-catenin in human osteosarcoma cells, we first detected endogenous FOXM1 and β-catenin levels in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus of U2OS, MG63, Sao2-2 and HOS cells. Consistent with previous studies, both FOXM1 and β-catenin were up-regulated in these osteosarcoma cells compared to hFOB1.19 cells (Supplementary Figure 1A). Additionally, the nuclear protein levels of these two proteins were much higher than those in the cytoplasm (Supplementary Figure 1A). Furthermore, we treated U2OS cells with Wnt3a to activate the Wnt signaling pathway, and then examined the amounts of β-catenin and FOXM1. Our results indicated that the expression of both proteins increased substantially upon Wnt3a treatment in the nucleus, in a time-dependent manner (Supplementary Figure 1B). These results suggested that the interaction of FOXM1 and β-catenin occurred in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus and, more importantly, the activation of Wnt signaling promoted the nuclear translocation of both FOXM1 and β-catenin.
Specific knockdown of FOXM1 or β-catenin had similar effects on osteosarcoma cells
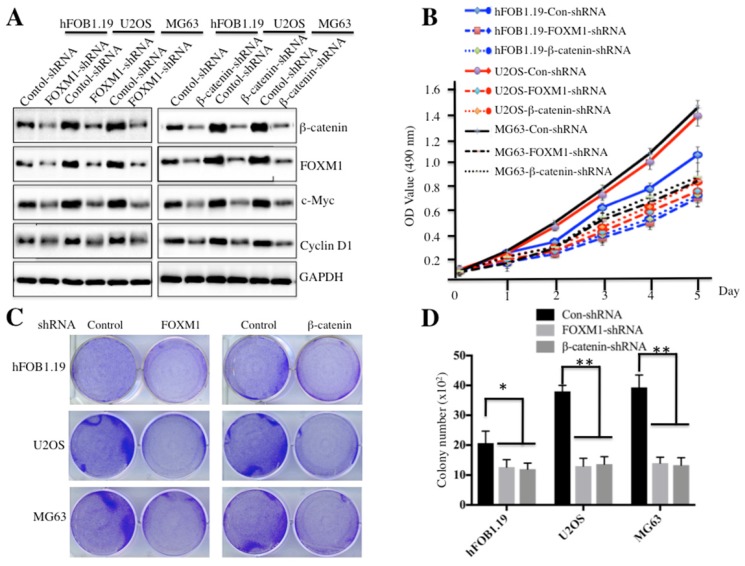
Because both FOXM1 and β-catenin are overexpressed in osteosarcoma cells, one question arises: their down-regulation could affect cell proliferation and colony formation ability, which would provide evidence for targeting FOXM1 and β-catenin in osteosarcoma therapy in the future. To confirm this hypothesis, we employed shRNAs to knock down either FOXM1 or β-catenin expression in hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cells. As shown in Figure 3A and supplementary Figure 2, knockdown of either FOXM1 or β-catenin resulted in the significant reduction of c-Myc and Cyclin D1 at both transcriptional and protein levels in all cell lines. Cells expressing lower FOXM1 or β-catenin were subjected to cell proliferation assay; our results indicated that knockdown of either FOXM1 or β-catenin in both U2OS and MG63 cells could lead to significant inhibition of cell growth (Figure 3B). In addition, colony formation assays indicated that a significant decrease of colony formation rates was also observed in U2OS and MG63 cells with either FOXM1 or β-catenin knocked-down (Figures 3C and 3D). These results further demonstrate that expression levels of FOXM1 and β-catenin are important for osteosarcoma cell growth, and inhibition of their expression is a promising strategy for cancer therapy.
Figure 3.
Knockdown of FOXM1 or β-Catenin inhibited osteosarcoma cell growth. Knockdown of FOXM1 or β-Catenin in hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cells resulted in attenuated expression of c-Myc and Cyclin D1. The hFOB1.19, U2OS or MG63 cells transfected with control-shRNA, FOXM1-shRNA or β-Catenin-shRNA were lysed and probed with anti-FOXM1, β-Catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 or GAPDH antibody. (B) Knockdown of FOXM1 or β-Catenin in hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cells inhibited cell proliferation. Cells used in (A) were subjected to the MTT assay to evaluate cell proliferation, and the cell viability was determined at 490 nm. (C-D) Knockdown of FOXM1 or β-Catenin in hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cells decreased the rate of colony formation. Cells (1 x 103) used in (A) were seeded onto 6-well plates, and cultured with 0.1 ml DMEM medium for two weeks. Then, cells were stained with 0.5% crystal violet (D), and the number of colonies was counted (E). Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. **P<0.001.
Up-regulation of miR-370 suppressed the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
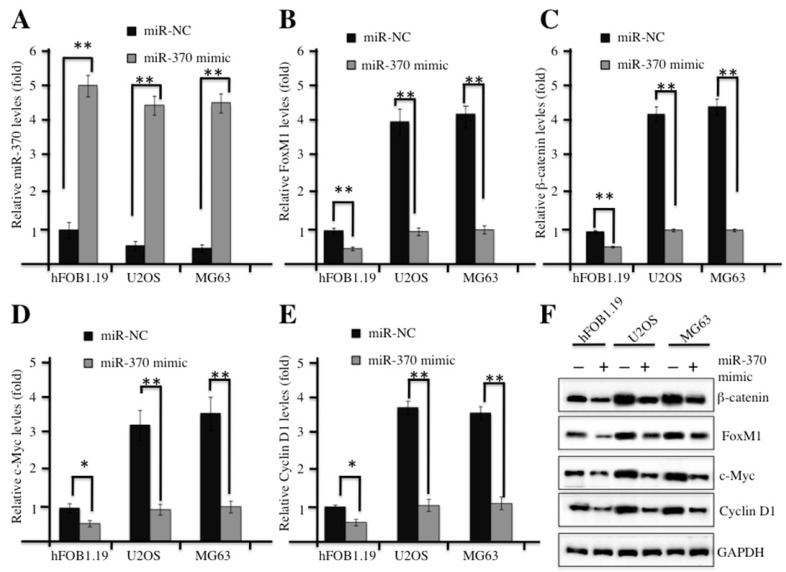
In our previous studies, we demonstrated that miR-370 was dramatically down-regulated in osteosarcoma cells, and it was able to directly target FOXM1 and reintroduction of FOXM1 could reverse the effect of miR-370 on osteosarcoma cells 24. Therefore, we next sought to examine whether overexpression of miR-370 could affect the Wnt/β-catenin signaling transduction. Commercial miR-370 mimics or their negative control miR-NC were transfected into hFOB1.19, U2OS or MG63 cells, respectively. Then, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis was undertaken to examine the expression of miR-370. A significant increase in miR-370 expression was observed in both hFOB1.19 and osteosarcoma cells transfected with miR-370 mimics, and these cells shared similar levels of miR-370 after transfection (Figure 4A). Strikingly, with the induction of miR-370, the mRNA levels of FOXM1, β-catenin, c-Myc and Cyclin D1 were dramatically reduced (Figures 4B-4E); similarly, the corresponding proteins were also down-regulated after miR-370 mimics transfection (Figure 4F). These results suggested the inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway upon the induction of miR-370.
Figure 4.
Up-regulation of miR-370 inhibited the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway. (A-E) Overexpression of miR-370 in hFOB1.19, MG63 and U2OS cells decreased the mRNA levels of FOXM1, β-Catenin, c-Myc and Cyclin D1. The hFOB1.19, MG63 and U2OS cells were transfected with miR-370 mimics or miR-NC for 24 h. Next, the expression of miR-370 (A), FOXM1 (B), β-Catenin (c), c-Myc (D) and Cyclin D1 (E) was determined by qRT-PCR. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. **P<0.001. (F) Cells used in (A) were lysed and probed with anti-FOXM1, β-Catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 or GAPDH antibody.
Pharmacological activation or blockage of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway affected miR-370 expression
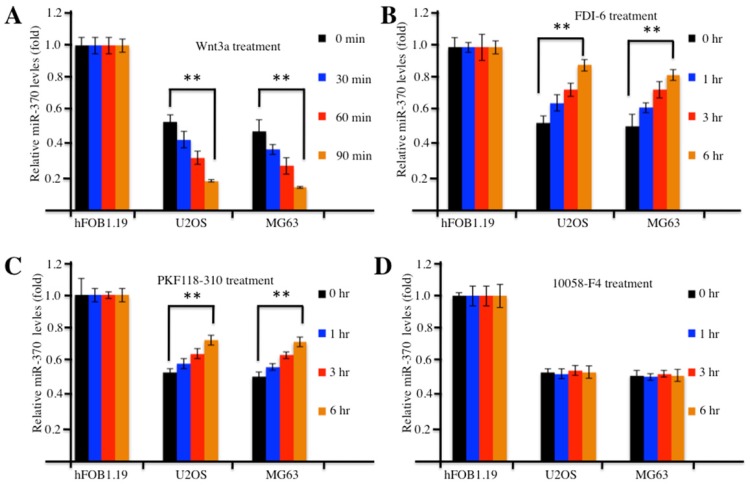
Because the overexpression of FOXM1 was able to reverse miR-370 effects (e.g., promoting cell proliferation and invasion) on osteosarcoma cells 24, we tried to determine whether the activation or inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway with the pharmacological treatments could affect level of miR-370. Accordingly, we treated hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cells with Wnt3a to activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and analyzed the expression of miR-370. Surprisingly, our results indicated that the expression of miR-370 decreased substantially upon Wnt3a treatment in a time-dependent manner in osteosarcoma cells compared with hFOB1.19 cells (Figure 5A), which suggested that the accumulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling downstream targets might regulate the expression of miR-370. To confirm this hypothesis, we further treated cells with FDI-6 (an inhibitor of FOXM1), PKF118-310 (an inhibitor of β-catenin) or 10058-F4 (an inhibitor of c-Myc) and investigated the expression of miR-370. The qRT-PCR results showed that miR-370 expression increased in a time-dependent manner in osteosarcoma cells treated with FDI-6 (Figure 5B) or PKF118-310 (Figure 5C), compared with the control cells, while miR-370 expression remained unchanged in osteosarcoma cells treated with 10058-F4 (Figure 5D). Meanwhile, we also examined the protein levels of FOXM1, β-catenin, c-Myc and Cyclin D1 in the treated cells. Contrarily to miR-370 expression, the protein levels of FOXM1, β-catenin, c-Myc and Cyclin D1 gradually increased over time upon Wnt3a treatment in osteosarcoma cells (Supplementary Figure 3A), while they decreased in cells treated with FDI-6 or PKF118-310 (Supplementary Figures 3B and 3C). However, no obvious change in the levels of FOXM1 and β-catenin was found in cells treated with 10058-F4 (Supplementary Figure 3D), even though, in the same cells, the level of c-Myc decreased over time (Supplementary Figure 3D). Therefore, our results suggested that the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling with Wnt3a could further down-regulate miR-370 expression, while the inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by FDI-6 or PKF118-310 was able to further increase the level of miR-370 in osteosarcoma cells. However, the expression of miR-370 in osteosarcoma cells treated with the inhibitors was not comparable to that in hFOB1.19 cells (Figure 5), indicating that these pharmacological reagents only partially affected miR-370 expression.
Figure 5.
Activation or inhibition of the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway affected expression of miR-370. (A) Wnt3a treatment resulted in decreased expression of miR-370 in U2OS and MG63 cells. The hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cells were treated with 20 ng/ml Wnt3a for 0, 30, 60 and 90 min, then expression of miR-370 was determined by qRT-PCR. (B-D) Treatment with FDI-6 and PKF118-310, but not treatment with 10058-F4, resulted in increased miR-370. The hFOB1.19, MG63 and U2OS cells were treated with FDI-6 (40 μM, B), PKF118-310 (2 μM, C) or 10058-F4 (25 μM, D) for 0, 1, 3 and 6 hr. Next, the expression of miR-370 was determined by qRT-PCR. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. **P<0.001.
Elevated DNA methylation resulted in down-regulation of miR-370
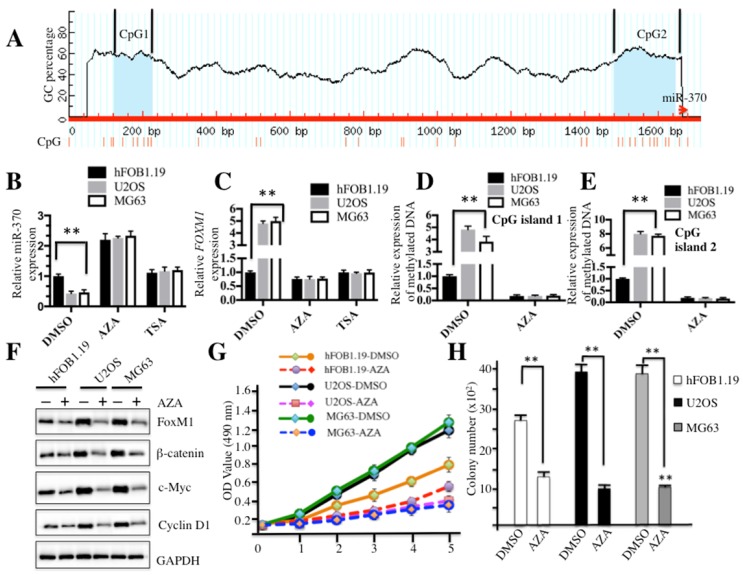
Because miR-370 is an important regulator of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, we sought to analyze the regulatory mechanism of miR-370 expression. By analyzing DNA sequences in the upstream (-1700) of miR-370 genomic locus, we identified two CpG islands located in the upstream of miR-370 genomic locus (Figure 6A). Since hypermethylation is a general event in carcinogenesis, we first investigated whether DNA methylation had an effect on miR-370 expression. Accordingly, hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cells were treated with the DNA methylation inhibitor AZA or acetylation inhibitor TSA, respectively, and then subjected to qRT-PCR analysis to evaluate the expression of miR-370 and FOXM1. The results demonstrated that the treatment with AZA was able to significantly increase miR-370 expression in both hFOB1.19 (∼2-fold induction) and osteosarcoma cells (∼4-fold induction) (Figure 6B), but not TSA treatment. Conversely, further analysis revealed that AZA could dramatically repress the expression of FOXM1 (Figure 6C). These results suggested that DNA methylation was important for miR-370 expression in osteosarcoma cells. Then, DNA methylation statuses of CpG island 1 and 2 were determined by using qMSP. The results indicated that both CpG islands were significantly methylated in U2OS and MG63 cells without AZA treatment compared to hFOB1.19 cells (Figures 6D and 6E). Meanwhile, we also detected the protein levels of FOXM1, β-catenin, c-Myc and Cyclin D1 after treatment with AZA. Osteosarcoma cells treated with AZA had lower protein levels of FOXM1, β-catenin, c-Myc and Cyclin D1 (Figure 6F), compared to non-treated cells. In addition, we also evaluated the effect of the AZA treatment on proliferation and colony formation ability of osteosarcoma cells. As shown in Figure 6G, the treatment with AZA greatly inhibited cell proliferation including that of hFOB1.19 cells. We also found that AZA treatment was able to repress the cell colony formation rates (Figure 6H and supplementary Figure 4). These results suggested that miR-370 could be silenced by DNA hypermethylation, leading to up-regulation of FOXM1, and eventually affecting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling transduction.
Figure 6.
DNA methylation affected the expression of miR-370 and the cell growth in osteosarcoma. (A) The upstream of miR-370 genomic locus had two CpG islands. CpG island prediction in the upstream of miR-370 genomic locus was performed in a database (http://www.urogene.org). The predicted two CpG islnds were indicated as island-1 and island-2. The genomic locus of miR-370 was indicated as red arrow. (B-C) Effects of AZA or TSA on miR-370 and FOXM1 expression in hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cell lines. The hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cells were treated with DMSO, AZA (1 μM) or TSA (300 nM), respectively. Then expression of miR-370 was determined by qRT-PCR. (D-E) Expression of methylated CpG islands with or without AZA treatment. The hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cell lines were treated with or without 1 μM AZA, then expression of methylated CpG island 1 and 2 was determined by qMSP analysis. (F) AZA treatment inhibited the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway. Cells used in (A) were lysed and immunobloted with anti-FOXM1, -β-Catenin, -c-Myc, -Cyclin D1 and -GAPDH antibodies, respectively. (G) AZA treatment inhibited cell proliferation. Cells used in (A) were subjected to the MTT assay to evaluate cell proliferation: cell viability was determined at 490 nm. (H) AZA treatment decreased colony formation ability. The hFOB1.19, U2OS and MG63 cells were seeded onto 6-well plates, and cultured with 0.1 ml DMEM medium supplemented with AZA (1 μM) for two weeks. Then, cells were stained with 0.5% crystal violet and the number of colonies was counted. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. **P<0.001.
Discussion
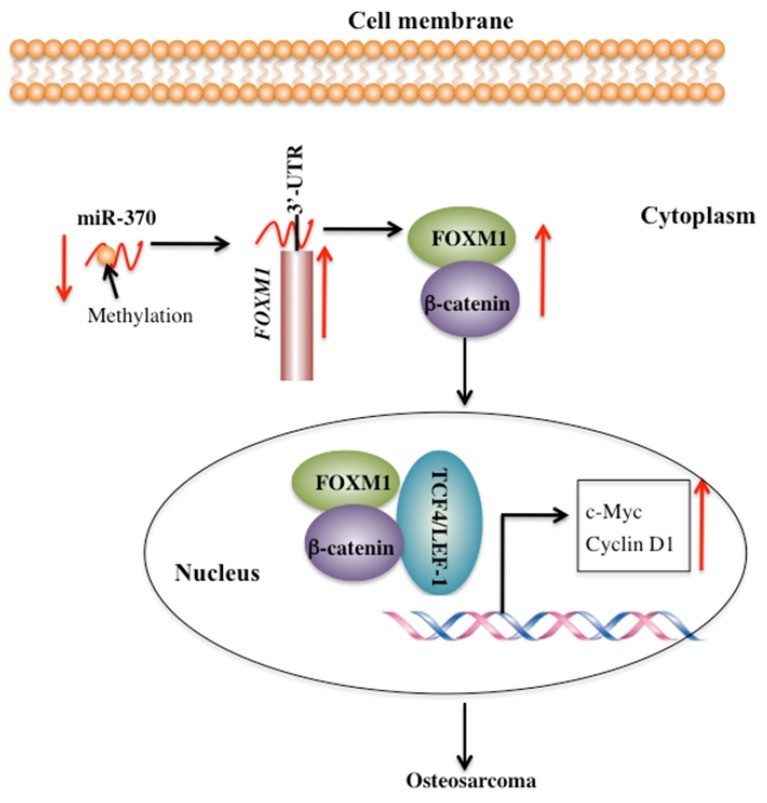
FOXM1 is aberrantly activated in many human cancers 19-24. However, little is known regarding the cause for the overexpression of FOXM1 and its downstream targets. Our previous study demonstrated that miR-370 directly targeted the 3'-UTR of FOXM1 to control osteosarcoma cell growth 24. In this study, we identified that DNA hypermethylation led to down-regulation of miR-370, thereby resulting in FOXM1 overexpression. In addition, we also found that FOXM1 directly bound β-catenin in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Their interaction could enhance their translocation to the nucleus, and to facilitate the formation of a functional complex with TCF4 on Wnt target-gene promoters, eventually activating the expression of c-Myc and Cyclin D1 (Figure 7).
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of the FOXM1/β-Catenin complex in human osteosarcoma cells. Elevated DNA methylation in the upstream region of miR-370 results in its down-regulation, which leads to up-regulation of FOXM1 gene. FOXM1 directly binds β-Catenin to form a complex and helps β-Catenin to translocate from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, where the FOXM1-β-Catenin complex interacts with the T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF) transcription factors, up-regulating the expression of downstream target genes of the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway such as c-Myc and Cyclin D1.
It appears that miRNAs are broadly involved in tumorigenesis through the targeting of critical genes regulating cancer-related signaling pathways 10-12. However, the mechanism underlying miRNAs dysregulation in cancer is not yet fully understood. Recent studies suggest that epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation and histone modifications play major roles in the regulation of miRNA expression 33, 34. Down-regulation of tumor suppressive miRNAs by CpG island hypermethylation is one of the most common mechanisms during tumorigenesis 35. Interestingly, previous studies have found that miR-370 is embedded within a CpG island 36, and experimental data also indicated that the attenuated expression of miR-370 in cancer cells was mediated by DNA methylation 36. In our study, we also identified two CpG islands located in the upstream of miR-370 genomic locus, and we examined the methylation status of these two CpG islands. Our results indicated that enhanced methylation level of CpG islands was in accordance with down-regulation of miR-370 in osteosarcoma cells, suggesting that the down-regulation of miR-370 is, at least, partly induced by DNA methylation in osteosarcoma cells. Furthermore, AZA treatment also repressed the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway because the induction of miR-370 inhibited the expression of FOXM1. These results suggested that re-expression of miR-370 could be an effective approach in osteosarcoma therapy and might contribute to the discovery of new therapeutic targets.
FOXM1 is a transcription factor. The identification of its downstream targets through transcriptional approaches and its interaction proteins through proteomics techniques are the most common methods to investigate its regulation roles and its involvement in different signaling pathways. Because the downstream targets of FOXM1 in osteosarcoma cells were unknown, in this study we focused on revealing its involvement in signal transduction. Fortunately, our two-step IP analysis minimized unspecific binding and identified β-catenin as a specific interaction partner of FOXM1. Further analyses indicated that FOXM1 activated the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by binding to β-catenin and enhancing β-catenin nuclear localization and transcriptional activity. These results were consistent with previous studies in glioma cells, suggesting that different cancer cells might share a conserved mechanism by which FOXM1 controls β-catenin nuclear accumulation and assembly of a transcription activation complex.
We determined the underlying mechanism through which miR-370 up-regulation suppressed osteosarcoma cell invasion and found that up-regulation of miR-370 could result in the inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Interestingly, pharmacological inhibition of FOXM1 by FDI-6 or β-catenin by PKF118-310 increased the level of miR-370. Although this effect was only partial because the level of miR-370 in osteosarcoma cells was not comparable to that in hFOB1.19 cells (Figure 5), this observation still attracted our attention. The mechanism underlying the changes of miR-370 level after these treatments is still unknown. Theoretically, these pharmacological inhibitors only affect the protein levels of FOXM1 and β-catenin. However, one possibility is that accumulation or attenuation of FOXM1 affects DNA methylation of CpG islands, which further regulates the level of miR-370. However, there is no evidence to support this hypothesis. Future analysis may focus on studying changes in DNA methylation after these pharmacological treatments to investigate this hypothesis. In addition, studies on the transcriptional function of FOXM1 and the identification of its downstream targets may also help us fully understand how FOXM1 and miR-370 function in osteosarcoma cells.
In summary, our studies revealed that FOXM1 interacted with β-catenin and that the DNA methylation-mediated attenuation of miR-370 resulted in FOXM1 overexpression, eventually contributing to the activation of β-catenin signaling in osteosarcoma cells. Our results further confirmed a conserved mechanism underlying the activation of β-catenin in tumorigenesis, and more importantly, they also provided promising new targets for osteosarcoma therapy in the future.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary figures.
Acknowledgments
We thank to Dr. Lin Wang from University of Colorado for his carefully revision of this paper.
Authors' contributions
C. Z., X. C. and K. W. designed the research. W. Z. and N. D. performed most of the experiments. Q. Z., T. S. and Z. L. performed some parts of the research. W. Z. and N. D analyzed data, tested statistics. C. Z organized the figures. C. Z., X. C. and K. W. wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
References
- 1.Durfee RA, Mohammed M, Luu HH. Review of Osteosarcoma and Current Management. Rheumatol Ther. 2016;3:221–43. doi: 10.1007/s40744-016-0046-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang W, Zhang L, Zheng K, Zhang X. miR-17-5p promotes the growth of osteosarcoma in a BRCC2-dependent mechanism. Oncol Rep; 2016. p. 35. 1473-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Qu F, Li CB, Yuan BT, Qi W, Li HL, Shen XZ. et al. MicroRNA-26a induces osteosarcoma cell growth and metastasis via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Oncol Lett. 2016;11:1592–6. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.4073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chen X, Chen XG, Hu X, Song T, Ou X, Zhang C. et al. MiR-34a and miR-203 Inhibit Survivin Expression to Control Cell Proliferation and Survival in Human Osteosarcoma Cells. J Cancer. 2016;7:1057–65. doi: 10.7150/jca.15061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pei H, Jin Z, Chen S, Sun X, Yu J, Guo W. MiR-135b promotes proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells via targeting FOXO1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;400:245–52. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Qu Y, Pan S, Kang M, Dong R, Zhao J. MicroRNA-150 functions as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma by targeting IGF2BP1. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:5275–84. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4389-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kobayashi E, Hornicek FJ, Duan Z. MicroRNA Involvement in Osteosarcoma. Sarcoma. 2012;2012:359739. doi: 10.1155/2012/359739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Novello C, Pazzaglia L, Cingolani C, Conti A, Quattrini I, Manara MC. et al. miRNA expression profile in human osteosarcoma: role of miR-1 and miR-133b in proliferation and cell cycle control. Int J Oncol. 2013;42:667–75. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sampson VB, Yoo S, Kumar A, Vetter NS, Kolb EA. MicroRNAs and Potential Targets in Osteosarcoma: Review. Front Pediatr. 2015;3:69. doi: 10.3389/fped.2015.00069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kulis M, Esteller M. DNA methylation and cancer. Adv Genet. 2010;70:27–56. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380866-0.60002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Klutstein M, Nejman D, Greenfield R, Cedar H. DNA Methylation in Cancer and Aging. Cancer Res. 2016;76:3446–50. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-3278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Reddington JP, Sproul D, Meehan RR. DNA methylation reprogramming in cancer: does it act by re-configuring the binding landscape of Polycomb repressive complexes? Bioessays. 2014;36:134–40. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yin H, Song P, Su R, Yang G, Dong L, Luo M. et al. DNA Methylation mediated down-regulating of MicroRNA-33b and its role in gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 2016;6:18824. doi: 10.1038/srep18824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ueda Y, Ando T, Nanjo S, Ushijima T, Sugiyama T. DNA methylation of microRNA-124a is a potential risk marker of colitis-associated cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:2444–51. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lv LV, Zhou J, Lin C, Hu G, Yi LU, Du J. et al. DNA methylation is involved in the aberrant expression of miR-133b in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2015;10:907–12. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Myatt SS, Lam EW. The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:847–59. doi: 10.1038/nrc2223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Saba R, Alsayed A, Zacny JP, Dudek AZ. The Role of Forkhead Box Protein M1 in Breast Cancer Progression and Resistance to Therapy. Int J Breast Cancer. 2016;2016:9768183. doi: 10.1155/2016/9768183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wierstra I. The transcription factor FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1): proliferation-specific expression, transcription factor function, target genes, mouse models, and normal biological roles. Adv Cancer Res. 2013;118:97–398. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407173-5.00004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kalinina OA, Kalinin SA, Polack EW, Mikaelian I, Panda S, Costa RH. et al. Sustained hepatic expression of FoxM1B in transgenic mice has minimal effects on hepatocellular carcinoma development but increases cell proliferation rates in preneoplastic and early neoplastic lesions. Oncogene. 2003;22:6266–76. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kalin TV, Wang IC, Ackerson TJ, Major ML, Detrisac CJ, Kalinichenko VV. et al. Increased levels of the FoxM1 transcription factor accelerate development and progression of prostate carcinomas in both TRAMP and LADY transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1712–20. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Madureira PA, Varshochi R, Constantinidou D, Francis RE, Coombes RC, Yao KM. et al. The Forkhead box M1 protein regulates the transcription of the estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:25167–76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603906200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim IM, Ackerson T, Ramakrishna S, Tretiakova M, Wang IC, Kalin TV. et al. The Forkhead Box m1 transcription factor stimulates the proliferation of tumor cells during development of lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2153–61. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang Z, Banerjee S, Kong D, Li Y, Sarkar FH. Down-regulation of Forkhead Box M1 transcription factor leads to the inhibition of invasion and angiogenesis of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:8293–300. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Duan N, Hu X, Yang X, Cheng H, Zhang W. MicroRNA-370 directly targets FOXM1 to inhibit cell growth and metastasis in osteosarcoma cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:10250–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yuan F, Wang W. MicroRNA-802 suppresses breast cancer proliferation through downregulation of FoxM1. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12:4647–51. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wang IC, Snyder J, Zhang Y, Lander J, Nakafuku Y, Lin J. et al. Foxm1 mediates cross talk between Kras/mitogen-activated protein kinase and canonical Wnt pathways during development of respiratory epithelium. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32:3838–50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00355-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ma RY, Tong TH, Leung WY, Yao KM. Raf/MEK/MAPK signaling stimulates the nuclear translocation and transactivating activity of FOXM1. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;647:113–23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-738-9_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhang N, Wei P, Gong A, Chiu WT, Lee HT, Colman H. et al. FoxM1 promotes beta-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:427–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.08.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen Y, Li Y, Xue J, Gong A, Yu G, Zhou A, Lin K, Zhang S, Zhang N, Gottardi CJ, Huang S. Wnt-induced deubiquitination FoxM1 ensures nucleus beta-catenin transactivation. EMBO J. 2016;35:668–84. doi: 10.15252/embj.201592810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chuang JC, Jones PA. Epigenetics and microRNAs. Pediatr Res. 2007;61:24R–29R. doi: 10.1203/pdr.0b013e3180457684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhang C, Guo H, Zhang J, Guo G, Schumaker KS, Guo Y. Arabidopsis cockayne syndrome A-like proteins 1A and 1B form a complex with CULLIN4 and damage DNA binding protein 1A and regulate the response to UV irradiation. Plant Cell. 2010;22:2353–69. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.073973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lievens S, Lemmens I, Tavernier J. Mammalian two-hybrids come of age. Trends Biochem Sci. 2009;34:579–88. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.06.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang Y, Li H, Zhang C, An X, Liu L, Stubbe J. et al. Conserved electron donor complex Dre2-Tah18 is required for ribonucleotide reductase metallocofactor assembly and DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:E1695–704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405204111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cedar H, Bergman Y. Linking DNA methylation and histone modification: patterns and paradigms. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:295–304. doi: 10.1038/nrg2540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Suzuki H, Maruyama R, Yamamoto E, Kai M. DNA methylation and microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Mol Oncol. 2012;6:567–78. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2012.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Meng F, Wehbe-Janek H, Henson R, Smith H, Patel T. Epigenetic regulation of microRNA-370 by interleukin-6 in malignant human cholangiocytes. Oncogene. 2008;27:378–86. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yamane K, Naito H, Wakabayashi T, Yoshida H, Muramatsu F, Iba T. et al. Regulation of SLD5 gene expression by miR-370 during acute growth of cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30941. doi: 10.1038/srep30941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary figures.