Abstract
Background:
Neonatal pain management guidelines have been released; however, there is insufficient systematic institutional support for the adoption of evidence-based pain management in Japan.
Purpose:
To evaluate the impact of a collaborative quality improvement program on the implementation of pain management improvements in Japanese neonatal intensive care units (NICUs).
Methods:
Seven Japanese level III NICUs participated in a neonatal pain management quality improvement program based on an Institute for Healthcare Improvement collaborative model. The NICUs developed evidence-based practice points for pain management and implemented these over a 12-month period. Changes were introduced through a series of Plan-Do-Study-Act cycles, and throughout the process, pain management quality indicators were tracked as performance measures. Jonckheere's trend test and the Cochran-Armitage test for trend were used to examine the changes in quality indicator implementations over time (baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months).
Findings:
Baseline pain management data from the 7 sites revealed substantial opportunities for improvement of pain management, and testing changes in the NICU setting resulted in measurable improvements in pain management. During the intervention phase, all participating sites introduced new pain assessment tools, and all sites developed electronic medical record forms to capture pain score, interventions, and infant responses to interventions.
Implications for Practice:
The use of collaborative quality improvement techniques played a key role in improving pain management in the NICUs.
Implications for Research:
Collaborative improvement programs provide an attractive strategy for solving evidence-practice gaps in the NICU setting.
Keywords: collaborative quality improvement, evidence-based practice, neonatal intensive care unit, neonate, pain management, quality improvement, quality indicators
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVE
In recent years, many governmental agencies, medical associations, universities, and other institutions have released evidence-based neonatal pain management guidelines1–3 as initiatives to standardize pain management care. The Japanese Guideline for Pain Prevention and Management4 was released in December 2014. This was expected to accelerate improvements in the care of pain in Japanese neonatal intensive care units (NICUs).
The release of a guideline does not ensure that it will be adopted into practice. A qualitative study of medical professionals in NICUs in Canada indicated that organizational factors, including hierarchical communication within the organization and restricted job-related discretionary authority, acted as obstacles to the adoption of evidence-based care.5 A study conducted in the United States reported that the degree of cooperation between physicians and nurses was significantly correlated with the practice of evidence-based pain management.6 In Japan, a 2012 survey7 of neonatal pain management in NICUs throughout the country showed that practice of evidence-based pain management was limited by obstacles at organizational and at staff levels, including the lack of educational materials and training opportunities, and the lack of formalized cooperation between medical professionals and family members.
In recent years, quality indicators (QIs) have been introduced to reduce the “evidence-practice gap” between ideal care and actual care. The use of QIs to monitor the progress of improvement efforts has been shown to be an effective method for improving the quality of practice. Previous quality studies have reported the use of QIs for pain assessment and pain relief by both local8,9 and collaborative groups.10,11
The Vermont Oxford Network, an international quality improvement collaborative dedicated to improving neonatal intensive care, introduced Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles to implement “potential better practices” that it had identified.12 Twelve facilities participated in the Vermont Oxford Network project to improve the quality of pain management.10,11 Among the reported interventions, a pain management form was added to the electronic medical record system to increase the frequency of pain assessment as the “fifth vital sign”; increased documentation of the use of opioids was also reported. A similar collaborative quality improvement project for the breastfeeding of extremely low birth-weight infants at 11 facilities reported increases in the breastfeeding rate and decreases in the prevalence of necrotizing enterocolitis.13
Thus, there is evidence that the use of collaborative quality improvement methods and PDSA cycles can accelerate the uptake of evidence-based pain management provided to newborns in NICUs. Therefore, in the present study, we conducted a trial pain management quality improvement collaborative program incorporating the use of PDSA cycles. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of the collaborative improvement program on the implementation of pain management improvements in NICUs in Japan.
METHODS
This study was a prospective pre-/postintervention study to improve neonatal pain management for invasive bedside procedures in Japan and was conducted from September 2014 to January 2016.
Participating Sites and Local Leaders
Seven sites were recruited for this project. In September 2014, an invitation to participate was sent to the neonatal physician chiefs and nursing managers at 100 level III perinatal medical centers with NICUs in addition to special care baby units throughout Japan. We selected the participating sites on the basis of the following criteria to cover various background hospitals: (1) organization of hospital management, (2) location, and (3) local ethics review committee approval before December 31, 2014. Each participating site selected a team of local leaders, including a designated site leader, 1 physician leader, 2 to 3 nurse leaders, and an administrative leader, to constitute the local pain management quality improvement team in the NICUs and special care baby units. The team leaders were provided with a written explanation of the study and were advised that participation as a local leader was voluntary.
This study was conducted with the approval of the respective ethics committees of our institution and of the participating sites.
Patients
The patients were neonates admitted to participating centers (both NICUs and special care baby units) between October 1, 2014, and January 27, 2016, following birth at the center or transfer from another facility. In this study, neonates older than 72 hours of life (excluding infants who were postoperative) were the specific targets of the pain management improvement efforts.
Because the object for interventions in this study was local leaders among participating sites, direct consent was not required from parents/guardians. Instead, a notice was posted at the entrances of the participating wards to introduce the study and to notify parents/guardians that patient medical records would be utilized in the study. The notice also advised that parents/guardians could refuse the use of their child's medical records for the study.
Interventions
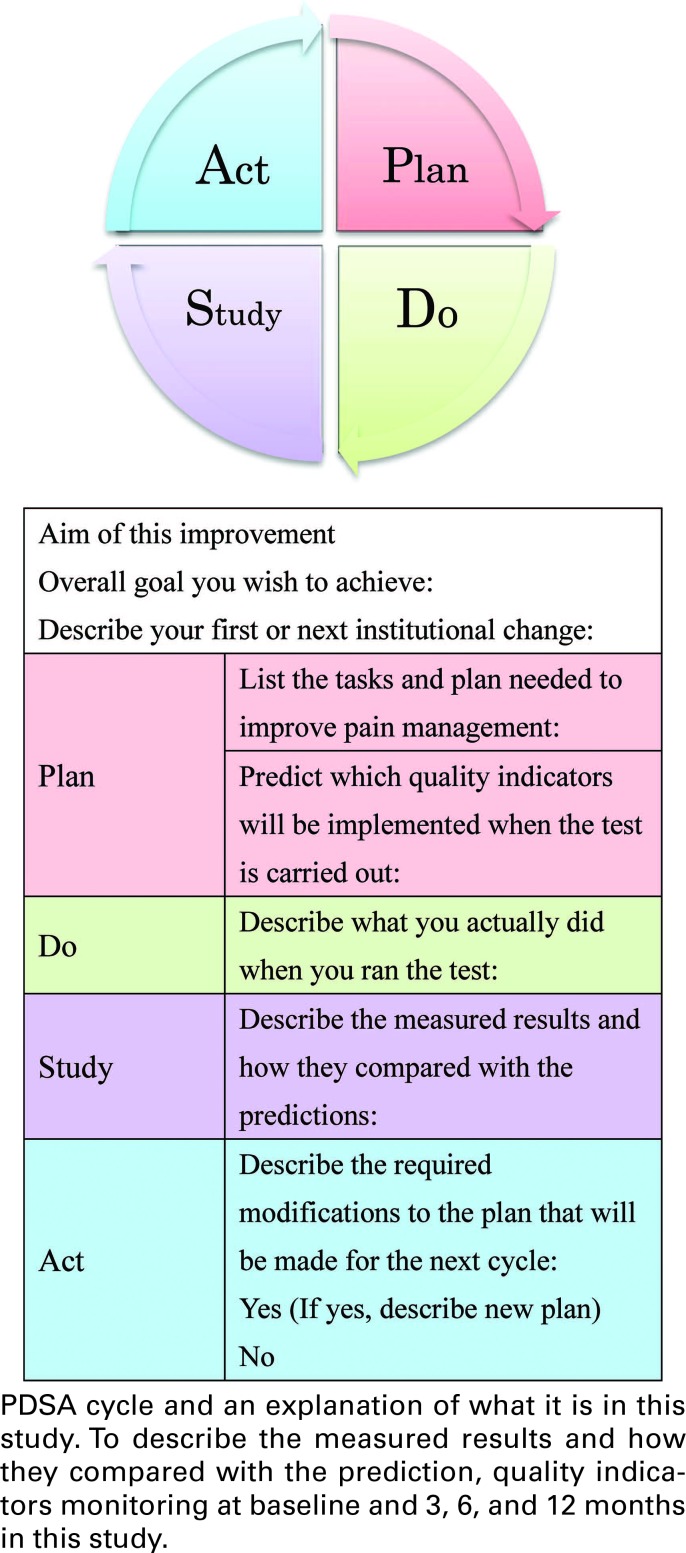
The Institute for Healthcare Improvement Collaborative Quality Improvement Model was used to guide the program.14 The key elements of the model include (1) the appointment of a local multidisciplinary team (within the participating site) that was trained to conduct small-scale tests of change and to help translate successful changes to standard practice; (2) provision of an education session (in this case, a 2-day session conducted in February 2015) on improvement methods and strategies, based on the Institute for Healthcare Improvement model15; (3) a supportive communication structure (in this case, ready access to a pain assessment expert for feedback during the test change period and to the participant contact list, which facilitated collaborative exchange between sites); (4) availability of best practice information; and (5) transparent data submission and reporting through the use of PDSA cycles (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1.
The authors developed comprehensive evidenced-based teaching material on pain management for invasive bedside procedures based on an extensive literature review. Previously, it was shown that local leaders improved the quality of neonatal pain management by acting as a catalyst for change, moving the process forward and maintaining orientation to the assigned tasks.10,11 Therefore, we selected 3 primary “active collaboration” categories of leader interventions: (1) provision of education on basic neonatal pain management, including neonatal pain sensation, the effect of pain experiences in neonates, measurement of pain, and pain prevention and relief; (2) provision of advanced education on neonatal pain and on teaching methods and collaboration with other medical staff working in pain management; and (3) testing changes in the local work setting through the use of PDSA cycles.
To capture the baseline status of pain management at the participating sites, we reviewed the electronic medical records for the documentation of pain assessment scale scores and pain relief following interventions from October 2014 to January 2015. The data were recorded on a study survey form created by the researchers, which was then mailed to the first author (M.O.). These baseline data were later reviewed at the February session.
The intervention phase ran from February 2015 to February 2016, during which time the site teams made numerous process improvements. In total, pain management outcome data were reported at 4 points in time: just prior to the February education session (baseline) and at 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months after the start of the collaborative program. We required participating sites to provide full transparency in reporting, with open sharing of successes and of barriers. We compared the data from the 4 points in time and provided feedback to the sites in the form of reports showing outcome trends for all the sites.
Outcome Measurement
To investigate whether the PDSA cycles led to an improvement in pain management during invasive bedside procedures, we developed QIs as the primary outcome based on current Japanese standards of care for neonatal pain management.16 The objective of these QIs was to quantify pain care and the effects of the pain management improvement activities at the study sites. The indicators were further elaborated using the Delphi method. A panel of 11 experts (including authors K.Y., R.F., and M.U.), consisting of physicians and nurses, evaluated the suitability of the initial indicators proposed by the first author (M.O.) following a review of the literature. This deliberation took place over 3 occasions and resulted in the selection of 4 structural indicators (QIs 8, 9, 11, and 12) and 8 process indicators (QIs 1-7 and 10) (Table 1). The 12 indicators allowed the results of pain management improvement initiatives to be quantified (Table 1) and were used to motivate improvement. During the February education session, we reviewed the baseline proportion of implementation of QIs at the participating sites with the team leaders from the respective sites; following the session, the team leaders discussed the findings with their staff members, set pain management aims for each site, and then selected the QIs for the upcoming year.
TABLE 1. QIs for Pain Management in the Participating Neonatal Intensive Care Unitsa.
| Calculation Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| QI | Description | Numerator | Denominator |
| 1 | Pain is monitored regularly by measuring vital signs | Number of patients who received regular pain monitoring during each shift by measuring vital signs | Number of hospitalized patients |
| 2 | Factors influencing the pain reaction are included in the pain assessment | Number of skin punctures with a pain assessment including factors influencing the pain reaction | Total number of skin punctures |
| 3 | A pain measurement has been performed | Number of skin punctures with a pain measurement | Total number of skin punctures |
| 4 | Nonpharmacological pain relief measures have been implemented | Number of skin punctures with nonpharmacological pain relief measures | Total number of skin punctures |
| 5 | The need for tracheal suctioning has been assessed | Number of patients who were assessed for the need for tracheal suctioning at each shift | Total number of patients |
| 6 | An explanation of the use of invasive procedures and pain relief measures has been provided to the parents/guardians | Number of patients whose parents/guardians received an explanation of invasive procedures and pain relief measures | Total number of patients |
| 7 | A pain care conference has been held with staff and related parties | Number of patients whose parent/guardians had a pain care conference with medical staff | Number of discharged patients |
| 8 | Medical staff have been provided with training on pain management | Number of nurses and physicians who have participated in annual hospital training for pain management | Total number of nurses and physicians |
| 9 | One person is in charge of coordinating training on pain management | Presence vs absence | |
| 10 | Individual pain management plans have been developed within 48 h of hospitalization | Number of patients for whom an individual pain management plan has been developed, including the content of invasive procedures after birth, pain response to the invasive procedures, which pain tool was used to measure pain, and evaluation of the effect of pain relief within 48 h of hospitalization | Number of hospitalized patients |
| 11 | An institutional protocol including pain assessment, pain prevention, and pain relief has been developed | Presence vs absence | |
| 12 | There is an organizational audit for pain management | Presence vs absence | |
Abbreviation: QI, quality indicator.
aQIs 1-8, 10: QI implementation proportion (%) = numerator/denominator × 100. QIs 9, 11, and 12: QI implementation = presence or absence.
Statistical Analysis
In this study, the QIs were used to measure the quality of inpatient neonatal care at each of the study sites. First, we calculated the proportion of implementation of QIs 1 to 8 and 10 from baseline to 12 months. Next, we used the Jonckheere's trend test to examine the changes in QI implementation among all sites over time (ie, at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months). We also counted the presence/absence of QIs 9, 11, and 12 and then used the Cochran-Armitage test for trend to examine the changes in QI implementation over time. The data were analyzed using SPSS version 20.0 (IBM SPSS Japan, Tokyo).
RESULTS
Participating Sites and Participants
Nineteen facilities applied to the pain management quality improvement collaborative program, and 7 centers were selected to participate in the 12-month trial (Table 2). All 7 centers remained actively involved during the 12-month implementation phase. Twenty-five clinical team leaders, including 7 physicians and 18 nurses, participated in this study. There was a mean of 56.4 (range: 43-90) staff nurses and a mean of 8.5 (range: 6-15) neonatologists at each of the participating sites. The total number of nurses and physicians among the participating sites was 517 at baseline.
TABLE 2. Participating Institutions.
| Hospital | Number of Beds | Total Number of Nurses and Physicians | Organization of Hospital Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hiroshima City Hiroshima Citizens Hospital | 9-bed NICU 24-bed SCBU |
68 (60 nurses and 8 physicians) |
City |
| Hiroshima Prefectural Hospital | 12-bed NICU 18-bed SCBU |
54 (48 nurses and 6 physicians) |
Prefecture |
| Japanese Red Cross Society Kyoto Daiichi Hospital | 9-bed NICU 18-bed SCBU |
58 (49 nurses and 9 physicians) |
Japanese Red Cross Society |
| Nagoya University Hospital | 12-bed NICU 24-bed SCBU |
67 (60 nurses and 7 physicians) |
National university |
| Saitama Medical Center | 60-bed NICU 48-bed SCBU |
161 (145 nurses and 16 physicians) |
Private university |
| Tokyo Women's Medical University | 15-bed NICU 24-bed SCBU |
55 (47 nurses and 8 physicians) |
Private university |
| Yamagata Prefectural Central Hospital | 9-bed NICU 18-bed SCBU |
54 (48 nurses and 6 physicians) |
Prefecture |
Abbreviations: NICU, neonatal intensive care unit; SCBU, special care baby unit.
Pain Documentation
At baseline, 2 of the participating sites were already documenting pain with recommended pain assessment scales4—the Neonatal Infant Pain Scale (NIPS) and the Face Scale for Pain Assessment of Preterm Infants (FSPAPI)17,18; the remaining sites reported issues related to the selection of the best pain assessment scale, the lack of opportunities for training on the use of a pain assessment scale, and the difficulty of assessing pain during procedures, requiring the staff to be shielded. Three participating sites were using electronic forms for pain assessment and pain relief documentation.
All the participating sites without a recommended pain assessment tool4 introduced these during the study period—1 site introduced the NIPS, 3 sites introduced the FSPAPI, and 1 site introduced both.
Quality Indicators
Table 3 shows the QIs that were implemented at each site during the 12-month period. Table 4 shows the number of admitted neonates who were older than 72 hours during the intervention phase and who were the targets for the QI implementation (this number was used in the calculation of the proportion of implementation at each site). Table 5 shows the outcome trends for each of the QIs over time (baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months). The total number of nurses and physicians among the participating sites who had undergone annual hospital education for pain management was 188 (36.3% of the total) at baseline, 330 (63.8%) at 3 months, 417 (80.6%) at 6 months, and 491 (94.9%) at 12 months.
TABLE 3. Implemented Measures at Each of the Participating Sitesa.
| Blinded Site | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QI | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | Total |
| 1 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 6 | |
| 2 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 5 | ||
| 3 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 6 | |
| 4 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 6 | |
| 5 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 5 | ||
| 6 | ○ | ○ | ○ | 3 | ||||
| 7 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 6 | |
| 8 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 7 |
| 9 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 6 | |
| 10 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 4 | |||
| 11 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | 6 | |
| 12 | ○ | 1 | ||||||
Abbreviation: QI, quality indicator.
aCircles (○) indicate implementation during the 12 months of testing improvements in the participating sites.
TABLE 4. Number of Admitted Neonates Older Than 72 Hours During the Intervention Phase.
| GA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Total No. of Patients | Mean, wk | Range, wk |
| Baseline | 90 | 36.2 | 24-66 |
| 3 mo | 82 | 35.9 | 24-79 |
| 6 mo | 75 | 37.3 | 24-78 |
| 12 mo | 88 | 35.3 | 23-58 |
Abbreviation: GA, gestational age.
TABLE 5. Outcome Trends for All Participating Sitesa.
| QI | Baseline | 3 mo | 6 mo | 12 mo | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (n = 6) | 0 | 0 (0-27.3) | 0 (0-100) | 85.7 (60-100) | .000 |
| 2 (n = 5) | 0 | 0 | 0 (0-100) | 0 (0-100) | .047 |
| 3 (n = 6) | 0 | 0 (0-71.4) | 40 (0-100) | 68 (29-100) | .001 |
| 4 (n = 6) | 0 (0-75) | 65.5 (0-100) | 66.5 (0-100) | 48 (29-100) | .105 |
| 5 (n = 5) | 18 (0-100) | 0 (0-100) | 100 (67-100) | 100 | .008 |
| 6 (n = 3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 80 (0-94) | .048 |
| 7 (n = 6) | 0 | 0 | 0 (0-71) | 0 (0-81) | .161 |
| 8 (n = 7) | 40 (0-100) | 50 (0-100) | 100 (40-100) | 100 (85.0-100) | .002 |
| 9 (n = 6) | 83.3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | .372 |
| 10 (n = 4) | 0 | 0 (0-100) | 75 (0-100) | 69 (0-100) | .031 |
| 11 (n = 6) | 0 | 33.3 | 50 | 66.6 | .101 |
| 12 (n = 1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ... |
Abbreviation: QI, quality indicator.
aQIs 1-8 and 10: Median (range) of implementation proportion among participating sites. QIs 9, 11, and 12: Percentage of implementation sites.
bP values were from Jonckheere's trend test for QIs 1-8 and 10 and from Cochran-Armitage test for trends for QIs 9 and 11. A number of sites were 4 at 6 months and 12 months for QI 5 because there were no patients with endotracheal intubation at 1 site.
DISCUSSION
The baseline data from the 7 sites revealed substantial opportunities for improvement in pain management. Testing change in the NICU setting through the use of PDSA cycles for selected QIs resulted in measurable improvements in pain management at all 7 participating sites. The precision of the statistical analysis was limited because the number of participating sites was small, but we confirmed a trend of increasing implementation rates of QI 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 10. While other pain management quality improvement activities have been demonstrated in NICUs,8–11 this report highlights possibilities for collaborative improvement in pain management across various types of organization of hospital management and various regions of hospitals in Japan. The key elements of this collaborative program, including (1) the presence of pain team leaders using PDSA cycles and leadership support for their activities from nurse managers and physician managers at each site, (2) a 2-day educational session with other participating sites, (3) a supportive communication structure involving experts and exchange of experiences among participating sites, and (4) availability of best practice information, might facilitate improvements in pain practice. The QIs in this study focused on pain assessment and relief of pain associated with invasive bedside procedures and did not evaluate postoperative pain management. It is difficult to develop QIs for postoperative pain management because of the lack of evidence for analgesia and sedation in neonates. Indeed, most guidelines for the prevention and management of pain in neonates have not included postoperative pain.1,2,4
In this study, 8 of the QIs were not in evidence at any of the participating sites at baseline—the reasons may be that these practices had not been implemented or that lack of specific electronic forms made these difficult to measure. According to site reporting during the intervention phase, all the sites introduced electronic medical record forms to capture the selected QIs within 6 months of starting the trial. The development of standardized documentation that includes pain score, interventions, and infant responses to interventions has been shown to significantly facilitate pain management.19,20 In the current study, the ability to record pain scores, interventions, and infant responses to interventions contributed to improved pain management because this information is needed for individualized planning (QIs 2, 3, 5, and 10). In addition, as was seen in a previous study,13 the implementation of routine pain monitoring by measuring vital signs (QI 1) and the use of standardized pain assessment tools increased during this study. While the Japanese version of the Premature Infant Pain Profile21,22 is also a recommended pain assessment tool,4 none of the sites selected the tool. Four sites selected the FSPAPI, which has also been validated in the Japanese population and is easier to score than other tools.17,18
Notably, the relative implementation of QI 6 increased only at 12 months after the start of the intervention period (Table 5). Parental involvement in pain management in the NICU is a relatively new area of research,23 and previous study showed a low level of information sharing and parental participation in pain management in Japanese NICUs.7 It is possible that the lack of practical examples of parental involvement in pain management made this a difficult improvement activity for the participating sites.
Quality improvement collaboratives were undertaken as a core activity of the Vermont Oxford Network Neonatal Intensive Care Quality Improvement Collaborative (NIC/Q) project in 1995.24 Since then, the benefits of collaborative improvement work have been documented across settings and by different groups,25 such as the California Perinatal Quality Care Collaborative, which showed the effectiveness of a multihospital collaborative quality improvement model compared with individual local projects.26 In Japan, the nonprofit Neonatal Research Network of Japan was launched in 2004 to advance research in neonatal medicine and has 192 member institutions to date; however, the Neonatal Research Network of Japan does not have a quality improvement collaborative program. In this study, the researchers planned and led this collaborative program without the support of a specific network; however, the fact that 19 institutions applied to participate suggests the need for a collaborative improvement program for pain management among Japanese NICUs. This is likely related to the absence of a systematic institutional approach to pain management and to insufficient collaboration between nurses and physicians in Japan.7 In this study, the total number of nurses and physicians educated in pain management among the participating sites increased (QI 8), which might promote collaboration between nurses and physicians and make a difference through quality improvement efforts in each unit (QIs 1-3, 5, 6, and 10). In addition, our program was a driver for evidenced-based pain management improvement among the participating sites.
Summary of Recommendations.
| What we know |
|
| What needs to be studied |
|
| What we can do today |
|
This study had 2 limitations. The outcomes in this study were selected by the participants themselves on the basis of their identification of deficiencies in pain management at their respective sites. Second, the data collection depended on the participants, and we did not actively participate or validate the data; as such, the findings in this study depend on the accuracy and transparency of the participants.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, the 7 sites participating in the collaborative quality improvement program had improved pain management during the 12-month intervention period. This program played a key supportive role, providing knowledge, structure, and feedback. The pain team leaders learned, discussed, and worked together to improve pain management of their unit, and the ability to track their progress in the implementation of QIs increased their motivation. While the optimal method for continuous improvement is not known, collaborative improvement programs provide an attractive means of promoting evidence-based practice to reduce evidence-practice gaps in the NICU setting.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the pain team members at the participating sites for their commitment to improving pain management in neonates. We also thank Eisuke Hida, PhD, for statistical consultation.
Footnotes
The work occurred at Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan.
This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI (grant numbers JP25713066 and JP26293471).
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.American Academy of Pediatrics; Committee on Fetus and Newborn and Section on Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine. Prevention and management of procedural pain in the neonate: an update. Pediatrics. 2016;137(2):e20154271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lago P, Garetti E, Merazzi D, et al. Guidelines for procedural pain in the newborn. Acta Paediatr. 2009;98(6):932–939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Association of Paediatric Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland. Good practice in postoperative and procedural pain management, 2nd edition. Paediatr Anaesth. 2012;22(suppl 1):S1–S79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Committee for the Establishment and Dissemination of the Japanese Guideline for Pain Prevention and Management in the NICU. [Japanese Guideline for Pain Prevention and Management] [Internet]. Tokyo, Japan: Committee for the Establishment and Dissemination of the Japanese Guideline for Pain Prevention and Management in the NICU; 2014. In Japanese. http://www.jspnm.com/topics/data/kaiin20150128.pdf. Accessed Jan 5, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Stevens B, Riahi S, Cardoso R, et al. The influence of context on pain practices in the NICU: perceptions of health care professionals. Qual Health Res. 2011;21(6):757–770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Latimer MA, Johnston CC, Ritchie JA, Clarke SP, Gilin D. Factors affecting delivery of evidence-based procedural pain care in hospitalized neonates. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2009;38(2):182–194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ozawa M, Yokoo K. Pain management of neonatal intensive care units in Japan. Acta Paediatr. 2013;102(4):366–372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lago P, Allegro A, Heun N. Improving newborn pain management: systematic pain assessment and operators' compliance with potentially better practices. J Clin Nurs. 2014;23(3–4):596–599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Reavey DA, Haney BM, Atchison L, Anderson B, Sandritter T, Pallotto EK. Improving pain assessment in the NICU: a quality improvement project. Adv Neonatal Care. 2014;14(3):144–153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sharek PJ, Powers R, Koehn A, Anand KJ. Evaluation and development of potentially better practices to improve pain management of neonates. Pediatrics. 2006;118(suppl 2):S78–S86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dunbar AE, III, Sharek PJ, Mickas NA, et al. Implementation and case-study results of potentially better practices to improve pain management of neonates. Pediatrics. 2006;118(suppl 2):S87–S94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Horbar JD, Plsek PE, Leahy K. NIC/Q 2000: establishing habits for improvement in neonatal intensive care units. Pediatrics. 2003;111(4, pt 2):e397–e410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee HC, Kurtin PS, Wight NE, et al. A quality improvement project to increase breast milk use in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2012;130(6):e1679–e1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.The Breakthrough Series: IHI's Collaborative Model for Achieving Breakthrough Improvement [series white paper] [Internet]. Boston: Institute for Healthcare Improvement; 2003. http://www.ncpc.org.uk/sites/default/files/Anita_IHIBreakthroughSerieswhitepaper2003.pdf. Accessed Jan 5, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Langley GL, Nolan KM, Nolan TW, Norman CL, Provost LP. The Improvement Guide: A Practical Approach to Enhancing Organizational Performance. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ozawa M, Funaba Y, Fukushima S. [Quality indicators for pain management in neonatal intensive care unit and growing care units: a modified Delphi survey of an expert panel]. J Japan Acad Neonatal Nurs. 2014;20(2):2–12. In Japanese. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yokoo K, Abe A. [Development of a face scale for pain assessment of preterm infants: computerized quantitative analysis of upper facial motions]. J Japan Acad Neonatal Nurs. 2010;16(1):11–18. In Japanese. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Abe A, Yokoo K. [Verification of reliability and validity of a face scale for pain assessment of preterm infants]. J Japan Acad Neonatal Nurs. 2010;16(1):19–24. In Japanese. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stevens B. Development and testing of a pediatric pain management sheet. Pediatr Nurs. 1990;16:543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.National Association of Neonatal Nurses. Newborn Pain Assessment and Management Guideline for Practice. Des Plaines, IL: Author National Association of Neonatal Nurses; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ozawa M, Kanda K, Hirata M, Kusakawa I, Suzuki C. [Utility of a Japanese version of the Premature Infant Pain Profile]. J Japan Acad Neonatal Nurs. 2010;16(1):28–33. In Japanese. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ozawa M, Isago N, Kanda K, Hirata M, Kusakawa I, Suzuki C. [Investigation of an equivalence of pain assessment by a Japanese version of the Premature Infant Pain Profile among neonatal nurses]. J Child Health. 2012;71(1):10–16. In Japanese. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Franck L, Oulton K, Bruce E. Parental involvement in neonatal pain management: an empirical and conceptual update. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2012;44:45–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Horbar JD, Rogowski J, Plsek PE, et al. NIC/Q Project Investigators of the Vermont Oxford Network. Collaborative quality improvement for neonatal intensive care. Pediatrics. 2001;107(1):14–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schouten LM, Hulscher ME, van Everdingen JJ, Huijsman R, Grol RP. Evidence for the impact of quality improvement collaboratives: systematic review. BMJ. 2008;336(7659):1491–1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lee HC, Powers RJ, Bennett MV, et al. Implementation methods for delivery room management: a quality improvement comparison study. Pediatrics. 2014;134(5):e1378–e1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]