Abstract
Voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channels are essential for the rapid upstroke of action potentials and the propagation of electrical signals in nerves and muscles. Defects of Nav channels are associated with a variety of channelopathies. More than 1000 disease-related mutations have been identified in Nav channels, with Nav1.1 and Nav1.5 each harboring more than 400 mutations. Nav channels represent major targets for a wide array of neurotoxins and drugs. Atomic structures of Nav channels are required to understand their function and disease mechanisms. The recently determined atomic structure of the rabbit voltage-gated calcium (Cav) channel Cav1.1 provides a template for homology-based structural modeling of the evolutionarily related Nav channels. In this Resource article, we summarized all the reported disease-related mutations in human Nav channels, generated a homologous model of human Nav1.7, and structurally mapped disease-associated mutations. Before the determination of structures of human Nav channels, the analysis presented here serves as the base framework for mechanistic investigation of Nav channelopathies and for potential structure-based drug discovery.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s13238-017-0372-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Nav channels, channelopathy, Nav1.7, structure modeling, pain
INTRODUCTION
Voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channels are essential for the rapid depolarization phase of action potential and play a key role in the electrical signaling in most excitable cells. Structurally, Nav channels are composed of one α subunit and one or more β subunits. The α subunit contains two functionally distinct structural entities, namely, the voltage-sensing domains (VSDs) and the ion-conducting pore domain (Catterall, 2012b, 2014). The β subunits, which bind to α subunit covalently or non-covalently, modulate membrane trafficking, voltage dependence, and channel gating kinetics (Catterall, 2012b, 2014). In mammals, Nav channels have nine known α members distributed in different excitable tissues. Specifically, Nav1.1, Nav1.2, Nav1.3, and Nav1.6 are the primary sodium channels in central nervous system (CNS), Nav1.4 is primarily expressed in skeletal muscle, Nav1.5 is mainly expressed in heart, and Nav1.7, Nav1.8, and Nav1.9 are mainly distributed in peripheral nervous system (Plummer and Meisler, 1999; Goldin, 2001; Catterall et al., 2005).
All α subunits share nearly identical structure topology—a canonical voltage-gated ion channel fold with four homologous repeats, each containing six transmembrane segments S1–S6. Specifically, S5–S6 segments form the pore domain that conducts selective sodium filtering, while S1–S4 segments constitute the voltage-sensing domain that controls voltage-dependent gating (Catterall, 2000). The voltage sensors in the VSDs are featured by a number of positively charged amino acids (arginine or lysine) located at every third position in the S4 segment. Upon membrane depolarization, movements of these charged residues in the S4 segment are coupled to the opening of the pore domain and the subsequent influx of sodium ions across cell membrane. The pore domain is structurally organized with a four-fold pseudo-symmetry. The pore (P) loops, which are supported by the P1 helix (corresponding to the P helix in potassium channel) and P2 helix between S5 and S6 segments in each repeat, constitute the selectivity filter (SF) (Corry and Thomas, 2012). Four amino acid residues (aspartate, glutamate, lysine, and alanine, DEKA, in repeats I, II, III, and IV, respectively) in the P loops are crucial for sodium selectivity. Mutating these residues to glutamates confers calcium selectivity, suggesting that the side chains of these amino acids are likely to interact directly with the sodium ions to determine ion selectivity (Heinemann et al., 1992; Sun et al., 1997).
Nav channels inactivate rapidly. A cluster of hydrophobic amino acids (isoleucine, phenylalanine, methionine, and threonine), namely the IFMT motif, located in the cytosolic regions of domain III and domain IV, are required for rapid inactivation. This is demonstrated by the fact that rapid inactivation could be achieved by titrating small peptides containing the IFMT motif (Vassilev et al., 1988; West et al., 1992).
Sodium channelopathies are a group of diseases caused by defective Nav channels, either, in most cases, of congenital nature or acquired nature (Tables 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10) (George, 2005; Catterall, 2012a; Kim, 2014). For example, Nav1.1 is primarily expressed in the soma of neuronal cells in the CNS, and mutations of Nav1.1 cause GEFS+2 (generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 2) (Catterall et al., 2010). Moreover, mutations of Nav1.1 are also the main causes of EIEE6 (epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 6) and ICEGTC (intractable childhood epilepsy with generalized tonic-clonic seizures) (Escayg and Goldin, 2010). Nav1.5 is the major sodium channel expressed in heart. Nav1.5 mutations may lead to various cardiac diseases such as LQT3 (long QT syndrome 3), BRGDA1 (Brugada syndrome 1), and SSS1 (sick sinus syndrome 1) (Olson et al., 2005; Song and Shou, 2012; Veerman et al., 2015). Nav1.7 is preferentially expressed in the sympathetic neurons, olfactory epithelium, and dorsal root ganglion sensory neurons, and plays a cardinal role in pain transmission (Djouhri et al., 2003; Dib-Hajj et al., 2013). Gain-of-function mutations of Nav1.7 are implicated in two distinct paroxysmal pain syndromes—IEM (primary erythermalgia) and PEPD (paroxysmal extreme pain disorder), while loss-of-function mutations of Nav1.7 inflict people with CIP (indifference to pain, congenital, autosomal recessive) (Lampert et al., 2010; Dib-Hajj et al., 2013). In all, Nav channel mutations play a central role in the pathophysiology of sodium channelopathies. Pharmacologic modulation of Nav channels may thereby represent a viable therapeutic approach for the treatment of many neurological disorders such as epilepsy, arrhythmia, and pain.
Table 1.
Structural mapping of disease-related mutations identified in human Nav1.7
| Related proteins | Mutations | Diseases | Structural position | Map on hNav1.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hNav1.7 | Q10R | IEM | N-terminus | Q10 |
| hNav1.7 | I62V | FEB | N-terminus | I62 |
| hNav1.7 | I136V | IEM | DI S1 | I136 |
| hNav1.7 | P149Q | FEB | DI S1-S2 | P149 |
| hNav1.7 | R185H | PEPD | DI S3 | R185 |
| hNav1.7 | R185H | SFN | DI S3 | R185 |
| hNav1.7 | S211P | IEM | DI S3-S4 | S211 |
| hNav1.7 | F216S | IEM | DI S4 | F216 |
| hNav1.7 | I228M | DS | DI S4 | I228 |
| hNav1.7 | I228M | SFN | DI S4 | I228 |
| hNav1.7 | I234T | IEM | DI S5 | I234 |
| hNav1.7 | S241T | IEM | DI S5 | S241 |
| hNav1.7 | L245V | IEM | DI S5 | L245 |
| hNav1.7 | N395K | IEM | DI S6 | N395 |
| hNav1.7 | V400M | IEM | DI S6 | V400 |
| hNav1.7 | E406K | IEM | DI S6 | E406 |
| hNav1.7 | S490N | FEB | DI - DII | S490 |
| hNav1.7 | E519K | DS | DI - DII | E519 |
| hNav1.7 | P610T | IEM | DI - DII | P610 |
| hNav1.7 | G616R | IEM | DI - DII | G616 |
| hNav1.7 | D623N | SFN | DI - DII | D623 |
| hNav1.7 | N641Y | FEB | DI - DII | N641 |
| hNav1.7 | K666R | FEB | DI - DII | K666 |
| hNav1.7 | K666R | DS | DI - DII | K666 |
| hNav1.7 | I695M | DS | DI - DII | I695 |
| hNav1.7 | C710Y | DS | DI - DII | C710 |
| hNav1.7 | I731K | SFN | DI - DII | I731 |
| hNav1.7 | I750V | SFN | DII S1 | I750 |
| hNav1.7 | I750V | DS | DII S1 | I750 |
| hNav1.7 | I750V | FEB | DII S1 | I750 |
| hNav1.7 | L834R | IEM | DII S4 | L834 |
| hNav1.7 | I859T | IEM | DII S5 | I859 |
| hNav1.7 | G867D | IEM | DII S5 | G867 |
| hNav1.7 | L869F | IEM | DII S5 | L869 |
| hNav1.7 | L869H | IEM | DII S5 | L869 |
| hNav1.7 | A874P | IEM | DII S5 | A874 |
| hNav1.7 | V883G | IEM | DII S5 | V883 |
| hNav1.7 | Q886E | IEM | DII S5 | Q886 |
| hNav1.7 | R907Q | CIP | DII S5-S6 | R907 |
| hNav1.7 | M943L | SFN | DII S5-S6 | M943 |
| hNav1.7 | V1002L | SFN | DII - DIII | V1002 |
| hNav1.7 | R1007C | PEPD | DII - DIII | R1007 |
| hNav1.7 | L1134F | DS | DII - DIII | L1134 |
| hNav1.7 | E1171Q | DS | DII - DIII | E1171 |
| hNav1.7 | A1247E | CIP | DIII S2 | A1247 |
| hNav1.7 | L1278V | DS | DIII S3-S4 | L1278 |
| hNav1.7 | V1309D | PEPD | DIII S4-S5 | V1309 |
| hNav1.7 | V1309F | PEPD | DIII S4-S5 | V1309 |
| hNav1.7 | V1310F | PEPD | DIII S4-S5 | V1310 |
| hNav1.7 | P1319L | IEM | DIII S4-S5 | P1319 |
| hNav1.7 | F1460V | IEM | DIII S6 | F1460 |
| hNav1.7 | I1472T | PEPD | DIII - DIV | I1472 |
| hNav1.7 | F1473V | PEPD | DIII - DIV | F1473 |
| hNav1.7 | T1475I | PEPD | DIII - DIV | T1475 |
| hNav1.7 | M1543I | SFN | DIV S2 | M1543 |
| hNav1.7 | G1618R | PEPD | DIV S4 | G1618 |
| hNav1.7 | L1623P | PEPD | DIV S4 | L1623 |
| hNav1.7 | M1638K | PEPD | DIV S5 | M1638 |
| hNav1.7 | A1643E | PEPD | DIV S5 | A1643 |
| hNav1.7 | A1643E | IEM | DIV S5 | A1643 |
| hNav1.7 | A1643G | IEM | DIV S5 | A1643 |
| hNav1.7 | A1643T | IEM | DIV S5 | A1643 |
| hNav1.7 | W1786R | CIP | C-terminus | W1786 |
IEM: Primary erythermalgia; PEPD: Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder; CIP: Indifference to pain, congenital, autosomal recessive; DS: Dravet syndrome; SFN: Small fiber neuropathy; FEB: Febrile seizures
Table 2.
Structural mapping of disease-related mutations identified in human Nav1.1
| Related proteins | Mutations | Diseases | Structural position | Map on hNav1.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hNav1.1 | R27T | GEFS+2 | N-terminus | Q25 |
| hNav1.1 | S74P | GEFS+2 | N-terminus | S72 |
| hNav1.1 | D188V | GEFS+2 | DI S3 | D186 |
| hNav1.1 | F218L | GEFS+2 | DI S4 | F216 |
| hNav1.1 | T254I | GEFS+2 | DI S5 | T252 |
| hNav1.1 | S291G | GEFS+2 | DI S5-S6 | S279 |
| hNav1.1 | R377Q | GEFS+2 | DI S5-S6 | R356 |
| hNav1.1 | Y388H | GEFS+2 | DI S5-S6 | Y367 |
| hNav1.1 | Y790C | GEFS+2 | DII S1-S2 | H766 |
| hNav1.1 | R859C | GEFS+2 | DII S4 | R835 |
| hNav1.1 | R859H | GEFS+2 | DII S4 | R835 |
| hNav1.1 | T875M | GEFS+2 | DII S4-S5 | T851 |
| hNav1.1 | I899T | GEFS+2 | DII S5 | I875 |
| hNav1.1 | N935H | GEFS+2 | DII S5-S6 | N911 |
| hNav1.1 | R946H | GEFS+2 | DII S5-S6 | R922 |
| hNav1.1 | M960T | GEFS+2 | DII S5-S6 | M936 |
| hNav1.1 | M973V | GEFS+2 | DII S6 | M949 |
| hNav1.1 | M976I | GEFS+2 | DII S6 | M952 |
| hNav1.1 | I978M | GEFS+2 | DII S6 | I954 |
| hNav1.1 | W1204R | GEFS+2 | DII - DIII | W1178 |
| hNav1.1 | W1204S | GEFS+2 | DII - DIII | W1178 |
| hNav1.1 | L1230F | GEFS+2 | DIII S1 | L1204 |
| hNav1.1 | K1249N | GEFS+2 | DIII S2 | K1223 |
| hNav1.1 | T1250M | GEFS+2 | DIII S2 | I1224 |
| hNav1.1 | K1270T | GEFS+2 | DIII S2 | K1244 |
| hNav1.1 | L1309F | GEFS+2 | DIII S3-S4 | L1283 |
| hNav1.1 | V1353L | GEFS+2 | DIII S5 | V1327 |
| hNav1.1 | V1366I | GEFS+2 | DIII S5 | V1340 |
| hNav1.1 | N1414D | GEFS+2 | DIII S5-S6 | N1388 |
| hNav1.1 | V1428A | GEFS+2 | DIII S5-S6 | V1402 |
| hNav1.1 | R1596H | GEFS+2 | DIV S2-S3 | R1570 |
| hNav1.1 | R1648H | GEFS+2 | DIV S4 | R1622 |
| hNav1.1 | I1656M | GEFS+2 | DIV S5 | I1630 |
| hNav1.1 | R1657C | GEFS+2 | DIV S5 | R1631 |
| hNav1.1 | A1685V | GEFS+2 | DIV S5 | A1659 |
| hNav1.1 | F1687S | GEFS+2 | DIV S5 | F1661 |
| hNav1.1 | P1739L | GEFS+2 | DIV S5-S6 | P1713 |
| hNav1.1 | D1742G | GEFS+2 | DIV S5-S6 | D1716 |
| hNav1.1 | F1765L | GEFS+2 | DIV S6 | Y1739 |
| hNav1.1 | E1795K | GEFS+2 | C-terminus | E1769 |
| hNav1.1 | M1852T | GEFS+2 | C-terminus | M1826 |
| hNav1.1 | V1857L | GEFS+2 | C-terminus | V1831 |
| hNav1.1 | D1866Y | GEFS+2 | C-terminus | D1840 |
| hNav1.1 | I1867T | GEFS+2 | C-terminus | I1841 |
| hNav1.1 | G58V | EIEE6 | N-terminus | G56 |
| hNav1.1 | L61F | EIEE6 | N-terminus | L59 |
| hNav1.1 | F63L | EIEE6 | N-terminus | F61 |
| hNav1.1 | I68T | EIEE6 | N-terminus | I66 |
| hNav1.1 | E78D | EIEE6 | N-terminus | E76 |
| hNav1.1 | D79H | EIEE6 | N-terminus | D77 |
| hNav1.1 | D79N | EIEE6 | N-terminus | D77 |
| hNav1.1 | Y84C | EIEE6 | N-terminus | Y82 |
| hNav1.1 | F90S | EIEE6 | N-terminus | F88 |
| hNav1.1 | I91T | EIEE6 | N-terminus | I89 |
| hNav1.1 | A98P | EIEE6 | N-terminus | T96 |
| hNav1.1 | R101Q | EIEE6 | N-terminus | R99 |
| hNav1.1 | R101W | EIEE6 | N-terminus | R99 |
| hNav1.1 | S103G | EIEE6 | N-terminus | N101 |
| hNav1.1 | T105I | EIEE6 | N-terminus | T103 |
| hNav1.1 | L108R | EIEE6 | N-terminus | L106 |
| hNav1.1 | T112I | EIEE6 | N-terminus | S110 |
| hNav1.1 | R118S | EIEE6 | N-terminus | R116 |
| hNav1.1 | I124N | EIEE6 | N-terminus | I122 |
| hNav1.1 | H127D | EIEE6 | N-terminus | H125 |
| hNav1.1 | T162P | EIEE6 | DI S2 | T160 |
| hNav1.1 | I171K | EIEE6 | DI S2 | V169 |
| hNav1.1 | I171R | EIEE6 | DI S2 | V169 |
| hNav1.1 | A175T | EIEE6 | DI S2-23 | A173 |
| hNav1.1 | A175V | EIEE6 | DI S2-S3 | A173 |
| hNav1.1 | G177E | EIEE6 | DI S2-S3 | G175 |
| hNav1.1 | C179R | EIEE6 | DI S2-S3 | C177 |
| hNav1.1 | W190R | EIEE6 | DI S3 | W188 |
| hNav1.1 | N191K | EIEE6 | DI S3 | N189 |
| hNav1.1 | N191Y | EIEE6 | DI S3 | N189 |
| hNav1.1 | D194G | EIEE6 | DI S3 | D192 |
| hNav1.1 | D194N | EIEE6 | DI S3 | D192 |
| hNav1.1 | T199R | EIEE6 | DI S3 | V197 |
| hNav1.1 | T217K | EIEE6 | DI S3-S4 | T215 |
| hNav1.1 | A223E | EIEE6 | DI S4 | A221 |
| hNav1.1 | T226M | EIEE6 | DI S4 | T224 |
| hNav1.1 | T226R | EIEE6 | DI S4 | T224 |
| hNav1.1 | I227S | EIEE6 | DI S4 | I225 |
| hNav1.1 | I227T | EIEE6 | DI S4 | I225 |
| hNav1.1 | G232S | EIEE6 | DI S4-S5 | G230 |
| hNav1.1 | L233R | EIEE6 | DI S5 | L231 |
| hNav1.1 | A239T | EIEE6 | DI S5 | A237 |
| hNav1.1 | A239V | EIEE6 | DI S5 | A237 |
| hNav1.1 | S243Y | EIEE6 | DI S5 | S241 |
| hNav1.1 | I252N | EIEE6 | DI S5 | I250 |
| hNav1.1 | S259R | EIEE6 | DI S5 | S257 |
| hNav1.1 | G265W | EIEE6 | DI S5 | G263 |
| hNav1.1 | C277R | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | C275 |
| hNav1.1 | W280C | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | N278 |
| hNav1.1 | W280R | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | N278 |
| hNav1.1 | P281A | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | S279 |
| hNav1.1 | P281L | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | S279 |
| hNav1.1 | P281S | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | S279 |
| hNav1.1 | E289V | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | E287 |
| hNav1.1 | T297I | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | – |
| hNav1.1 | R322I | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | R301 |
| hNav1.1 | S340F | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | T319 |
| hNav1.1 | A342V | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | S321 |
| hNav1.1 | G343D | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | G322 |
| hNav1.1 | C345R | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | C324 |
| hNav1.1 | C351W | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | C330 |
| hNav1.1 | G355D | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | G334 |
| hNav1.1 | R356G | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | R335 |
| hNav1.1 | N357I | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | N336 |
| hNav1.1 | P358T | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | P357 |
| hNav1.1 | N359S | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | D338 |
| hNav1.1 | T363P | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | T342 |
| hNav1.1 | T363R | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | T342 |
| hNav1.1 | D366E | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | D345 |
| hNav1.1 | L378Q | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | L357 |
| hNav1.1 | M379R | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | M358 |
| hNav1.1 | F383L | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | Y362 |
| hNav1.1 | W384R | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | M363 |
| hNav1.1 | R393C | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | R372 |
| hNav1.1 | R393H | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | R372 |
| hNav1.1 | R393S | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | R372 |
| hNav1.1 | M400V | EIEE6 | DI S5-S6 | M379 |
| hNav1.1 | F403L | EIEE6 | DI S6 | F383 |
| hNav1.1 | F403V | EIEE6 | DI S6 | F382 |
| hNav1.1 | V406F | EIEE6 | DI S6 | V385 |
| hNav1.1 | L409W | EIEE6 | DI S6 | L388 |
| hNav1.1 | Y413N | EIEE6 | DI S6 | Y392 |
| hNav1.1 | Y426C | EIEE6 | DI S6 | Y405 |
| hNav1.1 | Y426N | EIEE6 | DI S6 | Y405 |
| hNav1.1 | S525F | EIEE6 | DI - DII | S505 |
| hNav1.1 | S626G | EIEE6 | DI - DII | S606 |
| hNav1.1 | D674G | EIEE6 | DI - DII | D651 |
| hNav1.1 | N762D | EIEE6 | DI - DII | Y738 |
| hNav1.1 | L783P | EIEE6 | DII S1 | L759 |
| hNav1.1 | M785T | EIEE6 | DII S1-S2 | M761 |
| hNav1.1 | T812I | EIEE6 | DII S2 | A788 |
| hNav1.1 | T812R | EIEE6 | DII S2 | A788 |
| hNav1.1 | L842R | EIEE6 | DII S3 | L818 |
| hNav1.1 | S843R | EIEE6 | DII S3 | S819 |
| hNav1.1 | E846K | EIEE6 | DII S3 | E822 |
| hNav1.1 | R859C | EIEE6 | DII S4 | R835 |
| hNav1.1 | R862Q | EIEE6 | DII S4 | R838 |
| hNav1.1 | R865G | EIEE6 | DII S4 | R841 |
| hNav1.1 | T875K | EIEE6 | DII S4-S5 | T851 |
| hNav1.1 | T875M | EIEE6 | DII S4-S5 | T851 |
| hNav1.1 | L876I | EIEE6 | DII S5 | L852 |
| hNav1.1 | L890P | EIEE6 | DII S5 | L866 |
| hNav1.1 | V896F | EIEE6 | DII S5 | V872 |
| hNav1.1 | V896L | EIEE6 | DII S5 | V872 |
| hNav1.1 | F902C | EIEE6 | DII S5 | F878 |
| hNav1.1 | C927F | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | C903 |
| hNav1.1 | R931C | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | R907 |
| hNav1.1 | W932C | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | W908 |
| hNav1.1 | H933P | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | H909 |
| hNav1.1 | M934I | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | M910 |
| hNav1.1 | H939P | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | H915 |
| hNav1.1 | H939Q | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | H915 |
| hNav1.1 | H939Y | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | H915 |
| hNav1.1 | S940F | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | S916 |
| hNav1.1 | L942P | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | L918 |
| hNav1.1 | I943N | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | I919 |
| hNav1.1 | V944A | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | V920 |
| hNav1.1 | V944E | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | V920 |
| hNav1.1 | F945L | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | F921 |
| hNav1.1 | R946C | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | R922 |
| hNav1.1 | R946H | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | R922 |
| hNav1.1 | R946S | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | R922 |
| hNav1.1 | C949S | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | C925 |
| hNav1.1 | C949Y | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | C925 |
| hNav1.1 | G950E | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | G926 |
| hNav1.1 | G950R | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | G926 |
| hNav1.1 | W952G | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | W928 |
| hNav1.1 | E954K | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | E930 |
| hNav1.1 | M956K | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | M932 |
| hNav1.1 | W957L | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | W933 |
| hNav1.1 | C959R | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | C935 |
| hNav1.1 | M960V | EIEE6 | DII S5-S6 | M936 |
| hNav1.1 | M973K | EIEE6 | DII S6 | M949 |
| hNav1.1 | M976I | EIEE6 | DII S6 | M952 |
| hNav1.1 | G979V | EIEE6 | DII S6 | G955 |
| hNav1.1 | N985I | EIEE6 | DII S6 | N961 |
| hNav1.1 | L986F | EIEE6 | DII S6 | L962 |
| hNav1.1 | L986P | EIEE6 | DII S6 | L962 |
| hNav1.1 | F987L | EIEE6 | DII S6 | F963 |
| hNav1.1 | S993R | EIEE6 | DII - DIII | S969 |
| hNav1.1 | D998G | EIEE6 | DII - DIII | D974 |
| hNav1.1 | E1068K | EIEE6 | DII - DIII | E1045 |
| hNav1.1 | L1207P | EIEE6 | DII - DIII | I1181 |
| hNav1.1 | R1208K | EIEE6 | DII - DIII | R1182 |
| hNav1.1 | T1210K | EIEE6 | DII - DIII | T1184 |
| hNav1.1 | E1221K | EIEE6 | DIII S1 | E1195 |
| hNav1.1 | L1230F | EIEE6 | DIII S1 | L1204 |
| hNav1.1 | S1231R | EIEE6 | DIII S1 | S1205 |
| hNav1.1 | S1231T | EIEE6 | DIII S1 | S1205 |
| hNav1.1 | G1233R | EIEE6 | DIII S1 | G1207 |
| hNav1.1 | E1238D | EIEE6 | DIII S1-S2 | E1212 |
| hNav1.1 | D1239G | EIEE6 | DIII S1-S2 | D1213 |
| hNav1.1 | D1239Y | EIEE6 | DIII S1-S2 | D1213 |
| hNav1.1 | R1245Q | EIEE6 | DIII S1-S2 | K1219 |
| hNav1.1 | A1255D | EIEE6 | DIII S2 | A1229 |
| hNav1.1 | T1260P | EIEE6 | DIII S2 | T1234 |
| hNav1.1 | F1263L | EIEE6 | DIII S2 | F1237 |
| hNav1.1 | L1265P | EIEE6 | DIII S2 | L1239 |
| hNav1.1 | E1266A | EIEE6 | DIII S2 | E1240 |
| hNav1.1 | G1275V | EIEE6 | DIII S2-S3 | G1249 |
| hNav1.1 | W1284S | EIEE6 | DIII S3 | W1258 |
| hNav1.1 | L1287P | EIEE6 | DIII S3 | L1261 |
| hNav1.1 | D1288N | EIEE6 | DIII S3 | D1262 |
| hNav1.1 | R1316G | EIEE6 | DIII S4 | R1290 |
| hNav1.1 | R1316S | EIEE6 | DIII S4 | R1290 |
| hNav1.1 | A1320V | EIEE6 | DIII S4 | A1294 |
| hNav1.1 | A1326P | EIEE6 | DIII S4 | A1300 |
| hNav1.1 | S1328P | EIEE6 | DIII S4-S5 | S1302 |
| hNav1.1 | V1335M | EIEE6 | DIII S4-S5 | V1309 |
| hNav1.1 | A1339V | EIEE6 | DIII S4-S5 | A1313 |
| hNav1.1 | I1344M | EIEE6 | DIII S4-S5 | I1318 |
| hNav1.1 | V1350G | EIEE6 | DIII S5 | V1324 |
| hNav1.1 | L1355P | EIEE6 | DIII S5 | L1329 |
| hNav1.1 | W1358R | EIEE6 | DIII S5 | W1332 |
| hNav1.1 | W1358S | EIEE6 | DIII S5 | W1332 |
| hNav1.1 | N1367K | EIEE6 | DIII S5 | N1341 |
| hNav1.1 | A1370P | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | A1344 |
| hNav1.1 | N1378H | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | N1352 |
| hNav1.1 | N1378T | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | N1352 |
| hNav1.1 | F1385V | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | F1359 |
| hNav1.1 | V1390M | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | V1364 |
| hNav1.1 | N1391S | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | P1365 |
| hNav1.1 | H1393P | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | R1367 |
| hNav1.1 | T1394I | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | S1368 |
| hNav1.1 | C1396G | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | C1370 |
| hNav1.1 | C1396Y | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | C1370 |
| hNav1.1 | N1414Y | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | N1388 |
| hNav1.1 | D1416G | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | D1390 |
| hNav1.1 | N1417S | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | N1391 |
| hNav1.1 | V1418G | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | V1392 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1422C | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | Y1396 |
| hNav1.1 | L1423F | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | L1397 |
| hNav1.1 | L1426R | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | L1400 |
| hNav1.1 | Q1427P | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | Q1401 |
| hNav1.1 | F1431I | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | F1405 |
| hNav1.1 | G1433E | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | G1407 |
| hNav1.1 | G1433R | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | G1407 |
| hNav1.1 | G1433V | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | G1407 |
| hNav1.1 | W1434R | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | W1408 |
| hNav1.1 | I1437M | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | I1411 |
| hNav1.1 | A1441P | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | A1415 |
| hNav1.1 | Q1450K | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | Q1424 |
| hNav1.1 | Q1450R | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | Q1424 |
| hNav1.1 | P1451L | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | P1425 |
| hNav1.1 | P1451S | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | P1425 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1453C | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | Y1427 |
| hNav1.1 | E1454K | EIEE6 | DIII S5-S6 | E1428 |
| hNav1.1 | L1461I | EIEE6 | DIII S6 | I1435 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1462C | EIEE6 | DIII S6 | Y1436 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1462H | EIEE6 | DIII S6 | Y1436 |
| hNav1.1 | F1463S | EIEE6 | DIII S6 | F1437 |
| hNav1.1 | G1470W | EIEE6 | DIII S6 | G1444 |
| hNav1.1 | F1472S | EIEE6 | DIII S6 | F1446 |
| hNav1.1 | L1475S | EIEE6 | DIII S6 | L1449 |
| hNav1.1 | N1476K | EIEE6 | DIII S6 | N1450 |
| hNav1.1 | D1484G | EIEE6 | DIII S6 | D1458 |
| hNav1.1 | N1485Y | EIEE6 | DIII S6 | N1459 |
| hNav1.1 | E1503K | EIEE6 | DIII - DIV | E1477 |
| hNav1.1 | L1514S | EIEE6 | DIII - DIV | L1488 |
| hNav1.1 | V1538I | EIEE6 | DIII - DIV | V1512 |
| hNav1.1 | D1544A | EIEE6 | DIV S1 | D1518 |
| hNav1.1 | D1544G | EIEE6 | DIV S1 | D1518 |
| hNav1.1 | I1545V | EIEE6 | DIV S1 | I1519 |
| hNav1.1 | M1555R | EIEE6 | DIV S1 | M1529 |
| hNav1.1 | E1561K | EIEE6 | DIV S1-S2 | E1535 |
| hNav1.1 | V1579E | EIEE6 | DIV S2 | V1553 |
| hNav1.1 | G1586E | EIEE6 | DIV S2 | G1560 |
| hNav1.1 | C1588R | EIEE6 | DIV S2 | C1562 |
| hNav1.1 | L1592H | EIEE6 | DIV S2 | L1566 |
| hNav1.1 | L1592P | EIEE6 | DIV S2 | L1566 |
| hNav1.1 | R1596C | EIEE6 | DIV S2-S3 | R1570 |
| hNav1.1 | R1596L | EIEE6 | DIV S2-S3 | R1570 |
| hNav1.1 | N1605S | EIEE6 | DIV S3 | N1579 |
| hNav1.1 | D1608G | EIEE6 | DIV S3 | D1582 |
| hNav1.1 | D1608Y | EIEE6 | DIV S3 | D1582 |
| hNav1.1 | V1612I | EIEE6 | DIV S3 | V1586 |
| hNav1.1 | V1630L | EIEE6 | DIV S3-S4 | V1604 |
| hNav1.1 | V1630M | EIEE6 | DIV S3-S4 | V1604 |
| hNav1.1 | V1637E | EIEE6 | DIV S4 | V1611 |
| hNav1.1 | I1638N | EIEE6 | DIV S4 | I1612 |
| hNav1.1 | I1638T | EIEE6 | DIV S4 | I1612 |
| hNav1.1 | R1639G | EIEE6 | DIV S4 | R1613 |
| hNav1.1 | R1642S | EIEE6 | DIV S4 | R1616 |
| hNav1.1 | R1645Q | EIEE6 | DIV S4 | R1619 |
| hNav1.1 | R1648C | EIEE6 | DIV S4 | R1622 |
| hNav1.1 | R1648H | EIEE6 | DIV S4 | R1622 |
| hNav1.1 | A1653E | EIEE6 | DIV S4-S5 | A1627 |
| hNav1.1 | T1658M | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | T1632 |
| hNav1.1 | T1658R | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | T1632 |
| hNav1.1 | L1660P | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | L1634 |
| hNav1.1 | F1661S | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | F1635 |
| hNav1.1 | A1662V | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | A1636 |
| hNav1.1 | M1664K | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | M1638 |
| hNav1.1 | L1667P | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | L1641 |
| hNav1.1 | P1668A | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | P1642 |
| hNav1.1 | P1668L | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | P1642 |
| hNav1.1 | N1672I | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | N1646 |
| hNav1.1 | I1673T | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | I1647 |
| hNav1.1 | G1674R | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | G1648 |
| hNav1.1 | L1675R | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | L1649 |
| hNav1.1 | L1677F | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | L1651 |
| hNav1.1 | I1683T | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | I1657 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1684D | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | Y1658 |
| hNav1.1 | A1685D | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | A1659 |
| hNav1.1 | G1688W | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | G1662 |
| hNav1.1 | F1692S | EIEE6 | DIV S5 | F1666 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1694C | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | Y1668 |
| hNav1.1 | F1707V | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | F1681 |
| hNav1.1 | S1713N | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | S1687 |
| hNav1.1 | M1714K | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | M1688 |
| hNav1.1 | M1714R | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | M1688 |
| hNav1.1 | C1716R | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | C1690 |
| hNav1.1 | T1721R | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | T1695 |
| hNav1.1 | G1725C | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | G1699 |
| hNav1.1 | W1726R | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | W1700 |
| hNav1.1 | D1727G | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | D1701 |
| hNav1.1 | C1741R | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | C1715 |
| hNav1.1 | G1749E | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | G1723 |
| hNav1.1 | C1756G | EIEE6 | DIV S5-S6 | C1730 |
| hNav1.1 | G1762E | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | G1736 |
| hNav1.1 | I1763N | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | I1737 |
| hNav1.1 | I1770F | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | I1744 |
| hNav1.1 | I1770N | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | I1744 |
| hNav1.1 | I1770T | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | I1744 |
| hNav1.1 | I1771F | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | I1745 |
| hNav1.1 | I1771N | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | I1745 |
| hNav1.1 | S1773F | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | S1747 |
| hNav1.1 | M1780T | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | M1754 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1781C | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | Y1755 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1781H | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | Y1755 |
| hNav1.1 | I1782M | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | I1756 |
| hNav1.1 | I1782S | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | I1756 |
| hNav1.1 | A1783T | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | A1757 |
| hNav1.1 | A1783V | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | A1757 |
| hNav1.1 | E1787K | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | E1761 |
| hNav1.1 | N1788K | EIEE6 | DIV S6 | N1862 |
| hNav1.1 | A1792T | EIEE6 | C-terminus | A1766 |
| hNav1.1 | F1808I | EIEE6 | C-terminus | F1782 |
| hNav1.1 | W1812G | EIEE6 | C-terminus | W1786 |
| hNav1.1 | W1812S | EIEE6 | C-terminus | W1786 |
| hNav1.1 | F1831S | EIEE6 | C-terminus | F1805 |
| hNav1.1 | A1832P | EIEE6 | C-terminus | A1806 |
| hNav1.1 | L1835F | EIEE6 | C-terminus | L1809 |
| hNav1.1 | M1852K | EIEE6 | C-terminus | M1826 |
| hNav1.1 | P1855L | EIEE6 | C-terminus | P1829 |
| hNav1.1 | G1880E | EIEE6 | C-terminus | G1854 |
| hNav1.1 | E1881D | EIEE6 | C-terminus | E1855 |
| hNav1.1 | T1909I | EIEE6 | C-terminus | T1883 |
| hNav1.1 | I1922T | EIEE6 | C-terminus | I1896 |
| hNav1.1 | F90S | ICEGTC | N-terminus | F88 |
| hNav1.1 | R101Q | ICEGTC | N-terminus | R99 |
| hNav1.1 | F178S | ICEGTC | DI S2-S3 | F176 |
| hNav1.1 | I252M | ICEGTC | DI S5 | I250 |
| hNav1.1 | H290R | ICEGTC | DI S5-S6 | S288 |
| hNav1.1 | R393H | ICEGTC | DI S5-S6 | R372 |
| hNav1.1 | T808S | ICEGTC | DII S2 | T784 |
| hNav1.1 | V896I | ICEGTC | DII S5 | V872 |
| hNav1.1 | V944A | ICEGTC | DII S5-S6 | R920 |
| hNav1.1 | G979R | ICEGTC | DII S6 | G955 |
| hNav1.1 | V983A | ICEGTC | DII S6 | V959 |
| hNav1.1 | N1011I | ICEGTC | DII - DIII | N987 |
| hNav1.1 | R1213Q | ICEGTC | DII - DIII | K1187 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1254C | ICEGTC | DIII S2 | Y1228 |
| hNav1.1 | R1325T | ICEGTC | DIII S4 | R1299 |
| hNav1.1 | S1328P | ICEGTC | DIII S4-S5 | S1302 |
| hNav1.1 | F1357L | ICEGTC | DIII S5 | F1331 |
| hNav1.1 | V1366I | ICEGTC | DIII S5 | V1340 |
| hNav1.1 | C1376R | ICEGTC | DIII S5-S6 | C1350 |
| hNav1.1 | A1429D | ICEGTC | DIII S5-S6 | A1403 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1462H | ICEGTC | DIII S6 | Y1436 |
| hNav1.1 | M1511K | ICEGTC | DIII - DIV | M1485 |
| hNav1.1 | V1611F | ICEGTC | DIV S3 | V1585 |
| hNav1.1 | M1619V | ICEGTC | DIV S3 | M1593 |
| hNav1.1 | P1632S | ICEGTC | DIV S3-S4 | P1606 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1684S | ICEGTC | DIV S5 | Y1658 |
| hNav1.1 | T1709I | ICEGTC | DIV S5-S6 | T1683 |
| hNav1.1 | A1724P | ICEGTC | DIV S5-S6 | A1698 |
| hNav1.1 | Y1781C | ICEGTC | DIV S6 | Y1755 |
| hNav1.1 | F1808L | ICEGTC | C-terminus | F1782 |
| hNav1.1 | R1861W | ICEGTC | C-terminus | R1835 |
| hNav1.1 | T1174S | FHM3 | DII - DIII | S1148 |
| hNav1.1 | Q1489H | FHM3 | DIII S6 | Q1463 |
| hNav1.1 | Q1489K | FHM3 | DIII S6 | Q1463 |
| hNav1.1 | F1499L | FHM3 | DIII - DIV | F1473 |
| hNav1.1 | L1649Q | FHM3 | DIV S4 | L1623 |
| hNav1.1 | M145T | FEB3A | DI S1 | M143 |
| hNav1.1 | E1308D | FEB3A | DIII S3-S4 | D1282 |
GEFS+2: Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 2; EIEE6: Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 6; ICEGTC: Intractable childhood epilepsy with generalized tonic-clonic seizures; FHM3: Migraine, familial hemiplegic, 3; FEB3A: Febrile seizures, familial, 3A
Table 3.
Structural mapping of disease-related mutations identified in human Nav1.2
| Related proteins | Mutations | Diseases | Structural position | Map on hNav1.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hNav1.2 | E169G | EIEE11 | DI S2 | E166 |
| hNav1.2 | R188W | BFIS3 | DI S3 | R185 |
| hNav1.2 | V208E | BFIS3 | DI S3-S4 | V205 |
| hNav1.2 | N212D | EIEE11 | DI S3-S4 | N209 |
| hNav1.2 | V213D | EIEE11 | DI S3-S4 | V210 |
| hNav1.2 | R223Q | BFIS3 | DI S4 | R220 |
| hNav1.2 | T236S | EIEE11 | DI S5 | T233 |
| hNav1.2 | M252V | BFIS3 | DI S5 | M249 |
| hNav1.2 | V261M | BFIS3 | DI S5 | V258 |
| hNav1.2 | A263T | EIEE11 | DI S5 | A260 |
| hNav1.2 | A263V | EIEE11 | DI S5 | A260 |
| hNav1.2 | D322N | DS | DI - DII | D298 |
| hNav1.2 | F328V | DS | DI - DII | Y305 |
| hNav1.2 | E430Q | BFIS3 | DI - DII | E407 |
| hNav1.2 | D649N | DS | DI - DII | D623 |
| hNav1.2 | R853Q | EIEE11 | DII S4 | R838 |
| hNav1.2 | N876T | EIEE11 | DII S5 | N861 |
| hNav1.2 | V892I | BFIS3 | DII S5 | V877 |
| hNav1.2 | E999K | EIEE11 | DII - DIII | D984 |
| hNav1.2 | N1001K | BFIS3 | DII - DIII | N986 |
| hNav1.2 | L1003I | BFIS3 | DII - DIII | L988 |
| hNav1.2 | E1211K | EIEE11 | DIII S1 | E1195 |
| hNav1.2 | R1312T | EIEE11 | DIII S4 | R1296 |
| hNav1.2 | R1312T | DS | DIII S4 | R1296 |
| hNav1.2 | R1319Q | BFIS3 | DIII S4-S5 | R1303 |
| hNav1.2 | M1323V | EIEE11 | DIII S4-S5 | M1307 |
| hNav1.2 | V1326L | EIEE11 | DIII S4-S5 | V1310 |
| hNav1.2 | V1326D | EIEE11 | DIII S4-S5 | V1310 |
| hNav1.2 | L1330F | BFIS3 | DIII S4-S5 | L1314 |
| hNav1.2 | S1336Y | EIEE11 | DIII S4-S5 | S1320 |
| hNav1.2 | M1338T | EIEE11 | DIII S5 | M1322 |
| hNav1.2 | L1342P | BFIS3 | DIII S5 | L1326 |
| hNav1.2 | I1473M | EIEE11 | DIII S6 | I1457 |
| hNav1.2 | L1563V | BFIS3 | DIV S2 | L1547 |
| hNav1.2 | Y1589C | BFIS3 | DIV S2-S3 | Y1573 |
| hNav1.2 | I1596S | BFIS3 | DIV S3 | I1580 |
| hNav1.2 | T1623N | EIEE11 | DIV S3-S4 | T1607 |
| hNav1.2 | R1629L | EIEE11 | DIV S4 | R1613 |
| hNav1.2 | L1660Y | EIEE11 | DIV S5 | L1644 |
| hNav1.2 | R1918H | BFIS3 | C-terminus | R1902 |
BFIS3: Seizures, benign familial infantile 3; EIEE11: Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 11; DS: Dravet syndrome
Table 4.
Structural mapping of disease-related mutations identified in human Nav1.3
| Related proteins | Mutations | Diseases | Structural position | Map on hNav1.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hNav1.3 | K354Q | CPE | DI - DII | K332 |
| hNav1.3 | R357Q | CPE | DI - DII | R335 |
| hNav1.3 | D815N | CPE | DII S2-S3 | D799 |
| hNav1.3 | E1160K | CPE | DII - DIII | M1146 |
| hNav1.3 | M1372V | CPE | DIII S5-S6 | R1358 |
| hNav1.3 | G1862C | CPE | C-terminus | G1851 |
CPE: Cryptogenic partial epilepsy
Table 5.
Structural mapping of disease-related mutations identified in human Nav1.4
| Related proteins | Mutations | Diseases | Structural position | Map on hNav1.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hNav1.4 | Q270K | PMC | DI S5 | Q265 |
| hNav1.4 | I693T | PMC | DII S5 | I858 |
| hNav1.4 | T704M | PMC | DII S5 | T870 |
| hNav1.4 | S804F | PMC | DII - DIII | S970 |
| hNav1.4 | A1152D | PMC | DIII S4-S5 | A1313 |
| hNav1.4 | A1156T | PMC | DIII S4-S5 | A1317 |
| hNav1.4 | V1293I | PMC | DIII S6 | V1455 |
| hNav1.4 | G1306A | PMC | DIII S6 | G1468 |
| hNav1.4 | G1306E | PMC | DIII S6 | G1468 |
| hNav1.4 | G1306V | PMC | DIII S6 | G1468 |
| hNav1.4 | T1313M | PMC | DIII - DIV | T1475 |
| hNav1.4 | L1433R | PMC | DIV S3 | L1595 |
| hNav1.4 | L1436P | PMC | DIV S3 | L1598 |
| hNav1.4 | R1448C | PMC | DIV S4 | R1610 |
| hNav1.4 | R1448H | PMC | DIV S4 | R1610 |
| hNav1.4 | R1448L | PMC | DIV S4 | R1610 |
| hNav1.4 | G1456E | PMC | DIV S4 | G1618 |
| hNav1.4 | F1473S | PMC | DIV S5 | F1635 |
| hNav1.4 | V1589M | PMC | DIV S6 | V1751 |
| hNav1.4 | F1705I | PMC | C-terminus | F1867 |
| hNav1.4 | R222W | HOKPP2 | DI S4 | E217 |
| hNav1.4 | R669H | HOKPP2 | DII S4 | R835 |
| hNav1.4 | R672C | HOKPP2 | DII S4 | R838 |
| hNav1.4 | R672G | HOKPP2 | DII S4 | R838 |
| hNav1.4 | R672H | HOKPP2 | DII S4 | R838 |
| hNav1.4 | R672S | HOKPP2 | DII S4 | R838 |
| hNav1.4 | R1129Q | HOKPP2 | DIII S4 | R1290 |
| hNav1.4 | R1132Q | HOKPP2 | DIII S4 | R1293 |
| hNav1.4 | R1135C | HOKPP2 | DIII S4 | R1296 |
| hNav1.4 | R1135H | HOKPP2 | DIII S4 | R1299 |
| hNav1.4 | P1158S | HOKPP2 | DIII S4-S5 | P1319 |
| hNav1.4 | T704M | HYPP | DII S5 | T870 |
| hNav1.4 | V781I | HYPP | DII S6 | V947 |
| hNav1.4 | A1156T | HYPP | DIII S4-S5 | A1317 |
| hNav1.4 | L1433R | HYPP | DIV S3 | L1595 |
| hNav1.4 | M1592V | HYPP | DIV S6 | M1754 |
| hNav1.4 | R675G | NKPP | DII S4 | R841 |
| hNav1.4 | R675Q | NKPP | DII S4 | R841 |
| hNav1.4 | R675W | NKPP | DII S4 | R841 |
| hNav1.4 | V781I | NKPP | DII S6 | V947 |
| hNav1.4 | R1129Q | NKPP | DIII S4 | R1290 |
| hNav1.4 | M1592V | NKPP | DIV S6 | M1754 |
| hNav1.4 | I141V | MYOSCN4A | DI S1 | I136 |
| hNav1.4 | R225W | MYOSCN4A | DI S4 | R220 |
| hNav1.4 | N440K | MYOSCN4A | DI S6 | N395 |
| hNav1.4 | V445M | MYOSCN4A | DI - DII | V440 |
| hNav1.4 | E452K | MYOSCN4A | DI - DII | E447 |
| hNav1.4 | I588V | MYOSCN4A | DII S1 | I754 |
| hNav1.4 | F671S | MYOSCN4A | DII S4 | F837 |
| hNav1.4 | A715T | MYOSCN4A | DII S5 | A881 |
| hNav1.4 | S804N | MYOSCN4A | DII - DIII | S970 |
| hNav1.4 | A1156T | MYOSCN4A | DIII S4-S5 | A1317 |
| hNav1.4 | P1158L | MYOSCN4A | DIII S4-S5 | P1319 |
| hNav1.4 | I1160V | MYOSCN4A | DIII S4-S5 | I1321 |
| hNav1.4 | N1297K | MYOSCN4A | DIII S6 | I1457 |
| hNav1.4 | G1306E | MYOSCN4A | DIII S6 | G1468 |
| hNav1.4 | G1306V | MYOSCN4A | DIII S6 | G1468 |
| hNav1.4 | I1310N | MYOSCN4A | DIII - DIV | I1472 |
| hNav1.4 | M1476I | MYOSCN4A | DIV S5 | M1638 |
| hNav1.4 | A1481D | MYOSCN4A | DIV S5 | A1643 |
| hNav1.4 | Q1633E | MYOSCN4A | C-terminus | Q1795 |
| hNav1.4 | R104H | CMS16 | N-terminus | R99 |
| hNav1.4 | M203K | CMS16 | DI S3 | F198 |
| hNav1.4 | R225W | CMS16 | DI S4 | R220 |
| hNav1.4 | S246L | CMS16 | DI S5 | S241 |
| hNav1.4 | P382T | CMS16 | DI S5-S6 | P337 |
| hNav1.4 | D1069N | CMS16 | DIII S2 | D1230 |
| hNav1.4 | R1135C | CMS16 | DIII S4-S5 | R1299 |
| hNav1.4 | C1209F | CMS16 | DIII S5-S6 | C1370 |
| hNav1.4 | V1442E | CMS16 | DIV S3-S4 | V1604 |
| hNav1.4 | R1454W | CMS16 | DIV S4 | R1616 |
| hNav1.4 | R1457H | CMS16 | DIV S4 | R1619 |
PMC: Paramyotonia congenita of von Eulenburg; HOKPP2: Periodic paralysis hypokalemic 2; HYPP: Periodic paralysis hyperkalemic; NKPP: Periodic paralysis normokalemic; MYOSCN4A: Myotonia SCN4A-related; CMS16: Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 16
Table 6.
Structural mapping of disease-related mutations identified in human Nav1.5
| Related proteins | Mutations | Diseases | Structural position | Map on hNav1.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hNav1.5 | E161K | PFHB1A | DI S2 | E156 |
| hNav1.5 | R225W | PFHB1A | DI S4 | R220 |
| hNav1.5 | G298S | PFHB1A | DI S4-S5 | – |
| hNav1.5 | T512I | PFHB1A | DI - DII | V518 |
| hNav1.5 | G514C | PFHB1A | DI - DII | G520 |
| hNav1.5 | G752R | PFHB1A | DII S2-S3 | G779 |
| hNav1.5 | R1232W | PFHB1A | DIII S1-S2 | K1219 |
| hNav1.5 | D1275N | PFHB1A | DIII S3 | D1262 |
| hNav1.5 | D1595N | PFHB1A | DIII D3-S4 | D1582 |
| hNav1.5 | T1620K | PFHB1A | DIV S3-S4 | T1607 |
| hNav1.5 | G9V | LQT3 | N-terminus | G8 |
| hNav1.5 | R18Q | LQT3 | N-terminus | K17 |
| hNav1.5 | R27H | LQT3 | N-terminus | R26 |
| hNav1.5 | E30G | LQT3 | N-terminus | E29 |
| hNav1.5 | R43Q | LQT3 | N-terminus | K40 |
| hNav1.5 | E48K | LQT3 | N-terminus | D43 |
| hNav1.5 | P52S | LQT3 | N-terminus | P47 |
| hNav1.5 | R53Q | LQT3 | N-terminus | K48 |
| hNav1.5 | R104G | LQT3 | N-terminus | R99 |
| hNav1.5 | S115G | LQT3 | N-terminus | S110 |
| hNav1.5 | V125L | LQT3 | N-terminus | I125 |
| hNav1.5 | L212P | LQT3 | DI S3-S4 | L207 |
| hNav1.5 | R222Q | LQT3 | DI S4 | R217 |
| hNav1.5 | R225Q | LQT3 | DI S4 | R220 |
| hNav1.5 | R225W | LQT3 | DI S4 | R220 |
| hNav1.5 | V240M | LQT3 | DI S5 | V235 |
| hNav1.5 | Q245K | LQT3 | DI S5 | Q240 |
| hNav1.5 | V247L | LQT3 | DI S5 | L242 |
| hNav1.5 | N275K | LQT3 | DI S5-S6 | N270 |
| hNav1.5 | G289S | LQT3 | DI S5-S6 | E284 |
| hNav1.5 | R340W | LQT3 | DI S5-S6 | T329 |
| hNav1.5 | R367C | LQT3 | DI S5-S6 | R356 |
| hNav1.5 | T370M | LQT3 | DI S5-S6 | T359 |
| hNav1.5 | I397T | LQT3 | DI S6 | I386 |
| hNav1.5 | L404Q | LQT3 | DI S6 | L393 |
| hNav1.5 | N406K | LQT3 | DI S6 | N395 |
| hNav1.5 | L409V | LQT3 | DI S6 | L398 |
| hNav1.5 | V411M | LQT3 | DI S6 | V400 |
| hNav1.5 | A413E | LQT3 | DI S6 | A402 |
| hNav1.5 | A413T | LQT3 | DI S6 | A402 |
| hNav1.5 | E462A | LQT3 | DI - DII | E464 |
| hNav1.5 | E462K | LQT3 | DI - DII | E464 |
| hNav1.5 | F530V | LQT3 | DI - DII | F555 |
| hNav1.5 | R535Q | LQT3 | DI - DII | R562 |
| hNav1.5 | R569W | LQT3 | DI - DII | E596 |
| hNav1.5 | S571I | LQT3 | DI - DII | R598 |
| hNav1.5 | A572D | LQT3 | DI - DII | S599 |
| hNav1.5 | A572S | LQT3 | DI - DII | S599 |
| hNav1.5 | A572V | LQT3 | DI - DII | S599 |
| hNav1.5 | Q573E | LQT3 | DI - DII | S600 |
| hNav1.5 | G579R | LQT3 | DI - DII | S606 |
| hNav1.5 | G615E | LQT3 | DI - DII | N641 |
| hNav1.5 | L619F | LQT3 | DI - DII | L615 |
| hNav1.5 | P637L | LQT3 | DI - DII | – |
| hNav1.5 | G639R | LQT3 | DI - DII | K666 |
| hNav1.5 | P648L | LQT3 | DI - DII | L675 |
| hNav1.5 | E654K | LQT3 | DI - DII | N681 |
| hNav1.5 | L673P | LQT3 | DI - DII | V700 |
| hNav1.5 | R680H | LQT3 | DI - DII | Q708 |
| hNav1.5 | R689C | LQT3 | DI - DII | R716 |
| hNav1.5 | R689H | LQT3 | DI - DII | R716 |
| hNav1.5 | P701L | LQT3 | DI - DII | P728 |
| hNav1.5 | T731I | LQT3 | DII S1 | T758 |
| hNav1.5 | Q750R | LQT3 | DII S2 | A777 |
| hNav1.5 | D772N | LQT3 | DII S2-S3 | D799 |
| hNav1.5 | F816Y | LQT3 | DII S4 | F843 |
| hNav1.5 | I848F | LQT3 | DII S5 | I875 |
| hNav1.5 | S941N | LQT3 | DII - DIII | S970 |
| hNav1.5 | Q960K | LQT3 | DII - DIII | Q989 |
| hNav1.5 | R965L | LQT3 | DII - DIII | R994 |
| hNav1.5 | R971C | LQT3 | DII - DIII | N1000 |
| hNav1.5 | C981F | LQT3 | DII - DIII | – |
| hNav1.5 | A997S | LQT3 | DII - DIII | E1023 |
| hNav1.5 | C1004R | LQT3 | DII - DIII | Y1037 |
| hNav1.5 | E1053K | LQT3 | DII - DIII | E1095 |
| hNav1.5 | T1069M | LQT3 | DII - DIII | D1111 |
| hNav1.5 | A1100V | LQT3 | DII - DIII | – |
| hNav1.5 | D1114N | LQT3 | DII - DIII | – |
| hNav1.5 | D1166N | LQT3 | DII - DIII | A1153 |
| hNav1.5 | R1193Q | LQT3 | DII - DIII | N1180 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1199S | LQT3 | DII - DIII | Y1186 |
| hNav1.5 | E1225K | LQT3 | DIII S1-S2 | E1212 |
| hNav1.5 | E1231K | LQT3 | DIII S1-S2 | R1218 |
| hNav1.5 | F1250L | LQT3 | DIII S2 | F1237 |
| hNav1.5 | L1283M | LQT3 | DIII S3 | L1270 |
| hNav1.5 | E1295K | LQT3 | DIII S3-S4 | D1282 |
| hNav1.5 | T1304M | LQT3 | DIII S4 | T1291 |
| hNav1.5 | N1325S | LQT3 | DIII S4-S5 | N1312 |
| hNav1.5 | A1326S | LQT3 | DIII S4-S5 | A1313 |
| hNav1.5 | A1330P | LQT3 | DIII S4-S5 | A1317 |
| hNav1.5 | A1330T | LQT3 | DIII S4-S5 | A1317 |
| hNav1.5 | P1332L | LQT3 | DIII S4-S5 | P1319 |
| hNav1.5 | S1333Y | LQT3 | DIII S4-S5 | S1320 |
| hNav1.5 | I1334V | LQT3 | DIII S4-S5 | I1321 |
| hNav1.5 | L1338V | LQT3 | DIII S5 | L1325 |
| hNav1.5 | R1432S | LQT3 | DIII S5-S6 | V1419 |
| hNav1.5 | S1458Y | LQT3 | DIII S6 | S1445 |
| hNav1.5 | N1472S | LQT3 | DIII S6 | N1459 |
| hNav1.5 | F1473C | LQT3 | DIII S6 | F1460 |
| hNav1.5 | G1481E | LQT3 | DIII - DIV | G1468 |
| hNav1.5 | F1486L | LQT3 | DIII - DIV | F1473 |
| hNav1.5 | M1487L | LQT3 | DIII - DIV | M1474 |
| hNav1.5 | T1488R | LQT3 | DIII - DIV | T1475 |
| hNav1.5 | E1489D | LQT3 | DIII - DIV | E1476 |
| hNav1.5 | K1493R | LQT3 | DIII - DIV | K1480 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1495S | LQT3 | DIII - DIV | Y1482 |
| hNav1.5 | M1498V | LQT3 | DIII - DIV | M1485 |
| hNav1.5 | L1501V | LQT3 | DIII - DIV | L1488 |
| hNav1.5 | K1505N | LQT3 | DIII - DIV | K1492 |
| hNav1.5 | V1532I | LQT3 | DIV S1 | I1519 |
| hNav1.5 | L1560F | LQT3 | DIV S2 | L1547 |
| hNav1.5 | I1593M | LQT3 | DIV S3 | I1580 |
| hNav1.5 | F1594S | LQT3 | DIV S3 | F1581 |
| hNav1.5 | D1595N | LQT3 | DIV S3 | D1582 |
| hNav1.5 | F1596I | LQT3 | DIV S3 | F1583 |
| hNav1.5 | S1609W | LQT3 | DIV S3 | A1596 |
| hNav1.5 | T1620K | LQT3 | DIV S3-S4 | T1607 |
| hNav1.5 | R1623L | LQT3 | DIV S4 | R1610 |
| hNav1.5 | R1623Q | LQT3 | DIV S4 | R1610 |
| hNav1.5 | R1626H | LQT3 | DIV S4 | R1613 |
| hNav1.5 | R1626P | LQT3 | DIV S4 | R1613 |
| hNav1.5 | R1644C | LQT3 | DIV S5 | R1631 |
| hNav1.5 | R1644H | LQT3 | DIV S5 | R1631 |
| hNav1.5 | T1645M | LQT3 | DIV S5 | T1632 |
| hNav1.5 | L1650F | LQT3 | DIV S5 | L1637 |
| hNav1.5 | M1652R | LQT3 | DIV S5 | M1639 |
| hNav1.5 | M1652T | LQT3 | DIV S5 | M1639 |
| hNav1.5 | I1660V | LQT3 | DIV S5 | I1647 |
| hNav1.5 | V1667I | LQT3 | DIV S5 | V1654 |
| hNav1.5 | T1723N | LQT3 | DIV S5-S6 | S1710 |
| hNav1.5 | R1739W | LQT3 | DIV S5-S6 | E1727 |
| hNav1.5 | L1761F | LQT3 | DIV S6 | L1749 |
| hNav1.5 | L1761H | LQT3 | DIV S6 | L1749 |
| hNav1.5 | V1763M | LQT3 | DIV S6 | V1751 |
| hNav1.5 | M1766L | LQT3 | DIV S6 | M1754 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1767C | LQT3 | DIV S6 | Y1755 |
| hNav1.5 | I1768V | LQT3 | DIV S6 | I1756 |
| hNav1.5 | V1777M | LQT3 | C-terminus | V1765 |
| hNav1.5 | T1779M | LQT3 | C-terminus | T1767 |
| hNav1.5 | E1784K | LQT3 | C-terminus | E1772 |
| hNav1.5 | D1790G | LQT3 | C-terminus | D1778 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1795C | LQT3 | C-terminus | Y1783 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1795YD | LQT3 | C-terminus | Y1783 |
| hNav1.5 | D1819N | LQT3 | C-terminus | A1807 |
| hNav1.5 | L1825P | LQT3 | C-terminus | L1813 |
| hNav1.5 | R1826H | LQT3 | C-terminus | L1814 |
| hNav1.5 | D1839G | LQT3 | C-terminus | D1827 |
| hNav1.5 | R1897W | LQT3 | C-terminus | K1885 |
| hNav1.5 | E1901Q | LQT3 | C-terminus | E1889 |
| hNav1.5 | S1904L | LQT3 | C-terminus | S1892 |
| hNav1.5 | Q1909R | LQT3 | C-terminus | Q1897 |
| hNav1.5 | R1913H | LQT3 | C-terminus | R1901 |
| hNav1.5 | A1949S | LQT3 | C-terminus | F1934 |
| hNav1.5 | V1951L | LQT3 | C-terminus | N1936 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1977N | LQT3 | C-terminus | Y1958 |
| hNav1.5 | F2004L | LQT3 | C-terminus | D1982 |
| hNav1.5 | F2004V | LQT3 | C-terminus | D1982 |
| hNav1.5 | R2012C | LQT3 | C-terminus | – |
| hNav1.5 | R18Q | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | K17 |
| hNav1.5 | R27H | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | R26 |
| hNav1.5 | N70K | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | D65 |
| hNav1.5 | D84N | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | D79 |
| hNav1.5 | F93S | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | F88 |
| hNav1.5 | I94S | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | I89 |
| hNav1.5 | V95I | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | V90 |
| hNav1.5 | R104Q | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | R99 |
| hNav1.5 | R104W | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | R99 |
| hNav1.5 | N109K | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | P104 |
| hNav1.5 | R121Q | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | R116 |
| hNav1.5 | R121W | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | R116 |
| hNav1.5 | K126E | BRGDA1 | N-terminus | K121 |
| hNav1.5 | L136P | BRGDA1 | DI S1 | L131 |
| hNav1.5 | V146M | BRGDA1 | DI S1 | I141 |
| hNav1.5 | E161K | BRGDA1 | DI S2 | E156 |
| hNav1.5 | E161Q | BRGDA1 | DI S2 | E156 |
| hNav1.5 | K175N | BRGDA1 | DI S2 | K170 |
| hNav1.5 | A178G | BRGDA1 | DI S2-S3 | A173 |
| hNav1.5 | C182R | BRGDA1 | DI S2-S3 | C177 |
| hNav1.5 | A185V | BRGDA1 | DI S2-S3 | E180 |
| hNav1.5 | T187I | BRGDA1 | DI S3 | T182 |
| hNav1.5 | A204V | BRGDA1 | DI S3 | A199 |
| hNav1.5 | L212Q | BRGDA1 | DI S3-S4 | L207 |
| hNav1.5 | T220I | BRGDA1 | DI S4 | T215 |
| hNav1.5 | R222Q | BRGDA1 | DI S4 | R217 |
| hNav1.5 | V223L | BRGDA1 | DI S4 | V218 |
| hNav1.5 | R225W | BRGDA1 | DI S4 | R220 |
| hNav1.5 | A226V | BRGDA1 | DI S4 | A221 |
| hNav1.5 | I230V | BRGDA1 | DI S4 | T225 |
| hNav1.5 | V232I | BRGDA1 | DI S4 | V227 |
| hNav1.5 | V240M | BRGDA1 | DI S5 | V235 |
| hNav1.5 | Q270K | BRGDA1 | DI S5 | Q265 |
| hNav1.5 | L276Q | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | L271 |
| hNav1.5 | H278D | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | H273 |
| hNav1.5 | R282C | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | R277 |
| hNav1.5 | R282H | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | R277 |
| hNav1.5 | V294M | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | I289 |
| hNav1.5 | V300I | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | – |
| hNav1.5 | L315P | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | Y304 |
| hNav1.5 | G319S | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | G308 |
| hNav1.5 | T320N | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | S319 |
| hNav1.5 | L325R | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | L314 |
| hNav1.5 | P336L | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | P325 |
| hNav1.5 | G351D | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | G340 |
| hNav1.5 | G351V | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | G340 |
| hNav1.5 | T353I | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | T342 |
| hNav1.5 | D356N | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | D345 |
| hNav1.5 | R367C | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | R356 |
| hNav1.5 | R367H | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | R356 |
| hNav1.5 | R367L | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | R356 |
| hNav1.5 | M369K | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | M358 |
| hNav1.5 | W374G | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | W363 |
| hNav1.5 | R376H | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | N365 |
| hNav1.5 | G386E | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | G375 |
| hNav1.5 | G386R | BRGDA1 | DI S5-S6 | G375 |
| hNav1.5 | V396A | BRGDA1 | DI S6 | V385 |
| hNav1.5 | V396L | BRGDA1 | DI S6 | V385 |
| hNav1.5 | N406S | BRGDA1 | DI S6 | N395 |
| hNav1.5 | E439K | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | D428 |
| hNav1.5 | D501G | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | D507 |
| hNav1.5 | G514C | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | G520 |
| hNav1.5 | R526H | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | R540 |
| hNav1.5 | F532C | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | A546 |
| hNav1.5 | F543L | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | F570 |
| hNav1.5 | G552R | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | G579 |
| hNav1.5 | L567Q | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | P594 |
| hNav1.5 | G615E | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | N641 |
| hNav1.5 | L619F | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | L615 |
| hNav1.5 | R620C | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | E647 |
| hNav1.5 | T632M | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | G659 |
| hNav1.5 | P640A | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | K667 |
| hNav1.5 | A647D | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | L674 |
| hNav1.5 | P648L | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | L675 |
| hNav1.5 | R661W | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | R688 |
| hNav1.5 | H681P | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | Q708 |
| hNav1.5 | C683G | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | C710 |
| hNav1.5 | P701L | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | P728 |
| hNav1.5 | P717L | BRGDA1 | DI - DII | P744 |
| hNav1.5 | A735E | BRGDA1 | DII S1-S2 | A762 |
| hNav1.5 | A735V | BRGDA1 | DII S1-S2 | A762 |
| hNav1.5 | E746K | BRGDA1 | DII S2 | K773 |
| hNav1.5 | G752R | BRGDA1 | DII S2 | G779 |
| hNav1.5 | G758E | BRGDA1 | DII S2 | G785 |
| hNav1.5 | M764R | BRGDA1 | DII S2 | M791 |
| hNav1.5 | D772N | BRGDA1 | DII S2-S3 | D799 |
| hNav1.5 | P773S | BRGDA1 | DII S2-S3 | P800 |
| hNav1.5 | V789I | BRGDA1 | DII S3 | V816 |
| hNav1.5 | R808P | BRGDA1 | DII S4 | R835 |
| hNav1.5 | R814Q | BRGDA1 | DII S4 | R841 |
| hNav1.5 | L839P | BRGDA1 | DII S6 | L866 |
| hNav1.5 | F851L | BRGDA1 | DII S6 | F878 |
| hNav1.5 | E867Q | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | E894 |
| hNav1.5 | R878C | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | R907 |
| hNav1.5 | R878H | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | R907 |
| hNav1.5 | H886P | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | H915 |
| hNav1.5 | F892I | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | F921 |
| hNav1.5 | R893C | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | R922 |
| hNav1.5 | R893H | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | R922 |
| hNav1.5 | C896S | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | C925 |
| hNav1.5 | E901K | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | E930 |
| hNav1.5 | S910L | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | A939 |
| hNav1.5 | C915R | BRGDA1 | DII S5-S6 | C944 |
| hNav1.5 | L917R | BRGDA1 | DII S6 | I946 |
| hNav1.5 | N927S | BRGDA1 | DII S6 | N956 |
| hNav1.5 | L928P | BRGDA1 | DII S6 | L957 |
| hNav1.5 | L935P | BRGDA1 | DII S6 | L964 |
| hNav1.5 | R965C | BRGDA1 | DII - DIII | R994 |
| hNav1.5 | R965H | BRGDA1 | DII - DIII | R994 |
| hNav1.5 | A997T | BRGDA1 | DII - DIII | Q1026 |
| hNav1.5 | R1023H | BRGDA1 | DII - DIII | H1050 |
| hNav1.5 | E1053K | BRGDA1 | DII - DIII | E1095 |
| hNav1.5 | D1055G | BRGDA1 | DII - DIII | D1097 |
| hNav1.5 | S1079Y | BRGDA1 | DII - DIII | – |
| hNav1.5 | A1113V | BRGDA1 | DII - DIII | – |
| hNav1.5 | S1140T | BRGDA1 | DII - DIII | S1128 |
| hNav1.5 | R1193Q | BRGDA1 | DII - DIII | N1180 |
| hNav1.5 | S1219N | BRGDA1 | DIII S1 | S1206 |
| hNav1.5 | E1225K | BRGDA1 | DIII S1-S2 | E1212 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1228H | BRGDA1 | DIII S1-S2 | Y1215 |
| hNav1.5 | R1232Q | BRGDA1 | DIII S1-S2 | K1219 |
| hNav1.5 | R1232W | BRGDA1 | DIII S1-S2 | K1219 |
| hNav1.5 | K1236N | BRGDA1 | DIII S2 | K1223 |
| hNav1.5 | L1339P | BRGDA1 | DIII S2 | L1226 |
| hNav1.5 | E1240Q | BRGDA1 | DIII S2 | E1227 |
| hNav1.5 | D1243N | BRGDA1 | DIII S2 | D1230 |
| hNav1.5 | V1249D | BRGDA1 | DIII S2 | I1236 |
| hNav1.5 | E1253G | BRGDA1 | DIII S2 | E1240 |
| hNav1.5 | G1262S | BRGDA1 | DIII S2-S3 | G1249 |
| hNav1.5 | W1271C | BRGDA1 | DIII S3 | W1258 |
| hNav1.5 | D1275N | BRGDA1 | DIII S3 | D1262 |
| hNav1.5 | A1288G | BRGDA1 | DIII S3-S4 | A1275 |
| hNav1.5 | F1293S | BRGDA1 | DIII S3-S4 | Y1280 |
| hNav1.5 | L1311P | BRGDA1 | DIII S4 | L1298 |
| hNav1.5 | G1319V | BRGDA1 | DIII S4-S5 | G1306 |
| hNav1.5 | V1323G | BRGDA1 | DIII S4-S5 | V1310 |
| hNav1.5 | P1332L | BRGDA1 | DIII S4-S5 | P1319 |
| hNav1.5 | F1344L | BRGDA1 | DIII S5 | F1331 |
| hNav1.5 | F1344S | BRGDA1 | DIII S5 | F1331 |
| hNav1.5 | L1346I | BRGDA1 | DIII S5 | L1333 |
| hNav1.5 | L1346P | BRGDA1 | DIII S5 | L1333 |
| hNav1.5 | M1351R | BRGDA1 | DIII S5 | M1338 |
| hNav1.5 | V1353M | BRGDA1 | DIII S5 | V1340 |
| hNav1.5 | G1358W | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | G1345 |
| hNav1.5 | K1359N | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | K1346 |
| hNav1.5 | F1360C | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | F1347 |
| hNav1.5 | C1363Y | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | C1350 |
| hNav1.5 | S1382I | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | E1369 |
| hNav1.5 | V1405L | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | V1392 |
| hNav1.5 | V1405M | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | V1392 |
| hNav1.5 | G1406E | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | G1393 |
| hNav1.5 | G1406R | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | G1393 |
| hNav1.5 | G1408R | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | G1395 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1409C | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | Y1396 |
| hNav1.5 | L1412F | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | L1399 |
| hNav1.5 | K1419E | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | K1406 |
| hNav1.5 | G1420R | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | G1407 |
| hNav1.5 | A1427S | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | A1414 |
| hNav1.5 | A1428V | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | A1415 |
| hNav1.5 | R1432G | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | V1419 |
| hNav1.5 | R1432S | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | V1419 |
| hNav1.5 | G1433V | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | N1420 |
| hNav1.5 | P1438L | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | P1425 |
| hNav1.5 | E1441Q | BRGDA1 | DIII S5-S6 | E1428 |
| hNav1.5 | I1448L | BRGDA1 | DIII S6 | I1435 |
| hNav1.5 | I1448T | BRGDA1 | DIII S6 | I1435 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1449C | BRGDA1 | DIII S6 | Y1436 |
| hNav1.5 | V1451D | BRGDA1 | DIII S6 | V1438 |
| hNav1.5 | N1463Y | BRGDA1 | DIII S6 | N1450 |
| hNav1.5 | V1468F | BRGDA1 | DIII S6 | V1455 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1494N | BRGDA1 | DIII - DIV | Y1481 |
| hNav1.5 | L1501V | BRGDA1 | DIII - DIV | L1488 |
| hNav1.5 | G1502S | BRGDA1 | DIII - DIV | G1489 |
| hNav1.5 | R1512W | BRGDA1 | DIII - DIV | R1499 |
| hNav1.5 | I1521K | BRGDA1 | DIII - DIV | I1508 |
| hNav1.5 | V1525M | BRGDA1 | DIII - DIV | V1512 |
| hNav1.5 | K1527R | BRGDA1 | DIII - DIV | N1514 |
| hNav1.5 | E1548K | BRGDA1 | DIV S1-S2 | E1535 |
| hNav1.5 | A1569P | BRGDA1 | DIV S2 | I1556 |
| hNav1.5 | F1571C | BRGDA1 | DIV S2 | F1558 |
| hNav1.5 | E1574K | BRGDA1 | DIV S2 | E1561 |
| hNav1.5 | L1582P | BRGDA1 | DIV S2-S3 | L1569 |
| hNav1.5 | R1583C | BRGDA1 | DIV S2-S3 | R1570 |
| hNav1.5 | R1583H | BRGDA1 | DIV S2-S3 | R1570 |
| hNav1.5 | V1604M | BRGDA1 | DIV S3 | V1591 |
| hNav1.5 | Q1613L | BRGDA1 | DIV S3-S4 | E1600 |
| hNav1.5 | T1620M | BRGDA1 | DIV S3-S4 | T1607 |
| hNav1.5 | R1623Q | BRGDA1 | DIV S4 | R1610 |
| hNav1.5 | R1629Q | BRGDA1 | DIV S4 | R1616 |
| hNav1.5 | G1642E | BRGDA1 | DIV S5 | G1629 |
| hNav1.5 | R1644C | BRGDA1 | DIV S5 | R1631 |
| hNav1.5 | A1649V | BRGDA1 | DIV S5 | A1636 |
| hNav1.5 | I1660V | BRGDA1 | DIV S5 | I1647 |
| hNav1.5 | G1661R | BRGDA1 | DIV S5 | G1648 |
| hNav1.5 | V1667I | BRGDA1 | DIV S5 | V1654 |
| hNav1.5 | S1672Y | BRGDA1 | DIV S5 | A1659 |
| hNav1.5 | A1680T | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | A1667 |
| hNav1.5 | A1698T | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | G1685 |
| hNav1.5 | T1709M | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | T1696 |
| hNav1.5 | T1709R | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | T1696 |
| hNav1.5 | G1712S | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | G1699 |
| hNav1.5 | D1714G | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | D1701 |
| hNav1.5 | N1722D | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | N1709 |
| hNav1.5 | C1728R | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | C1715 |
| hNav1.5 | C1728W | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | C1715 |
| hNav1.5 | G1740R | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | G1728 |
| hNav1.5 | G1743E | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | G1731 |
| hNav1.5 | G1743R | BRGDA1 | DIV S5-S6 | G1731 |
| hNav1.5 | V1764F | BRGDA1 | DIV S6 | V1752 |
| hNav1.5 | T1779M | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | T1767 |
| hNav1.5 | E1784K | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | E1772 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1795H | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | Y1783 |
| hNav1.5 | Y1795YD | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | Y1783 |
| hNav1.5 | Q1832E | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | K1820 |
| hNav1.5 | C1850S | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | C1838 |
| hNav1.5 | V1861I | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | V1849 |
| hNav1.5 | K1872N | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | R1860 |
| hNav1.5 | V1903L | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | V1891 |
| hNav1.5 | A1924T | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | I1912 |
| hNav1.5 | G1935S | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | G1920 |
| hNav1.5 | E1938K | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | D1923 |
| hNav1.5 | V1951L | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | N1936 |
| hNav1.5 | I1968S | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | T1949 |
| hNav1.5 | F2004L | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | D1982 |
| hNav1.5 | F2004V | BRGDA1 | C-terminus | D1982 |
| hNav1.5 | T220I | SSS1 | DI S4 | T215 |
| hNav1.5 | A735V | SSS1 | DII S1-S2 | A762 |
| hNav1.5 | P1298L | SSS1 | DIII S3-S4 | P1285 |
| hNav1.5 | G1408R | SSS1 | DIII S5-S6 | G1395 |
| hNav1.5 | D1792N | SSS1 | C-terminus | E1780 |
| hNav1.5 | S1710L | VF1 | DIV S5-S6 | S1697 |
| hNav1.5 | F532C | SIDS | DI - DII | F557 |
| hNav1.5 | S941N | SIDS | DII - DIII | S970 |
| hNav1.5 | G1084S | SIDS | DII - DIII | – |
| hNav1.5 | S1333Y | SIDS | DIII S4-S5 | S1320 |
| hNav1.5 | F1705S | SIDS | DIV S5-S6 | F1692 |
| hNav1.5 | D1275N | ATRST1 | DIII S3 | D1262 |
| hNav1.5 | D1275N | CMD1E | DIII S3 | D1262 |
| hNav1.5 | M138I | ATFB10 | DI S1 | M133 |
| hNav1.5 | E428K | ATFB10 | DI - DII | K417 |
| hNav1.5 | H445D | ATFB10 | DI - DII | Q434 |
| hNav1.5 | N470K | ATFB10 | DI - DII | S472 |
| hNav1.5 | A572D | ATFB10 | DI - DII | S599 |
| hNav1.5 | E655K | ATFB10 | DI - DII | D682 |
| hNav1.5 | E1053K | ATFB10 | DII - DIII | E1095 |
| hNav1.5 | T1131I | ATFB10 | DII - DIII | E1140 |
| hNav1.5 | R1826C | ATFB10 | C-terminus | L1814 |
| hNav1.5 | V1951M | ATFB10 | C-terminus | N1936 |
| hNav1.5 | N1987K | ATFB10 | C-terminus | E1967 |
| hNav1.5 | R222Q | MEPPC | DI S4 | R217 |
PFHB1A: Progressive familial heart block 1A; LQT3: Long QT syndrome 3; BRGDA1: Brugada syndrome 1; SSS1: Sick sinus syndrome 1; VF1: Familial paroxysmal ventricular fibrillation 1; SIDS: Sudden infant death syndrome; ATRST1: Atrial standstill 1; CMD1E: Cardiomyopathy, dilated 1E; ATFB10: Atrial fibrillation, familial, 10; MEPPC: Multifocal ectopic Purkinje-related premature contraction
Table 7.
Structural mapping of disease-related mutations identified in human Nav1.6
| Related proteins | Mutations | Diseases | Structural position | Map on hNav1.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hNav1.6 | D58N | EIEE13 | N-terminus | D52 |
| hNav1.6 | F210L | EIEE13 | DI S3-S4 | F204 |
| hNav1.6 | G214D | EIEE13 | DI S3-S4 | G208 |
| hNav1.6 | N215R | EIEE13 | DI S3-S4 | N209 |
| hNav1.6 | V216D | EIEE13 | DI S3-S4 | V210 |
| hNav1.6 | R223G | EIEE13 | DI S4 | R217 |
| hNav1.6 | F260S | EIEE13 | DI S5 | F254 |
| hNav1.6 | L407F | EIEE13 | DI S6 | L398 |
| hNav1.6 | V410L | EIEE13 | DI - DII | V401 |
| hNav1.6 | E479V | EIEE13 | DI - DII | E464 |
| hNav1.6 | R530W | EIEE13 | DI - DII | H515 |
| hNav1.6 | R662C | EIEE13 | DI - DII | Q643 |
| hNav1.6 | T767I | EIEE13 | DII S1 | T758 |
| hNav1.6 | F846S | EIEE13 | DII S4 | F837 |
| hNav1.6 | R850Q | EIEE13 | DII S4 | R841 |
| hNav1.6 | L875Q | EIEE13 | DII S5 | L866 |
| hNav1.6 | A890T | EIEE13 | DII S5 | A881 |
| hNav1.6 | V960D | EIEE13 | DII S6 | V951 |
| hNav1.6 | N984K | EIEE13 | DII - DIII | N975 |
| hNav1.6 | I1327V | EIEE13 | DIII S4-S5 | I1321 |
| hNav1.6 | L1331V | EIEE13 | DIII S5 | L1325 |
| hNav1.6 | G1451S | EIEE13 | DIII S6 | G1444 |
| hNav1.6 | G1451S | EIEE13 | DIII S6 | G1444 |
| hNav1.6 | N1466K | EIEE13 | DIII S6 | N1459 |
| hNav1.6 | N1466T | EIEE13 | DIII S6 | N1459 |
| hNav1.6 | I1479V | EIEE13 | DIII - DIV | I1472 |
| hNav1.6 | E1483K | EIEE13 | DIII - DIV | E1476 |
| hNav1.6 | I1583T | EIEE13 | DIV S2-S3 | V1576 |
| hNav1.6 | V1592L | EIEE13 | DIV S3 | V1585 |
| hNav1.6 | S1596C | EIEE13 | DIV S3 | S1589 |
| hNav1.6 | I1605R | EIEE13 | DIV S3 | L1598 |
| hNav1.6 | R1617Q | EIEE13 | DIV S4 | R1610 |
| hNav1.6 | L1621W | EIEE13 | DIV S4 | L1614 |
| hNav1.6 | A1650T | EIEE13 | DIV S5 | A1643 |
| hNav1.6 | P1719R | EIEE13 | DIV S5-S6 | P1713 |
| hNav1.6 | N1768D | EIEE13 | DIV S6 | N1762 |
| hNav1.6 | Q1801E | EIEE13 | C-terminus | Q1795 |
| hNav1.6 | E1870D | EIEE13 | C-terminus | E1864 |
| hNav1.6 | R1872W | EIEE13 | C-terminus | R1866 |
| hNav1.6 | R1872Q | EIEE13 | C-terminus | R1866 |
| hNav1.6 | R1872L | EIEE13 | C-terminus | R1866 |
| hNav1.6 | N1877S | EIEE13 | C-terminus | N1871 |
EIEE13: Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 13
Table 8.
Structural mapping of disease-related mutations identified in human Nav1.8
| Related proteins | Mutations | Diseases | Structural position | Map on hNav1.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hNav1.8 | L554P | SFN | DI - DII | – |
| hNav1.8 | M650K | SFN | DI - DII | Y729 |
| hNav1.8 | A1304T | SFN | DIII S5 | A1344 |
| hNav1.8 | G1662S | SFN | DIV S5-S6 | G1699 |
| hNav1.8 | I1706V | SFN | DIV S6 | I1744 |
SFN: Small fiber neuropathy
Table 9.
Structural mapping of disease-related mutations identified in human Nav1.9
| Related proteins | Mutations | Diseases | Structural position | Map on hNav1.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hNav1.9 | R222H | FEPS3 | DI S4 | R214 |
| hNav1.9 | R222S | FEPS3 | DI S4 | R214 |
| hNav1.9 | R225C | FEPS3 | DI S4 | R217 |
| hNav1.9 | I381T | FEPS3 | DI S6 | V383 |
| hNav1.9 | G699R | FEPS3 | DII S5 | G864 |
| hNav1.9 | A808G | FEPS3 | DII S6 | A965 |
| hNav1.9 | L811P | HSAN7 | DII S6 | L968 |
| hNav1.9 | L1158P | FEPS3 | DIII S4 | L1301 |
| hNav1.9 | V1184A | HSAN7 | DIII S5 | V1327 |
FEPS3: Episodic pain syndrome, familial, 3; HSAN7: Neuropathy, hereditary sensory and autonomic, 7
Table 10.
Summary of sodium channelopathies
| Related proteins | Diseases |
|---|---|
| hNav1.1 | GEFS+2: Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 2 |
| EIEE6: Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 6 | |
| ICEGTC: Intractable childhood epilepsy with generalized tonic-clonic seizures | |
| FHM3: Migraine, familial hemiplegic, 3 | |
| FEB3A: Febrile seizures, familial, 3A | |
| hNav1.2 | BFIS3: Seizures, benign familial infantile 3 |
| EIEE11: Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 11 | |
| DS: Dravet syndrome | |
| hNav1.3 | CPE: Cryptogenic partial epilepsy |
| hNav1.4 | PMC: Paramyotonia congenita of von Eulenburg |
| HOKPP2: Periodic paralysis hypokalemic 2 | |
| HYPP: Periodic paralysis hyperkalemic | |
| NKPP: Periodic paralysis normokalemic | |
| MYOSCN4A: Myotonia SCN4A-related | |
| CMS16: Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 16 | |
| hNav1.5 | PFHB1A: Progressive familial heart block 1A |
| LQT3: Long QT syndrome 3 | |
| BRGDA1: Brugada syndrome 1 | |
| SSS1: Sick sinus syndrome 1 | |
| VF1: Familial paroxysmal ventricular fibrillation 1 | |
| SIDS: Sudden infant death syndrome | |
| ATRST1: Atrial standstill 1 | |
| CMD1E: Cardiomyopathy, dilated 1E | |
| ATFB10: Atrial fibrillation, familial, 10 | |
| MEPPC: Multifocal ectopic Purkinje-related premature contraction | |
| hNav1.6 | EIEE13: Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 13 |
| hNav1.7 | IEM: Primary erythermalgia |
| PEPD: Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder | |
| CIP: Indifference to pain, congenital, autosomal recessive | |
| DS: Dravet syndrome | |
| SFN: Small fiber neuropathy | |
| FEB: Febrile eizures | |
| hNav1.8 | SFN: Small fiber neuropathy |
| hNav1.9 | FEPS3: Episodic pain syndrome, familial, 3 |
| HSAN7: Neuropathy, hereditary sensory and autonomic, 7 |
Despite significant advancement in the understanding of Nav channel functions and their relevance to diseases, structural characterization of mammalian Nav channels at atomic level has been challenging, partly due to the substantial technical hurdles in producing mammalian Nav channel proteins in sufficient amount with acceptable purity. The two published bacterial Nav channel crystal structures, NavAb (Payandeh et al., 2011) and NavRh (Zhang et al., 2012), in their full-length have greatly improved our understanding of how those channels conduct and select sodium ions on a structural basis. This is further enhanced by the recently published cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the rabbit voltage-gated calcium (Cav) channel Cav1.1 (Wu et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2016), which, given the significant similarities between Cav and Nav channels, provides an excellent base model for studying the structure and function of the mammalian Nav channels in lieu of the elusive Nav channel structure (Wu et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2016). In this Resource article, we have built a structure model of the human sodium channel Nav1.7 based on the Cav1.1 cryo-EM structure (PDB code: 5GJV). Disease-related mutations of various Nav channels are systematically mapped onto this Nav1.7 structural model. As expected, most mutations are located in the VSDs and the pore domain, which corroborate the functional disturbance associated with the various conditions. The human Nav1.7 structure model may also provide a useful tool for the structure-based design of drugs that are able to therapeutically target the Nav channels.
STRUCTURE MODEL OF HUMAN SODIUM CHANNEL Nav1.7
Homology models of the mammalian Nav channels have been previously constructed based on the crystal structures of the eukaryotic potassium channels or the prokaryotic sodium channels (Tikhonov and Zhorov, 2012; Yang et al., 2012). However, the relevance of such models has been in question, since the eukaryotic sodium channels are known to be heterotetrameric while the prokaryotic sodium channels and the potassium channels are of homotetrameric nature.
We sought to build a homology-based structural model for human Nav1.7 because of the tremendous interest in drug development targeting this channel. The sequence identity and similarity between human Nav1.7 and rabbit Cav1.1 are 21 and 35%, respectively (Please refer to the online Supplementary Fig. 2 of Wu et al., 2016). Importantly, the key amino acids within the VSDs and the pore domains are highly conserved (Wu et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2016). The cryo-EM structure of rabbit Cav1.1 was then used as the template for homology modeling of human Nav1.7. The primary sequence of human Nav1.7 was aligned with rabbit Cav1.1 in MOE with manual adjustment when necessary. The structure model of human Nav1.7 was created with the Homology Model module in MOE using the GB/VI scoring function with AMBER12:EHT force field (MOE, 2016).
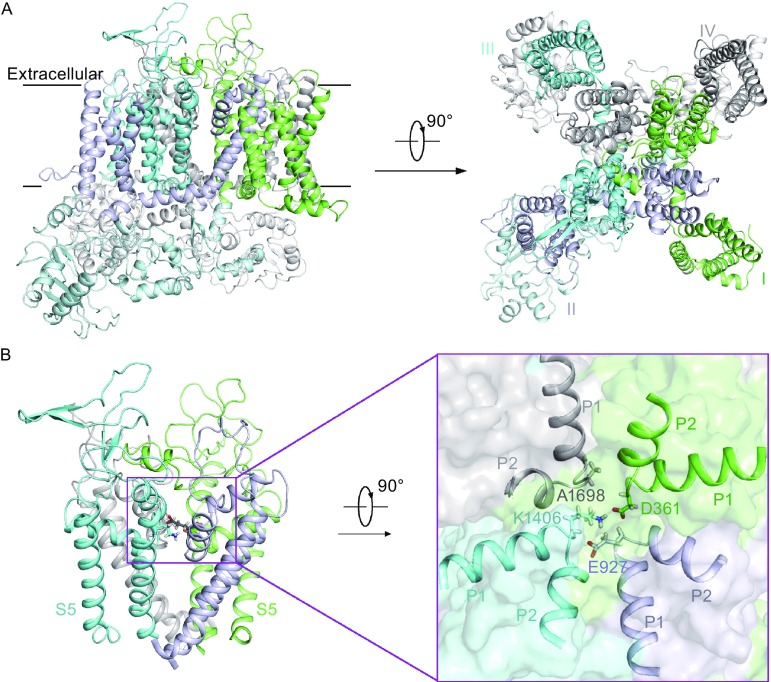
The human Nav1.7 model structure resembles the structure of rCav1.1 in general (Fig. 1A). However, the model exhibits pronounced differences from the calcium channel and bacterial sodium channels particularly in selectivity filter. The SF of Nav1.7 consists of four different amino acid residues DEKA (Fig. 1B). In contrast, the Cav1.1 SF is constituted by four repeated essential glutamic acids, EEEE, while NavAb and NavRh contain TLESWS or TLSSWE in each protomer, respectively. This human Nav1.7 structure model represents the first one-chain sodium channel model with asymmetric repeats and is expected to shed new light on the mammalian sodium channel functions.
Figure 1.
Homology model structure of human Nav1.7 sodium channel. (A) Intra-membrane view and extracellular view of the structure model of Nav1.7. The four domains are colored green, light blue, cyan, and gray for domain I, II, III, and IV, respectively. (B) The pore domain of Nav1.7 structure model. The S5–S6 segments of Nav1.7 are shown and the four selectivity filter amino acids are shown as sticks (left). A close-up view of the four SF residues, D361 in domain I, E927 in domain II, K1406 in domain III, and A1698 in domain IV (right)
MAPPING OF DISEASE-RELEVANT MUTATIONS ONTO THE Nav1.7 STRUCTURE MODEL
Human Nav1.7 sodium channel is preferentially expressed in the sensory neurons of dorsal root ganglia and sympathetic ganglia neurons, particularly within the nociceptors, which is essential for perceiving pain (Djouhri et al., 2003; Dib-Hajj et al., 2013). To date, about 60 mutations of Nav1.7 have been found to cause human pain syndromes including IEM, PEPD, CIP, SFN (small fiber neuropathy), DS (Dravet syndrome), and FEB (febrile seizure) (Fig. 2 and Table 1). We mapped all the reported Nav1.7 mutations onto this Nav1.7 structure model (Fig. 2). Nineteen out of 22 IEM mutations are located in the highly conserved regions of VSDs and the pore domain except for the Q10R, P610T, and G616R mutations (Fig. 2). Electrophysiology study showed that IEM mutations cause a prominent shift of the activation voltage toward a more negative region or delay deactivation, which results in neuron hyperexcitability (Choi et al., 2006; Lampert et al., 2006; Choi et al., 2009; Lampert et al., 2010). For example, mutation of A1643 within the S5 segment of domain IV to glycine (A1643G) generates a significant hyperpolarizing shift (Yang et al., 2016). Our structural analysis shows that only two IEM mutations F216S and L834R are located in the S4 positively charged segment that is directly responsible for transmembrane voltage sensing and channel activation. How other IEM mutations influence voltage sensing and channel functions is yet to be elucidated.
Figure 2.
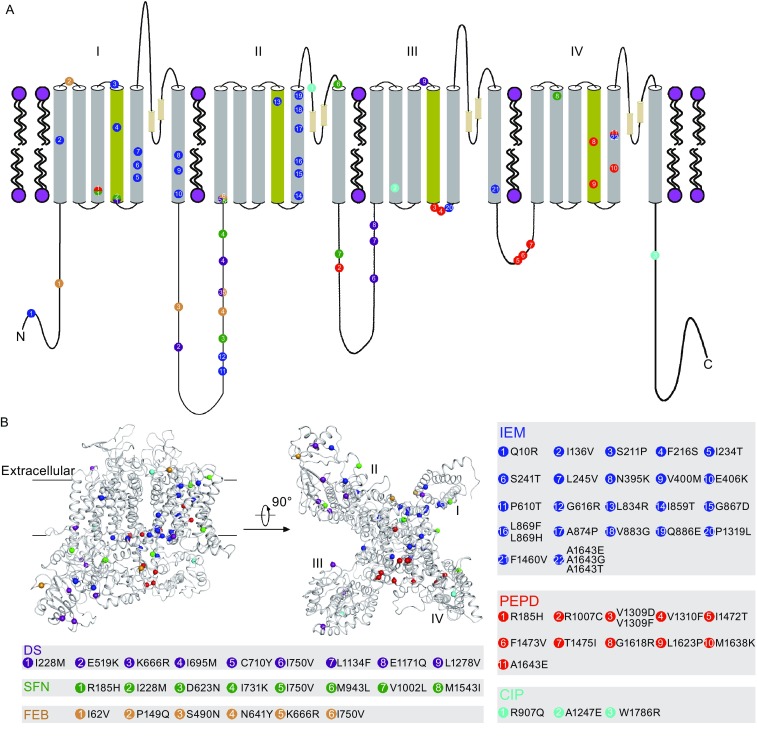
Amino acid locations of Nav1.7 disease-related mutations on the Nav1.7 structure model. (A) The topology of human Nav1.7 sodium channel. Cylinders represent the transmembrane segments, which are colored in gray except that the S4 voltage-sensing segments are colored in yellow. The lines represent the soluble regions between the transmembrane segments or the N/C-terminus. The two P helices between S5 and S6 segments are shown in cylinders. Mutations of Nav1.7 are discriminately mapped on the topology scheme of Nav1.7 by different colors, namely, IEM (blue), PEPD (red), CIP (cyan), DS (purple), SFN (green), and FEB (pink). (B) Intra-membrane view and intracellular views of the Nav1.7 structure model. Mapping of disease-related mutations onto the Nav1.7 structure model is highlighted by different colors. Summary of Nav1.7 mutations is shown in different gray boxes
The PEPD mutations are mostly characterized (nine out of 11) within the S4 segment, S4-S5 linker region, and the cytosolic regions of domain III and domain IV of Nav1.7 except for R185H and R1007C (Fig. 2A and Table 1). Specifically, I1472T, F1473V, and T1475I are within the IFMT motif (Fig. 2A), indicating that they may disturb channel inactivation. Indeed, IFMT mutations usually impair fast inactivation with consequently persistent currents (Fertleman et al., 2006). The V1309D, V1309F, and V1310F mutations are located in the S4-S5 linker region of domain III and they have been shown to cause moderate destabilization of fast inactivation (Jarecki et al., 2008). The G1618R mutation, located within the S4 segment of domain IV, impairs inactivation and retains a persistent current compared to the wild-type (WT) channel (Choi et al., 2011), while another domain IV S4 segment mutation, L1623P, significantly increases ramp current and shortens recovery time from inactivation (Suter et al., 2015). Moreover, electrophysiology study showed that M1638K mutation (within the S5 segment of domain IV) generates faster recovery from inactivation than the WT channel, producing greater currents and reducing the threshold with increased number of action potentials (Fertleman et al., 2006; Dib-Hajj et al., 2008). Another PEPD mutation, A1643E, also located in the S5 segment of domain IV, impedes channel full inactivation, which results in persistent inward currents (Estacion et al., 2008).
The CIP patients, characterized by lack of nociceptive perception, are mostly inflicted by Nav1.7 nonsense mutations, which result in premature protein truncations and inability to produce functional sodium channels. Only three mutations of Nav1.7, namely R907Q, A1247E, and W1786R, have been reported to be associated with CIP (Fig. 2 and Table 1). Diseases such as DS, SFN, and FEB are also known to be caused by Nav1.7 mutations (Fig. 2 and Table 1). For example, all eight SFN mutations have been characterized. Specifically, I228M, I731K, I750V, and M1543I mutations impair slow inactivation, D623N impedes slow and fast inactivation, while R185H, M943L, and V1002L mutations enhance resurgent currents (Faber et al., 2012a). On the other hand, Nav1.7 mutations that are associated with DS (nine mutations) and FEB (six mutations) have not been well characterized.
MAPPING OF OTHER HUMAN SODIUM CHANNEL DISEASE-RELATED MUTATIONS ONTO THE Nav1.7 STRUCTURE MODEL
Members of the human Nav channel family share high sequence similarity and mutations of these Nav channels are known to cause a vast variety of channelopathies. In order to better understand the role of those mutations in disturbing normal channel functions on a structural level, we mapped the disease-related mutations of other human Nav channels onto the Nav1.7 structure model based on the sequence alignment reported in Wu et al., 2016 (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
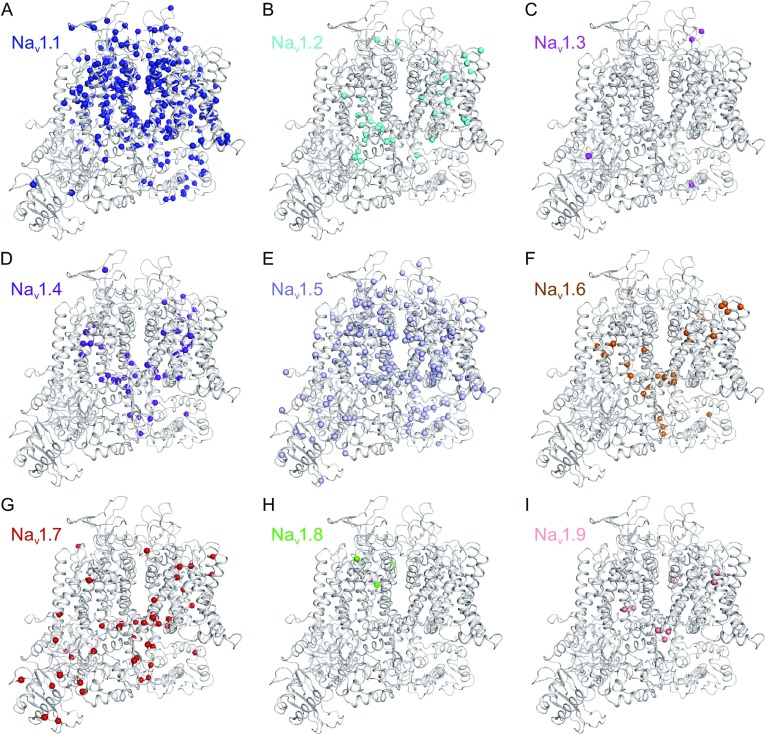
Mapping of Nav channel disease-related mutations onto the Nav1.7 structure model. The Nav1.7 channel is shown in cartoon from the intra-membrane view. The Cα atoms of the disease-related amino acids are shown in spheres. Mapped mutations from nine Nav sodium channels to the Nav1.7 structure model are differentiated by distinct colors, Nav1.1 (A, blue), Nav1.2 (B, cyan), Nav1.3 (C, magenta), Nav1.4 (D, purple blue), Nav1.5 (E, pale cyan), Nav1.6 (F, orange), Nav1.7 (G, red), Nav1.8 (H, green), and Nav1.9 (I, salmon)
Among all the nine Nav channels, Nav1.1 and Nav1.5 have the largest numbers of reported mutations (more than 400 each) (Fig. 3A and 3E), while Nav1.3, Nav1.8, and Nav1.9 have the least numbers (less than 10 each) (Fig. 3C, 3H, and 3I). Notably, mutations in Nav1.1, Nav1.2, Nav1.3, and Nav1.6 mainly cause epilepsies; those in Nav1.4 are related to myopathies; in Nav1.5 result in cardiac channelopathies; and in Nav1.7, Nav1.8, and Nav1.9 are associated with pain-related diseases (Fig. 3 and Tables 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10). Mapping of all Nav channel mutations onto the Nav1.7 structure model revealed that more than 80% of mutations are located in the VSDs and pore domains (Fig. 4A and 4B). Notably, disease-causing mutations are somewhat equally distributed in all four Nav channel domains, which account for more than 20 sodium channelopathies (Fig. 4C). Furthermore, mutations are also distributed in various regions of the pore domains, suggesting that they may disturb Nav channel functions by altering sodium ion selectivity and conductivity (Fig. 4D).
Figure 4.
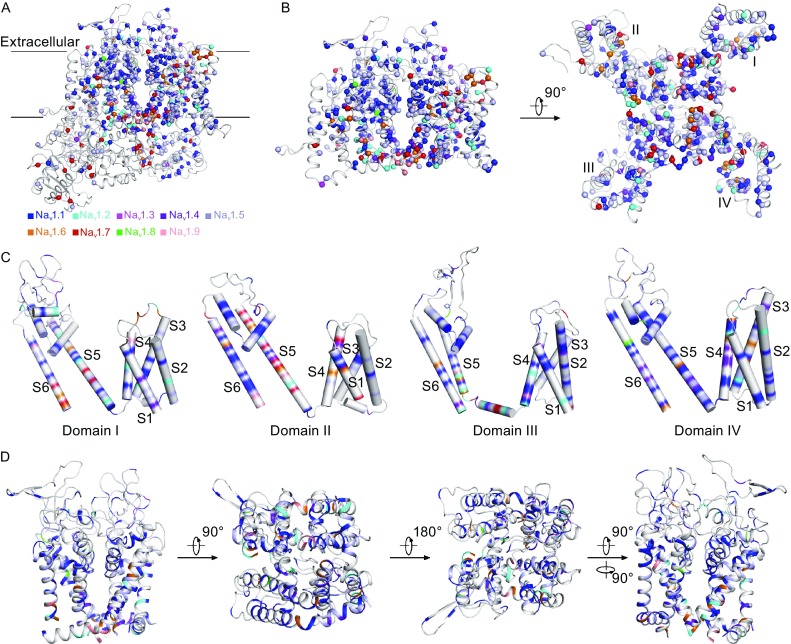
Mutations that cause sodium channelopathies are plotted on the Nav1.7 sodium channel model. (A) The amino acid residues related with sodium channelopathies are mapped on the Nav1.7 structure model. All mutated residues are shown in spheres and colored for Nav1.1 (blue), Nav1.2 (cyan), Nav1.3 (magenta), Nav1.4 (purple blue), Nav1.5 (pale cyan), Nav1.6 (orange), Nav1.7 (red), Nav1.8 (green), and Nav1.9 (salmon). (B) The distribution of sodium channelopathy-related mutations on the transmembrane regions of the Nav1.7 structure model. Mutations of the VSDs and the pore domain are shown from the intra-membrane and intracellular views. (C) The mutation distributions for the four domains. S1–S6 segments are shown in cylindrical helices. (D) Mapping mutations to the pore domain in four different views
Nav1.2 mutations are largely associated with various epilepsy diseases, including BFIS3 (seizures, benign familial infantile 3), EIEE11 (epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 11), and DS (Fig. 3B and Table 3). More than 30 Nav1.2 mutations have been discovered and some of them are now functionally characterized. Interestingly, electrophysiological studies showed that Nav1.2 mutations can either be loss-of-function (R1319Q and L1330F) or gain-of-function (M252V, V261M, L1563V, and Y1579C) (Misra et al., 2008; Liao et al., 2010; Lauxmann et al., 2013). It is noted that BFIS3 mutations in Nav1.2 create less pronounced changes in the activation and inactivation potentials than the EIEE11 mutations (Shi et al., 2012).
Only six missense mutations of Nav1.3 have so far been identified in patients with cryptogenic partial epilepsy (Fig. 3C and Table 4). Five of them, namely K354Q, R357Q, D815N, E1160K, and M1372V, have been characterized, all of which are gain-of-function mutations, consistent with the neuronal hyperexcitability phenotype (Estacion et al., 2010; Vanoye et al., 2014).
Nav1.4 is essential for controlling the muscle action potential and consequently crucial for skeletal muscle contraction. Mutations of Nav1.4 are related with various neuromuscular disorders including PMC (paramyotonia congenita of von Eulenburg), HOKPP2 (periodic paralysis hypokalemic 2), HYPP (periodic paralysis hyperkalemic), NKPP (periodic paralysis normokalemic), MYOSCN4A (myotonia SCN4A-related), and CMS16 (myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 16) (Fig. 3D and Table 5). Different disease-causing mutations alter the Nav1.4 channel function through distinct mechanisms. For example, CMS16 mutations R104H, P382T, and C1209F completely abolish the Nav1.4 channel’s ability to conduct sodium ion, while other mutations such as M203K, R225W, and D1069N cause reduced action potential amplitude, leading to impaired channel function (Zaharieva et al., 2016). Compared to the WT channel, a CMS16 voltage sensor mutant R1457H requires longer hyperpolarization to recover which results in increased fast inactivation (Arnold et al., 2015). On the other hand, a HOKPP2 mutation R1135H (the third arginine in the domain III voltage sensor) exhibits increased depolarization, suggesting that R1135H mutation be gain-of-function (Groome et al., 2014). A MYOSCN4A mutation I582V shows a hyperpolarizing shift of 6 mV, indicating the nature of this mutation be also gain-of-function (Corrochano et al., 2014).
Nav1.6 is one of the sodium channels expressed in human brain and mutations of Nav1.6 cause EIEE13 (epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 13) (Fig. 3F and Table 7). More than 40 Nav1.6 mutations have been discovered since 2012 (Fig. 3F and Table 7), and seven of them have been studied in the functional assays. Specifically, five Nav1.6 mutations, namely T767I, N984K, T1716I, N1768D, and R1872W/R1872Q/R1872L, are characterized as gain-of-function, which cause hyperpolarizing shift of inactivation voltage or increased persistent current (Veeramah et al., 2012; Estacion et al., 2014; Wagnon et al., 2016), while the other two mutations, R223G and G1451S, are loss-of-function (de Kovel et al., 2014; Blanchard et al., 2015).
Five Nav1.8 mutations are associated with SFN, a condition that is clinically characterized by autonomic dysfunction and burning pain in the distal extremities (Fig. 3H and Table 8). Electrophysiology study has shown that Nav1.8 mutations, specifically L554P, A1304T, G1662S, and I1706V, accelerate inactivation recovery and enhance activation, which result in hyperexcitability (Faber et al., 2012b; Huang et al., 2013; Han et al., 2014). However, another SFN Nav1.8 mutation M650K causes reduced excitability of C fibers (Kist et al., 2016).
FEPS3 (episodic pain syndrome, familial, 3) and HSAN7 (neuropathy, hereditary sensory and autonomic, 7) are thought to be caused by the nine missense gain-of-function mutations of Nav1.9 (Fig. 3I and Table 9). Specifically, compared to the WT channel, R225C and A808G mutations induce hyperexcitability of the DRG neurons (Zhang et al., 2013), G699R enhances activation (Han et al., 2015), L811P significantly increases current density (Leipold et al., 2013), L1158P enhances spontaneous firing (Huang et al., 2014), and V1184A alters the channel voltage dependence that results in channel opening in response to hyperpolarized potentials (Leipold et al., 2015).
DISEASE-RELATED MUTATIONS IN SODIUM CHANNELS Nav1.1 AND Nav1.5
Mutations of Nav1.1 are associated with several neurological disorders including GEFS+2, EIEE6, ICEGTC, FHM3 (migraine, familial hemiplegic, 3), and FEB3A (febrile seizures, familial, 3A) (Table 2 and Table 10). More than 400 mutations of Nav1.1 have been identified, approximately 10% account for GEFS+2 while 80% for EIEE6 (Fig. 5A and Table 2). By mapping the Nav1.1-related mutations to the Nav1.7 structure model, we identified that most mutations are located in the VSDs and the pore domain (Fig. 5A). For example, mutations of the four positively charged residues, R1639G, R1642S, R1645Q, and R1648C, are present in the domain IV S4 segment (Table 2), suggesting that these EIEE6 mutations may alter the voltage sensing behavior of the channel. In addition, it is noteworthy that Nav1.1 mutations can be either loss-of-function or gain-of-function (Catterall et al., 2010; Escayg and Goldin, 2010). For example, two GEFS+2 mutations W1204R and R1648H increase the level of persistent current through gain-of-function (Lossin et al., 2002), while the loss-of-function M145T mutation in FEB3A decreases 60% of the current density (Mantegazza et al., 2005).
Figure 5.
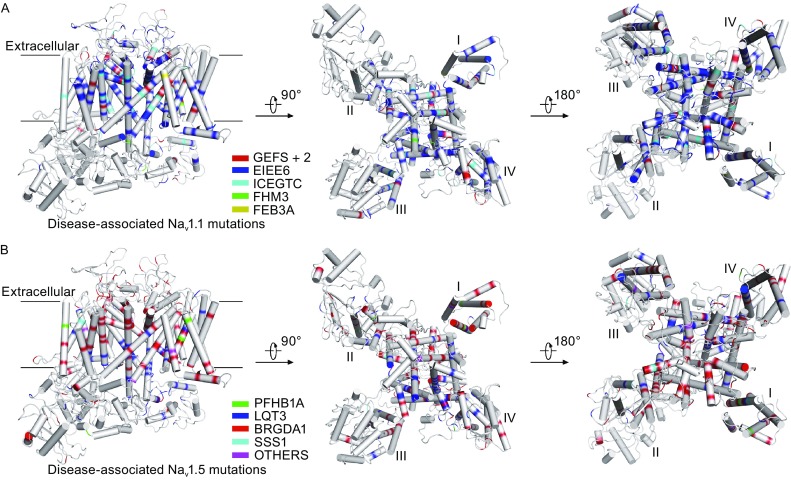
Distributions of the missense mutations in Nav1.1 and Nav1.5. (A) Distributions of Nav1.1 missense mutations on the Nav1.7 model structure. More than 400 mutations are mapped. Mutations from five Nav1.1-related diseases are shown from intra-membrane, intracellular, and extracellular views. The Nav1.7 model is shown in cylindrical helices and colored by GEFS+2 in red, EIEE6 in blue, ICEGTC in cyan, FHM3 in green, and FEB3A in yellow. (B) Distributions of Nav1.5 related-disease mutations on the Nav1.7 structure model. Mutations from Nav1.5 related diseases are shown from intra-membrane, intracellular, and extracellular views. Different diseases are colored in green for PFHB1A, blue for LQT3, red for BRGDA1, cyan for SSS1, and magenta for VF1, SIDS, ATRST1, CMD1E, ATFB10, and MEPPC
Nav1.5 is the primary sodium channel in the heart and is essential for the cardiac action potential initiation. More than 400 Nav1.5 mutations have been discovered and they are implicated in a wide variety of cardiac diseases—including PFHB1A (progressive familial heart block 1A), LQT3, BRGDA1, SSS1, VF1 (familial paroxysmal ventricular fibrillation 1), SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome), ATRST1 (atrial standstill 1), CMD1E (cardiomyopathy, dilated 1E), ATFB10 (atrial fibrillation, familial, 10), and MEPPC (multifocal ectopic Purkinje-related premature contractions) (Fig. 5B and Table 6). By mapping all the Nav1.5 mutations onto the Nav1.7 structure model, it shows that most mutations are located in the transmembrane regions of the channel, suggesting that these mutations might disturb voltage sensing or sodium conduction (Fig. 5B). Furthermore, about 50% of the Nav1.5 mutations account for BRGDA1, while 30% for LQT3. Similar to the case of Nav1.1, mutations in Nav1.5 can be either loss-of-function or gain-of-function. For example, loss-of-function mutations are associated with BRGDA1, CMD1E, SSS1, and ATFB10 (Tan et al., 2001; Smits et al., 2005; Makiyama et al., 2008; Laurent et al., 2012), while gain-of-function mutations of Nav1.5 are responsible for LQT3 (Remme et al., 2006), CMD1E, and ATFB10 (Olson et al., 2005), and most recently MEPPC (Swan et al., 2014).
CONCLUDING REMARKS
The Nav family of sodium channels are important drug targets for the pharmaceutical industry. However, no atomic structure of any mammalian Nav channels is currently available, preventing the establishment of an in-depth structure-function relationship for this important group of sodium channels and application of structure-based approach to rationally design compounds that are able to modulate the functions of those Nav channels in a disease relevant manner. Using the recently published cryo-EM structure of a rabbit Cav channel Cav1.1, we established an atomic level heterotetrameric structure model for the human Nav channel Nav1.7. Disease-related mutations of Nav1.7 and other members of the Nav family, which are largely responsible for many neurological disorders like epilepsies, pains, and myopathies, are mapped onto the structure model. Taken together the available functional data, we attempted to establish a rudimentary structure-function relationship for human Nav1.7 and other members of the Nav channel family. It is noticeable that sodium channelopathies can be attributed to both loss-of-function and gain-of-function mutations.
However, we must realize that the current Nav1.7 structural model has its limitation and the atomic resolution mammalian Nav channel structure is urgently needed. In recent years, cryo-EM technology is becoming a mainstream technology for structural biology, which is able to potentially overcome the significant technical hurdles in producing challenging proteins such as mammalian Nav channels in sufficient quality and the necessity of crystallization for structural elucidation. Detailed mechanisms of how the Nav channels sense voltage changes and conduct sodium ions can only be answered when such atomic resolution structures become available. We hope the Nav1.7 structure model presented here is a temporary surrogate to help understand the Nav channel functions, particularly those relevant to the various neurological diseases, at atomic level, and contributes to the structure-based rational design of the next generation Nav channel modulators.
SUMMARY OF DISEASE-RELATED MUTATIONS FOR SODIUM CHANNELS
Most of the Nav channel disease-related mutations are extracted from the UNIPROT websites:
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35498 (Nav1.1);
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q99250 (Nav1.2);
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35499 (Nav1.4);
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q14524 (Nav1.5);
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UQD0 (Nav1.6);
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q15858 (Nav1.7);
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9Y5Y9 (Nav1.8);
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UI33 (Nav1.9).
In the UNIPROT websites, there are no mutations described for Nav1.3. During literatures searching, we found that six mutations of Nav1.3 are associated with cryptogenic partial epilepsy. Except for the present mutations in the UNIPROT websites, we found additional mutations of Nav channels in literatures. All mutations are summarized in Tables 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. However, we recognize that our summary may not contain all Nav channel disease-related mutations owing to abundant literatures reporting Nav channel disease-related mutations and increasing volume of work describing new findings.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by funds from the National Basic Research Program (973 Program) (2015CB910101, 2016YFA0500402, 2014ZX09507003-006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (projects 31621092, 31630017, and 31611130036). The research of N.Y. was supported in part by an International Early Career Scientist grant from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and an endowed professorship from Bayer Healthcare.
ABBREVIATIONS
ATRST1, atrial standstill 1; BRGDA1, Brugada syndrome 1; Cav, voltage-gated calcium; CNS, central nervous system; cryo-EM, cryo-electron microscopy; DS, Dravet syndrome; FEB, febrile seizure; GEFS+2, generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus 2; HOKPP2, periodic paralysis hypokalemic 2; HYPP, periodic paralysis hyperkalemic; IEM, primary erythermalgia; LQT3, long QT syndrome 3; MEPPC, multifocal ectopic Purkinje-related premature contractions; Nav, voltage-gated sodium; NKPP, periodic paralysis normokalemic; PEPD, paroxysmal extreme pain disorder; PFHB1A, progressive familial heart block 1A; PMC, paramyotonia congenita of von Eulenburg; SF, selectivity filter; SFN, small fiber neuropathy; SIDS, sudden infant death syndrome; SSS1, sick sinus syndrome 1; VF1, familial paroxysmal ventricular fibrillation 1; VSDs, voltage-sensing domains
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICS GUIDELINES
Weiyun Huang, Minhao Liu, S. Frank Yan, and Nieng Yan declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s13238-017-0372-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
S. Frank Yan, Email: frank.yan@outlook.com.
Nieng Yan, Email: nyan@tsinghua.edu.cn.
References
- Arnold WD, Feldman DH, Ramirez S, He L, Kassar D, Quick A, Klassen TL, Lara M, Nguyen J, Kissel JT, et al. Defective fast inactivation recovery of Nav 1.4 in congenital myasthenic syndrome. Ann Neurol. 2015;77:840–850. doi: 10.1002/ana.24389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard MG, Willemsen MH, Walker JB, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG, Jongmans MC, Kleefstra T, van de Warrenburg BP, Praamstra P, Nicolai J, et al. De novo gain-of-function and loss-of-function mutations of SCN8A in patients with intellectual disabilities and epilepsy. J Med Genet. 2015;52:330–337. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall WA. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 2000;26:13–25. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall WA. Sodium channel mutations and epilepsy. In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Olsen RW, Delgado-Escueta AV, editors. Jasper’s basic mechanisms of the epilepsies. Bethesda: National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall WA. Voltage-gated sodium channels at 60: structure, function and pathophysiology. J Physiol. 2012;590:2577–2589. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.224204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall WA. Structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels at atomic resolution. Exp Physiol. 2014;99:35–51. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2013.071969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall WA, Goldin AL, Waxman SG. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57:397–409. doi: 10.1124/pr.57.4.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall WA, Kalume F, Oakley JC. NaV1.1 channels and epilepsy. J Physiol. 2010;588:1849–1859. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.187484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi JS, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. Inherited erythermalgia: limb pain from an S4 charge-neutral Na channelopathy. Neurology. 2006;67:1563–1567. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000231514.33603.1e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi JS, Zhang L, Dib-Hajj SD, Han C, Tyrrell L, Lin Z, Wang X, Yang Y, Waxman SG. Mexiletine-responsive erythromelalgia due to a new Na(v)1.7 mutation showing use-dependent current fall-off. Exp Neurol. 2009;216:383–389. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi JS, Boralevi F, Brissaud O, Sanchez-Martin J, Te Morsche RH, Dib-Hajj SD, Drenth JP, Waxman SG. Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder: a molecular lesion of peripheral neurons. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011;7:51–55. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2010.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrochano S, Mannikko R, Joyce PI, McGoldrick P, Wettstein J, Lassi G, Raja Rayan DL, Blanco G, Quinn C, Liavas A, et al. Novel mutations in human and mouse SCN4A implicate AMPK in myotonia and periodic paralysis. Brain. 2014;137:3171–3185. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corry B, Thomas M. Mechanism of ion permeation and selectivity in a voltage gated sodium channel. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:1840–1846. doi: 10.1021/ja210020h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kovel CG, Meisler MH, Brilstra EH, van Berkestijn FM, van’t Slot R, van Lieshout S, Nijman IJ, O’Brien JE, Hammer MF, Estacion M, et al. Characterization of a de novo SCN8A mutation in a patient with epileptic encephalopathy. Epilepsy Res. 2014;108:1511–1518. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2014.08.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dib-Hajj SD, Estacion M, Jarecki BW, Tyrrell L, Fischer TZ, Lawden M, Cummins TR, Waxman SG. Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder M1627K mutation in human Nav1.7 renders DRG neurons hyperexcitable. Mol Pain. 2008;4:37. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-4-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dib-Hajj SD, Yang Y, Black JA, Waxman SG. The Na(V)1.7 sodium channel: from molecule to man. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013;14:49–62. doi: 10.1038/nrn3404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djouhri L, Newton R, Levinson SR, Berry CM, Carruthers B, Lawson SN. Sensory and electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig sensory neurones expressing Nav 1.7 (PN1) Na+ channel alpha subunit protein. J Physiol. 2003;546:565–576. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.026559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escayg A, Goldin AL. Sodium channel SCN1A and epilepsy: mutations and mechanisms. Epilepsia. 2010;51:1650–1658. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02640.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estacion M, Dib-Hajj SD, Benke PJ, Te Morsche RH, Eastman EM, Macala LJ, Drenth JP, Waxman SG. NaV1.7 gain-of-function mutations as a continuum: A1632E displays physiological changes associated with erythromelalgia and paroxysmal extreme pain disorder mutations and produces symptoms of both disorders. J Neurosci. 2008;28:11079–11088. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3443-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estacion M, Gasser A, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. A sodium channel mutation linked to epilepsy increases ramp and persistent current of Nav1.3 and induces hyperexcitability in hippocampal neurons. Exp Neurol. 2010;224:362–368. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estacion M, O’Brien JE, Conravey A, Hammer MF, Waxman SG, Dib-Hajj SD, Meisler MH. A novel de novo mutation of SCN8A (Nav1.6) with enhanced channel activation in a child with epileptic encephalopathy. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;69:117–123. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.05.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber CG, Hoeijmakers JG, Ahn HS, Cheng X, Han C, Choi JS, Estacion M, Lauria G, Vanhoutte EK, Gerrits MM, et al. Gain of function Nanu1.7 mutations in idiopathic small fiber neuropathy. Ann Neurol. 2012;71:26–39. doi: 10.1002/ana.22485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber CG, Lauria G, Merkies IS, Cheng X, Han C, Ahn HS, Persson AK, Hoeijmakers JG, Gerrits MM, Pierro T, et al. Gain-of-function Nav1.8 mutations in painful neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:19444–19449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216080109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertleman CR, Baker MD, Parker KA, Moffatt S, Elmslie FV, Abrahamsen B, Ostman J, Klugbauer N, Wood JN, Gardiner RM, et al. SCN9A mutations in paroxysmal extreme pain disorder: allelic variants underlie distinct channel defects and phenotypes. Neuron. 2006;52:767–774. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George AL., Jr Inherited disorders of voltage-gated sodium channels. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1990–1999. doi: 10.1172/JCI25505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin AL. Resurgence of sodium channel research. Annu Rev Physiol. 2001;63:871–894. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groome JR, Lehmann-Horn F, Fan C, Wolf M, Winston V, Merlini L, Jurkat-Rott K. NaV1.4 mutations cause hypokalaemic periodic paralysis by disrupting IIIS4 movement during recovery. Brain. 2014;137:998–1008. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C, Vasylyev D, Macala LJ, Gerrits MM, Hoeijmakers JG, Bekelaar KJ, Dib-Hajj SD, Faber CG, Merkies IS, Waxman SG. The G1662S NaV1.8 mutation in small fibre neuropathy: impaired inactivation underlying DRG neuron hyperexcitability. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014;85:499–505. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2013-306095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C, Yang Y, de Greef BT, Hoeijmakers JG, Gerrits MM, Verhamme C, Qu J, Lauria G, Merkies IS, Faber CG, et al. The domain II S4-S5 linker in Nav1.9: a missense mutation enhances activation, impairs fast inactivation, and produces human painful neuropathy. Neuromol Med. 2015;17:158–169. doi: 10.1007/s12017-015-8347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann SH, Terlau H, Stuhmer W, Imoto K, Numa S. Calcium channel characteristics conferred on the sodium channel by single mutations. Nature. 1992;356:441–443. doi: 10.1038/356441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J, Yang Y, Zhao P, Gerrits MM, Hoeijmakers JG, Bekelaar K, Merkies IS, Faber CG, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. Small-fiber neuropathy Nav1.8 mutation shifts activation to hyperpolarized potentials and increases excitability of dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurosci. 2013;33:14087–14097. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2710-13.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J, Han C, Estacion M, Vasylyev D, Hoeijmakers JG, Gerrits MM, Tyrrell L, Lauria G, Faber CG, Dib-Hajj SD, et al. Gain-of-function mutations in sodium channel Na(v)1.9 in painful neuropathy. Brain. 2014;137:1627–1642. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarecki BW, Sheets PL, Jackson JO, 2nd, Cummins TR. Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder mutations within the D3/S4-S5 linker of Nav1.7 cause moderate destabilization of fast inactivation. J Physiol. 2008;586:4137–4153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.154906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim JB. Channelopathies. Korean J Pediatr. 2014;57:1–18. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2014.57.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kist AM, Sagafos D, Rush AM, Neacsu C, Eberhardt E, Schmidt R, Lunden LK, Orstavik K, Kaluza L, Meents J, et al. SCN10A mutation in a patient with erythromelalgia enhances C-fiber activity dependent slowing. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0161789. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert A, Dib-Hajj SD, Tyrrell L, Waxman SG. Size matters: erythromelalgia mutation S241T in Nav1.7 alters channel gating. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:36029–36035. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607637200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert A, O’Reilly AO, Reeh P, Leffler A. Sodium channelopathies and pain. Pflugers Arch. 2010;460:249–263. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0779-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G, Saal S, Amarouch MY, Beziau DM, Marsman RF, Faivre L, Barc J, Dina C, Bertaux G, Barthez O, et al. Multifocal ectopic Purkinje-related premature contractions: a new SCN5A-related cardiac channelopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:144–156. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.02.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauxmann S, Boutry-Kryza N, Rivier C, Mueller S, Hedrich UB, Maljevic S, Szepetowski P, Lerche H, Lesca G. An SCN2A mutation in a family with infantile seizures from Madagascar reveals an increased subthreshold Na(+) current. Epilepsia. 2013;54:e117–e121. doi: 10.1111/epi.12241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leipold E, Liebmann L, Korenke GC, Heinrich T, Giesselmann S, Baets J, Ebbinghaus M, Goral RO, Stodberg T, Hennings JC, et al. A de novo gain-of-function mutation in SCN11A causes loss of pain perception. Nat Genet. 2013;45:1399–1404. doi: 10.1038/ng.2767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leipold E, Hanson-Kahn A, Frick M, Gong P, Bernstein JA, Voigt M, Katona I, OliverGoral R, Altmuller J, Nurnberg P, et al. Cold-aggravated pain in humans caused by a hyperactive NaV1.9 channel mutant. Nat Commun. 2015;6:10049. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Y, Deprez L, Maljevic S, Pitsch J, Claes L, Hristova D, Jordanova A, Ala-Mello S, Bellan-Koch A, Blazevic D, et al. Molecular correlates of age-dependent seizures in an inherited neonatal-infantile epilepsy. Brain. 2010;133:1403–1414. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lossin C, Wang DW, Rhodes TH, Vanoye CG, George AL., Jr Molecular basis of an inherited epilepsy. Neuron. 2002;34:877–884. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00714-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makiyama T, Akao M, Shizuta S, Doi T, Nishiyama K, Oka Y, Ohno S, Nishio Y, Tsuji K, Itoh H, et al. A novel SCN5A gain-of-function mutation M1875T associated with familial atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:1326–1334. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantegazza M, Gambardella A, Rusconi R, Schiavon E, Annesi F, Cassulini RR, Labate A, Carrideo S, Chifari R, Canevini MP, et al. Identification of an Nav1.1 sodium channel (SCN1A) loss-of-function mutation associated with familial simple febrile seizures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:18177–18182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506818102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra SN, Kahlig KM, George AL., Jr Impaired NaV1.2 function and reduced cell surface expression in benign familial neonatal-infantile seizures. Epilepsia. 2008;49:1535–1545. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOE (2016) Molecular operating environment (MOE), 2013.08. Chemical Computing Group Inc, Montreal
- Olson TM, Michels VV, Ballew JD, Reyna SP, Karst ML, Herron KJ, Horton SC, Rodeheffer RJ, Anderson JL. Sodium channel mutations and susceptibility to heart failure and atrial fibrillation. JAMA. 2005;293:447–454. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.4.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payandeh J, Scheuer T, Zheng N, Catterall WA. The crystal structure of a voltage-gated sodium channel. Nature. 2011;475:353–358. doi: 10.1038/nature10238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer NW, Meisler MH. Evolution and diversity of mammalian sodium channel genes. Genomics. 1999;57:323–331. doi: 10.1006/geno.1998.5735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remme CA, Verkerk AO, Nuyens D, van Ginneken AC, van Brunschot S, Belterman CN, Wilders R, van Roon MA, Tan HL, Wilde AA, et al. Overlap syndrome of cardiac sodium channel disease in mice carrying the equivalent mutation of human SCN5A-1795insD. Circulation. 2006;114:2584–2594. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.653949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X, Yasumoto S, Kurahashi H, Nakagawa E, Fukasawa T, Uchiya S, Hirose S. Clinical spectrum of SCN2A mutations. Brain Dev. 2012;34:541–545. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2011.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smits JP, Koopmann TT, Wilders R, Veldkamp MW, Opthof T, Bhuiyan ZA, Mannens MM, Balser JR, Tan HL, Bezzina CR, et al. A mutation in the human cardiac sodium channel (E161K) contributes to sick sinus syndrome, conduction disease and Brugada syndrome in two families. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2005;38:969–981. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2005.02.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song W, Shou W. Cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5 mutations and cardiac arrhythmia. Pediatr Cardiol. 2012;33:943–949. doi: 10.1007/s00246-012-0303-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun YM, Favre I, Schild L, Moczydlowski E. On the structural basis for size-selective permeation of organic cations through the voltage-gated sodium channel—effect of alanine mutations at the DEKA locus on selectivity, inhibition by Ca2+ and H+, and molecular sieving. J Gen Physiol. 1997;110:693–715. doi: 10.1085/jgp.110.6.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter MR, Bhuiyan ZA, Laedermann CJ, Kuntzer T, Schaller M, Stauffacher MW, Roulet E, Abriel H, Decosterd I, Wider C. p. L1612P, a novel voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7 mutation inducing a cold sensitive paroxysmal extreme pain disorder. Anesthesiology. 2015;122:414–423. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan H, Amarouch MY, Leinonen J, Marjamaa A, Kucera JP, Laitinen-Forsblom PJ, Lahtinen AM, Palotie A, Kontula K, Toivonen L, et al. Gain-of-function mutation of the SCN5A gene causes exercise-induced polymorphic ventricular arrhythmias. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2014;7:771–781. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.114.000703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan HL, Bink-Boelkens MT, Bezzina CR, Viswanathan PC, Beaufort-Krol GC, van Tintelen PJ, van den Berg MP, Wilde AA, Balser JR. A sodium-channel mutation causes isolated cardiac conduction disease. Nature. 2001;409:1043–1047. doi: 10.1038/35059090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonov DB, Zhorov BS. Architecture and pore block of eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channels in view of NavAb bacterial sodium channel structure. Mol Pharmacol. 2012;82:97–104. doi: 10.1124/mol.112.078212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanoye CG, Gurnett CA, Holland KD, George AL, Jr, Kearney JA. Novel SCN3A variants associated with focal epilepsy in children. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;62:313–322. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.10.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev PM, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Identification of an intracellular peptide segment involved in sodium channel inactivation. Science. 1988;241:1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.2458625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veeramah KR, O’Brien JE, Meisler MH, Cheng X, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG, Talwar D, Girirajan S, Eichler EE, Restifo LL, et al. De novo pathogenic SCN8A mutation identified by whole-genome sequencing of a family quartet affected by infantile epileptic encephalopathy and SUDEP. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90:502–510. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerman CC, Wilde AA, Lodder EM. The cardiac sodium channel gene SCN5A and its gene product NaV1.5: role in physiology and pathophysiology. Gene. 2015;573:177–187. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.08.062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagnon JL, Barker BS, Hounshell JA, Haaxma CA, Shealy A, Moss T, Parikh S, Messer RD, Patel MK, Meisler MH. Pathogenic mechanism of recurrent mutations of SCN8A in epileptic encephalopathy. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2016;3:114–123. doi: 10.1002/acn3.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West JW, Patton DE, Scheuer T, Wang Y, Goldin AL, Catterall WA. A cluster of hydrophobic amino acid residues required for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:10910–10914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J, Yan Z, Li Z, Yan C, Lu S, Dong M, Yan N. Structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.1 complex. Science. 2015;350:aad2395. doi: 10.1126/science.aad2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J, Yan Z, Li Z, Qian X, Lu S, Dong M, Zhou Q, Yan N. Structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.1 at 3.6 A resolution. Nature. 2016;537:191–196. doi: 10.1038/nature19321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y, Dib-Hajj SD, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Tyrrell L, Estacion M, Waxman SG. Structural modelling and mutant cycle analysis predict pharmacoresponsiveness of a Na(V)1.7 mutant channel. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1186. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y, Huang J, Mis MA, Estacion M, Macala L, Shah P, Schulman BR, Horton DB, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. Nav 1.7-A1632G mutation from a family with inherited erythromelalgia: enhanced firing of dorsal root ganglia neurons evoked by thermal stimuli. J Neurosci. 2016;36:7511–7522. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0462-16.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaharieva IT, Thor MG, Oates EC, van Karnebeek C, Hendson G, Blom E, Witting N, Rasmussen M, Gabbett MT, Ravenscroft G, et al. Loss-of-function mutations in SCN4A cause severe foetal hypokinesia or ‘classical’ congenital myopathy. Brain. 2016;139:674–691. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Ren W, DeCaen P, Yan C, Tao X, Tang L, Wang J, Hasegawa K, Kumasaka T, He J, et al. Crystal structure of an orthologue of the NaChBac voltage-gated sodium channel. Nature. 2012;486:130–134. doi: 10.1038/486323e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang XY, Wen J, Yang W, Wang C, Gao L, Zheng LH, Wang T, Ran K, Li Y, Li X, et al. Gain-of-function mutations in SCN11A cause familial episodic pain. Am J Hum Genet. 2013;93:957–966. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.09.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.