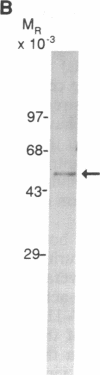
Abstract
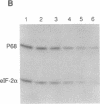
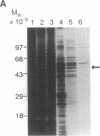
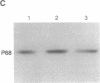
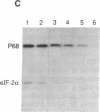
A number of eukaryotic viruses have evolved mechanisms to downregulate activity of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase (referred to as P68 based on its Mr of 68,000 in human cells). This control is essential because once activated, the P68 kinase phosphorylates its natural substrate, the alpha subunit of the eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor 2 (eIF-2), limiting functional eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor 2 available for protein synthesis initiation. We have previously shown that influenza virus encoded a specific mechanism to repress the autophosphorylation and activity of P68. Using in vitro assays for P68 inhibition, we now have purified, to near homogeneity, the P68 repressor from influenza virus-infected cells. The purified product inhibited both the autophosphorylation of P68 as well as phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor 2 by the kinase. We tested for both protease and phosphatase activity but found neither activity associated with the purified inhibitor. Surprisingly we found the purified repressor, which had an apparent Mr of approximately 58,000, was a cellular and not a viral-encoded protein. Possible mechanisms by which influenza virus activates this cellular regulator of the protein kinase, thereby minimizing potential antiviral effects of interferon, are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akkaraju G. R., Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S., Jagus R. Vaccinia specific kinase inhibitory factor prevents translational inhibition by double-stranded RNA in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10321–10325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Activation of the human P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase by individual reovirus s-class mRNAs: s1 mRNA is a potent activator relative to s4 mRNA. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black T. L., Safer B., Hovanessian A., Katze M. G. The cellular 68,000-Mr protein kinase is highly autophosphorylated and activated yet significantly degraded during poliovirus infection: implications for translational regulation. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2244–2251. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2244-2251.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. F., Galabru J., Lebon P., Safer B., Hovanessian A. G. Reduced activity of the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase during a heat shock stress. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12165–12171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Petryshyn R., Sonenberg N. Activation of double-stranded RNA-dependent kinase (dsl) by the TAR region of HIV-1 mRNA: a novel translational control mechanism. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90904-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkind P. R., Krug R. M. Purification of influenza viral complementary RNA: its genetic content and activity in wheat germ cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1464–1475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1464-1475.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Hovanessian A. Autophosphorylation of the protein kinase dependent on double-stranded RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15538–15544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Katze M. G., Robert N., Hovanessian A. G. The binding of double-stranded RNA and adenovirus VAI RNA to the interferon-induced protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):581–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O. Inborn resistance of ice to orthomyxoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;92:25–52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68069-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G. The double stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon: dsRNA-PK. J Interferon Res. 1989 Dec;9(6):641–647. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imani F., Jacobs B. L. Inhibitory activity for the interferon-induced protein kinase is associated with the reovirus serotype 1 sigma 3 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7887–7891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagus R., Anderson W. F., Safer B. The regulation of initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:127–185. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60484-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., DeCorato D., Safer B., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G. Adenovirus VAI RNA complexes with the 68 000 Mr protein kinase to regulate its autophosphorylation and activity. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):689–697. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Detjen B. M., Safer B., Krug R. M. Translational control by influenza virus: suppression of the kinase that phosphorylates the alpha subunit of initiation factor eIF-2 and selective translation of influenza viral mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1741–1750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Tomita J., Black T., Krug R. M., Safer B., Hovanessian A. Influenza virus regulates protein synthesis during infection by repressing autophosphorylation and activity of the cellular 68,000-Mr protein kinase. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3710–3717. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3710-3717.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny A., Safer B. Purification of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2-eukaryotic initiation factor 2B complex and characterization of its guanine nucleotide exchange activity during protein synthesis initiation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3402–3408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug R. M., Shaw M., Broni B., Shapiro G., Haller O. Inhibition of influenza viral mRNA synthesis in cells expressing the interferon-induced Mx gene product. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):201–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.201-206.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent A. G., Krust B., Galabru J., Svab J., Hovanessian A. G. Monoclonal antibodies to an interferon-induced Mr 68,000 protein and their use for the detection of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4341–4345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maran A., Mathews M. B. Characterization of the double-stranded RNA implicated in the inhibition of protein synthesis in cells infected with a mutant adenovirus defective for VA RNA. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90625-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Duncan R. F., Hershey J. W., Mathews M. B. Modification of protein synthesis initiation factors and the shut-off of host protein synthesis in adenovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Mariano T. M., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. A mechanism for the control of protein synthesis by adenovirus VA RNAI. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panniers R., Henshaw E. C. A GDP/GTP exchange factor essential for eukaryotic initiation factor 2 cycling in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells and its regulation by eukaryotic initiation factor 2 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7928–7934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel P. A., Merrick W. C., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. Regulation of a protein synthesis initiation factor by adenovirus virus-associated RNA. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):196–200. doi: 10.1038/313196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Katze M. G., Parkin N. T., Edery I., Hovanessian A. G., Sonenberg N. Control of the interferon-induced 68-kilodalton protein kinase by the HIV-1 tat gene product. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1216–1219. doi: 10.1126/science.2180064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B. 2B or not 2B: regulation of the catalytic utilization of eIF-2. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA prevents phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit subsequent to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Mariano T. M., Reichel P. A., Mathews M. B. Translational control by adenovirus: lack of virus-associated RNAI during adenovirus infection results in phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2 and inhibition of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szyszka R., Kudlicki W., Kramer G., Hardesty B., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. A type 1 phosphoprotein phosphatase active with phosphorylated Mr = 68,000 initiation factor 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3827–3831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Kumar R., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons and double-stranded RNA: selective inhibition by 2-aminopurine. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4289–4294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S. Characterization of a specific kinase inhibitory factor produced by vaccinia virus which inhibits the interferon-induced protein kinase. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Keller A., Whittemore L. A., Maniatis T. 2-Aminopurine selectively inhibits the induction of beta-interferon, c-fos, and c-myc gene expression. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):210–213. doi: 10.1126/science.3281258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]