The title compound, crystallizes with two independent molecules (A and B) in the asymmetric unit, which are far from planar. The aryl rings are inclined to one another by 58.77 (9)° in molecule A and by 36.95 (8)° in molecule B.
Keywords: crystal structure, pyrazol-3-amine, steric repulsion, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
The title compound, C15H13ClN4, crystallizes with two independent molecules (A and B) in the asymmetric unit, which are far from planar as a result of steric repulsion between the rings. The benzene and phenyl rings are inclined to the central pyrazole ring by 46.64 (10) and 17.87 (10)° in molecule A, and by 40.02 (10) and 14.18 (10)° in molecule B. The aromatic rings are inclined to one another by 58.77 (9)° in molecule A, and 36.95 (8)° in molecule B. In the crystal, the A and B molecules are linked by two pairs of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds forming A–B dimers. These are further linked by a fifth N—H⋯N hydrogen bond, forming tetramer-like units that stack along the a-axis direction, forming columns, which are in turn linked by C—H⋯π interactions, forming layers parallel to the ac plane.
Chemical context
The synthesis and reactions of benzodiazepin-2-ones and thiones have been studied in detail by our group (Gaponov et al., 2016 ▸; Okovytyy et al., 2009 ▸). The mechanism of ethanol-assisted hydrazinolysis of 1,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]diazepine-2-thiones (Fig. 1 ▸) has been modelled by quantum-chemical calculations (Okovytyy et al., 2009 ▸). However, instead of obtaining the previously suggested products (IIIa) and (IIIb), compounds N 1-(5-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)benzene-1,2-diamine (Ia) and its 5-chloro-derivative (Ib) were prepared from 4-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]diazepine-2-thiones (IIa) and (IIb) and hydrazine hydrate (Fig. 1 ▸). Aminopirazoles are useful building blocks for the synthesis of new pharmaceutical agents (Sakya et al., 2006 ▸) and agrochemicals (Yuan et al., 2013 ▸), due to their notable biological properties (Peng et al., 2013 ▸; Zhang et al., 2014 ▸; Ansari et al., 2017 ▸). The crystal structure analysis of the title compound, (Ib), was undertaken as it may help to provide a better understanding of the properties of aminopirazoles.
Figure 1.
Synthesis scheme for the title compound (Ib).
Structural commentary
There are two independent molecules (A and B) in the asymmetric unit of the title compound (Ib), as illustrated in Fig. 2 ▸. They are composed of three unsaturated rings, two of which are connected by a bridging amino group. The molecules are not planar as a result of steric repulsion between the rings, which results in some disturbance of the conjugation. Thus, the presence of a shortened intramolecular contact C2 ⋯ H11 [2.80 Å in molecule A and 2.81 Å in molecule B as compared with the sum of their van der Waals radii of 2.87 Å (Zefirov, 1997 ▸)], indicates the presence of repulsion between the pyrazole ring and the phenyl substituent. The steric strain is compensated for by the elongation of the C1—C10 bond: 1.486 (2) Å in molecule A and 1.482 (2) Å in molecule B compared to a mean bond length of 1.470 Å for a typical conjugated system (Bürgi & Dunitz, 1994 ▸). In addition, the C2—C1—C10 bond angle increases to 130.6 (2)° in both molecules, and the pyrazole and phenyl rings are twisted with respect to each other, with torsion angle C2—C1—C10—C11 being 18.1 (3)° in molecule A and −14.3 (3)° in molecule B.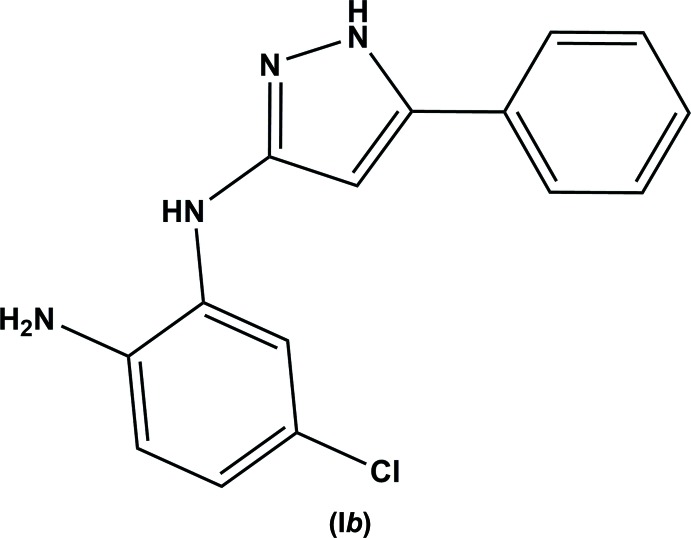
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of the two independent molecules (A and B) of compound (Ib), with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
There is an even stronger repulsion between the aminochlorophenyl and pyrazole rings linked through the bridging amino group [shortened intramolecular contacts are: C2⋯C9 = 3.25 Å (A), 3.21 Å (B); C2⋯H9 = 2.75 Å (A), 2.67 Å (B); H3⋯H4 = 2.28 Å for both molecules; C3⋯H9 = 2.76 Å for both molecules] leads to a greater twist of these unsaturated rings relative to each other; the dihedral angle between the mean planes N1/N2/C1–C3 and C4–C9 is 46.6 (1)° for molecule A and 40.0 (1)° for B. Moreover, the N3—C3 bonds [1.395 (3) Å in A and 1.394 (2) Å in B; mean value of 1.339 Å] and the N3—C4 bonds [1.408 (2) Å in A, 1.406 (2) Å in B; mean value of 1.353 Å] are elongated with respect to the mean values for such bonds, and the C2=C3—N3 bond angle is increased to 130.3 (2)° in A and 130.5 (2)° in B.
The bridging nitrogen atom, N3, has an almost planar configuration (the bond-angle sum is 356° in A and 358° in B). The N4H2 amino group has a pyramidal configuration (bond-angle sum is 329° in A and 325° in B). The C5—N4 bond, 1.422 (3) Å in A and 1.425 (3) Å in B, is elongated in comparison with the mean value of 1.394 Å; this elongation is probably caused by the involvement of the nitrogen lone pair in hydrogen bonding (Table 1 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg3 is the centroid of the C10A–C15A ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2A—H2NA⋯N4B i | 0.87 (2) | 2.44 (2) | 3.127 (3) | 136 (2) |
| N3A—H3NA⋯N1B i | 0.82 (2) | 2.17 (2) | 2.973 (2) | 168 (2) |
| N2B—H2NB⋯N4A i | 0.87 (2) | 2.50 (2) | 3.159 (3) | 134 (2) |
| N3B—H3NB⋯N1A i | 0.83 (2) | 2.20 (2) | 3.019 (2) | 169 (2) |
| N4B—H4ND⋯N1A ii | 0.89 (2) | 2.43 (2) | 3.207 (3) | 146 (2) |
| C11B—H11B⋯Cg3iii | 0.93 | 2.97 | 3.541 (2) | 121 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, molecules are linked by two pairs of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming A–B dimers (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 3 ▸). The dimers are linked by a fifth N—H⋯N hydrogen bond to form a tetramer-like arrangement (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 3 ▸). These stack up the a-axis direction, forming columns (Table 2 ▸ and Fig. 4 ▸), which are linked by C—H⋯π interactions, forming layers parallel to the ac plane.
Figure 3.
A view of the hydrogen-bonded (dashed lines; see Table 1 ▸) tetrameric units of compound (Ib). For clarity, only H atoms involved in hydrogen bonding have been included.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C15H13ClN4 |
| M r | 284.74 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 10.0709 (17), 20.322 (6), 13.886 (4) |
| β (°) | 102.776 (18) |
| V (Å3) | 2771.7 (12) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.27 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.20 × 0.10 × 0.10 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Agilent Xcalibur Sapphire3 |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012 ▸). |
| T min, T max | 0.649, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 15157, 4795, 3132 |
| R int | 0.027 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.595 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.037, 0.102, 0.94 |
| No. of reflections | 4795 |
| No. of parameters | 393 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.16, −0.21 |
Figure 4.
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of compound (Ib). The N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines and the C—H⋯π interactions as blue arrows (see Table 1 ▸). For clarity, only the H atoms involved in these interactions have been included.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.38, update February 2017; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for N,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-amine (S1; Fig. 5 ▸) gave only two relevant hits, viz. methyl 3-nitro-4-[(5-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)amino]benzoate (DIKSOG; Portilla et al., 2007 ▸) and N-(5-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)benzene-1,2-diamine (KUTFAH; Doumbia et al., 2010 ▸). They differ from compound (Ib) in the substituents on one of the aromatic rings (see Fig. 5 ▸). The molecule of DIKSOG is practically planar, probably owing to the formation of intramolecular N—H⋯O and C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds. In compound KUTFAH, while the phenyl ring is almost coplanar with the pyrazole ring (dihedral angle is ca 3.68° cf. 2.15° in DIKSOG), the o-aminophenyl ring is inclined to the pyrazole ring by ca 64.03° (cf. 5.61° in DIKSOG). This conformation is similar to that of compound (Ib). In the crystal of DIKSOG, molecules are linked by pairs of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming inversion dimers, while in the crystal of KUTFAH, molecules are linked into chains by N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds.
Figure 5.
CSD search substructure S1, and relevant hits, KUTFAH and DIKSOG.
Synthesis and crystallization
The initial 4-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]diazepine-2-thiones (IIa) and (IIb) were synthesized from the corresponding 4-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]diazepin-2-ones according to the procedure described previously (Solomko et al., 1990 ▸). The synthesis of the title compound (Ib) is illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸.
General procedure:
Hydrazine hydrate (0.5 ml, 85% aq. solution) was added to a solution of the corresponding 4-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]diazepine-2-thiones, (IIa) or (IIb), (5 mmol) in ethanol (40 ml). The mixture was heated at reflux for 3 h (TLC monitoring), then the solvent and the excess of hydrazine hydrate were removed under reduced pressure. The residue was washed with small amounts of cold alcohol. Colourless crystals of (Ia) and (Ib) were grown by recrystallization of the crude product from ethanol solution.
Spectroscopic and analytical data for (I a ):
Yield 0.91 g, 73%; m.p. 415–417 K [415–417 K from ethanol in accordance with Essassi & Salem (1985 ▸)]. IR ν max (KBr): 3410–3220, 2970, 1605, 1545, 1505, 1260, 1030, 920, 860, 810 cm−1. 1H NMR (DMSO-d 6, 400 MHz): δ 4.91 (s, 2H, NH2), 6.16 (s, 1H, CH), 6.40–6.79 (m, 3H, ArH + NH), 7.03–7.95 (m, 7H, ArH), 12.42 (s, 1H, NH) ppm. MS (EI) m/z (rel. intensity): 251 [M + H] (18), 250 [M +] (100), 249 [M – H] (52), 234 (8), 233 (7), 221 (5), 219 (13), 132 (18), 131 (10), 130 (5), 125 (5), 119 (16), 104 (6), 103 (8), 102 (4), 92 (4), 91 (4), 77 (9). Analysis calculated for C15H14N4 (250.12): C, 71.98; H, 5.64; N, 22.38; found: C, 72.12; H, 5.54; N, 22.26.
Spectroscopic and analytical data for (I b ):
Yield 0.99 g, 70%; m.p. 468–470 K. IR ν max (KBr): 3400–3210, 2975, 1600, 1560, 1500, 1250, 1145, 1000, 960, 920, 880, 855, 800 cm−1. 1H NMR (Solv, MHz): δ 4.95 (s, 2H, NH2), 6.27 (s, 1H, CH), 6.57–6.66 (m, 2H, ArH + NH), 7.30–7.79 (m, 7H, ArH), 12.49 (s, 1H, NH) ppm. MS (EI) m/z (rel. intensity): 285 [M + H] (34), 284 [M +] (100), 283 [M – H] (44), 269 (6), 268 (10), 267 (12), 255 (8), 253 (12), 168 (8), 167 (8), 166 (25), 165 (13), 164 (7), 131 (7), 119 (26), 104 (8), 103 (7), 102 (7), 91 (6), 77 (13). Analysis calculated for C15H13ClN4 (284.08): C, 63.27; H, 4.60; N, 19.68; found: C, 63.08; H, 4.71; N, 19.73.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. All of the H atoms could be located from difference-Fourier maps. The C-bound H atoms were included in calculated positions and treated as riding: C—H = 0.93 Å with 1.2U eq(C). The N-bound H atoms were located in difference-Fourier maps and freely refined.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007381/su5369sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007381/su5369Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007381/su5369Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 703162
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C15H13ClN4 | F(000) = 1184 |
| Mr = 284.74 | Dx = 1.365 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.0709 (17) Å | Cell parameters from 5031 reflections |
| b = 20.322 (6) Å | θ = 2.0–31.5° |
| c = 13.886 (4) Å | µ = 0.27 mm−1 |
| β = 102.776 (18)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 2771.7 (12) Å3 | Parallelepiped, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.20 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur Sapphire3 diffractometer | 4795 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 3132 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 16.1827 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.027 |
| ω–scan | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012). | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.649, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −24→24 |
| 15157 measured reflections | l = −16→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.102 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.94 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.064P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4795 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 393 parameters | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1A | 0.49786 (7) | 0.24353 (3) | 0.83066 (4) | 0.0730 (2) | |
| Cl1B | 0.96923 (7) | 0.24226 (3) | 0.84367 (4) | 0.0776 (2) | |
| N1A | 0.21769 (16) | 0.51489 (7) | 0.60279 (10) | 0.0457 (5) | |
| N2A | 0.18787 (17) | 0.55321 (8) | 0.67697 (11) | 0.0457 (5) | |
| N3A | 0.39006 (18) | 0.44024 (8) | 0.58852 (12) | 0.0492 (6) | |
| N4A | 0.55691 (19) | 0.39198 (9) | 0.47173 (13) | 0.0511 (6) | |
| C1A | 0.27518 (18) | 0.54304 (9) | 0.76473 (12) | 0.0415 (6) | |
| C2A | 0.36726 (19) | 0.49617 (9) | 0.74824 (12) | 0.0461 (6) | |
| C3A | 0.32764 (18) | 0.48054 (9) | 0.64684 (12) | 0.0411 (6) | |
| C4A | 0.46130 (18) | 0.38147 (8) | 0.61844 (12) | 0.0403 (6) | |
| C5A | 0.54902 (18) | 0.35744 (9) | 0.55934 (13) | 0.0421 (6) | |
| C6A | 0.61960 (19) | 0.29883 (9) | 0.58605 (14) | 0.0518 (7) | |
| C7A | 0.6070 (2) | 0.26396 (10) | 0.66977 (15) | 0.0580 (7) | |
| C8A | 0.5203 (2) | 0.28827 (9) | 0.72658 (13) | 0.0509 (7) | |
| C9A | 0.44765 (19) | 0.34626 (9) | 0.70194 (12) | 0.0460 (6) | |
| C10A | 0.26315 (19) | 0.57736 (8) | 0.85694 (12) | 0.0424 (6) | |
| C11A | 0.3742 (2) | 0.57789 (10) | 0.93726 (13) | 0.0539 (7) | |
| C12A | 0.3656 (2) | 0.60944 (11) | 1.02456 (15) | 0.0625 (8) | |
| C13A | 0.2459 (2) | 0.64019 (10) | 1.03356 (15) | 0.0594 (8) | |
| C14A | 0.1350 (2) | 0.63963 (10) | 0.95502 (15) | 0.0604 (8) | |
| C15A | 0.1432 (2) | 0.60866 (9) | 0.86679 (14) | 0.0533 (7) | |
| N1B | 0.72238 (17) | 0.52522 (8) | 0.62179 (11) | 0.0516 (5) | |
| N2B | 0.69078 (18) | 0.56217 (9) | 0.69663 (11) | 0.0513 (6) | |
| N3B | 0.88215 (17) | 0.44361 (8) | 0.60966 (12) | 0.0488 (6) | |
| N4B | 1.04647 (18) | 0.39335 (9) | 0.49141 (13) | 0.0510 (6) | |
| C1B | 0.76350 (18) | 0.54428 (9) | 0.78701 (12) | 0.0413 (6) | |
| C2B | 0.84788 (18) | 0.49384 (9) | 0.77092 (12) | 0.0451 (6) | |
| C3B | 0.81946 (18) | 0.48419 (9) | 0.66735 (12) | 0.0423 (6) | |
| C4B | 0.94813 (18) | 0.38342 (9) | 0.63783 (12) | 0.0420 (6) | |
| C5B | 1.03456 (18) | 0.35833 (9) | 0.57797 (13) | 0.0441 (6) | |
| C6B | 1.0996 (2) | 0.29824 (9) | 0.60360 (14) | 0.0543 (7) | |
| C7B | 1.0828 (2) | 0.26284 (10) | 0.68562 (15) | 0.0600 (8) | |
| C8B | 0.9971 (2) | 0.28790 (10) | 0.74217 (14) | 0.0539 (7) | |
| C9B | 0.93023 (19) | 0.34753 (9) | 0.71968 (13) | 0.0480 (6) | |
| C10B | 0.75168 (17) | 0.57770 (9) | 0.87960 (12) | 0.0403 (6) | |
| C11B | 0.8117 (2) | 0.54986 (10) | 0.97074 (13) | 0.0515 (7) | |
| C12B | 0.8070 (2) | 0.58188 (11) | 1.05840 (14) | 0.0563 (7) | |
| C13B | 0.74198 (19) | 0.64222 (10) | 1.05668 (14) | 0.0527 (7) | |
| C14B | 0.6804 (2) | 0.67007 (10) | 0.96768 (15) | 0.0573 (7) | |
| C15B | 0.6852 (2) | 0.63790 (9) | 0.87961 (14) | 0.0517 (7) | |
| H2NA | 0.120 (2) | 0.5806 (10) | 0.6599 (14) | 0.059 (6)* | |
| H3NA | 0.3590 (18) | 0.4435 (9) | 0.5292 (13) | 0.042 (5)* | |
| H2A | 0.44000 | 0.47860 | 0.79430 | 0.0550* | |
| H4NB | 0.631 (2) | 0.3782 (9) | 0.4504 (15) | 0.058 (6)* | |
| H4NA | 0.563 (2) | 0.4346 (12) | 0.4845 (16) | 0.076 (7)* | |
| H6A | 0.67640 | 0.28270 | 0.54700 | 0.0620* | |
| H7A | 0.65550 | 0.22520 | 0.68740 | 0.0700* | |
| H9A | 0.39010 | 0.36150 | 0.74100 | 0.0550* | |
| H11A | 0.45470 | 0.55700 | 0.93240 | 0.0650* | |
| H12A | 0.44070 | 0.60990 | 1.07740 | 0.0750* | |
| H13A | 0.24060 | 0.66100 | 1.09220 | 0.0710* | |
| H14A | 0.05440 | 0.66000 | 0.96080 | 0.0720* | |
| H15A | 0.06800 | 0.60880 | 0.81400 | 0.0640* | |
| H2B | 0.91050 | 0.47090 | 0.81830 | 0.0540* | |
| H2NB | 0.624 (2) | 0.5897 (10) | 0.6809 (15) | 0.059 (6)* | |
| H3NB | 0.8595 (18) | 0.4500 (9) | 0.5492 (14) | 0.045 (5)* | |
| H6B | 1.15590 | 0.28140 | 0.56470 | 0.0650* | |
| H4ND | 1.063 (2) | 0.4357 (11) | 0.5059 (15) | 0.065 (7)* | |
| H7B | 1.12810 | 0.22320 | 0.70220 | 0.0720* | |
| H4NC | 1.116 (2) | 0.3777 (10) | 0.4691 (15) | 0.062 (6)* | |
| H9B | 0.87370 | 0.36350 | 0.75900 | 0.0580* | |
| H11B | 0.85550 | 0.50940 | 0.97280 | 0.0620* | |
| H12B | 0.84760 | 0.56270 | 1.11850 | 0.0680* | |
| H13B | 0.74000 | 0.66370 | 1.11550 | 0.0630* | |
| H14B | 0.63570 | 0.71020 | 0.96620 | 0.0690* | |
| H15B | 0.64320 | 0.65700 | 0.81980 | 0.0620* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1A | 0.1159 (5) | 0.0493 (3) | 0.0465 (3) | −0.0072 (3) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.0085 (2) |
| Cl1B | 0.1147 (5) | 0.0600 (4) | 0.0563 (3) | 0.0078 (3) | 0.0148 (3) | 0.0152 (3) |
| N1A | 0.0554 (9) | 0.0491 (9) | 0.0332 (8) | 0.0080 (8) | 0.0110 (7) | −0.0007 (7) |
| N2A | 0.0530 (10) | 0.0473 (9) | 0.0363 (8) | 0.0095 (9) | 0.0087 (8) | −0.0029 (7) |
| N3A | 0.0674 (11) | 0.0510 (10) | 0.0297 (8) | 0.0155 (9) | 0.0120 (8) | 0.0032 (7) |
| N4A | 0.0593 (11) | 0.0478 (11) | 0.0510 (10) | 0.0010 (9) | 0.0224 (9) | −0.0045 (8) |
| C1A | 0.0506 (11) | 0.0394 (10) | 0.0353 (9) | −0.0022 (9) | 0.0110 (9) | 0.0019 (8) |
| C2A | 0.0547 (11) | 0.0487 (11) | 0.0330 (9) | 0.0085 (10) | 0.0059 (9) | 0.0024 (8) |
| C3A | 0.0503 (11) | 0.0394 (10) | 0.0349 (9) | 0.0028 (9) | 0.0122 (9) | 0.0033 (8) |
| C4A | 0.0456 (10) | 0.0374 (10) | 0.0349 (9) | 0.0002 (9) | 0.0025 (8) | −0.0057 (8) |
| C5A | 0.0448 (10) | 0.0397 (10) | 0.0403 (10) | −0.0049 (9) | 0.0065 (8) | −0.0070 (8) |
| C6A | 0.0520 (12) | 0.0440 (11) | 0.0577 (12) | 0.0048 (10) | 0.0085 (10) | −0.0110 (10) |
| C7A | 0.0652 (14) | 0.0389 (11) | 0.0615 (13) | 0.0079 (11) | −0.0037 (11) | −0.0020 (10) |
| C8A | 0.0666 (13) | 0.0386 (11) | 0.0404 (10) | −0.0064 (10) | −0.0032 (10) | −0.0010 (8) |
| C9A | 0.0557 (11) | 0.0439 (11) | 0.0363 (10) | −0.0007 (10) | 0.0059 (9) | −0.0035 (8) |
| C10A | 0.0543 (11) | 0.0378 (10) | 0.0365 (9) | −0.0060 (9) | 0.0130 (9) | −0.0006 (8) |
| C11A | 0.0550 (12) | 0.0610 (13) | 0.0452 (11) | −0.0021 (11) | 0.0103 (10) | −0.0064 (10) |
| C12A | 0.0704 (14) | 0.0710 (14) | 0.0434 (12) | −0.0096 (12) | 0.0070 (11) | −0.0121 (10) |
| C13A | 0.0803 (15) | 0.0569 (13) | 0.0451 (12) | −0.0094 (12) | 0.0224 (12) | −0.0136 (10) |
| C14A | 0.0703 (14) | 0.0598 (13) | 0.0566 (13) | 0.0066 (12) | 0.0261 (12) | −0.0080 (11) |
| C15A | 0.0580 (12) | 0.0562 (12) | 0.0448 (11) | 0.0044 (11) | 0.0096 (10) | −0.0028 (9) |
| N1B | 0.0612 (10) | 0.0596 (10) | 0.0348 (8) | 0.0172 (9) | 0.0124 (8) | 0.0032 (7) |
| N2B | 0.0591 (11) | 0.0596 (11) | 0.0360 (9) | 0.0234 (9) | 0.0123 (8) | 0.0060 (8) |
| N3B | 0.0626 (11) | 0.0525 (10) | 0.0327 (8) | 0.0131 (8) | 0.0135 (8) | 0.0021 (8) |
| N4B | 0.0554 (11) | 0.0484 (11) | 0.0526 (10) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0193 (9) | −0.0085 (8) |
| C1B | 0.0440 (10) | 0.0442 (10) | 0.0359 (9) | 0.0008 (9) | 0.0090 (8) | 0.0053 (8) |
| C2B | 0.0483 (11) | 0.0489 (11) | 0.0360 (10) | 0.0101 (9) | 0.0047 (8) | 0.0016 (8) |
| C3B | 0.0456 (11) | 0.0437 (10) | 0.0384 (10) | 0.0034 (9) | 0.0112 (9) | 0.0040 (8) |
| C4B | 0.0437 (10) | 0.0413 (10) | 0.0373 (10) | 0.0005 (9) | 0.0010 (8) | −0.0048 (8) |
| C5B | 0.0446 (10) | 0.0452 (11) | 0.0408 (10) | −0.0032 (9) | 0.0061 (8) | −0.0102 (9) |
| C6B | 0.0586 (12) | 0.0474 (12) | 0.0565 (12) | 0.0068 (10) | 0.0117 (10) | −0.0089 (10) |
| C7B | 0.0703 (14) | 0.0457 (12) | 0.0584 (13) | 0.0114 (11) | 0.0020 (11) | −0.0052 (10) |
| C8B | 0.0671 (13) | 0.0460 (12) | 0.0435 (10) | −0.0013 (11) | 0.0016 (10) | −0.0017 (9) |
| C9B | 0.0549 (12) | 0.0472 (11) | 0.0401 (10) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0066 (9) | −0.0033 (9) |
| C10B | 0.0416 (10) | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0380 (9) | −0.0035 (9) | 0.0119 (8) | 0.0025 (8) |
| C11B | 0.0607 (12) | 0.0507 (12) | 0.0423 (11) | 0.0063 (10) | 0.0096 (10) | 0.0021 (9) |
| C12B | 0.0603 (13) | 0.0687 (14) | 0.0383 (10) | −0.0018 (12) | 0.0073 (10) | 0.0015 (10) |
| C13B | 0.0583 (12) | 0.0567 (12) | 0.0459 (11) | −0.0104 (11) | 0.0178 (10) | −0.0134 (10) |
| C14B | 0.0655 (13) | 0.0531 (12) | 0.0565 (13) | 0.0059 (11) | 0.0206 (11) | −0.0018 (10) |
| C15B | 0.0596 (12) | 0.0520 (12) | 0.0451 (11) | 0.0099 (10) | 0.0148 (10) | 0.0075 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1A—C8A | 1.764 (2) | C7A—H7A | 0.9300 |
| Cl1B—C8B | 1.761 (2) | C9A—H9A | 0.9300 |
| N1A—C3A | 1.337 (2) | C11A—H11A | 0.9300 |
| N1A—N2A | 1.376 (2) | C12A—H12A | 0.9300 |
| N2A—C1A | 1.352 (2) | C13A—H13A | 0.9300 |
| N3A—C4A | 1.408 (2) | C14A—H14A | 0.9300 |
| N3A—C3A | 1.395 (2) | C15A—H15A | 0.9300 |
| N4A—C5A | 1.422 (3) | C1B—C2B | 1.381 (3) |
| C1A—C10A | 1.486 (2) | C1B—C10B | 1.482 (2) |
| C1A—C2A | 1.383 (3) | C2B—C3B | 1.417 (2) |
| C2A—C3A | 1.412 (2) | N2B—H2NB | 0.87 (2) |
| N2A—H2NA | 0.87 (2) | N3B—H3NB | 0.830 (19) |
| N3A—H3NA | 0.817 (18) | C4B—C9B | 1.395 (3) |
| C4A—C9A | 1.395 (2) | C4B—C5B | 1.424 (3) |
| N4A—H4NB | 0.91 (2) | N4B—H4ND | 0.89 (2) |
| N4A—H4NA | 0.88 (2) | N4B—H4NC | 0.89 (2) |
| C4A—C5A | 1.419 (3) | C5B—C6B | 1.394 (3) |
| C5A—C6A | 1.395 (3) | C6B—C7B | 1.389 (3) |
| C6A—C7A | 1.391 (3) | C7B—C8B | 1.386 (3) |
| C7A—C8A | 1.391 (3) | C8B—C9B | 1.388 (3) |
| C8A—C9A | 1.389 (3) | C10B—C11B | 1.396 (3) |
| C10A—C15A | 1.398 (3) | C10B—C15B | 1.395 (3) |
| C10A—C11A | 1.394 (3) | C11B—C12B | 1.390 (3) |
| C11A—C12A | 1.391 (3) | C12B—C13B | 1.388 (3) |
| C12A—C13A | 1.388 (3) | C13B—C14B | 1.376 (3) |
| C13A—C14A | 1.378 (3) | C14B—C15B | 1.397 (3) |
| C14A—C15A | 1.396 (3) | C2B—H2B | 0.9300 |
| N1B—N2B | 1.375 (2) | C6B—H6B | 0.9300 |
| N1B—C3B | 1.333 (2) | C7B—H7B | 0.9300 |
| C2A—H2A | 0.9300 | C9B—H9B | 0.9300 |
| N2B—C1B | 1.355 (2) | C11B—H11B | 0.9300 |
| N3B—C4B | 1.406 (2) | C12B—H12B | 0.9300 |
| N3B—C3B | 1.394 (2) | C13B—H13B | 0.9300 |
| N4B—C5B | 1.425 (3) | C14B—H14B | 0.9300 |
| C6A—H6A | 0.9300 | C15B—H15B | 0.9300 |
| N2A—N1A—C3A | 104.40 (14) | C10A—C15A—H15A | 120.00 |
| N1A—N2A—C1A | 112.47 (15) | C14A—C15A—H15A | 120.00 |
| C3A—N3A—C4A | 126.32 (15) | N2B—C1B—C2B | 105.97 (15) |
| N2A—C1A—C2A | 106.40 (15) | N2B—C1B—C10B | 123.35 (17) |
| N2A—C1A—C10A | 122.97 (16) | C2B—C1B—C10B | 130.61 (16) |
| C2A—C1A—C10A | 130.62 (16) | C1B—C2B—C3B | 105.88 (15) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A | 105.54 (16) | N1B—N2B—H2NB | 117.3 (14) |
| N1A—N2A—H2NA | 116.4 (13) | C1B—N2B—H2NB | 129.7 (14) |
| C1A—N2A—H2NA | 131.1 (13) | N1B—C3B—N3B | 118.36 (15) |
| N1A—C3A—N3A | 118.34 (15) | C3B—N3B—C4B | 126.95 (16) |
| C3A—N3A—H3NA | 114.6 (13) | C3B—N3B—H3NB | 115.5 (13) |
| C4A—N3A—H3NA | 115.0 (13) | C4B—N3B—H3NB | 115.1 (13) |
| N1A—C3A—C2A | 111.19 (16) | N1B—C3B—C2B | 110.95 (16) |
| N3A—C3A—C2A | 130.28 (17) | N3B—C3B—C2B | 130.52 (17) |
| H4NB—N4A—H4NA | 110.1 (18) | H4ND—N4B—H4NC | 107.7 (19) |
| C5A—C4A—C9A | 119.52 (16) | C5B—C4B—C9B | 119.60 (17) |
| C5A—N4A—H4NA | 109.1 (14) | C5B—N4B—H4NC | 109.7 (13) |
| N3A—C4A—C5A | 117.59 (15) | N3B—C4B—C5B | 117.48 (16) |
| N3A—C4A—C9A | 122.89 (16) | N3B—C4B—C9B | 122.91 (17) |
| C5A—N4A—H4NB | 109.5 (13) | C5B—N4B—H4ND | 109.8 (13) |
| N4A—C5A—C4A | 119.00 (16) | N4B—C5B—C4B | 119.34 (16) |
| N4A—C5A—C6A | 121.84 (17) | N4B—C5B—C6B | 122.04 (17) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A | 119.08 (16) | C4B—C5B—C6B | 118.54 (17) |
| C5A—C6A—C7A | 121.47 (18) | C5B—C6B—C7B | 121.84 (18) |
| C6A—C7A—C8A | 118.55 (18) | C6B—C7B—C8B | 118.58 (19) |
| C7A—C8A—C9A | 121.61 (17) | C7B—C8B—C9B | 121.69 (18) |
| Cl1A—C8A—C7A | 119.48 (15) | Cl1B—C8B—C7B | 119.31 (16) |
| Cl1A—C8A—C9A | 118.89 (15) | Cl1B—C8B—C9B | 118.99 (15) |
| C4A—C9A—C8A | 119.77 (17) | C4B—C9B—C8B | 119.74 (17) |
| C1A—C10A—C11A | 119.28 (17) | C1B—C10B—C11B | 119.94 (17) |
| C1A—C10A—C15A | 122.31 (16) | C1B—C10B—C15B | 122.19 (16) |
| C11A—C10A—C15A | 118.41 (16) | C11B—C10B—C15B | 117.84 (16) |
| C10A—C11A—C12A | 120.49 (19) | C10B—C11B—C12B | 120.82 (19) |
| C11A—C12A—C13A | 120.58 (19) | C11B—C12B—C13B | 120.38 (18) |
| C12A—C13A—C14A | 119.55 (19) | C12B—C13B—C14B | 119.74 (18) |
| C13A—C14A—C15A | 120.23 (19) | C13B—C14B—C15B | 119.86 (19) |
| C10A—C15A—C14A | 120.73 (18) | C10B—C15B—C14B | 121.34 (17) |
| N2B—N1B—C3B | 104.53 (14) | C1B—C2B—H2B | 127.00 |
| C3A—C2A—H2A | 127.00 | C3B—C2B—H2B | 127.00 |
| C1A—C2A—H2A | 127.00 | C5B—C6B—H6B | 119.00 |
| N1B—N2B—C1B | 112.66 (16) | C7B—C6B—H6B | 119.00 |
| C3B—N3B—C4B | 126.95 (16) | C6B—C7B—H7B | 121.00 |
| C5A—C6A—H6A | 119.00 | C8B—C7B—H7B | 121.00 |
| C7A—C6A—H6A | 119.00 | C4B—C9B—H9B | 120.00 |
| C8A—C7A—H7A | 121.00 | C8B—C9B—H9B | 120.00 |
| C6A—C7A—H7A | 121.00 | C10B—C11B—H11B | 120.00 |
| C8A—C9A—H9A | 120.00 | C12B—C11B—H11B | 120.00 |
| C4A—C9A—H9A | 120.00 | C11B—C12B—H12B | 120.00 |
| C10A—C11A—H11A | 120.00 | C13B—C12B—H12B | 120.00 |
| C12A—C11A—H11A | 120.00 | C12B—C13B—H13B | 120.00 |
| C11A—C12A—H12A | 120.00 | C14B—C13B—H13B | 120.00 |
| C13A—C12A—H12A | 120.00 | C13B—C14B—H14B | 120.00 |
| C14A—C13A—H13A | 120.00 | C15B—C14B—H14B | 120.00 |
| C12A—C13A—H13A | 120.00 | C10B—C15B—H15B | 119.00 |
| C13A—C14A—H14A | 120.00 | C14B—C15B—H15B | 119.00 |
| C15A—C14A—H14A | 120.00 | ||
| C3A—N1A—N2A—C1A | −0.5 (2) | C3B—N1B—N2B—C1B | −1.2 (2) |
| N2A—N1A—C3A—N3A | −175.01 (16) | N2B—N1B—C3B—N3B | −174.38 (17) |
| N2A—N1A—C3A—C2A | 0.5 (2) | N2B—N1B—C3B—C2B | 1.2 (2) |
| N1A—N2A—C1A—C2A | 0.2 (2) | N1B—N2B—C1B—C2B | 0.7 (2) |
| N1A—N2A—C1A—C10A | −178.67 (16) | N1B—N2B—C1B—C10B | 178.09 (17) |
| C4A—N3A—C3A—N1A | −149.84 (18) | C4B—N3B—C3B—N1B | −156.03 (18) |
| C4A—N3A—C3A—C2A | 35.7 (3) | C4B—N3B—C3B—C2B | 29.4 (3) |
| C3A—N3A—C4A—C5A | −162.61 (18) | C3B—N3B—C4B—C5B | −164.28 (18) |
| C3A—N3A—C4A—C9A | 18.2 (3) | C3B—N3B—C4B—C9B | 16.9 (3) |
| N2A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 0.1 (2) | N2B—C1B—C2B—C3B | 0.1 (2) |
| C10A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 178.87 (19) | C10B—C1B—C2B—C3B | −177.05 (19) |
| N2A—C1A—C10A—C11A | −163.29 (18) | N2B—C1B—C10B—C11B | 169.08 (19) |
| N2A—C1A—C10A—C15A | 17.6 (3) | N2B—C1B—C10B—C15B | −12.8 (3) |
| C2A—C1A—C10A—C11A | 18.1 (3) | C2B—C1B—C10B—C11B | −14.3 (3) |
| C2A—C1A—C10A—C15A | −161.0 (2) | C2B—C1B—C10B—C15B | 163.8 (2) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—N1A | −0.4 (2) | C1B—C2B—C3B—N1B | −0.8 (2) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—N3A | 174.43 (19) | C1B—C2B—C3B—N3B | 174.08 (19) |
| N3A—C4A—C5A—N4A | −2.4 (3) | N3B—C4B—C5B—N4B | −2.3 (3) |
| N3A—C4A—C5A—C6A | −179.06 (17) | N3B—C4B—C5B—C6B | −179.09 (17) |
| C9A—C4A—C5A—N4A | 176.89 (17) | C9B—C4B—C5B—N4B | 176.51 (17) |
| C9A—C4A—C5A—C6A | 0.2 (3) | C9B—C4B—C5B—C6B | −0.3 (3) |
| N3A—C4A—C9A—C8A | 179.43 (17) | N3B—C4B—C9B—C8B | 178.98 (18) |
| C5A—C4A—C9A—C8A | 0.2 (3) | C5B—C4B—C9B—C8B | 0.2 (3) |
| N4A—C5A—C6A—C7A | −177.36 (18) | N4B—C5B—C6B—C7B | −177.05 (19) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A—C7A | −0.7 (3) | C4B—C5B—C6B—C7B | −0.4 (3) |
| C5A—C6A—C7A—C8A | 0.9 (3) | C5B—C6B—C7B—C8B | 1.0 (3) |
| C6A—C7A—C8A—Cl1A | 177.79 (15) | C6B—C7B—C8B—Cl1B | 177.56 (16) |
| C6A—C7A—C8A—C9A | −0.4 (3) | C6B—C7B—C8B—C9B | −1.1 (3) |
| Cl1A—C8A—C9A—C4A | −178.35 (14) | Cl1B—C8B—C9B—C4B | −178.18 (15) |
| C7A—C8A—C9A—C4A | −0.1 (3) | C7B—C8B—C9B—C4B | 0.5 (3) |
| C1A—C10A—C11A—C12A | −179.78 (18) | C1B—C10B—C11B—C12B | 177.10 (18) |
| C15A—C10A—C11A—C12A | −0.6 (3) | C15B—C10B—C11B—C12B | −1.1 (3) |
| C1A—C10A—C15A—C14A | 179.10 (17) | C1B—C10B—C15B—C14B | −177.09 (18) |
| C11A—C10A—C15A—C14A | −0.1 (3) | C11B—C10B—C15B—C14B | 1.0 (3) |
| C10A—C11A—C12A—C13A | 0.8 (3) | C10B—C11B—C12B—C13B | 0.2 (3) |
| C11A—C12A—C13A—C14A | −0.3 (3) | C11B—C12B—C13B—C14B | 0.8 (3) |
| C12A—C13A—C14A—C15A | −0.4 (3) | C12B—C13B—C14B—C15B | −0.8 (3) |
| C13A—C14A—C15A—C10A | 0.5 (3) | C13B—C14B—C15B—C10B | −0.1 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg3 is the centroid of the C10A–C15A ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2A—H2NA···N4Bi | 0.87 (2) | 2.44 (2) | 3.127 (3) | 136 (2) |
| N3A—H3NA···N1Bi | 0.82 (2) | 2.17 (2) | 2.973 (2) | 168 (2) |
| N2B—H2NB···N4Ai | 0.87 (2) | 2.50 (2) | 3.159 (3) | 134 (2) |
| N3B—H3NB···N1Ai | 0.83 (2) | 2.20 (2) | 3.019 (2) | 169 (2) |
| N4B—H4ND···N1Aii | 0.89 (2) | 2.43 (2) | 3.207 (3) | 146 (2) |
| C11B—H11B···Cg3iii | 0.93 | 2.97 | 3.541 (2) | 121 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2.
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Ansari, A., Ali, A., Asif, M. & Shamsuzzaman, S. (2017). New J. Chem. 41, 16–41.
- Bürgi, H.-B. & Dunitz, J. D. (1994). Structure Correlation, Vol. 2, pp. 767–784. Weinheim: VCH.
- Doumbia, M. L., Bouhfid, R., Essassi, E. M. & El Ammari, L. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Essassi, E. M. & Salem, M. (1985). Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 94, 755–758.
- Gaponov, A. A., Zlenko, E. T., Shishkina, S. V., Shishkin, O. V., Antypenko, O. M., Tretiakov, S. V. & Palchikov, V. A. (2016). Med. Chem. Res. 25, 1768–1780.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Okovytyy, S. I., Sviatenko, L., Gaponov, A., Tarabara, I., Kasyan, L. & Leszczynski, J. (2009). J. Phys. Chem. A, 113, 11376–11381. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.-M., Cai, G.-X. & Zhou, C.-H. (2013). Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 13, 1963–2010. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Portilla, J., Mata, E. G., Cobo, J., Low, J. N. & Glidewell, C. (2007). Acta Cryst. C63, o510–o513. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sakya, S. M., Lundy DeMello, K. M., Minich, M. L., Rast, B., Shavnya, A., Rafka, R. J., Koss, D. A., Cheng, H., Li, J., Jaynes, B. H., Ziegler, C. B., Mann, D. W., Petras, C. F., Seibel, S. B., Silvia, A. M., George, D. M., Lund, L. A., Denis, S. S., Hickman, A., Haven, M. L. & Lynch, M. P. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16, 288–292. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Solomko, Z. F., Sharbatyan, P. A., Gaponov, A. A. & Avraraenko, V. I. (1990). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 26, 341–345.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.-G., Wu, H.-X., Lu, M.-L., Song, G.-P. & Xu, H.-H. (2013). J. Agric. Food Chem. 61, 4236–4241. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zefirov, Yu. V. (1997). Kristallografiya, 42, 936–958.
- Zhang, Z., Ojo, K. K., Vidadala, R., Huang, W., Geiger, J. A., Scheele, S., Choi, R., Reid, M. C., Keyloun, K. R., Rivas, K., Siddaramaiah, L. K., Comess, K. M., Robinson, K. P., Merta, P. J., Kifle, L., Hol, W. G. J., Parsons, M., Merritt, E. A., Maly, D. J., Verlinde, C. L. M. J., Van Voorhis, W. C. & Fan, E. (2014). ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 5, 40–44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007381/su5369sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007381/su5369Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007381/su5369Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 703162
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report







