Abstract
Brunner’s gland hamartoma (BGH) is an extremely rare benign digestive tumor, generally located in the duodenal bulb. We report the case of a 51-year-old asymptomatic man with a large pedunculated BGH arising from the pylorus. It was successfully removed en bloc by endoscopic resection.
Keywords: Brunner Glands, Hamartoma, Pylorus
INTRODUCTION
Brunner’s glands were first described by Brunner in 1688. They are branched acino-tubular glands located in the submucosa and lined with cuboidal-to-columnar clear cells in the glands and cuboidal cells in the duct.1 These glands are most commonly located in the duodenum, although they may be found infrequently in the pylorus.2
Brunner’s gland hamartoma (BGH) is a rare tumor that was first described by Salvioli in 1876.2 BGH represents 5-10% of small bowel tumors and occurs most commonly in the fifth and sixth decade of life, with no gender or race predominance. Most of the lesions are small, asymptomatic and detected incidentally. Clinical symptoms are caused by obstruction, leading to postprandial pain and bleeding.3 Other, less common presentations of BGH include recurrent acute pancreatitis and duodenal intussusception.3 The distribution of BGH is duodenal bulb (57%), the second (27%) and third (5%) portions of the duodenum, the pyloric channel (5%), jejunum (2%), and proximal ileum (2%).4 They are mostly pedunculated, and generally sized from 1 to 9 cm in diameter, although Brunner’s gland polyps greater than 2 cm are exceedingly rare.1,3
Brunner’s gland hamartoma can be treated either by endoscopic or surgical excision.1,2 We report a case of successful endoscopic removal of a BGH arising from the pylorus.
CASE REPORT
A 51-year-old man underwent upper endoscopy and colonoscopy as a part of a routine health survey. He was asymptomatic, and his medical history and physical examination were unremarkable. Routine blood tests including a complete blood cell count and chemistry studies had normal results. Some diverticula and a small adenoma (2 mm) were found in his colonoscopy. Gastroduodenoscopy demonstrated a 15 × 14 × 8 mm pendunculated polyp covered with normal mucosa and originating from the pylorus (Figure 1A and B). The tumor was resected by diathermic polypectomy without complications. The urease test was negative.
Figure 1. – A - Endoscopic view of the pyloric polyp with white light; B - Pyloric Brunner’s gland hamartoma; virtual chromoendoscopy (i-scan).
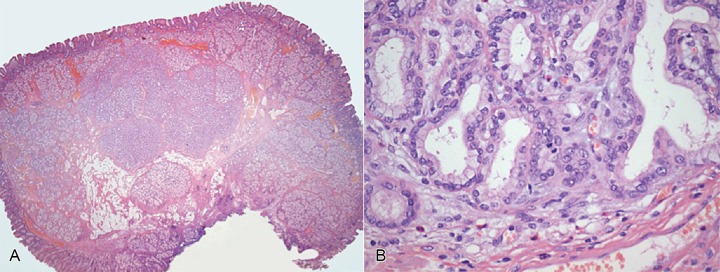
Histological sections showed diffuse hyperplasia of Brunner’s glands in lobular aggregates, interspersed with fibrous bundles and foci of adipose tissue. The lesion was lined with flattened duodenal mucosa with foci of pyloric metaplasia, findings consistent with a diagnosis of hamartoma. A central area (Figure 2A) showed the substitution of Brunner’s glands by a lobulated nodular growth of tubular glands with reduced cytoplasmatic mucin, mild nuclear and architectural atypia, rare mitotic figures and a slightly reactive desmoplastic stroma (Figure 2B). These findings were interpreted as an atypical hyperplasia, as defined by Sakurai et al.,5 since Ki67 staining was only mildly elevated (less than 5%) and unequivocal features of malignancy were not seen. Resection margins were clear.
Figure 2. – Photomicrography of the Brunner’s gland hamartoma: A - central nodular area of atypical lobular growth (H&E, 12.5x); B - atypical hyperplasia. Packed tubular glands with mild nuclear atypia, mitotic figures (in the center) and slight stromal desmoplasia (H&E, 400x).
DISCUSSION
The exact prevalence of BGH is difficult to determine because of the variation in nomenclature throughout the medical literature. The most common localization is the duodenum.6 Only 5% of these lesions arise from the pyloric channel.4 Although commonly an incidental finding, BGH has been associated with pain, obstruction, hemorrhage and intussusception.6
Accurate diagnosis of BGH can be demanding, a combination of upper endoscopy or barium contrast studies of the small bowel can be helpful.7 However, since these are submucosal lesions, endoscopic biopsies may be nondiagnostic and, on the other hand, endoscopic ultrasound can be very useful.2,7 Finally, the precise diagnosis is only made on histopathologic evaluation of the resection specimen.8
The distinction between Brunner’s gland hyperplasia and Brunner’s gland hamartomas is arbitrary. Brunner’s gland hyperplasia is considered if the lesion is <5 mm in size, either solitary or multiple, and BGH is named if it is >5 mm and unique.1 Brunner’s gland hyperplasia is commonly encountered in association with peptic duodenitis. Endoscopically, it presents as a nodular duodenitis. This nodularity should be distinguished from genuine single polyps, referred to as Brunner’s gland hamartoma or adenoma.9,10 In view of the nomenclature generally used for the gastrointestinal tract, the term “adenoma” is considered a misnomer because the lesion is not neoplastic,9 the histologic architecture of these lesions consists of a combination of ductal and acinar structures with fibromuscular and adipose elements.4 Therefore, the best term for these uncommon lesions is really hamartoma, even though the etiology is basically unknown.9 Nevertheless, many factors were proposed for its pathogenesis, such as local irritation, parasympathetic activity, chronic pancreatitis, Helicobacter pylori infection and Billtoth II reconstruction. Other differential diagnosis includes leiomyomas, adenomas, lipomas, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, adenocarcinomas, carcinoids, lymphomas, leiomyosarcomas, pancreatic or ampullary neoplasm.1
Asymptomatic small BGH usually requires no therapy. Although, treatment is suggested for larger tumors, even if asymptomatic, to prevent development of complications such as bleeding or obstruction.1 Surgery has been the traditional method of treatment of these lesions.2 However, endoscopic excision can be a less invasive alternative.3 Recurrence after endoscopic or surgical excision has not been reported.1 The present case showed a BGH with atypical histology in an unusual localization that was treated with endoscopic polypectomy.
Footnotes
Lenz L, Felipe-Silva A, Nakao F, et al. Pyloric Brunner’s gland hamartoma with atypical hyperplasia. Autopsy Case Rep [Internet]. 2013; 3(4): 49-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.4322/acr.2013.039
REFERENCES
- 1.Jung Y, Chung IK, Lee TH, et al. Successful endoscopic resection of large pedunculated Brunner’s gland hamartoma causing gastrointestinal bleeding arising from the pylorus. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2013;7:304-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000354138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Block KP, Frick TJ, Warner TF. Gastrointestinal bleeding from a Brunner’s gland hamartoma: characterization by endoscopy, computed tomography, and endoscopic ultrasound. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:1581-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.02124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shemesh E, Ben Horin S, Barshack I, Bar-Meir S. Brunner’s gland hamartoma presenting as a large duodenal polyp. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000;52:435-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mge.2000.108291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bayan K, Tuzun Y, Yilmaz S, Yilmaz G, Bilici A. Pyloric giant Brunner’s gland hamartoma as a cause of both duodenojejunal intussusception and obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2009;20:52-6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sakurai T, Sakashita H, Honjo G, Kasyu I, Manabe T. Gastric foveolar metaplasia with dysplastic changes in Brunner gland hyperplasia: possible precursor lesions for Brunner gland adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:1442-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.pas.0000180449.15827.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Patel ND, Levy AD, Mehrotra AK, Sobin LH. Brunner’s gland hyperplasia and hamartoma: imaging features with clinicopathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187:715-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.2214/AJR.05.0564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mumtaz R, Shah IA, Ramirez FC. Brunner’s gland hamartoma simulating a pancreatic mass with duodenal obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:932-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0016-5107(02)70380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Melzer E. Giant Brunner’s gland hamartoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:314-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mge.2003.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shepherd N, Warren B, Wiliiams G. Morson and Dawson’s gastrointestinal pathology. 5th ed. West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kyungeun K, Jang S, Song H. Clinicopathologic characteristics and mucin expression in brunner’s gland proliferating lesions. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:194-201. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]