Abstract
Natural killer (NK) cells are cytotoxic innate lymphocytes that play an important role in viral clearance. NK cell responses to viral infections were originally believed to be non-specific and lacked immune memory recall responses. It is now appreciated that NK cell responses to viral infections can be specific and in some cases memory recall responses are established. Increasing evidence also illuminates the complexity of NK cell interactions with both innate and adaptive immune cells. Here, we summarize the evidence for NK cell-specific memory responses to viral infections and the intricate reciprocal interactions between NK cells and other immune cells that dictate their activation and effector functions.
Introduction
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphocytes that play an integral role in the host’s immune defense against pathogens. NK cells have the unique ability to recognize and lyse target cells without prior exposure. Patients with genetic mutations resulting in diminished NK cell numbers or function succumb to recurrent herpesvirus, varicella virus, and papillomavirus infections [1]–[4], highlighting the importance of NK cells in controlling certain viral infections. NK cell responses were believed to be non-specific due to expression of germ-line encoded receptors that do not recombine to generate antigen-specific receptors like T and B cells [5]. It was thought that NK cells served to control viral burden by broadly lysing virus-infected cells until the adaptive immune system developed specific anti-viral responses. However, NK cell responses can be specific and they interact with both innate and adaptive immune cells to coordinate appropriate anti-viral responses [reviewed in 6 and 7]. Here we summarize recent findings of NK cell specificity through the generation of long-lived memory cells and how NK cells coordinate an anti-viral response with other immune cells.
NK cell Memory
Immunological memory responses are the basis for vaccination and protect the host from secondary encounters with lethal and recurring pathogens. The memory T and B lymphocytes of the adaptive immune system are highly specific and provide quick and robust defenses. These memory response characteristics are now attributed to NK cells in certain situations. First appreciated in studies of delayed contact hypersensitivity, NK cells displaying properties of memory have been demonstrated in response to alloantigens and infectious agents, during homeostatic proliferation, and can be elicited by cytokine stimulation [8]–[11], [12**], [13]. Molecular mechanisms governing the generation of memory NK cells are beyond the scope of this article and are reviewed elsewhere [6], [7], [14].
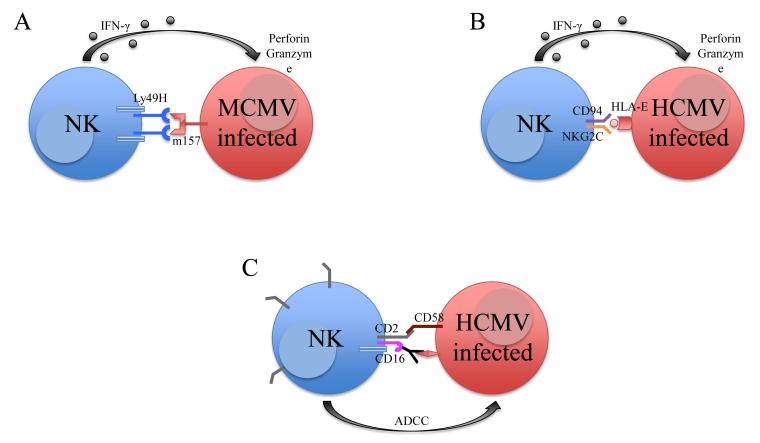
Viral infections induce the generation of memory cells in the T, B, and now NK cell populations. Studies of mouse cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection identified a subset of Ly49H+ NK cells in C57BL/6 mice that specifically recognize the MCMV-encoded glycoprotein m157 [15]–[17]. In 2009, Sun et al. [13] reported the expansion, contraction, and persistence of Ly49H+ NK cells after MCMV infection (Figure 1a). These cells conferred specific protection against MCMV re-challenge and not other heterologous infections, indicating that these are MCMV-specific memory NK cells [13], [18**]. The Ly49H-m157 interaction is crucial for host control of MCMV infection. Infection with MCMVG1F, a strain in which a m157 variant recognizes both the activating Ly49H and the inhibitory Ly49C receptor, rendered mice more susceptible to low dose infection. Ly49C competed for m157 binding and diminished Ly49H-mediated activation by destabilizing NK cell-MCMV-infected target cell contact. However, cis-interactions of Ly49C with major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) expressed on the NK cells restricted binding of Ly49C to m157 on MCMV-infected cells, thus allowing sufficient Ly49H-mediated activation to provide for limited host protection [19**], [20**]. A recent study reported that 50% of Ly49H+ NK cells in C57BL/6 mice co-express the inhibitory receptor NKR-P1B. Expression of NKR-P1B inhibited the proliferation and protection of Ly49H+ cells during MCMV infection, but did not alter secretion of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and granzymes [21**]. It is unknown whether NKR-P1B expression affects the generation of Ly49H+ memory NK cells, although this seems likely. Additionally, animal models of herpes simplex virus, influenza, and simian immunodeficiency virus infection also revealed the existence of memory NK cells. In these studies, NK cells previously exposed to viral antigens conferred enhanced IFN-γ production, cytotoxicity, and protection upon re-challenge [9], [22]–[24], [25*], [26]. The ligand and NK cell receptor(s) responsible for protection against these viruses (other than MCMV) are unknown and identifying them will give scientists insight into controlling these viral infections in humans.
Figure 1. Expansion of NK cells in cytomegalovirus infection.
Ly49H-m157 interaction in MCMV infection (A) and CD94-NKG2C and HLA-E interaction in HCMV infection (B) induces NK cell production of IFN-γ and lysis of target cell. NK cells persist as memory cells. (C) Synergy of CD2 and CD16 for effective antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) of HCMV-infected cells in KLRC2−/− humans.
Many investigators have also identified a potential pool of memory NK cells in humans. Gumá et al. first reported the expansion and persistence of CD94+NKG2C+ NK cells in human CMV-seropositive, but not in HCMV-seronegative, individuals [27]–[29]. Other investigators have also described the expansion of NKG2C+ NK cells in chikungunya, hepatitis B and C, Epstein-Barr (EBV), and hanta virus infections [30]–[33]. However, individuals in these studies were also infected with HCMV, so expansion of the NKG2C+ NK cells likely resulted from subclinical reactivation of HCMV in these patients. Emerging evidence has elucidated the specificity of NKG2C+ NK cell expansion in response to HCMV infection. Björkström et al. did not observe expansion of NKG2C+ NK cells or any particular NK cell subset during recurrent herpes simplex virus-2 infection [34] and Hendricks et al. found that acute EBV infection in HCMV-seropositive and seronegative individuals did not induce expansion of NKG2C+ NK cells [35**]. Both studies indicate that the expansion of NKG2C+ NK cells is specific to HCMV and not HSV or EBV infections. Degranulation of NKG2C+ NK cells is triggered by co-culture with HCMV-infected primary human endothelial cells but not HCMV-infected fibroblasts or monocyte-derived dendritic cells [36*]. Further, NK cell expansion is dependent on expression of the NKG2C ligand, HLA-E, on the infected cells and interleukin (IL)-12 produced by myeloid cells (Figure 1b) [37]. Interestingly, HMCV-seropositive individuals possessing a homozygous null allele of KLRC2 (the gene encoding NKG2C) remain asymptotic and healthy, suggesting that NK cells possess redundant pathways in response to HCMV. In these individuals, the adaptive (or memory) NK cells (defined as FcεRIγ− and/or Syk−) expressed elevated levels of CD2, which synergized with CD16 to activate NK cells in HCMV infection [38**]. Binding of CD2 to CD58, upregulated on HCMV-infected fibroblasts, is critical to induce CD16-dependent antibody-mediated activation of NKG2C+ NK cells (Figure 1c) [39**]. Further insight into NKG2C+ NK cells are described in a recent review by Rölle and Brodin [40].
Modulation of the Innate Immune Response
NK cells participate in complex interactions with neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells during viral infections. The appreciation of NK cell interactions with neutrophils has emerged in the past decade with reports describing multiple factors regulating mutual maturation, activation, and effector functions [41], [42]. In vitro co-culture experiments with human NK cells revealed that IL-15- or IL-18-activated NK cells modulated neutrophil activation and survival via IFN-γ and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) to perpetuate an immune response [43]. Alternatively, human NK cells may induce neutrophil apoptosis via NKp46 and Fas-dependent mechanisms to limit inflammation and further activation of immune responses [44]. In mouse models, IL-22 production by CD3−NK1.1+ (possibly NK cells, but more likely type 3 innate lymphocytes), CD3+NK1.1+, and T cells was necessary for neutrophil recruitment to MCMV-infected tissues to control acute infection [45]. Reciprocally, neutrophils modulate NK cell maturation, activation, function, homeostasis, cytokine production, and NK cell licensing [46], [47**], [48*], [49*].
Macrophages secrete cytokines and express ligands to modulate NK cell responses during viral infections [50]. NK cells can readily kill virus-infected macrophages to limit viral burden, as well as cytokines that these virus-infected macrophages secrete. Romo et al. found that M1 macrophages were more resistant to HCMV infection than M2 macrophages. M1 macrophages secreted inflammatory cytokines that triggered autologous NK cells to produce IFN-γ, whereas M2 macrophages produced limited cytokines and did not induce robust NK cell responses [51], [52]. Another study found that inflammatory monocytes and NK cells contribute to MCMV control via CD155 and DNAM-1 interactions. The MCMV-encoded protein m20.1 induced downregulation of CD155 in infected monocytes to evade immune detection by the DNAM-1 activating receptor on NK cells [53**]. Furthermore, Quillay et al. described inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 infection in the decidua during the first trimester of pregnancy. Decidua NK cells prevented the establishment of HIV-1 infection of decidua macrophages in a cell-contact and unknown soluble factor-dependent mechanism [54*]. The intricate cross talk between macrophages and NK cells served to modulate anti-viral immune responses.
Dendritic cells (DC) are potent antigen-presenting cells that initiate the adaptive immune response. NK cells interact with DCs to reciprocally activate and influence subsequent effector functions [55]–[59]. NK cells are recruited to secondary lymphoid organs to assist in modulating the adaptive immune response [60]–[62*]. In vitro IL-2-activated human NK cells induced DC maturation and increased their ability to activate and polarize naïve CD4+ T cells. These polarized CD4+ T cells potently increased their ability to induce antigen-specific cytotoxic CD8+ T cell responses [63], [64]. Reciprocally, activated DCs increased NK cell production of IFN-γ and tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which further induced DC maturation in a cell contact-dependent manner [65], [66].
DC-NK cell interactions vary between different viral infections. In vitro and in vivo systemic HSV infection revealed that inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-α and TNF-α from DCs promote NK cell degranulation and IFN-γ production [67**], [68]. Engagement of the activating receptor, NKG2D, on NK cells and NKG2D ligands induced on DCs by IL-18 were important for NK cell activation in vaccinia infection, whereas IL-15 from DCs and NKG2D engagement on NK cells were necessary for HIV-specific priming and control of infection in CD4+ T cells [69*], [70*]. Additionally, DCs stimulated with HIV-1 Gag-virus-like particles induced robust antigen-specific NK cell proliferation, IFN-γ production, and cytotoxicity against HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells [71]. Immune responses are dampened by NK cell-mediated lysis of DCs by limiting viral load and activation of the adaptive immune response. DCs activated by different toll-like receptor ligands upregulated expression of CD155 and CD112, which bind to DNAM-1 on NK cells to induce cytolysis of immature and mature DCs [72]. GM-CSF treatment of DC upregulates CD155 and ICAM-1, which can induce NK cell-mediated lysis of DCs [73*]. NK cells lysed HSV-2 and Dengue virus-infected DCs because expression of HLA class I molecules were downregulated [74], [75*].
Certain DC-NK cell interactions favor viral persistence and immune escape. Patients with chronic hepatitis B infection have elevated DC activation, but failed to induce NK cell cytotoxicity in co-culture systems [76], [77]. In MCMV infection, IL-10 produced by DCs suppressed DC-NK cell crosstalk, which impaired MCMV-specific CD4+ T cell priming and supported viral latency [78]. Of note, HIV opsonized by complement and antibody altered DC cytokine and chemokine responses, which resulted in decreased recruitment of NK cells to the mucosa to control initial HIV infection [79**]. This may result in the poor activation of the adaptive immune response against HIV, which highlights the importance of DC-NK cell responses in controlling viral burden and anti-viral T cell responses. Table 1 lists detailed interactions between NK cells and innate cells mentioned in this review.
Table 1. Interactions of NK cells with other immune cells.
Table specifies the experimental model and the effects of the interactions
| NK cell cross talk with: | Interaction | Experimental Model | Referenc e |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils | NKp46 and Fas-mediated apoptosis of neutrophils | Human PBMC co-culture Aseptic inflammation |
44 |
| IL-22 from T, CD3+NK1.1+ T, and CD3−NK1.1+ cells mediated neutrophil recruitment into infected areas |
Mouse cytomegalovirus | 45 | |
| TLR-activated neutrophils secreted chemokines and ROS to recruit and activate NK cells IL-8, IL-1β, and IL-18 conditioning of NK cells induced DC maturation and CD4+ T cell activation |
Human PBMC co-culture TLR stimulations |
47 | |
| Macrophages/ monocytes |
M1 induced NK cells to secrete IFN-γ NKp46-, DNAM-1-, 2B4-mediated degranulation |
Human PBMC co-culture Human cytomegalovirus |
51 |
| IL-12-activated NK lyse M2 readily M1 induced NK cells to secrete IFN-γ NKp46 induced cytotoxicity 2B4-induced IFN-γ DNAM-1-induced both |
Human PBMC co-culture LPS or bacillus Calmette-Guérin |
52 | |
| DNAM-1 and CD155 control infection CCL2 and iNOS production by monocytes |
Mouse cytomegalovirus | 53 | |
| Cell contact required - unknown receptors Unknown soluble factor |
Human immunodeficiency virus |
54 | |
| Dendritic cells | IFN-α and TNF-α from DCs promoted NK cell degranulation and IFN-γ production |
Human PBMC co-culture and mouse model of herpes simplex virus |
67
68 |
| IL-18 signaling induced Rae-1 expression on DC NK cells required IL-18 and NKG2D ligation for activation |
Mouse Vaccinia | 69 | |
| DC-derived IL-15 and NKG2D ligands are necessary for NK cell activation to control HIV-infected CD4+ T cells |
Human PBMC co-culture Human immunodeficiency virus |
70 | |
| Gag-VLPs induced DC cytokines that activated NK cells to lyse HIV-infected CD4+ T cells |
Human PBMC co-culture and mouse model of human immunodeficiency virus |
71 | |
| HSV-2 viral protein ICP47 mediated downregulation of HLA-C on infected cells resulting in NK cell lysis |
Human PBMC co-culture Herpes simplex virus |
74 | |
| Infected DCs downregulated HLA class I and secreted type I IFN and TNF-α to induce NK cell lysis and IFN-γ production NK cell killing via Fas-FasL and perforin-granzyme |
Human PBMC co-culture Dengue virus |
75 | |
| TLR9-matured DCs poorly activated NK cells due to decreased IFN-α and OX40L expression |
Human PBMC co-culture from chronic hepatitis B virus patients |
76 | |
| Matured DCs poorly activated NK cells | 77 | ||
| IL-10 suppressed cross talk and NK priming of CD4+ T cells NKG2D- and NKp46 mediated cross talk |
Mouse cytomegalovirus | 78 | |
| HIV exposed-DCs secreted CCL3 and CXCL10 to recruit NK cells for effector functions |
Human PBMC co-culture Human immunodeficiency virus |
79 | |
| CD4+ T cells | NK cells lysed activated CD4+ T cells via perforin and not Fas or TNF virus |
Mouse lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus |
84 |
| CCL21 and CXCL10 from NK cells recruited T cells to peripheral lymph nodes Perforin-mediated apoptosis was necessary for DC antigen uptake |
Mouse model of influenza | 89 | |
| HSV-exposed NK cells upregulated HLA-DQ and HLA-DR to form synapses with CD4+ T cells |
Human PBMC co-culture Herpes simplex virus |
91 | |
| IL-21-activated NK cells produced macrophage inhibitory factor to induce differentiation of central memory CD4+ T cells |
Mouse study Human biopsies |
92 | |
| IL-2 from antigen-specific CD4+ T cells was necessary for NK cell activation, IFN-γ, and cytotoxicity |
Simian immunodeficiency virus | 93 | |
| KIR3DS1+ NK cells suppressed HIV-1 replication in infected HLA-F-expressing CD4+ T cell |
Human PBMC co-culture Human immunodeficiency virus |
94 |
Modulation of the Adaptive Immune Response
Besides indirectly modulating adaptive immune responses by limiting or perpetuating recruitment and cytokine production of innate immune cells, NK cells can directly control anti-viral T cell responses [80]–[82]. Study of persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection in mice revealed that viral inoculum doses dictated host NK cell responses. At medium viral doses, NK cells facilitated fatal pathology by lysing activated CD4+ T cells, thereby promoting higher viral burden, CD8+ T cell exhaustion, and subsequent death of the host. Conversely at high viral doses, NK cells prevented fatal pathology by limiting excessive CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses, allowing viral persistence, and survival of the host [83], [84*]. In these studies, NK cells altered the cytokine milieu and the polarization of T cell responses. Furthermore, chronic LCMV infection impairs the development of memory CD8+ T cells [85*]. Conversely, depletion of NK cells results in increased antigen presentation, CD4+ T cell expansion, improved CD8+ T cell responses, elevated numbers of follicular helper T cells, and antibody responses, suggesting that NK cells have dual roles in anti-viral responses [86], [87**], [88*].
A similar phenomenon is observed in influenza infection. In one study, mice infected with a sublethal dose of influenza revealed that NK cells were beneficial. IFN-γ produced by NK cells enhanced DC migration and T cell recruitment to the draining lymph node. NK cell depletion significantly diminished the generation of flu-specific T cells [89]. However, another report suggests that NK cells are detrimental to lethal doses of influenza. Depletion of NK cells resulted in reduced recruitment of innate cells, inflammatory cytokines, and lung pathology [90]. Both models of viral infections suggest that NK cells may have dual functions in modulating the adaptive system.
Emerging evidence suggests that NK-T cell interactions are more complicated than originally perceived. Human NK cells cultured with UV-inactivated HSV-1 and HSV-2 upregulated expression of HLA-DQ and HLA-DR and formed immunological synapses with autologous CD4+ T cells. This interaction induced CD4+ T cell activation and IFN-γ production [91]. In another study, IL-21 induced expansion of HLA-DR+ CD86+ NKp44− NK cells, which enhanced the development of central memory CD4+ T cells [92**]. Furthermore, CD4+ T cell depletion or IL-2 neutralization in macaque SIV-controllers decreased NK cell activation and cytokine production. Interestingly, anti-retroviral therapy in SIV-non-controllers re-established NK cell activation and cytokine production, suggesting that NK cells and CD4+ T cells cooperate to control SIV infection [93]. A recent study found that HLA-F binding to the activating receptor, KIR3DS1, induces NK cell degranulation and cytokine production. KIR3DS1+ NK cells suppressed viral replication of HIV-1-infected autologous human CD4+ T cells, which had upregulated HLA-F expression [94**].
NK cells indirectly modulate CD8+ T cell responses. MCMV infection with a strain lacking m157 expression abolishes Ly49H+ NK cell recognition and initial viral control. Mice infected with a low dose of the m157-deficient MCMV demonstrated increased viral load, early DC maturation, and elevated amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which resulted in an enhanced early CD8+ T cell response [95]. Conversely, a mouse model of hepatitis B (HBV) infection revealed a positive correlation between HBV-specific CD8+ T cells and NK cells. Depletion of NK cells resulted in diminished CD8+ T cell frequencies and adoptive transfer of HBV-exposed NK cells was sufficient to restore CD8+ T cell function [96*]. However, it is unclear whether CD4+ T cells and DCs participate in coordinating NK cell and CD8+ T cell responses in this model. In humans, a study revealed that the elderly have increased percentages of both NKG2C+ NK cells and CD8+ T cells in response to HCMV infection compared with the young [97*], suggesting that NK cells may tune the CD8+ T cell responses to complement their control of viral burden.
Concluding Remarks
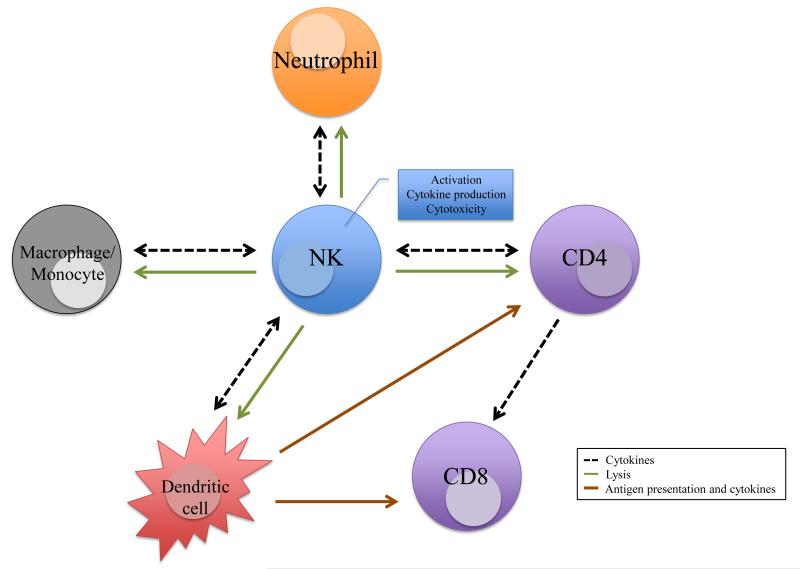
NK cells provide immune protection from different viral infections. Evidence in animal models and human studies indicate that NK cells can develop long -lasting antigen-specific memory cells. Identification of the viral antigens and the NK cell receptor(s) responsible for many of these functions remain to be determined. Although specific NK cell responses depend on viral context, they generally require other cells to coordinate effective anti-viral responses (Figure 2). NK cells interact with neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells to regulate the cytokine milieu, initial viral load, and CD4+ T cell responses. NK cells also directly limit CD4+ T cells and their effects on CD8+ T cells. Much more needs to be understood to fully grasp how NK cells respond to viral infections.
Figure 2. NK cell interactions and their effects on other immune cells.
NK cells modulate other immune cells to coordinate anti-viral immune responses. Interactions with neutrophils, macrophages, monocytes, and dendritic cells results in mutual activation or NK cell-mediated lysis to limit responses. NK cells directly or indirectly modulate CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses.
Highlights.
NK cells generate long-lived antigen-specific memory cells
NK cells regulate viral load and cytokine production of innate immune cells
NK cells indirectly modulate adaptive immune responses via innate immune cells
NK cells directly limit CD4+ T cell responses and their effects on CD8+ T cells
Acknowledgements
We thank the Lanier laboratory for helpful comments and discussions. We apologize to those whose work we were unable to discuss due to space limitations. VCL is supported by the Graduate Research Fellowship from the National Science Foundation. LLL is supported by National Institutes of Health grant AI068129 and the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy. LLL is an American Cancer Society Professor.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- [1].Biron CA, Byron KS, Sullivan JL. Severe herpesvirus infections in an adolescent without natural killer cells. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:1731–1735. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906293202605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Notarangelo LD, Mazzolari E. Natural killer cell deficiencies and severe varicella infection. J Pediatr. 2006;148:563–564. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2005.06.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Orange JS. Human natural killer cell deficiencies and susceptibility to infection. Microbes Infect Inst Pasteur. 2002;4:1545–1558. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(02)00038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Mace EM, Hsu AP, Monaco-Shawver L, Makedonas G, Rosen JB, Dropulic L, Cohen JI, Frenkel EP, Bagwell JC, Sullivan JL, et al. Mutations in GATA2 cause human NK cell deficiency with specific loss of the CD56(bright) subset. Blood. 2013;121:2669–2677. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-09-453969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Lanier LL, Phillips JH, Hackett J, Tutt M, Kumar V. Natural killer cells: definition of a cell type rather than a function. J Immunol. 1986;137:2735–2739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].O’Sullivan TE, Sun JC, Lanier LL. Natural Killer Cell Memory. Immunity. 2015;43:634–645. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.09.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Cerwenka A, Lanier LL. Natural killer cell memory in infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16:112–123. doi: 10.1038/nri.2015.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].O’Leary JG, Goodarzi M, Drayton DL, von Andrian UH. T cell- and B cell-independent adaptive immunity mediated by natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:507–516. doi: 10.1038/ni1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Paust S, Gill HS, Wang BZ, Flynn MP, Moseman EA, Senman B, Szczepanik M, Telenti A, Askenase PW, Compans RW, von Andrian UH. Critical role for the chemokine receptor CXCR6 in NK cell-mediated antigen-specific memory of haptens and viruses. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:1127–1135. doi: 10.1038/ni.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Cooper MA, Elliott JM, Keyel PA, Yang L, Carrero JA, Yokoyama WM. Cytokine-induced memory-like natural killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:1915–1919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813192106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Prlic M, Blazar BR, Farrar MA, Jameson SC. In vivo survival and homeostatic proliferation of natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 2003;197:967–976. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12]**.Nabekura T, Lanier LL. Antigen-specific expansion and differentiation of natural killer cells by alloantigen stimulation. J Exp Med. 2014;211:2455–2465. doi: 10.1084/jem.20140798. Identifies the expansion and differentiation of Ly49D+Ly49A− NK cells in response to alloantigen stimulation.
- [13].Sun JC, Beilke JN, Lanier LL. Adaptive immune features of natural killer cells. Nature. 2009;457:557–561. doi: 10.1038/nature07665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Hendricks DW, Min-Oo G, Lanier LL. Sweet Is the Memory of Past Troubles: NK Cells Remember. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;395:147–171. doi: 10.1007/82_2015_447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Arase H, Mocarski ES, Campbell AE, Hill AB, Lanier LL. Direct recognition of cytomegalovirus by activating and inhibitory NK cell receptors. Science. 2002;296:1323–1326. doi: 10.1126/science.1070884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Daniels KA, Devora G, Lai WC, O’Donnell CL, Bennett M, Welsh RM. Murine cytomegalovirus is regulated by a discrete subset of natural killer cells reactive with monoclonal antibody to Ly49H. J Exp Med. 2001;194:29–44. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Smith HRC, Heusel JW, Mehta IK, Kim S, Dorner BG, Naidenko OV, Iizuka K, Furukawa H, Beckman DL, Pingel JT, et al. Recognition of a virus-encoded ligand by a natural killer cell activation receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:8826–8831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.092258599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18]**.Min-Oo G, Lanier LL. Cytomegalovirus generates long-lived antigen-specific NK cells with diminished bystander activation to heterologous infection. J Exp Med. 2014;211:2669–2680. doi: 10.1084/jem.20141172. Demonstrates the antigen specificity of MCMV-induced Ly49H+ memory NK cells.
- [19]**.Forbes CA, Scalzo AA, Degli-Esposti MA, Coudert JD. Ly49C-dependent control of MCMV Infection by NK cells is cis-regulated by MHC Class I molecules. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10:e1004161. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004161. With Ref. [20**] demonstrates that Ly49C restricts NK cell control of MCMV.
- [20]**.Forbes CA, Scalzo AA, Degli-Esposti MA, Coudert JD. Ly49C Impairs NK Cell Memory in Mouse Cytomegalovirus Infection. J Immunol. 2016;197:128–140. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600199. With Ref. [19**] demonstrates that Ly49C restricts NK cell control of MCMV.
- [21]**.Rahim MMA, Wight A, Mahmoud AB, Aguilar OA, Lee SH, Vidal SM, Carlyle JR, Makrigiannis AP. Expansion and Protection by a Virus-Specific NK Cell Subset Lacking Expression of the Inhibitory NKR-P1B Receptor during Murine Cytomegalovirus Infection. J Immunol. 2016;197:2325–2337. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600776. Demonstrates that co-expression of NKR-P1B on Ly49H+ NK cells restrict MCMV control.
- [22].Abdul-Careem MF, Lee AJ, Pek EA, Gill N, Gillgrass AE, Chew MV, Reid S, Ashkar AA. Genital HSV-2 infection induces short-term NK cell memory. PloS One. 2012;7:e32821. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Gillard GO, Bivas-Benita M, Hovav AH, Grandpre LE, Panas MW, Seaman MS, Haynes BF, Letvin NK. Thy1+ NK cells from vaccinia virus-primed mice confer protection against vaccinia virus challenge in the absence of adaptive lymphocytes. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002141. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].van Helden MJG, Zaiss DMW, Sijts AJAM. CCR2 defines a distinct population of NK cells and mediates their migration during influenza virus infection in mice. PloS One. 2012;7:e52027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25]*.Reeves RK, Li H, Jost S, Blass E, Li H, Schafer JL, Varner V, Manickam C, Eslamizar L, Altfeld M, et al. Antigen-specific NK cell memory in rhesus macaques. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:927–932. doi: 10.1038/ni.3227. Demonstrates the persistence of SIV-specific memory NK cells from vaccination and viral infection.
- [26].Giavedoni LD, Velasquillo MC, Parodi LM, Hubbard GB, Hodara VL. Cytokine expression, natural killer cell activation, and phenotypic changes in lymphoid cells from rhesus macaques during acute infection with pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 2000;74:1648–1657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.4.1648-1657.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Gumá M, Angulo A, Vilches C, Gómez-Lozano N, Malats N, López-Botet M. Imprint of human cytomegalovirus infection on the NK cell receptor repertoire. Blood. 2004;104:3664–3671. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-05-2058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Gumá M, Budt M, Sáez A, Brckalo T, Hengel H, Angulo A, López-Botet M. Expansion of CD94/NKG2C+ NK cells in response to human cytomegalovirus-infected fibroblasts. Blood. 2006;107:3624–3631. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-09-3682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Lopez-Vergès S, Milush JM, Schwartz BS, Pando MJ, Jarjoura J, York VA, Houchins JP, Miller S, Kang SM, Norris PJ, et al. Expansion of a unique CD57+NKG2Chi natural killer cell subset during acute human cytomegalovirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:14725–14732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1110900108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Petitdemange C, Becquart P, Wauquier N, Béziat V, Debré P, Leroy EM, Vieillard V. Unconventional repertoire profile is imprinted during acute chikungunya infection for natural killer cells polarization toward cytotoxicity. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002268. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Béziat V, Dalgard O, Asselah T, Halfon P, Bedossa P, Boudifa A, Hervier B, Theodorou I, Martinot M, Debré P, et al. CMV drives clonal expansion of NKG2C+ NK cells expressing self-specific KIRs in chronic hepatitis patients. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42:447–457. doi: 10.1002/eji.201141826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Saghafian-Hedengren S, Sohlberg E, Theorell J, Carvalho-Queiroz C, Nagy N, Persson JO, Nilsson C, Bryceson YT, Sverremark-Ekström E. Epstein-Barr virus coinfection in children boosts cytomegalovirus-induced differentiation of natural killer cells. J Virol. 2013;87:13446–13455. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02382-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Björkström NK, Lindgren T, Stoltz M, Fauriat C, Braun M, Evander M, Michaëlsson J, Malmberg KJ, Klingström J, Ahlm C, Ljunggren HG. Rapid expansion and long-term persistence of elevated NK cell numbers in humans infected with hantavirus. J Exp Med. 2011;208:13–21. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Björkström NK, Svensson A, Malmberg KJ, Eriksson K, Ljunggren HG. Characterization of natural killer cell phenotype and function during recurrent human HSV-2 infection. PloS One. 2011;6:e27664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35]**.Hendricks DW, Balfour HH, Dunmire SK, Schmeling DO, Hogquist KA, Lanier LL. Cutting edge: NKG2C(hi)CD57+ NK cells respond specifically to acute infection with cytomegalovirus and not Epstein-Barr virus. J Immunol. 2014;192:4492–4496. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303211. Demonstrates the specificity of HCMV-induced NKG2C+ memory NK cells.
- [36]*.Djaoud Z, Riou R, Gavlovsky PJ, Mehlal S, Bressollette C, Gérard N, Gagne K, Charreau B, Retière C. Cytomegalovirus-Infected Primary Endothelial Cells Trigger NKG2C+ Natural Killer Cells. J Innate Immun. 2016;8:374–385. doi: 10.1159/000445320. Demonstrates that degranulation of NKG2C+ NK cells is triggered by co-culture with HCMV-infected primary human endothelial cells.
- [37].Rölle A, Pollmann J, Ewen EM, Le VTK, Halenius A, Hengel H, Cerwenka A. IL-12-producing monocytes and HLA-E control HCMV-driven NKG2C+ NK cell expansion. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:5305–5316. doi: 10.1172/JCI77440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [38]**.Liu LL, Landskron J, Ask EH, Enqvist M, Sohlberg E, Traherne JA, Hammer Q, J. Goodridge JP, Larsson S, Jayaraman J, et al. Critical Role of CD2 Co-stimulation in Adaptive Natural Killer Cell Responses Revealed in NKG2C-Deficient Humans. Cell Rep. 2016;15:1088–1099. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.04.005. With Ref. [39**] identifies synergy of CD2- and CD16-mediated NK cell activation in HCMV infection.
- [39]**.Rölle A, Halenius A, Ewen EM, Cerwenka A, Hengel H, Momburg F. CD2-CD58 interactions are pivotal for the activation and function of adaptive natural killer cells in human cytomegalovirus infection. Eur J Immunol. 2016 doi: 10.1002/eji.201646492. With Ref. [38**] identifies synergy of CD2- and CD16-mediated NK cell activation in HCMV infection.
- [40].Rölle A, Brodin P. Immune Adaptation to Environmental Influence: The Case of NK Cells and HCMV. Trends Immunol. 2016;37:233–243. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [41].Mócsai A. Diverse novel functions of neutrophils in immunity, inflammation, and beyond. J Exp Med. 2013;210:1283–1299. doi: 10.1084/jem.20122220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [42].Scapini P, Cassatella MA. Social networking of human neutrophils within the immune system. Blood. 2014;124:710–719. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-453217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [43].Costantini C, Micheletti A, Calzetti F, Perbellini O, Pizzolo G, Cassatella MA. Neutrophil activation and survival are modulated by interaction with NK cells. Int Immunol. 2010;22:827–838. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxq434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [44].Thorén FB, Riise RE, Ousbäck J, Della Chiesa M, Alsterholm M, Marcenaro E, Pesce S, Prato C, Cantoni C, Bylund J, et al. Human NK Cells induce neutrophil apoptosis via an NKp46- and Fas-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 2012;188:1668–1674. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [45].Stacey MA, Marsden M, Pham NTA, Clare S, Dolton G, Stack G, Jones E, Klenerman P, Gallimore AM, Taylor PR, et al. Neutrophils recruited by IL-22 in peripheral tissues function as TRAIL-dependent antiviral effectors against MCMV. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15:471–483. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [46].Jaeger BN, Donadieu J, Cognet C, Bernat C, Ordoñez-Rueda D, Barlogis V, Mahlaoui N, Fenis A, Narni-Mancinelli E, Beaupain B, et al. Neutrophil depletion impairs natural killer cell maturation, function, and homeostasis. J Exp Med. 2012;209:565–580. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [47]**.Riise RE, Bernson E, Aurelius J, Martner A, Pesce S, Della Chiesa M, Marcenaro E, Bylund J, Hellstrand K, Moretta L, et al. TLR-Stimulated Neutrophils Instruct NK Cells To Trigger Dendritic Cell Maturation and Promote Adaptive T Cell Responses. J Immunol. 2015;195:1121–1128. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500709. Illustrates the interaction between neutrophils and NK cells in coordinating an immune response.
- [48]*.Pliyev BK, Kalintseva MV, Abdulaeva SV, Yarygin KN, Savchenko VG. Neutrophil microparticles modulate cytokine production by natural killer cells. Cytokine. 2014;65:126–129. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.11.010. Demonstrates the effects of neutrophil microparticles on NK cells to produce anti-inflammatory cytokines.
- [49]*.Amano K, Hirayama M, Azuma E, Iwamoto S, Keida Y, Komada Y. Neutrophils induced licensing of natural killer cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2015 doi: 10.1155/2015/747680. Demonstrates the promotion of NK cell licensing by neutrophils.
- [50].Michel T, Hentges F, Zimmer J. Consequences of the crosstalk between monocytes/macrophages and natural killer cells. Front Immunol. 2012 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [51].Romo N, Magri G, Muntasell A, Heredia G, Baía D, Angulo A, Guma M, López-Botet M. Natural killer cell-mediated response to human cytomegalovirus-infected macrophages is modulated by their functional polarization. J Leukoc Biol. 2011;90:717–726. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0311171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [52].Bellora F, Castriconi R, Dondero A, Reggiardo G, Moretta L, Mantovani A, Moretta A, Bottino C. The interaction of human natural killer cells with either unpolarized or polarized macrophages results in different functional outcomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:21659–21664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007654108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [53]**.Lenac Rovis T, Kucan Brlic P, Kaynan N, Juranic Lisnic V, Brizic I, Jordan S, Tomic A, Kvestak D, Babic M, Tsukerman P, et al. Inflammatory monocytes and NK cells play a crucial role in DNAM-1-dependent control of cytomegalovirus infection. J Exp Med. 2016;213:1835–1850. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151899. Identifies DNAM-1 as a critical component of monocyte and NK cell interactions during MCMV infection.
- [54]*.Quillay H, El Costa H, Duriez M, Marlin R, Cannou C, Madec Y, de Truchis C, Rahmati M, Barré-Sinoussi F, Nugeyre MT, Menu E. NK cells control HIV-1 infection of macrophages through soluble factors and cellular contacts in the human decidua. Retrovirology. 2016 doi: 10.1186/s12977-016-0271-z. Demonstrates control of HIV-1 in decidual macrophages by NK cells.
- [55].Ferlazzo G, Pack M, Thomas D, Paludan C, Schmid D, Strowig T, Bougras G, Muller WA, Moretta L, Münz C. Distinct roles of IL-12 and IL-15 in human natural killer cell activation by dendritic cells from secondary lymphoid organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:16606–16611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407522101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [56].Vitale M, Della Chiesa M, Carlomagno S, Romagnani C, Thiel A, Moretta L, Moretta A. The small subset of CD56brightCD16- natural killer cells is selectively responsible for both cell proliferation and interferon-gamma production upon interaction with dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:1715–1722. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [57].Vitale M, Della Chiesa M, Carlomagno S, Pende D, Aricò M, Moretta L, Moretta A. NK-dependent DC maturation is mediated by TNFalpha and IFNgamma released upon engagement of the NKp30 triggering receptor. Blood. 2005;106:566–571. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-4035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [58].Mortier E, Woo T, Advincula R, Gozalo A, Ma A. IL-15Ralpha chaperones IL-15 to stable dendritic cell membrane complexes that activate NK cells via trans presentation. J Exp Med. 2008;205:1213–1225. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [59].Moretta A. Natural killer cells and dendritic cells: rendezvous in abused tissues. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:957–964. doi: 10.1038/nri956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [60].Fehniger TA, Cooper MA, Nuovo GJ, Cella M, Facchetti F, Colonna M, Caligiuri MA. CD56bright natural killer cells are present in human lymph nodes and are activated by T cell-derived IL-2: a potential new link between adaptive and innate immunity. Blood. 2003;101:3052–3057. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-09-2876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [61].Martín-Fontecha A, Thomsen LL, Brett S, Gerard C, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F. Induced recruitment of NK cells to lymph nodes provides IFN-gamma for T(H)1 priming. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:1260–1265. doi: 10.1038/ni1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [62]*.Lawler C, Tan CSE, Simas JP, Stevenson PG. Type 1 interferons and NK cells restrict gamma-herpesvirus lymph node infection. J Virol. 2016 doi: 10.1128/JVI.01108-16. Illustrates the importance of NK cell recruitment to the lymph node during viral infection.
- [63].Mailliard RB, Son YI, Redlinger R, Coates PT, Giermasz A, Morel PA, Storkus WJ, Kalinski P. Dendritic cells mediate NK cell help for Th1 and CTL responses: two-signal requirement for the induction of NK cell helper function. J Immunol. 2003;171:2366–2373. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.5.2366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [64].Morandi B, Bougras G, Muller WA, Ferlazzo G, Münz C. NK cells of human secondary lymphoid tissues enhance T cell polarization via IFN-gamma secretion. Eur J Immunol. 2006;36:2394–2400. doi: 10.1002/eji.200636290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [65].Gerosa F, Baldani-Guerra B, Nisii C, Marchesini V, Carra G, Trinchieri G. Reciprocal activating interaction between natural killer cells and dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 2002;195:327–333. doi: 10.1084/jem.20010938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [66].Goldszmid RS, Caspar P, Rivollier A, White S, Dzutsev A, Hieny S, Kelsall B, Trinchieri G, Sher A. NK cell-derived interferon-γ orchestrates cellular dynamics and the differentiation of monocytes into dendritic cells at the site of infection. Immunity. 2012;36:1047–1059. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [67]**.Vogel K, Thomann S, Vogel B, Schuster P, Schmidt B. Both plasmacytoid dendritic cells and monocytes stimulate natural killer cells early during human herpes simplex virus type 1 infections. Immunology. 2014;143:588–600. doi: 10.1111/imm.12337. With Ref. [68] demonstrates NK cell activation by herpes simplex virus-exposed dendritic cells.
- [68].Swiecki M, Wang Y, Gilfillan S, Colonna M. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells contribute to systemic but not local antiviral responses to HSV infections. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003728. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [69]*.Brandstadter JD, Huang X, Yang Y. NK cell-extrinsic IL-18 signaling is required for efficient NK-cell activation by vaccinia virus. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44:2659–2666. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344134. Demonstrates IL-18 signaling and NKG2D engagement from dendritic cells are required for NK cell-mediated control of vaccinia virus.
- [70]*.Moreno-Nieves UY, Didier C, Lévy Y, Barré-Sinoussi F, Scott-Algara D, ANRS HIV Vaccine Network (AHVN) NK cells are primed by ANRS MVA(HIV)-infected DCs, via a mechanism involving NKG2D and membrane-bound IL-15, to control HIV-1 infection in CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44:2370–2379. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344149. Demonstrates activation of NK cells with HIV-1-infected dendritic cells requires IL-15 signaling and NKG2D engagement.
- [71].Chang MO, Suzuki T, Suzuki H, Takaku H. HIV-1 Gag-virus-like particles induce natural killer cell immune responses via activation and maturation of dendritic cells. J Innate Immun. 2012;4:187–200. doi: 10.1159/000329226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [72].Pende D, Castriconi R, Romagnani P, Spaggiari GM, Marcenaro S, Dondero A, Lazzeri E, Lasagni L, Martini S, River P, et al. Expression of the DNAM-1 ligands, Nectin-2 (CD112) and poliovirus receptor (CD155), on dendritic cells: relevance for natural killer-dendritic cell interaction. Blood. 2006;107:2030–2036. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-07-2696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [73]*.Smith LE, Olszewski MA, Georgoudaki AM, Wagner AK, Hägglöf T, Karlsson MCI, Dominguez-Villar M, Garcia-Cozar F, Mueller S, Ravens I, et al. Sensitivity of dendritic cells to NK-mediated lysis depends on the inflammatory environment and is modulated by CD54/CD226-driven interactions. J Leukoc Biol. 2016 doi: 10.1189/jlb.3A0615-271RR. Demonstrates lysis of GM-CSF activated dendritic cells by NK cells is mediated by DNAM-1 and LFA-1.
- [74].Elboim M, Grodzovski I, Djian E, Wolf DG, Mandelboim O. HSV-2 specifically down regulates HLA-C expression to render HSV-2-infected DCs susceptible to NK cell killing. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003226. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [75]*.Lim DSL, Yawata N, Selva KJ, Li N, Tsai CY, Yeong LH, Liong KH, Ooi EE, Chong NK, Ng ML, et al. The combination of type I IFN, TNF-α, and cell surface receptor engagement with dendritic cells enables NK cells to overcome immune evasion by dengue virus. J Immunol. 2014;193:5065–5075. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302240. Demonstrates cytokine- and contact-dependent interactions between dendritic cells and NK cells in response to Dengue virus infection.
- [76].Martinet J, Dufeu-Duchesne T, Bruder Costa J, Larrat S, Marlu A, Leroy V, Plumas J, Aspord C. Altered functions of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and reduced cytolytic activity of natural killer cells in patients with chronic HBV infection. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:1586–1596. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.08.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [77].Tjwa ETTL, van Oord GW, Biesta PJ, Boonstra A, Janssen HLA, Woltman AM. Restoration of TLR3-activated myeloid dendritic cell activity leads to improved natural killer cell function in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol. 2012;86:4102–4109. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07000-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [78].Mandaric S, Walton SM, Rülicke T, Richter K, Girard-Madoux MJH, Clausen BE, Zurunic A, Kamanaka M, Flavell RA, Jonjic S, Oxenius A. IL-10 suppression of NK/DC crosstalk leads to poor priming of MCMV-specific CD4 T cells and prolonged MCMV persistence. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:e1002846. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [79]**.Ellegård R, Crisci E, Andersson J, Shankar EM, Nyström S, Hinkula J, Larsson M. Impaired NK Cell Activation and Chemotaxis toward Dendritic Cells Exposed to Complement-Opsonized HIV-1. J Immunol. 2015;195:1698–1704. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500618. Illustrates impaired NK cell recruitment by dendritic cells exposed to complement-opsonized HIV-1 virus.
- [80].Su HC, Nguyen KB, Salazar-Mather TP, Ruzek MC, Dalod MY, Biron CA. NK cell functions restrain T cell responses during viral infections. Eur J Immunol. 2001;31:3048–3055. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(2001010)31:10<3048::aid-immu3048>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [81].Krebs P, Barnes MJ, Lampe K, Whitley K, Bahjat KS, Beutler B, Janssen E, Hoebe K. NK-cell-mediated killing of target cells triggers robust antigen-specific T-cell-mediated and humoral responses. Blood. 2009;113:6593–6602. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-01-201467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [82].Cook KD, Waggoner SN, Whitmire JK. NK cells and their ability to modulate T cells during virus infections. Crit Rev Immunol. 2014;34:359–388. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2014010604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [83].Waggoner SN, Cornberg M, Selin LK, Welsh RM. Natural killer cells act as rheostats modulating antiviral T cells. Nature. 2012;481:394–398. doi: 10.1038/nature10624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [84]*.Waggoner SN, Daniels KA, Welsh RM. Therapeutic depletion of natural killer cells controls persistent infection. J Virol. 2014;88:1953–1960. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03002-13. With Ref. [83, 86, and 87**] demonstrates dual functions of NK cells in controlling T cell responses in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection.
- [85]**.Stelekati E, Shin H, Doering TA, Dolfi DV, Ziegler CG, Beiting DP, Dawson L, Liboon J, Wolski D, Ali MAA, et al. Bystander chronic infection negatively impacts development of CD8(+) T cell memory. Immunity. 2014;40:801–813. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.010. Demonstrates the impairment of memory CD8+ T cell generation due to chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection.
- [86].Cook KD, Whitmire JK. The depletion of NK cells prevents T cell exhaustion to efficiently control disseminating virus infection. J Immunol. 2013;190:641–649. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [87]**.Cook KD, Kline HC, Whitmire JK. NK cells inhibit humoral immunity by reducing the abundance of CD4+ T follicular helper cells during a chronic virus infection. J Leukoc Biol. 2015;98:153–162. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4HI1214-594R. With Ref. [83, 84*, and 86] demonstrates dual functions of NK cells in controlling T cell responses in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection.
- [88]*.Crouse J, Bedenikovic G, Wiesel M, Ibberson M, Xenarios I, Von Laer D, Kalinke U, Vivier E, Jonjic S, Oxenius A. Type I interferons protect T cells against NK cell attack mediated by the activating receptor NCR1. Immunity. 2014;40:961–973. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.05.003. Demonstrates interferon sensing by CD4+ T cells protects against NK cells-mediated lysis.
- [89].Ge MQ, Ho AWS, Tang Y, Wong KHS, Chua BYL, Gasser S, Kemeny DM. NK cells regulate CD8+ T cell priming and dendritic cell migration during influenza A infection by IFN-γ and perforin-dependent mechanisms. J Immunol. 2012;189:2099–2109. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [90].Abdul-Careem MF, Mian MF, Yue G, Gillgrass A, Chenoweth MJ, Barra NG, Chew MV, Chan T, Al-Garawi AA, Jordana M, Ashkar AA. Critical role of natural killer cells in lung immunopathology during influenza infection in mice. J Infect Dis. 2012;206:167–177. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [91].Kim M, Osborne NR, Zeng W, Donaghy H, McKinnon K, Jackson DC, Cunningham AL. Herpes simplex virus antigens directly activate NK cells via TLR2, thus facilitating their presentation to CD4 T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2012;188:4158–4170. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [92]**.Loyon R, Picard E, Mauvais O, Queiroz L, Mougey V, Pallandre JR, Galaine J, Mercier-Letondal P, Kellerman G, Chaput N, et al. IL-21-Induced MHC Class II+ NK Cells Promote the Expansion of Human Uncommitted CD4+ Central Memory T Cells in a Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor-Dependent Manner. J Immunol. 2016;197:85–96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501147. Demonstrates that IL-21 induces a subset of NK cells to modulate the development of central memory CD4+ T cells.
- [93].Vargas-Inchaustegui DA, Xiao P, Tuero I, Patterson LJ, Robert-Guroff M. NK and CD4+ T cell cooperative immune responses correlate with control of disease in a macaque simian immunodeficiency virus infection model. J Immunol. 2012;189:1878–1885. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [94]**.Garcia-Beltran WF, Hölzemer A, Martrus G, Chung AW, Pacheco Y, Simoneau CR, Rucevic M, Lamothe-Molina PA, Pertel T, Kim TE, et al. Open conformers of HLA-F are high-affinity ligands of the activating NK-cell receptor KIR3DS1. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:1067–1074. doi: 10.1038/ni.3513. Demonstrates that KIR3DS1 binds to HLA-F on HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells to induce NK cell effector functions.
- [95].Mitrović M, Arapović J, Jordan S, Fodil-Cornu N, Ebert S, Vidal SM, Krmpotić A, Reddehase MJ, Jonjić S. The NK cell response to mouse cytomegalovirus infection affects the level and kinetics of the early CD8(+) T-cell response. J Virol. 2012;86:2165–2175. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06042-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [96]*.Zheng M, Sun R, Wei H, Tian Z. NK Cells Help Induce Anti-Hepatitis B Virus CD8+ T Cell Immunity in Mice. J Immunol. 2016;196:4122–4131. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500846. Describes a mouse model of hepatitis B infection where there is a positive correlation between HBV-specific CD8+ T cells and NK cells.
- [97]*.Bayard C, Lepetitcorps H, Roux A, Larsen M, Fastenackels A, Salle V, Vieillard V, Marchant A, Stern M, Boddaert J, et al. Coordinated expansion of both memory T cells and NK cells in response to CMV infection in humans. Eur J Immunol. 2016;46:1168–1179. doi: 10.1002/eji.201546179. Describes a human study where age positively correlates with increased percentages of NKG2C+ NK cells and CD8+ T cells.