Abstract
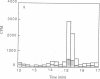
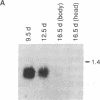
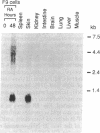
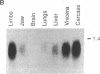
The vitamin A derivative retinoic acid is known to be a potent agent for control of differentiation and proliferation of epithelial cells and to exert profound effects on pattern formation during embryogenesis. Its action at the molecular level appears to be mediated by two distinct classes of proteins: a family of nuclear receptors that regulates gene transcription in a ligand-dependent fashion and a small cellular retinoic acid-binding protein (CRABP) for which a precise function remains to be elucidated. In this report, we describe the identification (by molecular cloning of its cDNA) of an isoform of CRABP, referred to as CRABP-II, expressed at high levels during mouse embryogenesis and in adult skin. We also show that CRABP-II mRNA levels are induced by at least 50-fold upon treatment of F9 teratocarcinoma cells with retinoic acid. The up-regulation of the gene encoding CRABP-II by its ligand suggests that CRABP-II might be involved in a feedback regulatory role in the mechanism of action of retinoic acid on cellular differentiation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. S., Siu C. H. Purification and partial characterization of a novel binding protein for retinoic acid from neonatal rat. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9326–9332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D., Lernhardt E., Pfahl M. A new retinoic acid receptor identified from a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):669–672. doi: 10.1038/333669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P. Retinoids, homeobox genes, and limb morphogenesis. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1285–1294. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Ruberte E., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Stoner C. M., Gudas L. J., Chambon P. Differential expression of genes encoding alpha, beta and gamma retinoic acid receptors and CRABP in the developing limbs of the mouse. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):702–705. doi: 10.1038/342702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Ong E. S., Evans R. M., Tabin C. J. Spatial and temporal expression of the retinoic acid receptor in the regenerating amphibian limb. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):566–569. doi: 10.1038/337566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Shago M., Zirngibl R., Tate P., Rossant J., Varmuza S. Identification of a novel isoform of the retinoic acid receptor gamma expressed in the mouse embryo. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2335–2340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Yang N., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):91–94. doi: 10.1038/331091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Momoi T., Momoi M. The presence of a novel cellular retinoic acid-binding protein in chick embryos: purification and partial characterization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):1302–1308. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammer E. J., Chen D. T., Hoar R. M., Agnish N. D., Benke P. J., Braun J. T., Curry C. J., Fernhoff P. M., Grix A. W., Jr, Lott I. T. Retinoic acid embryopathy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 3;313(14):837–841. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510033131401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Demmer L. A., Sweetser D. A., Ong D. E., Gordon J. I. Rat cellular retinol-binding protein II: use of a cloned cDNA to define its primary structure, tissue-specific expression, and developmental regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5779–5783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R. Effects of vitamin A and its analogs (retinoids) on normal and neoplastic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 12;605(1):33–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Ong D. E., Summerbell D., Chytil F., Hirst E. A. Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein and the role of retinoic acid in the development of the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1989 Sep;135(1):124–132. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Ong D. E., Summerbell D., Chytil F. Spatial distribution of cellular protein binding to retinoic acid in the chick limb bud. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):733–735. doi: 10.1038/335733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson M. H., Spurr N. K., Saksena P., Busch C., Nordlinder H., Peterson P. A., Rask L., Sundelin J. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone corresponding to bovine cellular retinoic-acid-binding protein and chromosomal localization of the corresponding human gene. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):45–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Castro A. V., Toth-Rogler L. E., Wei L. N., Nguyen-Huu M. C. Spatial and temporal pattern of expression of the cellular retinoic acid-binding protein and the cellular retinol-binding protein during mouse embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8813–8817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F. W., Wilk A. L., Kelsey F. O. Teratogen update: vitamin A congeners. Teratology. 1986 Jun;33(3):355–364. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420330315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner C. M., Gudas L. J. Mouse cellular retinoic acid binding protein: cloning, complementary DNA sequence, and messenger RNA expression during the retinoic acid-induced differentiation of F9 wild type and RA-3-10 mutant teratocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1497–1504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundelin J., Anundi H., Trägårdh L., Eriksson U., Lind P., Ronne H., Peterson P. A., Rask L. The primary structure of rat liver cellular retinol-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6488–6493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaller C., Eichele G. Identification and spatial distribution of retinoids in the developing chick limb bud. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):625–628. doi: 10.1038/327625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Krust A., Petkovich M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Cloning of murine alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors and a novel receptor gamma predominantly expressed in skin. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):714–717. doi: 10.1038/339714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]