Abstract
Animal integumentary coloration plays a crucial role in visual communication and camouflage, and varies extensively among and within species and populations. To understand the pressures underlying such diversity, it is essential to elucidate the mechanisms by which animals have created novel integumentary coloration. Colours can be produced by selective absorption of light by skin pigments, through light scattering by structured or unstructured tissues, or by a combination of pigments and nanostructures. In this review, we highlight our current understanding of the interactions between pigments and structural integumentary tissues and molecules. We analyse the available evidence suggesting that these combined mechanisms are capable of creating colours and optical properties unachievable by either mechanism alone, thereby effectively expanding the animal colour palette. Moreover, structural and pigmentary colour mechanisms frequently interact in unexpected and overlooked ways, suggesting that classification of colours as being of any particular type may be difficult. Finally, we discuss how these mixtures are useful for investigating the largely unknown genetic, developmental and physical processes generating phenotypic diversity.
This article is part of the themed issue ‘Animal coloration: production, perception, function and application’.
Keywords: nanostructures, pigments, integument, colour
1. Introduction
Integumentary colours serve in crypsis, advertisement for mates, aposematism (warning) and startling prey (reviewed in [1]), and the pigments and structures that produce them serve non-communication functions like thermoregulation and resistance to mechanical wear (reviewed in [2]). These colours are produced by a variety of pigment molecules, nanostructures or a combination of both [3]. This mechanistic diversity provides complex opportunities for natural and sexual selection on the many functions of integumentary colour. Thus, colour is a fundamental aspect of the physiology and functional morphology of integuments and has probably played a critical role in all stages of its evolution.
Understanding how morphological and chemical properties relate to function is a central goal of physiology that has been relatively unexplored in coloured integumentary tissues in general. This is a critical gap both at a fundamental level and because it provides a window into the evolution of integuments and their associated colours. While several recent review papers have thoroughly covered the mechanisms and/or evolution of structural coloration [4–7] and pigments [8,9] as far as we are aware only a brief section of one [3] has explicitly covered how these mechanisms interact to produce colour. Here we aim to cover this topic in greater detail, including information from mostly animals and, to a lesser extent, plants. We hope to illustrate that interactions between colour production mechanisms are more common than typically thought. With this in mind, we begin by describing the complex colour production systems in poikilothermic vertebrates. We then discuss how even ‘pigmentary’ colours may be affected by structural components via their interactions with disordered nanostructures. We primarily focus on terrestrial organisms, but the principles described here probably also hold true for aquatic organisms. This is because our focus is on the colours as measured objectively by a spectrophotometer and not how organisms perceive them in different habitats. We focus on the wavelengths from 300 to 700 nm, primarily because little data exist outside of these wavelengths, and they are relevant to many organisms including birds and butterflies [3].
2. Overview of colour production mechanisms
Perhaps the most straightforward mechanism of colour production is deposition of pigments. Pigments selectively absorb some wavelengths of light while allowing others to be reflected, and their absorption profile depends on their underlying chemistry [8]. Of the more than five classes of pigments identified in animals, the most common are melanins and carotenoids [8,10]. Melanin is the most widespread colour-producing pigment in animals and creates a broad range of black, brown and grey colours (figure 1a, figure 2II) through broadband light absorption across the visible spectrum [10]. There are two chemical variants of melanin, black eumelanin and rusty red (rufous) phaeomelanin [11]. In vertebrates, both types are produced within organelles called melanosomes that are deposited directly from melanocytes into the developing integument [12]. Therefore, unlike other pigments, which are diffusely deposited, melanins are contained within discrete elements. Pure eu- and phaeomelanosomes are easily distinguished morphologically (rod-shaped versus spherical, respectively [13]); however, most melanin-based feather colours are produced by a mixture of the two in varying concentrations of eumelanin and phaeomelanin [10]. In invertebrates, melanin appears in transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to be diffusely deposited [3,14] although it is unclear whether the electron-dense material is indeed melanin since only limited chemical tests have been performed on such samples. As thus might be expected, little is known about the pathway of melanogenesis in insects. Indeed, Hsiung et al. [15] recently demonstrated the presence of melanin in spiders using Raman spectroscopy, despite the absence of known melanin-production genes in spiders. Overall, melanin remains an intensively studied but still mysterious and poorly understood group of pigments.
Figure 1.
Examples of colours produced by different mechanisms. (a) Melanin-based black colour of an anglerfish Melanocetus johnsonii. (b) Red pterin pigments in the butterfly Pachliopta hector. (c) Blue structural colour in feathers of the laughing kookaburra Dacelo novaeguineae. (d) Scales from the gecko Phelsuma lineata with melanic (black), structural (blue), pteridine (orange) and mixed structural-pigmentary (green) colours. (e) American goldfinch (Spinus tristis) with yellow feathers resulting from a yellow carotenoid pigment absorbing from a white structural background. (f) Budgerigar (Melopsittacus undulatus) with green feathers resulting from the interaction between a pigment and ordered nanostructure. (g) Leucistic (i.e. lacking melanin) Steller's jay (Cyanocitta sterlleri) illustrating the effects of loss of melanin on blue structural colour production. (h) Golden-breasted Starling (Cosmopsarus regius) with iridescent colours produced by ordered arrays of melanosomes in feathers. (i) Live (top) and cooked (bottom) Homarus lobster showing change in carotenoid colour with protein binding. (j) Eggs of the tinamou species Eudromia elegans (green) and Nothura maculosa (black) with glossy colours produced by smooth surfaces and pigments. (k) Tarantula Poecilotheria metallica, whose blue colours have their iridescence reduced by microscale structuring of the hairs. (l) Dwarf chameleons Bradypodion pumilum can change colour by altering the arrangement of their coloured tissues. Photo credits: (a) Australian National Fish Collection, CSIRO, (b) Wikimedia commons, (c,d) Liliana D'Alba, (e) Flickr (JD 2003), (f) Flickr (Chobist Budgerigar), (g) Bill Schmoker, (h) Liliana D'Alba, (i) Paul Stainthorp (top), Sven Kullander (bottom), (j) Liliana D'Alba, (k) Cathy Keifer and (l) Charles J. Sharp. All photos used by permission or by Common Creative License.
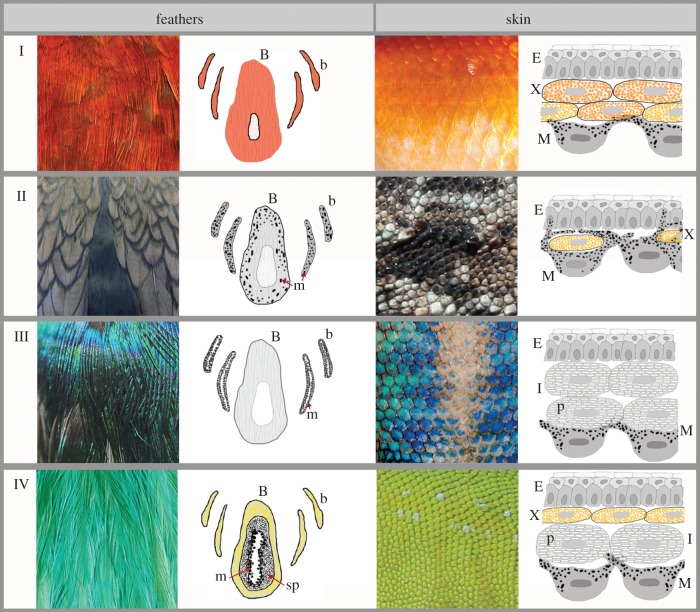
Figure 2.
Mechanisms leading to the production of colours in feathers and skin (fish, reptile and amphibian). (I) Colours produced predominantly by red or yellow pigments (e.g. carotenoids, pteridines), (II) dark browns and blacks produced by melanins, (III) examples of predominantly structural coloration, (IV) examples of combined pigmentary and structural colours. Drawings on the centre left represent cross sections of feather barbs and barbules; B = feather barb, b = barbule, m = melanosome, sp = keratinous spongy layer. Drawings on the far right demonstrate cross sections of fish, amphibian and reptile epidermis showing layers of different chromatophores; E = epidermis, x = xanthophore, M = melanophore, I = iridiphore.
By contrast to melanin, carotenoid pigments in animals are acquired through the diet (they are produced endogenously by plants, algae and photosynthetic pigments [16]) and produce bright red, orange and yellow colours [17]. They are chemically characterized by long chains of carbon with double and single bonds (polyenes) sometimes terminated by rings. Polyenes determine the light absorption properties of carotenoids, which peak around blue wavelengths [17]. This property limits them to production of longer-wavelength colours. Pterin pigments found in butterflies (figure 1b) [18,19] strongly absorb at a range of wavelengths, enabling production of colours from white to red [19]. Psittacofulvins, found in parrots, are produced endogenously and generate colours similar to those of carotenoids, while copper-containing turacoverdins in Turacos (family Musophagidae) enable production of green colour [20]. Bile pigments like biliverdin in avian eggs can produce even shorter-wavelength hues [20].
The second major mechanism of colour production is termed structural coloration and is produced by scattering of light from nano-scale reflective tissues (nanostructures) that periodically vary in refractive index (RI). Most blue, violet and ultraviolet (UV) colours, as well as all iridescent colours, are produced via structural colours [21,22]. For example, iridescent structural colours in birds are generally produced by laminar or crystalline arrays of melanin granules embedded in keratin [3,6]. Light is scattered at the interfaces of these materials that differ in refractive index (RI: a measurement of how light is altered as it moves through a material [3]). By contrast, amorphous arrays of keratin and air within feather barbs are probably responsible for producing the non-iridescent blue, turquoise, violet and UV colours found in a number of species (figure 1c) [3,6]. Unlike pigments, structural mechanisms appear to be capable of producing colours across the visible spectrum from UV to red [7] through the use of a limited number of materials (e.g. chitin, keratin, melanin) with diverse nanostructural architectures.
3. Combined structural and pigmentary colours
Although they are frequently analysed in isolation from one another, structural and pigmentary colours often interact. Indeed, in some cases it can be difficult to state with certainty whether nanostructures or pigments produce a given colour. In other cases, these combinations may enable the attainment of colours that are not possible, or are attained only with difficulty, by either mechanism alone [23,24]. In some cases, pigments and nanostructures that interact are intricately intertwined in a complex and dynamic system.
Ectothermic vertebrates have diverse colours that result from the interactions among different components of a multilayered, three-dimensional dermal system that often contains multiple pigment types and structural features (figure 2, right hand column) [25]. The interaction among these layers, collectively known as ‘the dermal chromatophore unit’ [26], determines the overall reflectance of the skin, and changes in any of these components can modify the resulting colour. Four dermal cell layers are involved in colour production in fish [27], amphibians [26] and reptiles [28,29]. The layer closest to the epidermis consists of xanthophore and/or erythrophore cells, which use carotenoid or pteridine pigments, respectively, to generate yellow and orange hues.
Iridophore cells form the middle layer, and these produce structural colours ranging from white to purple through thin-layer interference and scatter or diffraction of light from the transparent, nano-scaled purine or guanine crystals inside them [26–30]. The size, shape, orientation and number of crystalline platelets determine the colour produced by iridophores [31,32]. The deepest cell layer is formed by melanophores, which, depending on the amount of melanin contained in them, determine the overall darkness of the body by producing black or brown colours.
The close interaction between and the precise co-localization of pigment (xanthophores, erythrophores and melanophores) and structural (iridophores) cells generate extensive variation in integumentary colours. For example, Phelsuma geckos exhibit a body colour scheme that includes all three, pigmentary, structural and melanic colorations (figure 1d) [33]. The authors showed that fine variation in blue/green hues is caused by the ratio of structural blue iridophores (with specific crystal size and organization) to yellow xanthophores. Reflectivity of red dorsal marks, formed by red erythrophores, depends on the underlying layer of iridophores that contain disorganized crystals acting as broadband reflectors.
Grether et al. [34] presented a generalized model to calculate reflectance from coloured integuments such as these containing both structural and pigmentary elements. They applied this method to multicomponent chromatophores of poikilotherm vertebrates that include both coherently scattering iridophores and light-absorbing pigments. The method compartmentalizes transmission (T) and reflectance (R) of any number of layers such as (in the case of non-iridescent green feathers): (1) outer cortex, which may include carotenoids; (2) coherent scattering nanostructure, either spongy keratin or melanin arrays; and (3) central vacuole and barb ramus keratin, often including carotenoids and melanin. This model could be used to produce comprehensive analyses of colour-producing integument, provided that the thickness and complex refractive indices of the component materials can be accurately determined. Thickness can be calculated using electron microscope (EM) images (assuming that the EM preparation steps do not alter these values, which can in some cases be checked using minimally prepared samples on the scanning electron microscope (SEM)) and complex RI of keratin and pigment can be calculated using a number of methods [35]. A variety of tools can then be used to model colour production by colour-producing nanostructures. For example, although it has been criticized [36,37], the Fourier tool normalizes 2D Fourier power distributions to reflectance spectra given the number of light-scattering interfaces and the RI difference. For multilayer nanostructures, the matrix method or finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) analysis directly outputs predicted reflectance spectra (reviewed in [35]). In this way, the complex interactions between multiple components of skin colour can be holistically modelled. However, other, less well-understood interactions may also need to be taken into consideration in these and other animals.
(a). Interactions between disordered nanostructures and pigments
Pigments in natural materials are by necessity encased in some other structural material such as keratin, chitin and cellulose (figure 2I). Because light interacts with these materials, as well as the pigments themselves, even classic examples of ‘pigment-based’ colours like yellow feathers may in fact have a structural component, such as an array of randomly sized and spaced sub-micron air holes in a keratin matrix (figure 1e) [38,39]. A thicker array could incoherently scatter more light, increasing brightness. Pigments selectively absorb certain wavelengths of light and create colour by absorbing light from the substrate in which they are deposited [38]. Thus, the colours they produce depend not only on which wavelengths they absorb but also on brightness of the encasing substrate. For example, a thicker incoherent array may produce a brighter white colour than a duller one [39], and, given the same amount of pigment, will therefore produce a brighter yellow colour.
How strong is this effect? While some studies have shown that, compared to variation in structural components, pigment concentration has a stronger effect on colour output [40], others have shown that their effects are comparable [41,42]. This has led to the intriguing hypothesis that the signalling properties of carotenoid deposition and structural whiteness are decoupled, and thus that feathers may contain multiple types of information [41,42]. This hypothesis is contingent on understanding both the mechanisms and development of white feathers, but thus far they are both largely unknown. It is clear, however, that the coupling of white and other structurally coloured feathers with pigments enables variation (particularly achromatic variation) that would probably not be possible with pigments alone.
(b). Interactions between ordered nanostructures and pigments
This coupling of pigments and nanostructures is even more apparent in non-iridescent green colours of feathers, which may be difficult to produce without structure–pigment combinations (the green colours produced by turacoverdin pigments are produced by a pigment that requires large quantities of copper, which is probably difficult to obtain from the diet [20]). Iridescent green colour can be produced in feathers, generally in the barbules, by coherent scattering of light by layers of keratin and melanin (figure 2II) [6]. In addition, some olive-green colours are produced by combination of carotenoid pigments in the barb and melanin in the barbules [22]. However, bright non-iridescent greens (figure 1f) in all cases other than turacos are produced by a combination of quasi-ordered spongy keratin arrays and carotenoid or psittacofulvin pigments (figure 2IV) [6,22,23,43,44]. These pigments appear to be placed in the keratin cortex of barbs, above the colour-producing nanostructures [43]. Traditionally, it was thought that the yellow pigments and blue quasi-ordered keratin nanostructures mixed together to form the green colour [6]. However, recent work has shown that the spongy layer is tuned to produce peak reflectance in the green wavelengths, but that the overall curve is quite broad and includes considerable reflectance in the blue wavelengths [43]. The pigment absorbs these blue wavelengths, enabling saturation of the green peak and green colour visibility. A similar mechanism of selective absorption coupled with a colour-producing nanostructure causes green colour in some butterflies [45]. The breadth of peaks created by quasi-ordered nanostructures appears to be consistent regardless of the hue they produce. Because the majority of them are blue, however, the ‘spillover’ reflectance is in the UV and thus invisible to human eyes. Thus, quasi-ordered spongy layers produce what appears to be blue to the human eye, but is UV to birds. Quasi-ordered nanostructures with a more spherical morphology (as opposed to a more ‘channel-like’ morphology) produce more saturated blue colours that have additional small short-wavelength peaks caused by double scattering [46,47]. No spongy structure has been shown to produce any longer-wavelength colour than green, and indeed a theoretical paper [48] has shown that it is not possible due to double scattering that would cause, for example, red-tuned nanostructures to appear violet due to double-scattering peaks in the blue-green (but see [44]). In theory, co-localized pigments could absorb these additional peaks as they do for non-iridescent green, but we have not seen any evidence that these combinations occur in nature.
Production of non-iridescent blue colour by birds also involves co-localized melanosomes (figure 2III). These melanin-filled organelles are typically found basal to the spongy layer and serve the critical function of absorbing incoherently scattered white light [36,39,49]. Only a certain percentage of light is scattered by the spongy layer to produce blue, and the remainder is scattered incoherently. Without the broadband absorption provided by melanin, this white colour illumination would swamp out the blue, leading to a whitish colour with only a hint of blue. This principle has been demonstrated both experimentally through production of synthetic optical materials [50] and through comparison of colour and nanostructure between normal and naturally amelanotic blue Steller's Jay feathers (figure 1g) [49]. Melanosomes localized above or within spongy layers prevent light from reaching them, leading to black colour [51,52]. In some cases, several spongy-layer cells surround a single layer of melanosomes [6], but how this affects colour has not been examined. Iridescent hairs in golden moles [53] also contain a backing layer of melanosomes that may enhance the saturation of the colour. Some butterflies similarly use either selective or broadband absorbance to enhance or otherwise alter colours produced by nanostructures [54].
The iridescent colours of birds are produced by a number of optical processes including scattering, interference and diffraction from organized arrays of melanosomes in feather barbules (figure 1h, figure 2III) [6]. These melanosomes can be solid or hollow, spherical or rod-shaped, flattened or round and can form thin films, multilayers, square or hexagonal arrays and other ordered nanostructural forms. As light moves through these heterogeneous materials, it is scattered at their interfaces (e.g. keratin/air or melanin/air), transmitted and/or absorbed. Whether the non-scattered light is transmitted and/or absorbed depends on the relative properties of the materials, for example, in terms of differences in their RI. Keratin absorbs light negligibly, but melanin has broadband absorbance that decreases with increasing wavelength [55]. This means that it acts as both a pigment and a scattering nanostructural material: its high RI (approx. 1.7–2, [3,56,57]) enables a sharp contrast with lower RI materials like keratin, while its absorbance prevents incoherent scattering, increasing saturation, while at the same time lowering overall reflectance (brightness). Thus, the brightest iridescent colours in birds like hummingbirds have the thinnest melanin layers and the smallest melanin volume fractions [58]. The pigmentary properties of melanin thus play a significant role in their production of structural colour, and therefore iridescent colours in birds can properly be considered to be structure–pigment interactions.
4. Interaction between proteins and pigments
Proteins themselves can alter the hue produced by carotenoids and carotenoid–nanostructure interactions. Pure carotenoids absorb light in the wavelengths between 400 and 500 nm, producing intense yellow, orange and red colours. However, these colours can change to blue, purple or green when carotenoids form complexes with structural (i.e. non-enzymatic) proteins [59]. In invertebrates, carotenoid–protein interactions known as carotenoproteins have a considerable effect on the light-absorption properties of the pigment, leading to drastic shifts in colour. For example, mollusk shell colour is produced by the presence of polyenes (polyunsaturated organic compounds containing one or more sequences of single and double carbon–carbon bonds) embedded in a matrix of proteins and aragonite. Interspecific variation in colour in the senatorial scallop Chlamys senatoria can be due to the formation of specific polyene pigment–protein complexes leading to the modification of colour with the same pigment [60]. In the lobster carapace, the binding of astaxanthin by protein in the carotenoprotein complex α-crustacyanin causes a redistribution of electron density and a reorientation of the carotenoid molecules in the complex, and results in a shift from 488 to 632 nm (explaining the change in colour from blue, seen in live animals, to red colour as in cooked or dehydrated lobster (figure 1i) [61]).
A similar phenomenon has been observed in vertebrate tissues. Here, carotenoids are seldom found free as they become susceptible to oxidative damage and may be broken down rapidly if exposed to oxidizing species or free radicals.
In feathers, fish and reptile scales, carotenoids are usually stabilized by the proteins to which they are strongly bound [62,63]. Owing to variations in protein composition, different pigment–protein interactions can result. The same carotenoid in feathers of the same species can be yellow, orange or red depending on the protein binding. For example, the same carotenoid (ɛ,ɛ-carotene-3,3′-dione) produces red and yellow colours in goldfinch Carduelis carduelis feathers [62]. More recently, Mendes-Pinto et al. [64] reported a more striking difference in feather colour, varying from red (scarlet ibis) to orange (summer tanager) to violet purple (white-browed purpletuft). All three colours are produced by the same pigment, canthaxanthin (β,β-carotene-4,4′-dione). Its physical conformation and thus light-absorbing properties vary with how it is bound to keratin, which in turn is determined by the molecular conformation of keratin's binding site. Thus, carotenoid-based colours can be altered by the molecular conformation of the keratin substrate to which they are bound. In other cases, pigments and nano- or macrostructures can interact to produce additional optical features.
5. Additional optical features produced by structure–pigment interactions
(a). Gloss
Many coloured materials have a characteristic shiny appearance that is frequently referred to as gloss [65]. While it has been defined and quantified in numerous ways [66], gloss generally indicates how well a surface reflects light in a specular (‘mirror-like’, in the same amount and at the same angle at which it strikes the material) manner. Because most natural materials reflect both specularly and diffusely (‘cloud-like’, in which light is scattered at other angles), it is typically necessary to take both types of reflectance into consideration. Thus, it can be useful to quantify gloss as the ratio of specular to diffuse reflectance (Hunter's contrast gloss) with higher values indicating higher gloss. Glossy materials also tend to show greater polarization because specular light is polarized while diffuse light is not [66]. Although gloss can vary with angle, it is distinct from iridescence, in which hue itself changes with angle of incidence. Indeed, although many glossy materials are also iridescent [67], others are not [68]. This is in part because, unlike iridescence, gloss can be produced by mechanisms distinct from those that make the colours themselves. Smooth surfaces produce gloss because they lack the surface roughness (e.g. cracks, bumps and other topographic features) that diffusely scatter light. Any coloured material can therefore be glossy if its surface roughness is below a certain threshold (i.e. Rayleigh's criterion [66]). For example, pigments produce the green colours of tinamou eggs, but their smooth surfaces produce gloss (figure 1j) [69] that other eggs with similar colours lack. Other morphological features like flattening (lack of curvature) may also enhance gloss [68]. Because pigments frequently produce the base hue, and morphology enhances specular reflection, gloss is a clear case of combined structural and pigmentary coloration. Interestingly, barbules of glossy black feathers are not any smoother than those of matte black feathers [67]. In this case, apparent glossiness appears to be a form of subtle iridescence produced by weakly organized thin films. This suggests that the gloss of iridescent materials may be mechanistically distinct and produced by the nanostructures themselves. In other words, perceived gloss of some iridescent materials may be a feature of the iridescence itself. While this hypothesis warrants additional investigation, it is clear that gloss-enhancing morphologies enable production of optical effects that could not be achieved with a single colour production mechanism.
Glossy colours are intriguing from a sensory perspective because they are generally more specular (‘shinier’) than matte colours, and maintain that specularity over a broader range of angles than iridescent colours. Gloss may thus be a mechanism for enhancing visibility and may be selected for either separately or in conjunction with pigments or colour-producing nanostructures. Almost no studies thus far have yet addressed these possibilities.
(b). Enhancement and reduction of iridescence by macrostructure
Iridescence itself may also be enhanced by structural modifications. Iridescent barbs and hairs are typically associated with flattened morphologies [6,70] perhaps to increase the surface area available for reflection, but also perhaps because flat surfaces have enhanced change in colour with angle of light incidence, i.e. iridescence. This is because planar (e.g. Bragg) stacks can only display colour in the specular direction. As the angle of specular incidence or viewing changes, the optical path length of the light changes, leading to production of different colours. Curving these planar stacks leads to a reduction in iridescence due to a loss of variation in optical path length. At any given angle of viewing, a majority of the optical paths traversed by light through a curved Bragg stack will be of the correct length to produce the primary colour [71,72]. This phenomenon was proposed by Dyck [72] for curved barbules in pigeon feathers, by Vignolini et al. for iridescent seeds [73] and Kolle et al. [71] for synthetic iridescent colour-changing fibres. Hsiung et al. [74] hypothesized that curvature plus the addition of lobes similarly reduced iridescence of tarantula hairs (figure 1k) and confirmed this hypothesis both through optical finite-element analysis and nanoscale 3D printing. The addition of curvature by itself dramatically reduced iridescence of the multilayer structure, while lobing had a more modest effect. Experimental and theoretical analysis thus supports the hypothesis that curvature is a general mechanism for iridescence reduction.
By contrast, iridescence of other integumentary nanostructures appears to be enhanced by macroscale features. The bright colours of the bird-of-paradise Lawe's parotia (Parotia lawesii) abruptly change colour from orange to blue with small changes in viewing angle because their boomerang-shaped barbules contain a blue-reflecting plane flanked by two orange-reflecting planes [75]. Hummingbirds have even more sharply curved barbule shapes, and their feather colours can only be viewed from a limited range of angles, appearing black from other angles. While Greenewalt et al. [58] noted this morphology over 40 years ago, its potential connection to the iridescent properties of hummingbirds has yet to be quantified.
6. Functional relevance
Colour appearance can vary at different timescales [76–78]. For example, feather colour can change after molt, with important implications for signal function. Beyond its contribution to expansion of the colour palette of organisms, an interface between pigments and structures makes faster fluctuations in colour expression possible. Because carotenoids cannot be synthesized de novo and must be sequestered from the environment [16], their acquisition and ultimate manifestation in tissues will depend on their spatial and temporal availability.
For example, the foot colours of blue-footed boobies are extremely variable, ranging from bright blue-green turquoise (reflectance peak at 540 nm) to dark blue (440 nm) [79]. Foot colours change rapidly and vary seasonally, and those rapid ranges are influenced by food and carotenoid availability [80]. Although seasonal [81], nutritional [82] and age-dependent [83] changes in structural feather colour have been previously reported, to our knowledge, no attempt has been made to test whether variations in structural-pigmentary feather colour could also be influenced by carotenoid feather content.
The tight interaction between pigments and structures plays an important role in many vertebrates’ behaviour and communication as it allows a highly variable expression of colour. Organisms like some lizards that are capable of rapid physiological colour change (which occurs due to the dispersion or concentration of pigment granules within chromatophores) are able to respond to changes in their visual, social or thermal environment [84]. The benefits of dynamic colour expression are exemplified by the extraordinary camouflage strategies observed in animals that can quickly adapt their colour response to different predators, as well as backgrounds as is the case in dwarf chameleons (Bradypodion spp.; (figure 1l) [84]). Other forms of rapid colour change are involved in signalling in a social context, whether allowing organisms to advertise their dominance status, or performing territorial or mating displays. While rapid colour change on some body parts is exclusively used as social signals, another important advantage of the interaction between chromatophores is that it allows a temperature-dependent colour change that facilitates rapid rise to body temperatures suitable for physical activities. For example, bearded dragons (Pogona vitticeps) darken rapidly when exposed to cold temperature to increase solar absorption and reach their preferred body temperature of 35°C, which allows optimal activity [85]. Future work should focus on identification of the developmental mechanisms responsible for the control of the size, shape and orientation of nanocrystals, and the superposition of specific chromatophore types.
7. Conclusion
We have here highlighted some of the more classic examples of pigment–nanostructure interactions, as well as some that are less well known. Some of these latter interactions, including white structure–pigment and macrostructure–pigment, suggest that classification of colour mechanisms may be more blurry and uncertain than previously thought. This is important to consider with regard to the ecology and evolution of coloration, as different physiological mechanisms and developmental/genetic pathways may be involved in production of the final phenotype. Classification of some colours as entirely pigmentary, for example, is convenient but may not capture the entirety of the phenotype. Moreover, combined colour mechanisms enable animals to produce colours that may be otherwise difficult or impossible to reach [23,24]. Green colours in birds are a clear example of such a hue [43], but other optical effects like gloss [65] and reduced iridescence [74] may also have other, still undiscovered effects on colour evolution.
Competing interests
We declare we have no competing interests.
Funding
The study is supported by Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (grant no. G007117N) and Air Force Office of Scientific Research (grant no. FA9550-16-1-0331).
References
- 1.Land M, Nilsson D. 2002. Animal eyes. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bortolotti GR. 2006. Natural selection and avian coloration: protection, concealment, advertisement, or deception? In Bird coloration, Function and evolution vol. 2, (eds Hill GE, McGraw KJ), pp. 3–35. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shawkey MD, Morehouse NI, Vukusic P. 2009. A protean palette: colour materials and mixing in birds and butterflies. J R. Soc. Interface 6, S221–S231. ( 10.1098/rsif.2008.0459.focus) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fu Y, Tippets CA, Donev EU, Lopez R. 2016. Structural colors: from natural to artificial systems. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 8, 758–775. ( 10.1002/wnan.1396) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhao Y, Xie Z, Gu H, Zhu C, Gu Z. 2012. Bio-inspired variable structural color materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 3297–3317. ( 10.1039/c2cs15267c) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Prum RO. 2006. Anatomy, physics and evolution of avian structural colors. In Bird coloration: mechanisms vol. I, (eds Hill GE, MncGraw KJ) Mechanisms and measurements, pp. 295–353. Boston, MA: Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Srinivasarao M. 1999. Nano-optics in the biological world: beetles, butterflies, birds, and moths. Chem. Rev. 997, 1935–1962. ( 10.1021/cr970080y) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.McGraw KJ. 2006. Mechanics of carotenoid-based coloration. In Bird coloration vol. I, (eds Hill GE, McGraw KJ) Mechanisms and measurements, pp. 177–242. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Thomas DB. 2014. Ancient origins and multiple appearances of carotenoid-pigmented feathers in birds. Proc. R. Soc. B 281, 20140806 ( 10.1098/rspb.2014.0806) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.McGraw KJ. 2006. Mechanics of melanin-based coloration. In Bird coloration, vol. 1 (eds Hill GE, McGraw KJ), pp. 243–294. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Prota G. 1992. Melanins and melanogenesis. New York, NY: Academic Press. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bagnara JT, Hadley ME. 1973. Chromatophores and colour change, the comparative physiology of animal pigmentation. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liu Y, Kempf VR, Nofsinger JB, Weinerty EE, Rudnicki M, Wakamatsu K, Ito S, Simon JD. 2003. Comparison of the structural and physical properties of human hair eumelanin following enzymatic or acid/base extraction. Pigment Cell Res. 16, 355–365. ( 10.1034/j.1600-0749.2003.00059.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vukusic P, Sambles JR, Lawrence CR. 2004. Structurally assisted blackness in butterfly scales. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 271, S237–S239. ( 10.1098/rsbl.2003.0150) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hsiung BK, Blackledge TA, Shawkey MD. 2015. Spiders do have melanin after all. J. Exp. Biol. 21, 3632–3635. ( 10.1242/jeb.128801) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Goodwin TW. 1984. The biochemistry of the carotenoids. New York, NY: Chapman and Hall. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Britton G. 1995. Structure and properties of carotenoids in relation to function. FASEB J. 9, 1551–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Morehouse NI, Vukusic P, Rutowski RL. 2007. Pterin pigment granules are responsible for both broadband light scattering and wavelength selective absorption in the wing scales of pierid butterflies. Proc. R. Soc. B 27, 359–366. ( 10.1098/rspb.2006.3730) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wilts BD, Wijnen B, Leertouwer HL, Steiner U, Stavenga DG. 2017. Extreme refractive index wing scale beads containing dense pterin pigments cause the bright colors of Pierid butterflies. Adv. Opt. Mater. 5, 1600879. ( 10.1002/adom.201600879) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McGraw KJ. 2006. Mechanics of uncommon colors: pterins, porphyrins, and psittacofulvins. In Bird coloration, vol. 1 (eds Hill GE and McGraw KJ), pp. 354–398. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Auber L. 1957. The structures producing ‘non-iridescent’ blue color in bird-feathers. J. Zool. 129, 455–486. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dyck J. 1976. Structural colors. Proc. Int. Ornithol. Congr. 16, 426–437. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dyck J. 1971. Structure and spectral reflectance of green and blue feathers of the Lovebird (Agapornis roseicollis). Biol. Skr. 18, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stoddard MC, Prum RO. 2011. How colorful are birds? Evolution of the avian plumage color gamut. Behav Ecol. 22, 1042–1052. ( 10.1093/beheco/arr088) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bagnara JT. 1998. Comparative anatomy and physiology of pigment cells in nonmammalian tissues. In The pigmentary system (eds Nordlund JJ, Boissy RE, Hearing VJ, King RA, Ortonne J), pp. 9–40. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bagnara JT, Taylor JD, Hadley MC. 1968. The dermal chromatophore unit. J. Cell Biol. 38, 67–79. ( 10.1083/jcb.38.1.67) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schliwa M. 1986. The skin of fishes including cyclostomes: pigment cells. In Biology of the integument Vertebrates, vol. 2, (eds Bereiter-Hahn J, Matoltsy AG, Richards KS), pp. 65–77. Berlin, Germany: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Landmann L. l986 Reptilian skin. In Biology of the vertebrates (eds Bereiter-Hahn J, Matoltsy AG, Richards KS), pp. 150–187. Berlin, Germany: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cooper WE, Greenberg N. 1992. Reptilian coloration and behavior. In Biology of the Reptilia, vol. 18, pp. 298–422. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kuriyama T, Miyaji K, Sugimoto M, Hasegawa M. 2006. Ultrastructure of the dermal chromatophores in a lizard (Scincidae: Plestiodon latiscutatus) with conspicuous body and tail coloration. Zool. Sci. 23, 793–799. ( 10.2108/zsj.23.793) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Morrison RL. 1995. A transmission electron microscopic (TEM) method for determining structural colors reflected by lizard iridophore. Pigment Cell Res. 8, 28–36. ( 10.1111/j.1600-0749.1995.tb00771.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Morrison RL, Matthew SR, Frost-Mason SK. 1995. Cellular basis of color differences in three morphs of the lizard Sceloporus undulatus erythrocheilus. Copeia 1995, 397–408. ( 10.2307/1446903) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Saenko SV, Teyssier J, Van Der Marel D, Milinkovitch MC. 2013. Precise colocalization of interacting structural and pigmentary elements generates extensive color pattern variation in Phelsuma lizards. BMC Biol. 11, 105 ( 10.1186/1741-7007-11-105) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Grether GF, Kolluru GR, Nersissian K. 2004. Individual colour patches as multicomponent signals. Biol. Rev. 79, 583–610. ( 10.1017/S1464793103006390) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vukusic P, Stavenga DG. 2009. Physical methods for investigating structural colours in biological systems. J. Roy. Soc. Interface 6, S133–S148. ( 10.1098/rsif.2008.0386.focus) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Parnell AJ, et al. 2015. Spatially modulated structural colour in bird feathers. Sci. Rep. 5, 18317 ( 10.1038/srep18317) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shawkey MD, Estes AM, Siefferman LM, Hill GE. 2003. Nanostructure predicts intraspecific variation in ultraviolet–blue plumage colour. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 270, 1455–1460. ( 10.1098/rspb.2003.2390) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shawkey MD, Hill GE. 2005. Carotenoids need structural colors to shine. Biol. Lett. 1, 121–124. ( 10.1098/rsbl.2004.0289) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mason CW. 1923. Structural colors in feathers II. J Phys. Chem. 27, 401–448. ( 10.1021/j150230a001) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shawkey MD, Hill GE, McGraw KJ, Hood WR, Huggins K. 2006. An experimental test of the contributions and condition dependence of microstructure and carotenoids in yellow plumage coloration. Proc. R. Soc. B 273, 2985–2991. ( 10.1098/rspb.2006.3675) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Evans SR, Sheldon BC. 2012. Quantitative genetics of a carotenoid-based color: heritability and persistent natal environmental effects in the great tit. Am. Nat. 179, 79–94. ( 10.1086/663198) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jacot A, Romero-Diaz C, Tschirren B, Richner H, Fitze PS. 2010. Dissecting carotenoid from structural components of carotenoid-based coloration: a field experiment with great tits (Parus major). Am. Nat. 176, 55–62. ( 10.1086/653000) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.D'Alba L, Kieffer L, Shawkey MD. 2012. Relative contributions of pigments and biophotonic nanostructures to natural color production: a case study in budgerigar (Melopsittacus undulatus) feathers. J. Exp. Biol. 215, 1272–1277. ( 10.1242/jeb.064907) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Stavenga DG, Tinbergen J, Leertouwer HL, Wilts BD. 2011. Kingfisher feathers–colouration by pigments, spongy nanostructures and thin films. J. Exp. Biol. 214, 3960–3967. ( 10.1242/jeb.062620) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wilts BD, Michielsen K, De Raedt H, Stavenga DG. 2011. Iridescence and spectral filtering of the gyroid-type photonic crystals in Parides sesostris wing scales. Interface Focus 2, 681–687. ( 10.1098/rsfs.2011.0082) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Noh H, Liew SF, Saranathan V, Prum RO, Mochrie SGJ, Dufresne ER, Cao H. 2010. Double scattering of light from biophotonic nanostructures with short-range order. Opt. Express 18, 11 942–11 948. ( 10.1364/OE.18.011942) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Noh H, Liew SF, Saranathan V, Mochrie SGJ, Prum RO, Dufresne ER, Cao H. 2010. How noniridescent colors are generated by quasi-ordered structures of bird feathers. Adv. Mater. 22, 2871–2880. ( 10.1002/adma.200903699) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Magkiriadou S, Park JG, Kim YS, Manoharan VN. 2014. Absence of red structural color in photonic glasses, bird feathers, and certain beetles. Phys. Rev. 90, 062302 ( 10.1103/PhysRevA.90.062302) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Shawkey MD, Hill GE. 2006. Significance of a basal melanin layer to production of non-iridescent structural plumage color: evidence from an amelanotic Steller's jay (Cyanocitta stelleri). J. Exp. Biol. 209, 1245–1250. ( 10.1242/jeb.02115) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang Y, et al. 2015. Using cuttlefish ink as an additive to produce non-iridescent structural colors of high color visibility. Adv. Mater. 27, 4719–4724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Doucet SM, Shawkey MD, Rathburn MK, Mays HL, Montgomerie R. 2004. Concordant evolution of plumage colour, feather microstructure and a melanocortin receptor gene between mainland and island populations of a fairy–wren. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 271, 1663–1670. ( 10.1098/rspb.2004.2779) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Driskell AC, Prum RO, Pruett-Jones S. 2010. The evolution of black plumage from blue in Australian fairy-wrens (Maluridae): genetic and structural evidence. J Avian Biol. 41, 505–514. ( 10.1111/j.1600-048X.2009.04823.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Snyder HK, et al. 2012. Iridescent colour production in hairs of blind golden moles (Chrysochloridae). Biol. Lett. 83, 393–396. ( 10.1098/rsbl.2011.1168) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Trzeciak TM, Wilts BD, Stavenga DG, Vukusic P. 2012. Variable multilayer reflection together with long-pass filtering pigment determines the wing coloration of Papilionid butterflies of the Nireus group. Opt. Exp. 20, 8877–8890. ( 10.1364/OE.20.008877) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Simon JD, Peles DN. 2010. The red and the black. Acct. Chem. Res. 43, 1452–1460. ( 10.1021/ar100079y) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Stavenga DG, Leertouwer HL, Osorio DC, Wilts BD. 2015. High refractive index of melanin in shiny occipital feathers of a bird of paradise. Light Sci. Appl. 4, e243 ( 10.1038/lsa.2015.16) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Stavenga DG, Leertouwer HL, Hariyama T, De Raedt HA, Wilts BD, Zeil J. 2012. Sexual dichromatism of the damselfly Calopteryx japonica caused by a melanin-chitin multilayer in the male wing veins. PLoS ONE 7, e49743 ( 10.1371/journal.pone.0049743) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Greenewalt CH, Brandt W, Friel DD. 1960. The iridescent colors of hummingbird feathers. Proc. Am. Phil. Soc. 104, 249–253. ( 10.1364/josa.50.001005) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Weesie RJ, Askin D, Jansen FJHM, de Groot HJM, Lugtenburg J, Britton G. 1995. Protein–chromophore interactions in a-crustacyanin, the major blue carotenoprotein from the carapace of the lobster, Homarus gammarus: a study by 13C magic angle spinning NMR. FEBS Lett. 362, 34–38. ( 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00191-B) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hedegaard C, Bardeau JF, Chateigner D. 2006. Molluscan shell pigments: an in situ resonance Raman study. J. Mollus. Stud. 72, 157–162. ( 10.1093/mollus/eyi062) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Cianci M, Rizkallah PJ, Olczak A, Raftery J, Chayen NE, Zagalsky PF, Helliwell JR. 2002. The molecular basis of the coloration mechanism in lobster shell: β-crustacyanin at 32-Å resolution. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 9795–9800. ( 10.1073/pnas.152088999) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Stradi R, Celentano G, Rossi E, Rovati G, Pastore M. 1995. Carotenoids in bird plumage. I. The carotenoid pattern in a series of Palearctic Carduelinae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 110, 131–143. ( 10.1016/0305-0491(94)00136-I) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Schiedt K. 1998. Absorption and metabolism of carotenoids in birds, fish and crustaceans. In Carotenoids, Biosynthesis and metabolism, vol. 3 (eds Britton G, Liaaen-Jensen S, Pfander H), pp. 285–358. Basel, Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mendes-Pinto MM, LaFountain AM, Stoddard MC, Prum RO, Frank HA, Robert B. 2012. Variation in carotenoid–protein interaction in bird feathers produces novel plumage coloration. J. R. Soc. Interface 9, 3338–3350. ( 10.1098/rsif.2012.0471) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Toomey MB, Butler MW, Meadows MG, Taylor LA, Fokidis HB, McGraw KJ. 2010. A novel method for quantifying the glossiness of animals. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 64, 1047–1055. ( 10.1007/s00265-010-0926-z) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Hunter RS. 1937. Methods of determining gloss. J. R. Natl Bur. Stand. 18, 19–39. ( 10.6028/jres.018.006) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Maia R, D'Alba L, Shawkey MD. 2011. What makes a feather shine? A nanostructural basis for glossy black colours in feathers. Proc. R. Soc. B 278, 1973–1980. ( 10.1098/rspb.2010.1637) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Iskandar JP, Eliason CM, Astrop T, Igic B, Maia R, Shawkey MD. 2016. Morphological basis of glossy red plumage colours. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 119, 477–487. ( 10.1111/bij.12810) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Igic B, et al. 2015. A nanostructural basis for gloss of avian eggshells. J. R. Soc. Interface 12, 20141210 ( 10.1098/rsif.2014.1210) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Eliason CM, Shawkey MD. 2011. Decreased hydrophobicity of iridescent feathers: a potential cost of shiny plumage. J. Exp. Biol. 21413, 2157–2163. ( 10.1242/jeb.055822) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kolle M, Lethbridge A, Kreysing M, Baumberg JJ, Aizenberg J, Vukusic P. 2013. Bio-inspired band-gap tunable elastic optical multilayer fibers. Adv. Mater. 25, 2239–2245. ( 10.1002/adma.201203529) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Dyck J. 1987. Structure and light reflection of green feathers of fruit doves (Ptilinopus spp) and an imperial pigeon (Ducula concinna). Biol. Skr. 30, 1–43 [Google Scholar]
- 73.Vignolini S, Rudall PJ, Rowland AV, Reed A, Moyroud E, Faden RB, Baumberg JJ, Glover BJ, Steiner U. 2012. Pointillist structural color in Pollia fruit. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 15 712–15 715. ( 10.1073/pnas.1210105109) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Hsiung B, Siddique RH, Jiang L, Liu Y, Lu Y, Shawkey MD, Blackledge TA. 2016. Tarantula-inspired noniridescent photonics with long-range order. Adv. Opt. Mater. 5, 1600599 ( 10.1002/adom.201600599) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Wilts BD, Michielsen K, De Raedt H, Stavenga DG. 2014. Sparkling feather reflections of a bird-of-paradise explained by finite-difference time-domain modeling. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 4363–4368. ( 10.1073/pnas.1323611111) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.McGraw KJ, Hill GE. 2004. Plumage color as a dynamic trait: carotenoid pigmentation of male house finches (Carpodacus mexicanus) fades during the breeding season. Can. J. Zool. 82, 734–738. ( 10.1139/z04-043) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Delhey K, Kempenaers B. 2006. Age differences in blue tit Parus caeruleus plumage colour: within-individual changes or colour-biased survival? J Avian Biol. 37, 339–348. ( 10.1111/j.2006.0908-8857.03655.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Evans SR, Summers AG, Sheldon BC. 2012. Seasonality of carotenoid-based plumage coloration: modeling wavelength-specific change through spectral reconstruction. J Avian Biol. 43, 234–243. ( 10.1111/j.1600-048X.2012.05654.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Torres R, Velando A. 2003. A dynamic trait affects continuous pair assessment in the blue-footed booby, Sula nebouxii. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 55, 65–72. ( 10.1007/s00265-003-0669-1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Velando A, Beamonte-Barrientos R, Torres R. 2006. Pigment-based skin colour in the blue-footed booby: an honest signal of current condition used by females to adjust reproductive investment. Oecologia 149, 535–542. ( 10.1007/s00442-006-0457-5) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Delhey K, Peters A, Johnsen A, Kempenaers B. 2006. Seasonal changes in blue tit crown color: do they signal individual quality? Behav. Ecol. 17, 790–798. ( 10.1093/beheco/arl012) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.McGraw KJ, Mackillop EA, Dale J, Hauber ME. 2002. Different colors reveal different information: how nutritional stress affects the expression of melanin- and structurally based ornamental plumage. J Exp. Biol. 205, 3747–3755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Keyser AJ, Hill GE. 1999. Condition-dependent variation in the blue–ultraviolet coloration of a structurally based plumage ornament. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 266, 771–777. ( 10.1098/rspb.1999.0704) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Stuart-Fox D, Moussalli A. 2009. Camouflage, communication and thermoregulation: lessons from colour changing organisms. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 364, 463–470. ( 10.1098/rstb.2008.0254) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Smith KR, Cadena V, Endler JA, Porter WP, Kearney MR, Stuart-Fox D. 2016. Colour change on different body regions provides thermal and signalling advantages in bearded dragon lizards. Proc. R. Soc. B 283, 20160626 ( 10.1098/rspb.2016.0626) [DOI] [Google Scholar]