The synthesis and structure of the title piperidine derivative is reported. It is one of a second generation of compounds designed and synthesized based on a very potent and selective α9α10 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist ZZ161C, which has shown analgesic effects in a chemotherapy-induced neuropathy animal model.
Keywords: crystal structure, biphenyl system, piperidine ring, bis-tertiary ammonium salt
Abstract
The title compound, C28H32N2, (I), is one of a second generation of compounds designed and synthesized based on a very potent and selective α9α10 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist ZZ161C {1,1′-[[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diylbis(prop-2-yne-3,1-diyl)]bis(3,4-dimethylpyridin-1-ium) bromide}, which has shown analgesic effects in a chemotherapy-induced neuropathy animal model. Compound (I) was synthesized by the reaction of 4,4′-bis(3-bromoprop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl with piperidine at room temperature in acetonitrile. The single-crystal used for X-ray analysis was obtained by dissolving (I) in a mixture of dichloromethane and methanol, followed by slow evaporation of the solvent. In the crystal of (I), the biphenyl moiety has a twisted conformation, with a dihedral angle of 25.93 (4)° between the benzene rings. Both piperidine head groups in (I) are in the chair conformation and are oriented so that the N-atom lone pairs of each piperidine group point away from the central biphenyl moiety.
Chemical context
The α9α10 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is a novel therapeutic target with potential significance for pain management. Previous studies have shown that antagonism of the α9α10 nAChR by the non-peptide small molecule, ZZ161C {10-[(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diyl bis(prop-2-yne-3,1-diyl)]bis(3,4-dimethylpyridin-1-ium) bromide} produced analgesia in the vincristine-induced neuropathic pain model in rats (Zheng et al., 2011 ▸; Wala et al., 2012 ▸). In order to improve the drug-like and pharmacokinetic properties of ZZ161C, the title compound (I) was designed and synthesized. Compound (I) is a biphenyl system with ethynyl appendages at the 4 and 4′ positions, as in ZZ161C, but the terminal aza-aromatic rings have been replaced by piperidine moieties. Single-crystal X-ray analysis of compound (I) was used to determine the structural conformation of the compound.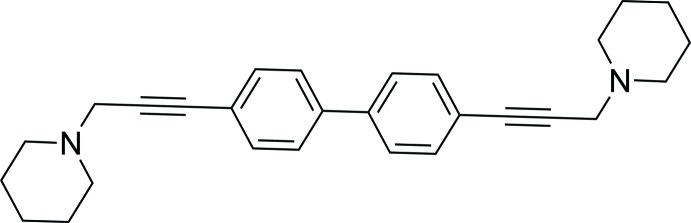
Structural commentary
The title compound (I) is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. X-ray crystallographic study was conducted in order to determine the geometry of the biphenyl system as well as to obtain detailed information about the conformation of the terminal piperidine groups. In compound (I), the biphenyl rings (C9-C14) and (C15-C20) are non-coplanar, with a dihedral angle of 25.93 (4)° between them. The torsion angles of the ethynyl groups between the planes of the phenyl rings and the piperidine ring N atoms are 167.49 (9) and 34.01 (12)° (defined by atoms N1/C6/C9/C10, N2/C23/C18/C19, respectively). The lone pair on each N atom is oriented away from the biphenyl core of the molecule.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of (I), with ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
Aside from weak van der Waals interactions, there are no noteworthy intermolecular contacts in (I). The molecules pack into layers in the ab plane bounded top and bottom by piperidine groups, which in turn stack along c.
Database survey
A search of the November 2014 release of the Cambridge Structure Database (Groom et al., 2016 ▸), with updates through May 2015, using the program Mogul (Bruno et al., 2004 ▸) for 4,4′-substituted biphenyl fragments was conducted. The search was restricted to purely organic, solvent-free structures with R <5% and Cl as the heaviest element. There were over 1000 hits, which produced a bimodal distribution of biphenyl torsion angles with a tight peak at 0° and a broader peak centred at 30°. Therefore the biphenyl torsion angle in (I) is not unusual.
Synthesis and crystallization
Synthetic procedure: The intermediate 4,4′-bis(3-bromoprop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl (Wan et al., 2015 ▸) was obtained utilizing a previously reported procedure; compound (I) was synthesized by reacting piperidine with this intermediate.
To a suspension of 4,4′-bis(3-bromoprop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl (100.0 mg, 0.26 mmol) in acetonitrile (7 mL), piperidine (66.4 mg, 0.78 mmol) was added at room temperature and the mixture was stirred continuously for 2 h, resulting in the formation of compound (I). Acetonitrile was removed under vacuum and the mixture was partitioned between water (50 mL) and dichloromethane (50 mL). The dichloromethane layer was collected and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Sodium sulfate was removed by filtration, and the filtrate containing crude (I) was concentrated and purified by column chromatography (dichloromethane/methanol) to afford pure compound (I) in 80% yield.
Crystallization: Light-yellow crystals of compound (I) suitable for X-ray analysis were grown in a mixture of dichloromethane and methanol (2:1) by slow evaporation of the solvent at room temperature over a period of 24 h.
1H-NMR (400 Mz, CDCl3): δ 7.51 (q, 8H), 3.53 (s, 4H), 2.62 (s, 8H), 1.65–1.71 (m, 8H), 1.47 (s, 4H) ppm.
1C-NMR (100 Mz, CDCl3): δ 140.07, 132.35, 126.91, 122.54, 85.25, 53.56, 48.62, 25.93, 23.93 ppm.
Refinement details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1 ▸. H atoms were found in difference-Fourier maps, but subsequently included in the refinement using riding models, with constrained distances set to 0.94 Å (Csp 2—H) and 0.98 Å (R 2—CH2). U iso(H) values were set to 1.2U eq of the attached carbon atom.
Table 1. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C28H32N2 |
| M r | 396.55 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C2/c |
| Temperature (K) | 210 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 40.2728 (8), 6.9679 (1), 16.0119 (3) |
| β (°) | 92.588 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 4488.63 (14) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.51 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.25 × 0.24 × 0.05 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker X8 Proteum diffractometer |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.822, 0.942 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 28464, 4089, 3656 |
| R int | 0.040 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.603 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.038, 0.120, 1.08 |
| No. of reflections | 4089 |
| No. of parameters | 272 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.15, −0.14 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007277/sj5530sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007277/sj5530Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007277/sj5530Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1550512
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This investigation was supported by the Arkansas Research Alliance (ARA).
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C28H32N2 | F(000) = 1712 |
| Mr = 396.55 | Dx = 1.174 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 40.2728 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 9828 reflections |
| b = 6.9679 (1) Å | θ = 2.2–68.5° |
| c = 16.0119 (3) Å | µ = 0.51 mm−1 |
| β = 92.588 (1)° | T = 210 K |
| V = 4488.63 (14) Å3 | Plate, light yellow |
| Z = 8 | 0.25 × 0.24 × 0.05 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker X8 Proteum diffractometer | 4089 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus rotating anode | 3656 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 5.6 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.040 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 68.5°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | h = −48→48 |
| Tmin = 0.822, Tmax = 0.942 | k = −8→7 |
| 28464 measured reflections | l = −12→19 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.120 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0642P)2 + 1.3326P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4089 reflections | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 272 parameters | Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.00034 (8) |
Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was mounted using polyisobutene oil on the tip of a fine glass fibre, which was fastened in a copper mounting pin with electrical solder. It was placed directly into the cold gas stream of a liquid-nitrogen based cryostat (Hope, 1994; Parkin & Hope, 1998). At 90K the diffraction pattern showed some diffuse scatter and the Bragg diffraction spots were fuzzy. Visual inspection of crystal integrity and diffraction quality vs temperature established a safe temperature for data collection of -63° C. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement progress was checked using Platon (Spek, 2009) and by an R-tensor (Parkin, 2000). The final model was further checked with the IUCr utility checkCIF. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.09256 (2) | 0.51979 (13) | 0.25747 (5) | 0.0358 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.40754 (2) | 0.51181 (13) | 0.99141 (5) | 0.0375 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.08446 (3) | 0.34286 (16) | 0.30095 (7) | 0.0408 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.0960 | 0.3411 | 0.3561 | 0.049* | |
| H1B | 0.0921 | 0.2325 | 0.2692 | 0.049* | |
| C2 | 0.04725 (3) | 0.32626 (19) | 0.31130 (8) | 0.0510 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.0358 | 0.3157 | 0.2562 | 0.061* | |
| H2B | 0.0426 | 0.2097 | 0.3429 | 0.061* | |
| C3 | 0.03424 (3) | 0.4991 (2) | 0.35658 (8) | 0.0531 (3) | |
| H3A | 0.0432 | 0.4996 | 0.4145 | 0.064* | |
| H3B | 0.0100 | 0.4920 | 0.3576 | 0.064* | |
| C4 | 0.04421 (3) | 0.6818 (2) | 0.31330 (8) | 0.0524 (3) | |
| H4A | 0.0375 | 0.7929 | 0.3461 | 0.063* | |
| H4B | 0.0327 | 0.6893 | 0.2581 | 0.063* | |
| C5 | 0.08159 (3) | 0.68738 (16) | 0.30341 (7) | 0.0429 (3) | |
| H5A | 0.0874 | 0.8043 | 0.2734 | 0.051* | |
| H5B | 0.0930 | 0.6906 | 0.3587 | 0.051* | |
| C6 | 0.12794 (3) | 0.52990 (17) | 0.24185 (7) | 0.0408 (3) | |
| H6A | 0.1319 | 0.6458 | 0.2091 | 0.049* | |
| H6B | 0.1337 | 0.4192 | 0.2077 | 0.049* | |
| C7 | 0.15040 (3) | 0.53310 (16) | 0.31739 (7) | 0.0390 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.16846 (3) | 0.53582 (15) | 0.37892 (7) | 0.0363 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.19232 (3) | 0.53774 (13) | 0.44832 (6) | 0.0326 (2) | |
| C10 | 0.22585 (3) | 0.50840 (14) | 0.43383 (6) | 0.0335 (2) | |
| H10A | 0.2324 | 0.4867 | 0.3790 | 0.040* | |
| C11 | 0.24966 (2) | 0.51066 (14) | 0.49867 (6) | 0.0313 (2) | |
| H11A | 0.2721 | 0.4898 | 0.4873 | 0.038* | |
| C12 | 0.24091 (2) | 0.54353 (13) | 0.58071 (6) | 0.0284 (2) | |
| C13 | 0.20725 (2) | 0.57162 (15) | 0.59484 (6) | 0.0355 (2) | |
| H13A | 0.2007 | 0.5932 | 0.6497 | 0.043* | |
| C14 | 0.18335 (3) | 0.56848 (16) | 0.53020 (6) | 0.0378 (3) | |
| H14A | 0.1609 | 0.5872 | 0.5416 | 0.045* | |
| C15 | 0.26622 (2) | 0.54789 (13) | 0.65079 (6) | 0.0281 (2) | |
| C16 | 0.26055 (2) | 0.64996 (14) | 0.72383 (6) | 0.0326 (2) | |
| H16A | 0.2409 | 0.7220 | 0.7272 | 0.039* | |
| C17 | 0.28313 (2) | 0.64730 (14) | 0.79115 (6) | 0.0331 (2) | |
| H17A | 0.2786 | 0.7173 | 0.8395 | 0.040* | |
| C18 | 0.31256 (2) | 0.54258 (14) | 0.78869 (6) | 0.0316 (2) | |
| C19 | 0.31910 (2) | 0.44566 (15) | 0.71481 (6) | 0.0337 (2) | |
| H19A | 0.3391 | 0.3779 | 0.7108 | 0.040* | |
| C20 | 0.29630 (2) | 0.44858 (14) | 0.64742 (6) | 0.0312 (2) | |
| H20A | 0.3012 | 0.3823 | 0.5983 | 0.037* | |
| C21 | 0.33448 (2) | 0.53494 (15) | 0.86180 (6) | 0.0352 (2) | |
| C22 | 0.35066 (3) | 0.53208 (16) | 0.92647 (7) | 0.0390 (3) | |
| C23 | 0.37192 (3) | 0.52602 (18) | 1.00433 (7) | 0.0424 (3) | |
| H23A | 0.3679 | 0.6422 | 1.0368 | 0.051* | |
| H23B | 0.3653 | 0.4158 | 1.0377 | 0.051* | |
| C24 | 0.41943 (3) | 0.68044 (16) | 0.94747 (7) | 0.0413 (3) | |
| H24A | 0.4138 | 0.7965 | 0.9784 | 0.050* | |
| H24B | 0.4083 | 0.6878 | 0.8919 | 0.050* | |
| C25 | 0.45676 (3) | 0.67152 (19) | 0.93867 (7) | 0.0498 (3) | |
| H25A | 0.4640 | 0.7830 | 0.9069 | 0.060* | |
| H25B | 0.4680 | 0.6759 | 0.9942 | 0.060* | |
| C26 | 0.46631 (3) | 0.48932 (19) | 0.89439 (8) | 0.0519 (3) | |
| H26A | 0.4906 | 0.4800 | 0.8937 | 0.062* | |
| H26B | 0.4575 | 0.4927 | 0.8364 | 0.062* | |
| C27 | 0.45268 (3) | 0.3159 (2) | 0.93827 (8) | 0.0528 (3) | |
| H27A | 0.4638 | 0.3029 | 0.9937 | 0.063* | |
| H27B | 0.4572 | 0.2000 | 0.9061 | 0.063* | |
| C28 | 0.41548 (3) | 0.33533 (17) | 0.94746 (7) | 0.0434 (3) | |
| H28A | 0.4042 | 0.3357 | 0.8920 | 0.052* | |
| H28B | 0.4074 | 0.2248 | 0.9784 | 0.052* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0341 (5) | 0.0429 (5) | 0.0297 (4) | −0.0006 (4) | −0.0047 (3) | 0.0028 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0329 (5) | 0.0501 (6) | 0.0288 (4) | −0.0020 (4) | −0.0046 (3) | 0.0012 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0456 (6) | 0.0379 (6) | 0.0388 (6) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | −0.0013 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0479 (7) | 0.0545 (7) | 0.0509 (7) | −0.0114 (6) | 0.0054 (5) | −0.0028 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0438 (7) | 0.0675 (8) | 0.0488 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0096 (5) | 0.0003 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0492 (7) | 0.0564 (8) | 0.0514 (7) | 0.0146 (6) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0027 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0485 (6) | 0.0378 (6) | 0.0418 (6) | 0.0030 (5) | −0.0050 (5) | 0.0029 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0363 (6) | 0.0528 (7) | 0.0326 (5) | −0.0018 (5) | −0.0045 (4) | 0.0057 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0356 (6) | 0.0426 (6) | 0.0382 (6) | −0.0008 (4) | −0.0042 (5) | 0.0025 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0361 (6) | 0.0345 (6) | 0.0379 (6) | 0.0006 (4) | −0.0034 (4) | 0.0011 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0348 (5) | 0.0269 (5) | 0.0356 (5) | −0.0001 (4) | −0.0053 (4) | 0.0016 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0388 (5) | 0.0324 (5) | 0.0293 (5) | −0.0012 (4) | 0.0001 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0299 (5) | 0.0302 (5) | 0.0338 (5) | −0.0006 (4) | 0.0016 (4) | −0.0001 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0312 (5) | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0315 (5) | 0.0001 (3) | −0.0002 (4) | 0.0012 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0335 (5) | 0.0411 (6) | 0.0319 (5) | 0.0060 (4) | 0.0009 (4) | −0.0022 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0304 (5) | 0.0434 (6) | 0.0393 (6) | 0.0064 (4) | −0.0013 (4) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0293 (5) | 0.0249 (5) | 0.0300 (5) | −0.0009 (4) | 0.0008 (4) | 0.0020 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0319 (5) | 0.0316 (5) | 0.0343 (5) | 0.0047 (4) | 0.0014 (4) | −0.0016 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0351 (5) | 0.0330 (5) | 0.0310 (5) | −0.0002 (4) | 0.0005 (4) | −0.0033 (4) |
| C18 | 0.0298 (5) | 0.0300 (5) | 0.0346 (5) | −0.0044 (4) | −0.0020 (4) | 0.0020 (4) |
| C19 | 0.0276 (5) | 0.0342 (5) | 0.0391 (5) | 0.0032 (4) | −0.0006 (4) | −0.0011 (4) |
| C20 | 0.0304 (5) | 0.0309 (5) | 0.0323 (5) | 0.0014 (4) | 0.0017 (4) | −0.0033 (4) |
| C21 | 0.0312 (5) | 0.0365 (6) | 0.0375 (6) | −0.0030 (4) | −0.0015 (4) | 0.0005 (4) |
| C22 | 0.0330 (5) | 0.0461 (6) | 0.0374 (6) | −0.0026 (4) | −0.0026 (4) | −0.0007 (4) |
| C23 | 0.0344 (6) | 0.0607 (7) | 0.0317 (5) | −0.0029 (5) | −0.0031 (4) | −0.0023 (5) |
| C24 | 0.0420 (6) | 0.0419 (6) | 0.0394 (6) | −0.0032 (5) | −0.0036 (4) | −0.0013 (5) |
| C25 | 0.0415 (6) | 0.0599 (8) | 0.0479 (7) | −0.0104 (5) | −0.0007 (5) | 0.0020 (5) |
| C26 | 0.0401 (7) | 0.0682 (8) | 0.0480 (7) | 0.0049 (6) | 0.0079 (5) | 0.0065 (6) |
| C27 | 0.0494 (7) | 0.0566 (8) | 0.0523 (7) | 0.0125 (6) | 0.0025 (5) | 0.0084 (6) |
| C28 | 0.0464 (6) | 0.0425 (6) | 0.0408 (6) | 0.0004 (5) | −0.0026 (5) | 0.0045 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C5 | 1.4592 (14) | C13—C14 | 1.3814 (14) |
| N1—C6 | 1.4595 (14) | C13—H13A | 0.9400 |
| N1—C1 | 1.4599 (14) | C14—H14A | 0.9400 |
| N2—C28 | 1.4596 (15) | C15—C16 | 1.3964 (13) |
| N2—C24 | 1.4614 (14) | C15—C20 | 1.3985 (13) |
| N2—C23 | 1.4616 (14) | C16—C17 | 1.3787 (13) |
| C1—C2 | 1.5194 (16) | C16—H16A | 0.9400 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9800 | C17—C18 | 1.3938 (14) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9800 | C17—H17A | 0.9400 |
| C2—C3 | 1.5113 (18) | C18—C19 | 1.3974 (14) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9800 | C18—C21 | 1.4352 (13) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9800 | C19—C20 | 1.3849 (13) |
| C3—C4 | 1.5126 (19) | C19—H19A | 0.9400 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9800 | C20—H20A | 0.9400 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9800 | C21—C22 | 1.1984 (15) |
| C4—C5 | 1.5210 (16) | C22—C23 | 1.4807 (14) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9800 | C23—H23A | 0.9800 |
| C4—H4B | 0.9800 | C23—H23B | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9800 | C24—C25 | 1.5176 (15) |
| C5—H5B | 0.9800 | C24—H24A | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.4776 (14) | C24—H24B | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9800 | C25—C26 | 1.5123 (18) |
| C6—H6B | 0.9800 | C25—H25A | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.1980 (15) | C25—H25B | 0.9800 |
| C8—C9 | 1.4360 (13) | C26—C27 | 1.5133 (18) |
| C9—C14 | 1.3921 (15) | C26—H26A | 0.9800 |
| C9—C10 | 1.3956 (14) | C26—H26B | 0.9800 |
| C10—C11 | 1.3810 (14) | C27—C28 | 1.5177 (16) |
| C10—H10A | 0.9400 | C27—H27A | 0.9800 |
| C11—C12 | 1.3944 (14) | C27—H27B | 0.9800 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9400 | C28—H28A | 0.9800 |
| C12—C13 | 1.3979 (13) | C28—H28B | 0.9800 |
| C12—C15 | 1.4817 (13) | ||
| C5—N1—C6 | 111.59 (9) | C13—C14—C9 | 120.42 (9) |
| C5—N1—C1 | 110.87 (8) | C13—C14—H14A | 119.8 |
| C6—N1—C1 | 111.31 (8) | C9—C14—H14A | 119.8 |
| C28—N2—C24 | 111.19 (8) | C16—C15—C20 | 117.33 (9) |
| C28—N2—C23 | 111.30 (9) | C16—C15—C12 | 120.78 (8) |
| C24—N2—C23 | 111.03 (9) | C20—C15—C12 | 121.89 (8) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 111.04 (9) | C17—C16—C15 | 121.39 (9) |
| N1—C1—H1A | 109.4 | C17—C16—H16A | 119.3 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.4 | C15—C16—H16A | 119.3 |
| N1—C1—H1B | 109.4 | C16—C17—C18 | 121.11 (9) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.4 | C16—C17—H17A | 119.4 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 108.0 | C18—C17—H17A | 119.4 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 110.89 (10) | C17—C18—C19 | 118.03 (9) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.5 | C17—C18—C21 | 119.27 (9) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | C19—C18—C21 | 122.69 (9) |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C20—C19—C18 | 120.59 (9) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C20—C19—H19A | 119.7 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.0 | C18—C19—H19A | 119.7 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 110.24 (10) | C19—C20—C15 | 121.48 (9) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.6 | C19—C20—H20A | 119.3 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 109.6 | C15—C20—H20A | 119.3 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.6 | C22—C21—C18 | 174.81 (11) |
| C4—C3—H3B | 109.6 | C21—C22—C23 | 177.50 (11) |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.1 | N2—C23—C22 | 114.63 (9) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 110.71 (10) | N2—C23—H23A | 108.6 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.5 | C22—C23—H23A | 108.6 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.5 | N2—C23—H23B | 108.6 |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C22—C23—H23B | 108.6 |
| C5—C4—H4B | 109.5 | H23A—C23—H23B | 107.6 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 108.1 | N2—C24—C25 | 111.07 (9) |
| N1—C5—C4 | 110.83 (9) | N2—C24—H24A | 109.4 |
| N1—C5—H5A | 109.5 | C25—C24—H24A | 109.4 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 109.5 | N2—C24—H24B | 109.4 |
| N1—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C25—C24—H24B | 109.4 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 109.5 | H24A—C24—H24B | 108.0 |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 108.1 | C26—C25—C24 | 110.61 (10) |
| N1—C6—C7 | 115.27 (9) | C26—C25—H25A | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—H6A | 108.5 | C24—C25—H25A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 108.5 | C26—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—H6B | 108.5 | C24—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6B | 108.5 | H25A—C25—H25B | 108.1 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 107.5 | C25—C26—C27 | 110.31 (10) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 179.62 (12) | C25—C26—H26A | 109.6 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 175.36 (11) | C27—C26—H26A | 109.6 |
| C14—C9—C10 | 118.25 (9) | C25—C26—H26B | 109.6 |
| C14—C9—C8 | 122.49 (9) | C27—C26—H26B | 109.6 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.26 (9) | H26A—C26—H26B | 108.1 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 121.15 (9) | C26—C27—C28 | 110.76 (10) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 119.4 | C26—C27—H27A | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 119.4 | C28—C27—H27A | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 120.92 (9) | C26—C27—H27B | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—H11A | 119.5 | C28—C27—H27B | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11A | 119.5 | H27A—C27—H27B | 108.1 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 117.61 (9) | N2—C28—C27 | 111.13 (9) |
| C11—C12—C15 | 121.50 (8) | N2—C28—H28A | 109.4 |
| C13—C12—C15 | 120.90 (8) | C27—C28—H28A | 109.4 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 121.63 (9) | N2—C28—H28B | 109.4 |
| C14—C13—H13A | 119.2 | C27—C28—H28B | 109.4 |
| C12—C13—H13A | 119.2 | H28A—C28—H28B | 108.0 |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | 59.37 (11) | C11—C12—C15—C20 | −26.18 (13) |
| C6—N1—C1—C2 | −175.79 (9) | C13—C12—C15—C20 | 153.55 (10) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −56.43 (13) | C20—C15—C16—C17 | −2.33 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 53.55 (14) | C12—C15—C16—C17 | 176.66 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −53.83 (14) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.11 (15) |
| C6—N1—C5—C4 | 175.67 (9) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 2.24 (14) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | −59.65 (11) | C16—C17—C18—C21 | −176.50 (9) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 57.03 (13) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −2.32 (14) |
| C5—N1—C6—C7 | 62.09 (12) | C21—C18—C19—C20 | 176.37 (9) |
| C1—N1—C6—C7 | −62.35 (12) | C18—C19—C20—C15 | 0.08 (15) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | −0.34 (14) | C16—C15—C20—C19 | 2.24 (14) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 179.46 (9) | C12—C15—C20—C19 | −176.74 (8) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.38 (14) | C28—N2—C23—C22 | −61.65 (12) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.76 (14) | C24—N2—C23—C22 | 62.79 (12) |
| C10—C11—C12—C15 | −179.51 (8) | C28—N2—C24—C25 | −58.93 (11) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.43 (15) | C23—N2—C24—C25 | 176.57 (9) |
| C15—C12—C13—C14 | 179.83 (9) | N2—C24—C25—C26 | 56.67 (12) |
| C12—C13—C14—C9 | −0.29 (16) | C24—C25—C26—C27 | −54.12 (13) |
| C10—C9—C14—C13 | 0.67 (15) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | 53.94 (14) |
| C8—C9—C14—C13 | −179.13 (9) | C24—N2—C28—C27 | 58.70 (11) |
| C11—C12—C15—C16 | 154.88 (10) | C23—N2—C28—C27 | −176.96 (9) |
| C13—C12—C15—C16 | −25.40 (13) | C26—C27—C28—N2 | −56.26 (13) |
References
- Bruker (2006). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruno, I. J., Cole, J. C., Kessler, M., Luo, J., Motherwell, W. D. S., Purkis, L. H., Smith, B. R., Taylor, R., Cooper, R. I., Harris, S. E. & Orpen, A. G. (2004). J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 44, 2133–2144. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Parkin, S. (2013). CIFFIX, http://xray.uky.edu/people/parkin/programs/ciffix
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Wala, E. P., Crooks, P. A., McIntosh, J. M. & Holtman, J. R. (2012). Anesth. Analg. 115, 713–720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wan, A., Penthala, N. R., Fifer, E. K., Parkin, S. & Crooks, P. A. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, 1132–1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G., Zhang, Z., Dowell, C., Wala, E., Dwoskin, L. P., Holton, J. R., McIntosh, J. M. & Crooks, P. A. (2011). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21, 2476–2479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007277/sj5530sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007277/sj5530Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007277/sj5530Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1550512
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



