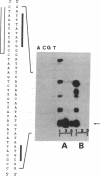
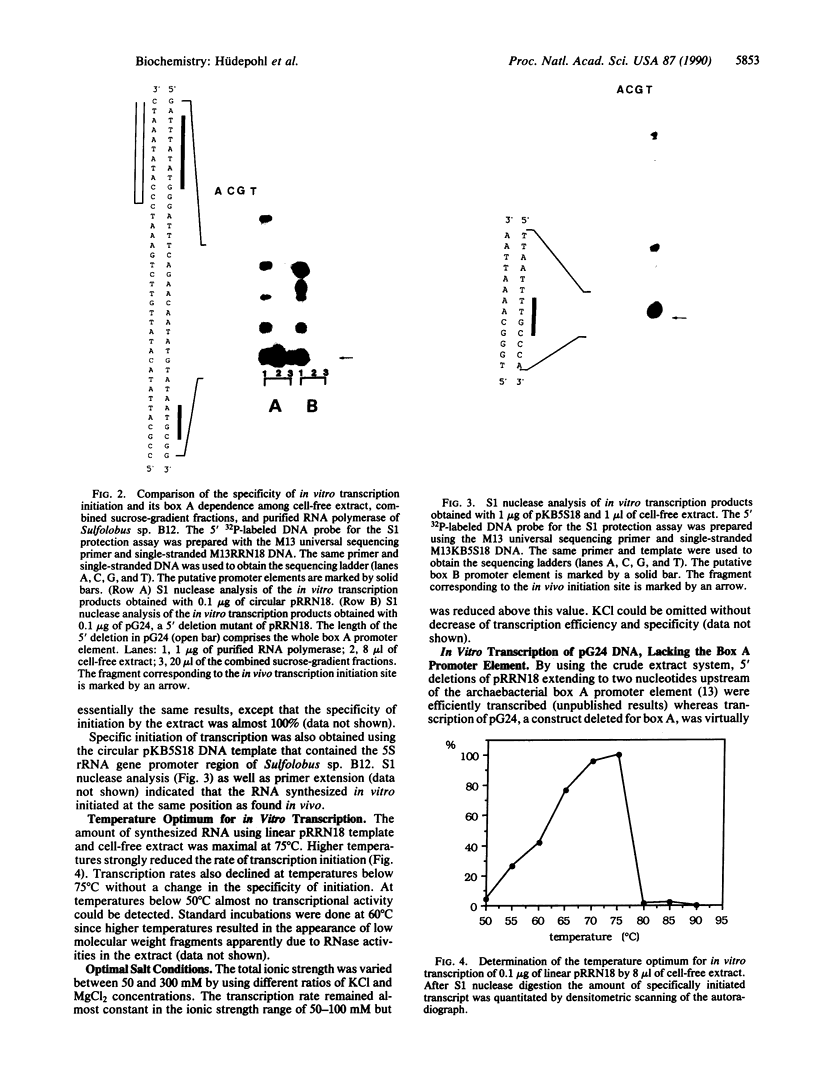
Abstract
We describe a cell-free transcription system for the archaebacterium Sulfolobus sp. B12 that specifically initiates transcription at the 5S rRNA-encoding DNA and the 16S/23S rRNA-encoding DNA promoters of the same species. With this crude extract system, specific initiation was absolutely dependent on the box A motif, a highly conserved promoter element in archaebacteria located approximately 25 base pairs upstream of transcription initiation sites. In vitro transcription of the rRNA genes by purified RNA polymerase, however, resulted in semi-specific, box A-independent initiation, indicating that factor(s) in the crude extract were necessary for the highly specific box A-dependent transcription. Fractionation of the cell-free extract by sucrose-gradient centrifugation resulted in the identification of a low molecular weight fraction complementing purified RNA polymerase to an extract-like specificity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldea M., Claverie-Martín F., Díaz-Torres M. R., Kushner S. R. Transcript mapping using [35S]DNA probes, trichloroacetate solvent and dideoxy sequencing ladders: a rapid method for identification of transcriptional start points. Gene. 1988 May 15;65(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90421-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Brock K. M., Belly R. T., Weiss R. L. Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(1):54–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00408082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Thomm M., Beckler G. S., Frey G., Stetter K. O., Reeve J. N. An archaebacterial RNA polymerase binding site and transcription initiation of the hisA gene in Methanococcus vannielii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):135–150. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gropp F., Palm P., Zillig W. Expression and regulation of Halobacterium halobium phage phi H genes. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):182–188. doi: 10.1139/m89-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne M., Pfeifer F. Expression of two gas vacuole protein genes in Halobacterium halobium and other related species. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Sep;218(3):437–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00332407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Dathan N. A., Parry H. D., Carbon P., Krol A. Changing the RNA polymerase specificity of U snRNA gene promoters. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G. Use of sodium trichloroacetate and mung bean nuclease to increase sensitivity and precision during transcript mapping. Anal Biochem. 1986 Oct;158(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90605-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prangishvilli D., Zillig W., Gierl A., Biesert L., Holz I. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of thermoacidophilic archaebacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;122(3):471–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Voos W., Kaniecki J., Grampp B., Schulz W., Zillig W. Putative promoter elements for the ribosomal RNA genes of the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus sp. strain B12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5581–5595. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Zillig W. Analysis of transcription in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus indicates that archaebacterial promoters are homologous to eukaryotic pol II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):1–19. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Groot Koerkamp M. J., Tabak H. F. Mitochondrial RNA polymerase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: composition and mechanism of promoter recognition. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3255–3262. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03192.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Koerkamp M. J., Touw E. P., Tabak H. F. Specificity factor of yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase. Purification and interaction with core RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12785–12791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac A. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(1):31–90. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomm M., Stetter K. O. Transcription in methanogens. Evidence for specific in vitro transcription of the purified DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):345–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomm M., Wich G. An archaebacterial promoter element for stable RNA genes with homology to the TATA box of higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):151–163. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeats S., McWilliam P., Zillig W. A plasmid in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1035–1038. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Palm P., Reiter W. D., Gropp F., Pühler G., Klenk H. P. Comparative evaluation of gene expression in archaebacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 2;173(3):473–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Stetter K. O., Janeković D. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from the archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):597–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Zechel K., Halbwachs H. J. A new method of large scale preparation of highly purified DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from E. coli. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Feb;351(2):221–224. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1970.351.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]