Abstract
This report describes the clinical, macroscopic, histopathological and immunohistochemical features of a spontaneous multicentric extraskeletal sarcoma in an adult male African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). It also provides a succinct up-to-date review on neoplasia in this species. On autopsy examination, main gross findings included a moderately demarcated cranial mass and a multilobulated, caudal intra-abdominal mass. The cranial mass had perforated the underlying temporal and occipital bones and had extended into the cranial vault and was compressing the surface of the cerebellum and cerebrum. Histologic, histochemical and immunohistochemical analyses supported a diagnosis of multicentric poorly differentiated spindle cell sarcoma with fibrosarcomatous, storiform and myxoid foci. The high incidence of neoplasia and cross similarities renders the African hedgehog a suitable species for comparative pathology studies.
Keywords: Atelerix albiventris, Erinaceidae, sarcoma, soft tissue tumor
The African pigmy hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris; Family Erinaceidae) has become an increasingly popular pet in many countries. As a consequence, knowledge on health and disease aspects of this species has correspondingly increased, and neoplasia has been recognized as a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in captive individuals [33]. Table 1 presents neoplastic conditions currently described in the literature for this species. While aged individuals appear to be at increased risk, no gender predisposition has been identified.
Table 1. Neoplastic disease processes reported in the literature for African pygmy hedgehogs (Atelerix albiventris), per organ system.
| System | Type of neoplasm | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Integument | Fibrosarcoma | [35, 37,38,39, 48] |
| Hemangiosarcoma, epithelioid hemangiosarcoma | [39] | |
| Histiocytic sarcoma | [27] | |
| Lipoma | [17] | |
| Liposarcoma | [47] | |
| Malignant fibrous histiocytoma | [20] | |
| Mast cell tumour | [39,40,41,42] | |
| Nerve sheath tumour (schwannoma, neurofibrosarcoma) | [35, 37,38,39,40, 48] | |
| Osteosarcoma | [34, 38] | |
| Plasmacytoma | [35, 37,38,39, 48] | |
| Sebaceous gland carcinoma | [10, 17, 45] | |
| T-cell lymphoma | [45] | |
| Undifferentiated/poorly differentiated sarcoma | [39, 40] | |
| Hemolymphatic | Eosinophilic leukemia | [9, 19, 25] |
| Lymphoma | [20, 38,39,40,41] | |
| Myelogenous leukemia, Myeloproliferative disease with leukemia | [17, 20, 39] | |
| Multicentric epitheliotropic lymphoma | [6] | |
| Splenic carcinoid | [24] | |
| Splenic lymphoma (with cerebellar involvement) | [4] | |
| Disseminated histiocytic sarcoma | [31] | |
| Digestive | Colonic mucinous adenocarcinoma | [17] |
| Gastric adenocarcinoma | [17] | |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | [39] | |
| Intestinal adenocarcinoma | [17] | |
| Intestinal lymphoma | [18] | |
| Large intestine plasmacytoma | [36] | |
| Odontogenic fibroma | [49] | |
| Oral fibrosarcoma | [39] | |
| Oral/oronasal squamous cell carcinoma | [5, 39, 43] | |
| Respiratory | Bronchoalveolar carcinoma | [17] |
| Endocrine | Adrenal cortical carcinoma | [21, 39] |
| Malignant neuroendocrine tumour | [39] | |
| Pancreatic islet cell carcinoma | [17] | |
| Pancreatic islet cell tumour | [39] | |
| Parathyroid adenoma | [32] | |
| Pheochromocytoma | [17] | |
| Pituitary adenoma | [39] | |
| Follicular thyroid adenoma/carcinoma | [32] | |
| Thyroid adenocarcinoma | [39] | |
| Thyroid C-cell carcinoma | [23, 28] | |
| Reproductive | Bilateral malignant ovarian teratoma with peritoneal metastasis | [44] |
| Endometrial polyp | [27] | |
| Ovarian granulosa cell tumour | [48] | |
| Uterine adenomas | [39] | |
| Uterine adenocarcinoma | [39] | |
| Uterine adenoleiomyoma | [27] | |
| Uterine adenoleiomyosarcoma | [27] | |
| Uterine adenosarcoma | [27] | |
| Uterine endometrial stromal sarcoma | [27, 39, 47] | |
| Uterine leiomyoma | [34] | |
| Uterine leiomyosarcoma | [39] | |
| Uterine spindle cell sarcoma | [8] | |
| Vaginal spindle cell sarcoma | [35] | |
| Vaginal tunic neurofibrosarcoma | [17] | |
| Penile myxoma | [46] | |
| Nervous | Astrocytomas (anaplastic, gemistocytic) | [14,15,16, 30] |
| Microglioma | [14] | |
| Mixed Glioma (Oligoastrocytoma) | [1] | |
| Heart | Hemangioma | [32] |
| Musculoskeletal | Osteoma/Lumbar parosteal sarcomaa)/rib/skull osteomaa)/ osteosarcoma/maxilla osteochondroma | [17, 32] |
| Rib osteoblastic osteosarcoma | [2] | |
| Mammary gland | Adenocarcinoma | [37, 39, 48] |
| Carcinoma | [26, 37, 39] | |
| Papillary adenoma | [37, 39] | |
| Special senses | Primary Epithelial Tumour of the Lacrimal Gland | [22] |
| Retrobulbal acinic cell carcinoma | [13] | |
a) Retrovirus-like particles were identified by electron microscopy.
Most hedgehog tumors are malignant and are reported to have a poor prognosis [38, 39]. The organ systems most often involved include the integumentary, hemolymphatic, digestive, endocrine and reproductive systems [38, 39]. Mesenchymal tumors typically involve the musculoskeletal system and are reported to be less common than either epithelial or round cell tumors [39].
Diagnosis of soft tissue sarcoma (STS) largely relies on histological, immunohistochemical, molecular and/or genetic features. Anatomical location and ultrastructure are also helpful in the diagnosis. More than 50 histological subtypes of STS have been recognized in human medicine and are often associated with unique clinical, prognostic and therapeutic features. Several histological grading systems have been published and correlate with prognosis in humans [12] and in veterinary species, mainly dogs [29]. Histopathological typing and grading, mitotic count and tumor necrosis are the most significant parameters to prognosticate clinical course and therapy [12].
In veterinary medicine, STS includes peripheral nerve sheath tumors (nonbrachial plexus), fibrosarcoma, liposarcoma, perivascular wall tumors, pleomorphic sarcoma, malignant mesenchymoma and undifferentiated sarcomas (US). This report describes the clinical, macroscopic, histopathological, histochemical and immunohistological features of a spontaneous multicentric extraskeletal sarcoma in an adult, male, pet African hedgehog.
A 220 g, two-year-old, intact male, white and brown African pygmy hedgehog was presented to the Veterinary Medical Teaching Hospital at Texas A&M University for inability to walk normally for an undetermined period of time. Previous health problems included resolved acariasis by Caparinia tripilis and mild ataxic gait of unknown aetiology; yet, ‘Wobbly Hedgehog Syndrome’ (WHS) was suspected. On physical examination, the patient was weak, thin and severely ataxic. Attempts to walk resulted in whole body tremors with a lean towards the right. Motor control and proprioception were intact, but weakness and ataxia were present in all four limbs. Palpation of the abdomen revealed a large, firm lobulated mass in the caudal abdomen. Whole body computed tomography analysis revealed an osteolytic neoplasm on the right dorsal head that invaded the skull causing compression and displacement of the brain, and a large mass in the caudal abdomen that displaced the intestine cranial and dorsal to the mass. Major consideration was given to neoplastic disease; however, the organ of origin of the abdominal mass was uncertain. Given a poor prognosis, euthanasia was elected and an autopsy followed.
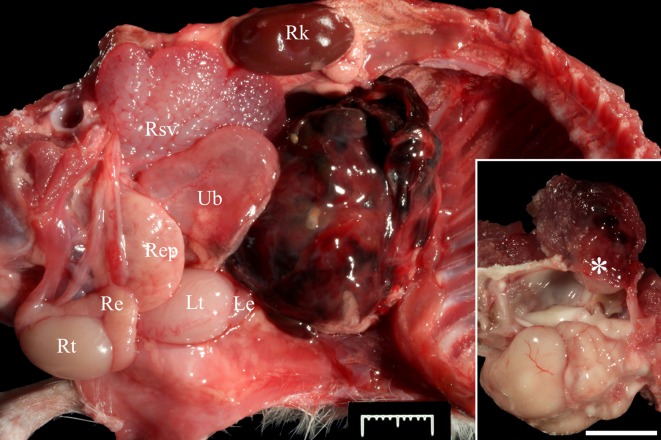
Upon dissection of the peritoneal cavity, a 3 × 2.6 × 3.1 cm firm, mottled dark red multilobulated mass with subserosal strands of clotted blood, was attached to the cranial serosal surface of the left spermatic cord (Fig. 1). Additionally, a 6 × 6 × 6 mm, tan to dark red, moderately well-demarcated and firm mass was noted between the ventral surfaces of the right caudal temporal musculature and periosteal surface. The mass perforated the underlying temporal and occipital bones and extended into the cranial vault for a distance of approximately 3 mm where it mildly compressed the underlying cerebellum and cerebrum (Inset Fig. 1). Lungs were grossly normal and free of metastatic nodules. Selected tissues including lung samples were collected and fixed in 4% buffered formalin and processed as routine for histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses. Masson’s trichrome stain was performed on selected tissue sections.
Fig. 1.
Peritoneal cavity of an African pygmy hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). The right abdominal and thoracic walls, digestive tract, liver and thoracic organs have been removed. A dark red, firm, multilobulated mass with subserosal strands of clotted blood is attached to the cranial serosal surface of the left spermatic cord (not visible in this image). Re: right epididymis; Rep: right external prostate; Rk: right kidney; Rsv: right seminal vesicle; Rt: right testicle; Le: left epididymis; Lt: left testicle; Ub: urinary bladder. Bar=1 cm. Inset: Oblique dorsolateral (left) view of the skull. The left hemi-neurocranium has been removed. A mottled tan to dark red, moderately well-demarcated and friable mass is between the ventral surface of the right caudal temporal musculature and the underlying periosteum (asterisk). The mass focally perforates the underlying temporal and occipital bones and extends into the cranial vault approximately 3 mm. Bar=1 cm.
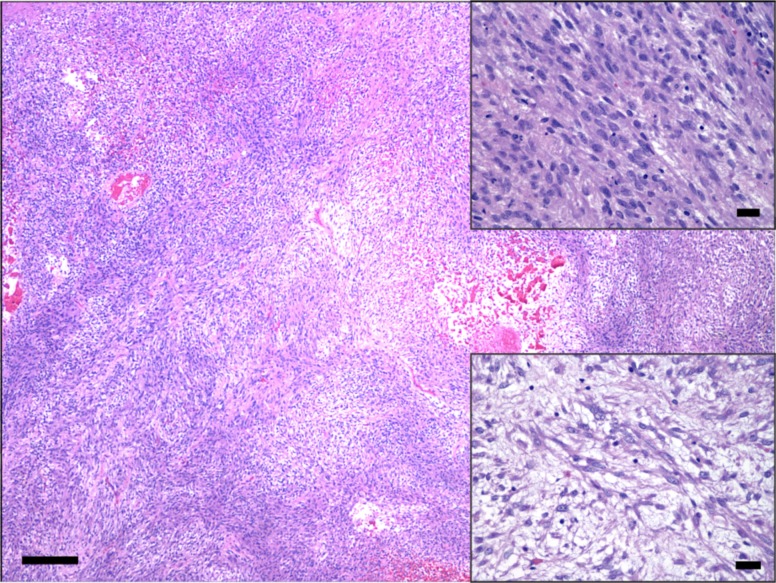
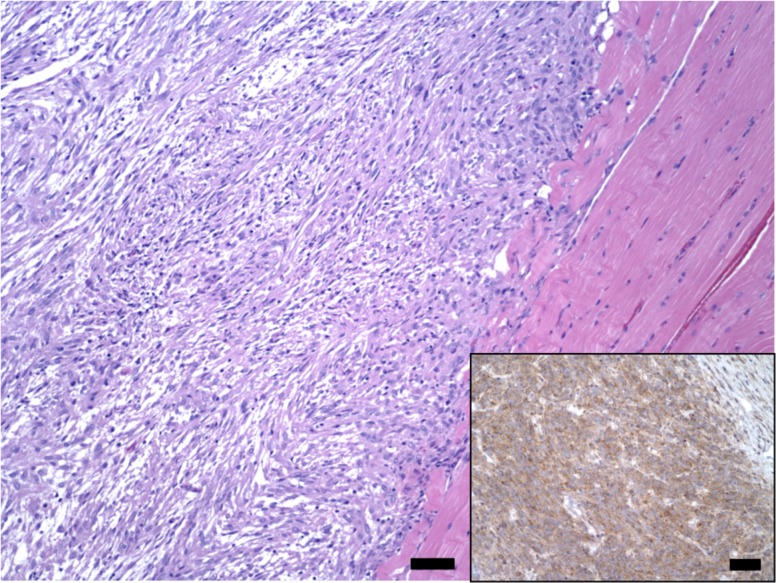
Histologically, both the right temporoparietal and abdominal masses consisted of loose to densely packed spindle-shaped neoplastic cells arranged in interlacing bundles and sweeping fascicles occasionally angled in a ‘herringbone pattern’. Tumor tissue formed large lobules supported and delineated by fibrovascular connective stroma (Figs. 2 and 3). Tumor cells had small to moderate amounts of eosinophilic fibrillary cytoplasm with indistinct borders. Nuclei were oval with finely stippled chromatin and contained a nucleolus (Fig. 2). Anisocytosis and anisokaryosis were moderate, and karyomegaly and binucleation were occasional. Mitotic count averaged 3–4 per ten 400 × fields, distributed mostly toward the leading edges of the neoplasm. Single cell necrosis/apoptosis was frequent. The center of the abdominal neoplasm contained large areas of necrosis with hemorrhage, fibrin and variably mineralized necrotic small caliber vessels. Multifocal areas wherein tumor cells adopted a storiform pattern coexisted with myxoid foci (Fig. 2). Tumor cells merged indistinctly with the supporting connective trabeculae, which were mostly composed of a stellate population of plump fibroblasts and a loosened edematous mat of collagen fibers. Small numbers of lymphocytes, plasma cells and hemosiderin-laden macrophages accompanied infiltrates of tumor cells. No lymphovascular invasion was noted. Additionally, tumor cells of the cranial neoplasm infiltrated the right temporal muscle and dissected between scattered atrophic, degenerate and necrotic skeletal muscle fibers that in some areas had been replaced by tumor cell infiltrates (Fig. 3). Masson’s trichrome staining revealed inconsistent intercalated intra-tumor foci with none to mild collagen production, resembling fibrosarcomatous change.
Fig. 2.
Low magnification photomicrograph of the intra-abdominal soft tissue sarcoma. Neoplastic spindle-shaped cells are arranged in loose or densely packed interlacing, haphazardly oriented bundles. HE. Bar=200 µm. Right upper inset: Tumor cells have small to moderate amounts of eosinophilic fibrillary cytoplasm with indistinct borders, and nuclei are oval with finely stippled chromatin and a nucleolus. HE. Bar=20 µm. Right lower inset: Area of tumor myxoid differentiation. HE. Bar=20 µm.
Fig. 3.
Low magnification photomicrograph of the right temporal soft tissue sarcoma. Tumor cells display variable ‘herringbone pattern’. HE. Bar=50 µm. Inset: Approximately 100% of the tumor cells in this section show moderate to marked, granular to diffuse cytoplasmic immunolabeling for vimentin. IHC. Bar=20 µm.
Approximately 80–100% of the tumor cells showed moderate to marked, granular to diffuse cytoplasmic immunolabeling for vimentin (monoclonal; 1 in 3,000 dilution; Biogen, Istanbul, Turkey) (Fig. 3). Tumor cells did not display immunopositivity for desmin (monoclonal; 1 in 10 dilution; Biocare, Concord, CA, U.S.A.), smooth muscle actin (SMA; monoclonal; 1 in 1,500 dilution; Dako, Glostrup, Denmark), α-sarcomeric actin (monoclonal; 1 in 100 dilution; Dako), myoglobin (Myo; polyclonal; ready to use; Cell Marque, Rocklin, CA, U.S.A.), S-100 (monoclonal; ready to use; Cell Marque), factor VIII (polyclonal; ready to use; Cell Marque), cluster of differentiation (CD)-31 (monoclonal; ready to use; Cell Marque) and ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1; polyclonal; 1 in 1,500; Wako, Osaka, Japan). Although scattered tumor foci resembled fibrosarcoma, overall the above histopathological, histochemical and immunophenotypical findings rendered a diagnosis of spontaneous, extraskeletal, multicentric, poorly differentiated soft tissue spindle cell sarcoma most appropriate.
Additional relevant histopathological findings included marked, bilaterally symmetrical white matter spongiosus with axonal degeneration and loss, rare acute neuronal degeneration and necrosis, and mild astrocytosis in the midbrain, cerebellum and brainstem, and the ventrolateral and dorsal funiculi in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spinal cord. These changes were consistent with those described in ‘Wobbly Hedgehog Syndrome’ (WHS) [16].
In the present case, the histological, histochemical and immunohistochemical features of the tumor cells in both neoplastic growths are suggestive of a poorly differentiated grade 2/3 soft tissue sarcoma with a unique multicentric nature and a highly aggressive and infiltrative behavior for the neoplasm located in the right temporoparietal region. Ultrastructural and genetic analyses might prove useful tools for a most definitive diagnosis in STS cases [3, 11]. According to the veterinary convention, several types of STS, namely fibrosarcoma and undifferentiated sarcomas (US), have been reported in this species (Table 1). Well differentiated fibrosarcomas have been described involving the integumentary system and the oral cavity in this species [35, 37,38,39, 48]. Particularly, poorly differentiated or US were reported affecting the vagina [35] and the skin and subcutis [39] of two African pygmy hedgehogs. In the former, tumor cells showed immunopositivity for CD10, NSE and vimentin. Similar osteolytic and destructive neoplastic behavior to the present right temporoparietal neoplasm was noticed in a lumbar parosteal sarcoma with chondroid and osteoid differentiation in an African hedgehog [32]. The neoplasm had eroded through the dorsal laminae of the lumbar vertebrae and extended into the vertebral canal, compressing the spinal cord and extending down the epineurium of spinal nerve roots. Interestingly, the authors found probable retroviral virions associated with multicentric sarcomas in the former and another case. In our case, no tissue was available for ultrastructural analysis, so a viral aetiology for these neoplasms remains unknown.
Metastasis in the present case is unlikely given absence of lymphovascular invasion in tissue sections examined and in the lungs. Multifocality and multicentricity are two somewhat confusing concepts in tumor development [7]. While multifocal tumors (typically due to local/regional metastasis) originate from a unique cellular clone and grow multifocally in a single organ, multicentric tumors develop simultaneously in more than one organ but without a clonal relationship with respect to their carcinogenesis [7]. Therapeutic response differences may exist between single (unicentric), multicentric and multiple (regional metastatic) tumors [7]. In the present case, although tumor clonality was not assessed, the phenotypical and immunophenotypical features of the tumor growths, along with their distribution, support a multicentric nature. To the author’s knowledge, no STS with similar anatomical, histological and immunohistochemical features has been reported to date in this species.
Histological findings in the central nervous system are those described in WHS [11] and are likely to have played a major role in neurologic signs displayed by this patient, along with mild compression of the temporal mass on the brain and speculative neoplasia-related pain.
This case report expands the body of knowledge of neoplastic disease in African hedgehogs, in particular of STS, which appear to be underrepresented [35]. The high incidence of neoplasia and cross similarities renders the African hedgehog a suitable species for comparative pathology studies.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the laboratory personnel at the veterinary histology laboratory of the University of Georgia and Texas A&M for their technical assistance.
REFERENCES
- 1.Benneter S. S., Summers B. A., Schulz-Schaeffer W. J., Härtig W., Mollidor J., Schöniger S.2014. Mixed Glioma (Oligoastrocytoma) in the brain of an African Hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Comp. Pathol. 151: 420–424. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2014.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Benoit-Biancamano M. O., D’Anjou M. A., Girard C., Langlois I.2006. Rib osteoblastic osteosarcoma in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 18: 415–418. doi: 10.1177/104063870601800420 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bridge J. A.2014. The role of cytogenetics and molecular diagnostics in the diagnosis of soft-tissue tumors. Mod. Pathol. 27Suppl 1: S80–S97. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Burballa A., Martinez J., Martorell J.2012. Splenic lymphoma with cerebellar involvement in an African hedgehog (Atelerix Albiventris). J. Exot. Pet Med. 21: 255–259. doi: 10.1053/j.jepm.2012.06.020 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cho H. M., Soo Choi U. I, Lee H. B.2013. Cytologic aspects of oral squamous cell carcinoma in a captive African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). Korean Soc. Vet. Clin. 30: 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chung T. H., Kim H. J., Choi U. S.2014. Multicentric epitheliotropic T-cell lymphoma in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). Vet. Clin. Pathol. 43: 601–604. doi: 10.1111/vcp.12192 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.de Werra C., Donzelli I., Perone P., Di Micco R., Orabona G.2009. Multifocal and multicentric tumors. pp. 129–142. In: Multiple Primary Malignancies. (Renda, A. ed.), Springer-Verlag Mailand, Milan. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Done L. B., Deem S. L., Fiorello C. V.2007. Surgical and medical management of a uterine spindle cell tumor in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 38: 601–603. doi: 10.1638/2006-0066R.1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Escobar-Alarcón D. K., Reyes-Matute A., Méndez-Bernal A., Flores-Pineda K., López-Mayagoitia A.2016. Chronic eosinophilic leukemia in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). Braz. J. Vet. Path. 9: 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Finkelstein A., Hoover J. P., Confer A. W.2008. Cutaneous epithelioid variant hemangiosarcoma in a captive African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Exot. Pet Med. 17: 49–53. doi: 10.1053/j.jepm.2007.12.009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fletcher C. D., Hogendoorn P., Mertens F., Bridge J.2013. World Health Organization: Classification of Tumors of Soft Tissue and Bone. IARC Press. Lyon. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fletcher C. D. M., Rydholm A., Singer S., Sundaram M., Coindre J. M.2002. Soft tissue tumors: epidemiology, clinical features, histopathological typing and grading. pp. 12–18. In: World Health Organization Classification of Tumors: Pathology and Genetics. Tumors of Soft Tissue and Bone. (Fletcher, C.D.M., Krishnan, U. and Mertens, F., eds.), IARC Press. Lyon. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fukuzawa R., Fukuzawa K., Abe H., Nagai T., Kameyama K.2004. Acinic cell carcinoma in an African pygmy hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). Vet. Clin. Pathol. 33: 39–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-165X.2004.tb00348.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Garner M. M., Kiupel M., Munoz J. F.2010. Brain tumors in African hedgehogs (Atelerix albiventris). Association of avian veterinarians. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gibson C. J., Parry N. M. A., Jakowski R. M., Eshar D.2008. Anaplastic astrocytoma in the spinal cord of an African pygmy hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). Vet. Pathol. 45: 934–938. doi: 10.1354/vp.45-6-934 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Graesser D., Spraker T. R., Dressen P., Garner M. M. T., Raymond J., Terwilliger G., Kim J., Madri J. A.2006. Wobbly Hedgehog syndrome in African pygmy hedgehogs (Atelerix spp.). J. Exot. Pet Med. 15: 59–65. doi: 10.1053/j.jepm.2005.11.010 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Heatley J. F., Mauldin G. E., Cho D. Y.2005. A review of neoplasia in the captive African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Exot. Pet Med. 14: 182–192. doi: 10.1016/j.saep.2005.07.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Helmer P. J.2000. Abnormal hematologic findings in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris) with gastrointestinal lymphosarcoma. Can. Vet. J. 41: 489–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Higbie C. T., Eshar D., Choudhary S., Pohlman L. M., Ganta C. R., Andrews G.2016. Eosinophilic leukemia in a pet African hedgehog (Atelerix Albiventris). J. Exot. Pet Med. 25: 65–71. doi: 10.1053/j.jepm.2015.12.012 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hruban Z., Vardiman J., Meehan T., Frye F., Carter W. E.1992. Haematopoietic malignancies in zoo animals. J. Comp. Pathol. 106: 15–24. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(92)90064-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Juan-Sallés C., Raymond J. T., Garner M. M., Paras A.2006. Adrenocortical carcinoma in three captive African hedgehogs (Atelerix albiventris). J. Exot. Pet Med. 15: 278–280. doi: 10.1053/j.jepm.2006.09.008 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim E, Kim J., Jeong J., Cho H., Choi U., Lee K., Kim N., Kim M., Lee H.2012. Primary epithelial tumor of the lacrimal gland in a African pygmy hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Vet. Clin 29: 154–154. [Google Scholar]
- 23.LaRue M. K., Flesner B. K., Higbie C. T., Dehghanpir S., Crossland N., Nevarez J. G., Tully T. N., Grasperge B. J., Langohr I. M., Shiomitsu K.2016. Treatment of a thyroid tumor in an African pygmy hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Exot. Pet Med. 25: 226–230. doi: 10.1053/j.jepm.2016.04.007 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lowden L. R., Davies J. L.2016. Malignant neuroendocrine tumour (Carcinoid) of the spleen in an African pygmy hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Comp. Pathol. 155: 88–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2016.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Martínez-Jiménez D., Garner B., Coutermarsh-Ott S., Burrell C., Clark S., Nabity M., Díaz-Delgado J., Rodrigues-Hoffmann A., Zaks K., Proença L., Divers S., Saba C., Cazzini P.2017. Eosinophilic leukemia in three African pygmy hedgehogs (Atelerix albiventris) and validation of Luna stain. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 29: 217–223. doi: 10.1177/1040638716687603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Matute A. R., Bernal A. M., Lezama J. R., Guadalupe M. P. L., Antonio G. A. M.2014. Sebaceous gland carcinoma and mammary gland carcinoma in an African hedgehog (Ateletrix albiventris). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 45: 682–685. doi: 10.1638/2013-0191R3.1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mikaelian I., Reavill D. R., Practice A.2004. Spontaneous proliferative lesions and tumors of the uterus of captive African hedgehogs (Atelerix albiventris). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 35: 216–220. doi: 10.1638/01-077 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Miller D. L., Styer E. L., Stobaeus J. K., Norton T. M.2002. Thyroid c-cell carcinoma in an African pygmy hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 33: 392–396. doi: 10.1638/1042-7260(2002)033[0392:TCCCIA]2.0.CO;2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Milovancev M., Hauck M., Keller C., Stranahan L. W., Mansoor A., Malarkey D. E.2015. Comparative pathology of canine soft tissue sarcomas: possible models of human non-rhabdomyosarcoma soft tissue sarcomas. J. Comp. Pathol. 152: 22–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2014.09.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nakata M., Miwa Y., Itou T., Uchida K., Nakayama H., Sakai T.2011. Astrocytoma in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris) suspected wobbly hedgehog syndrome. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 73: 1333–1335. doi: 10.1292/jvms.10-0341 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ogihara K., Itoh T., Mizuno Y., Tamukai K., Madarame H.2016. Disseminated histiocytic sarcoma in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Comp. Pathol. 155: 361–364. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2016.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Peauroi J. R., Lowenstine L. J., Munn R. J., Wilson D. W.1994. Multicentric skeletal sarcomas associated with probable retrovirus particles in two African hedgehogs (Atelerix albiventris). Vet. Pathol. 31: 481–484. doi: 10.1177/030098589403100415 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pei-Chi H., Jane-Fang Y., Lih-Chiann W.2015. A retrospective study of the medical status on 63 African hedgehogs (Atelerix Albiventris) at the Taipei Zoo from 2003 to 2011. J. Exot. Pet Med. 24: 105–111. doi: 10.1053/j.jepm.2014.11.003 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Phair K., Carpenter J. W., Marrow J., Andrews G., Bawa B.2011. Management of an extraskeletal osteosarcoma in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Exot. Pet Med. 20: 151–155. doi: 10.1053/j.jepm.2011.02.011 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ramos-Vara J. A.2001. Soft tissue sarcomas in the African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris): microscopic and immunohistologic study of three cases. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 13: 442–445. doi: 10.1177/104063870101300517 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ramos-Vara J. A., Miller M. A., Craft D.1998. Intestinal plasmacytoma in an African hedgehog. J. Wildl. Dis. 34: 377–380. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-34.2.377 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Raymond J. T., Gerner M.2000. Mammary gland tumors in captive African hedgehogs. J. Wildl. Dis. 36: 405–408. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-36.2.405 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Raymond J. T., Garner M. M.2001. Spontaneous Tumors in Hedgehogs: A Retrospective Study of Fifty Cases. pp. 326–327. Joint Conference of the American Association of Zoo Veterinarians, American Association of Wildlife Veterinarians, Association of Reptilian and Amphibian Veterinarians, and the National Association of Zoo and Wildlife Veterinarians, Orlando. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Raymond J. T., Garner M. M.2001. Spontaneous tumours in captive African hedgehogs (Atelerix albiventris): a retrospective study. J. Comp. Pathol. 124: 128–133. doi: 10.1053/jcpa.2000.0441 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Raymond J. T., White M. R.1999. Necropsy and histopathologic findings in 14 African hedgehogs (Atelerix albiventris): a retrospective study. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 30: 273–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Raymond J. T., Clarke K. A., Schafer K. A.1998. Intestinal lymphosarcoma in captive African hedgehogs. J. Wildl. Dis. 34: 801–806. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-34.4.801 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Raymond J. T., White M. R., Janovitz E. B.1997. Malignant mast cell tumor in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Wildl. Dis. 33: 140–142. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-33.1.140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rivera R. Y. R., Janovitz E. B.1992. Oronasal squamous cell carcinoma in an African hedgehog (Erinaceidae albiventris). J. Wildl. Dis. 28: 148–150. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-28.1.148 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Song S. H., Park N. W., Jung S. K., Kim J. H., Eom K. D.2014. Bilateral malignant ovarian teratoma with peritoneal metastasis in a captive African pygmy hedgehog (Atelerix Albiventris). J. Exot. Pet Med. 23: 403–408. doi: 10.1053/j.jepm.2014.07.009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Spugnini E. P., Pagotto A., Zazzera F., D’Avino A., Caruso G., Citro G., Baldi A.2008. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). In Vivo 22: 43–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Takami Y., Yasuda N., Une Y.2017. Myxoma of the penis in an African pygmy hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 79: 171–174. doi: 10.1292/jvms.16-0294 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tsai F. Y., Chang H. M., Chang H. K., Kao J. P., Liao J. W.2016. Case report: endometrial stroma sarcoma and liposarcoma in an African hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris). Taiwan Vet. J. 42: 181–186. doi: 10.1142/S1682648515720117 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wellehan J. F. X., Southorn E., Smith D. A., Taylor W. M.2003. Surgical removal of a mammary adenocarcinoma and a granulosa cell tumor in an African pygmy hedgehog. Can. Vet. J. 44: 235–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wozniak-Biel A., Janeczek M., Janus I., Nowak M.2015. Surgical resection of peripheral odontogenic fibromas in African pygmy hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris): a case study. BMC Vet. Res. 11: 145. doi: 10.1186/s12917-015-0455-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]