Abstract
The gene encoding N epsilon-(indole-3-acetyl)-L-lysine synthetase, iaaL, from Pseudomonas savastanoi was localized within a 4.25-kilobase EcoRI fragment derived from pIAA1 of oleander strain EW 2009. Two open reading frames of 606 and 1188 nucleotides were identified upon sequencing, which directed the in vitro synthesis of Mr 21,000 and Mr 44,000 proteins. Expression of an open reading frame-2 subclone, pMON686, in Escherichia coli indicates that (indole-3-acetyl)-L-lysine synthetase is encoded solely by open reading frame-2. Hydrophobicity plots of the deduced open reading frame-1 protein suggest that it may be a membrane-bound protein, whereas the predicted iaaL gene product possesses considerable hydrophilic character, consistent with the demonstration of (indole-3-acetyl)-L-lysine synthetase activity in cell-free aqueous extracts. No nucleotide or protein homologies were found between iaaL and any sequences contained within the GenBank or National Biomedical Research Foundation data bases (April 13, 1989).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D. A., Gordon M. P. Cytokinin production by Agrobacterium and Pseudomonas spp. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4242–4248. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4242-4248.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Kosuge T. Cloning characterization of iaaM, a virulence determinant of Pseudomonas savastanoi. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):40–46. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.40-46.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Kosuge T. Involvement of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid in indoleacetic acid synthesis in Pseudomonas savastanoi. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):950–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.950-957.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass N. L., Kosuge T. Cloning of the gene for indoleacetic acid-lysine synthetase from Pseudomonas syringae subsp. savastanoi. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):598–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.598-603.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass N. L., Kosuge T. Role of indoleacetic acid-lysine synthetase in regulation of indoleacetic acid pool size and virulence of Pseudomonas syringae subsp. savastanoi. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2367–2373. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2367-2373.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
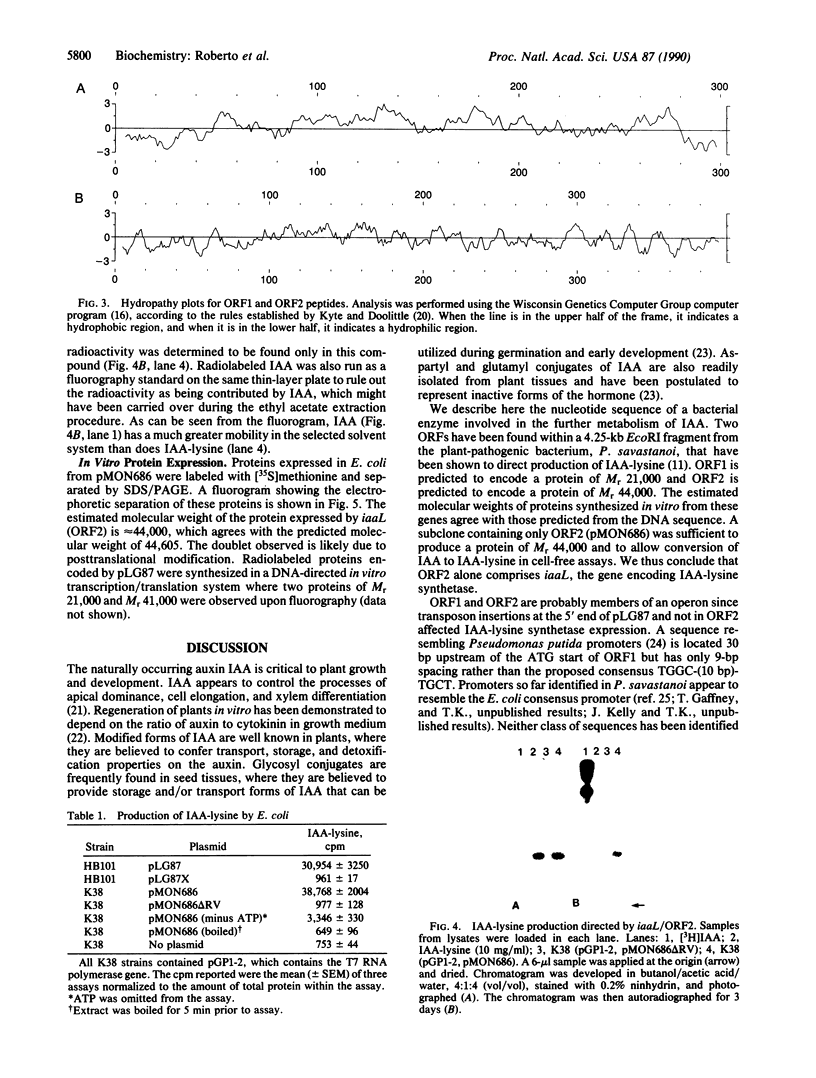
- Hutzinger O., Kosuge T. Microbial synthesis and degradation of indole-3-acetic acid. 3. The isolation and characterization of indole-3-acetyl-epsilon-L-lysine. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):601–605. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlow J. L., Kosuge T. Tryptophan and indoleacetic acid transport in the olive and oleander knot organism pseudomonas savastanoi (E.F. Smith) Stevens. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):211–219. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell G. K., Morris R. O. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a Pseudomonas savastanoi cytokinin biosynthetic gene: homology with Agrobacterium tumefaciens tmr and tzs loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2555–2565. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOOG F., MILLER C. O. Chemical regulation of growth and organ formation in plant tissues cultured in vitro. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1957;11:118–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmülling T., Schell J., Spena A. Single genes from Agrobacterium rhizogenes influence plant development. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2621–2629. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Hugly S., Buchholz W. G., Thomashow L. S. Molecular basis for the auxin-independent phenotype of crown gall tumor tissues. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):616–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3511528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White F. F., Taylor B. H., Huffman G. A., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Molecular and genetic analysis of the transferred DNA regions of the root-inducing plasmid of Agrobacterium rhizogenes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):33–44. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.33-44.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]