The three title compounds are centrosymmetric. Their packing features chains linked by either pairwise C—H⋯O or C—H⋯π interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, bischalcone, methoxyphenyl ring, enone bridge, C—H⋯O hydrogen bond, C—H⋯π interactions
Abstract
In the title compounds, (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one], C26H22O4 (I), (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis[1-(3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one], C26H22O4 (II) and (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis[1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one], C28H26O6 (III), the asymmetric unit consists of a half-molecule, completed by crystallographic inversion symmetry. The dihedral angles between the central and terminal benzene rings are 56.98 (8), 7.74 (7) and 7.73 (7)° for (I), (II) and (III), respectively. In the crystal of (I), molecules are linked by pairs of C—H⋯π interactions into chains running parallel to [101]. The packing for (II) and (III), features inversion dimers linked by pairs of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming R 2 2(16) and R 2 2(14) ring motifs, respectively, as parts of [201] and [101] chains, respectively.
Chemical context
Chalcones and their derivatives are natural or synthetic 1,3-diaryl-2-propenones that may exist in cis and trans isomeric forms, the trans form being thermodynamically stable. The α,β-unsaturated enone C=C—C(=O)—C moiety in the chalcone structure plays an important role in the biological activities of these species (Husain et al., 2013 ▸; Abdel Ghani et al., 2008 ▸). As a result of the -enone system, these molecules present relatively low redox potentials and have a greater probability of undergoing electron-transfer reactions. Apart from the biological activities, the photophysical properties of chalcone derivatives also attracted considerable attention from both chemists and physicists. Many chalcone derivatives have been reported in relation to non-linear optics (NLO), photorefractive polymers, holographic recording materials and fluorescent probes for sensing metal ions (Ruzié et al., 2009 ▸; Wei et al., 2011 ▸; Chandra Shekhara Shetty et al., 2016 ▸). As part of our studies in this area, we report herein the syntheses and structures of three new bischalcone derivatives, (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C26H22O4 (I), (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1-(3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C26H22O4 (II) and (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C28H26O6 (III).
Structural commentary
The molecular structures of (I)–(III) are shown in Figs. 1 ▸–3 ▸ ▸, respectively. The asymmetric unit of each compound consists of a half-molecule, with the complete molecule generated by a crystallographic inversion centre at the centroid of the central benzene ring.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of (I), showing 40% probability displacement ellipsoids. [Symmetry code: (A) −x, 1 − y, −z.]
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of (II), showing 40% probability displacement ellipsoids. [Symmetry code: (A) 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z.]
Figure 3.
The molecular structure of (III), showing 40% probability displacement ellipsoids. [Symmetry code: (A) 2 − x, −y, 1 − z.]
Each compound is constructed from two aromatic rings (centre benzene and terminal methoxyphenyl rings), which are linked by a C=C—C(=O)—C enone bridge. Despite having an extra methoxy substituent, the conformation of compounds (II) and (III) are very similar, as indicated by the dihedral angles between the rings of 7.74 (7) and 7.73 (7)°, respectively. The enone linkage moiety of compounds (II) and (III) has similar torsion angles [O1—C7—C8—C9 = 0.2 (2) and 7.3 (2)°, respectively], but compound (II) has a higher overall planarity than compound (III), as its enone bridge forms a smaller torsion angle with the methoxyphenyl ring [C1—C6—C7—O1 = −6.5 (2)°] and benzene ring [C8—C9—C10—C11 = −1.7 (2)°; C1—C6—C7—O1 = 7.3 (2)° and C8—C9—C10—C11 = −5.6 (2)° in (III)]. Compared to the nearly coplanar arrangement of rings in compounds (II) and (III), compound (I) is substantially twisted [O1—C7—C8—C9 = −13.5 (2)° and C1—C6—C7—O1 = 143.60 (15)°] about the enone bridge, which may arise from steric repulsion with the ortho-O2 atom. Hence, the dihedral angle between the 2-methoxyphenyl and benzene rings in (I) increases to 56.98 (8)°. Key torsion angles are tabulated in Table 1 ▸. The C atoms of the methoxy groups are close to the planes of their attached rings in all cases: for (I), deviation of C13 = 0.163 (2) Å, for (II), deviation of C13 = 0.329 (2) Å, and for (III), deviations of C13 and C14 = 0.091 (2) and −0.266 (2) Å, respectively.
Table 1. Selected torsion and dihedral angles (°) for compounds (I)–(III).
Dihedral 1 is the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the terminal methoxyphenyl and central benzene rings.
| Compound | C1—C6—C7—O1 | O1—C7—C8—C9 | C8—C9—C10—C11 | Dihedral 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | −13.5 (2) | 143.60 (15) | 167.44 (15) | 56.98 (8) |
| (II) | 0.2 (2) | 6.5 (2) | −1.6 (2) | 7.74 (7) |
| (III) | 7.3 (2) | 7.3 (2) | −5.6 (2) | 7.73 (7) |
Supramolecular features
The packing of (I) is consolidated by a weak C—H⋯π contact (Table 2 ▸) involving a hydrogen atom from the phenyl ring and the centroid of the central benzene ring (C10–C12/C10A–C12A). This C—H⋯π interaction connects the molecules of (I) into chains parallel to the [101] direction with a C—H⋯π distance of 2.74 Å (Fig. 4 ▸). In the supramolecular assemblies of compounds (II) and (III), the molecules are connected by pairs of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 2 ▸) into inversion dimers, which form  (16) and
(16) and  (14) ring motifs, respectively. The dimers are parts of [201] chains (Fig. 5 ▸) in (II), while molecules in compound (III) are parts of chains propagating in the [101] direction (Fig. 6 ▸).
(14) ring motifs, respectively. The dimers are parts of [201] chains (Fig. 5 ▸) in (II), while molecules in compound (III) are parts of chains propagating in the [101] direction (Fig. 6 ▸).
Table 2. Hydrogen-bonding geometry (Å, °) for compounds (I)–(III).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C10–C12/C10A–C12A ring.
| Compound | D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | C5—H5A⋯Cg1i | 0.93 | 2.74 | 3.491 (3) | 139 |
| (II) | C13—H13C⋯O1ii | 0.96 | 2.60 | 3.503 (3) | 157 |
| (III) | C12—H12A⋯O1iii | 0.96 | 2.47 | 3.337 (3) | 156 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 1 + x, y, 1 + z; (ii) 3 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z; (iii) 1 − x, −y, −z.
Figure 4.
Fragment of a [101] chain of molecules of (I) linked by pairs of weak C—H⋯π interactions (dashed lines).
Figure 5.
Fragment of a [201] chain of molecules of (II) linked by pairs of weak C—H⋯O interactions (dashed lines).
Figure 6.
Fragment of a [101] chain of molecules of (III) linked by pairs of weak C—H⋯O interactions (dashed lines).
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.38, last update November 2016; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) using (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one) as the main skeleton, revealed the presence of four structures containing the bischalcone moiety with different substituents, similar to the title compounds in this study. These include 3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis[1-(X)prop-2-en-1-one], where X = 2-hydroxyphenyl (DIDNUB; Gaur & Mishra, 2013 ▸), 4-chlorophenyl (KIKFUG; Harrison et al., 2007 ▸), 4-methoxyphenyl (UDUPUF; Harrison et al., 2007a
▸) and 3,4-methoxyphenyl (UDUQAM; Harrison et al., 2007b
▸). It is notable that UDUPUF and UDUQAH are positional isomers of compounds (I) and (II), and (III), respectively, differing from them only in the location of the methoxy substituent (see scheme below). The dihedral angles between the central and terminal phenyl ring in these compounds vary from 10.9 to 46.3°. In terms of the title compounds, (II) and (III) are more planar [7.74 (7) and 7.73 (7)°] while compound (I) is more twisted [56.98 (8)°]. The supramolecular assembly in UDUPUF also depends upon a single C—H⋯O hydrogen bond between inversion-related pairs of molecules, forming a centrosymmetric dimer.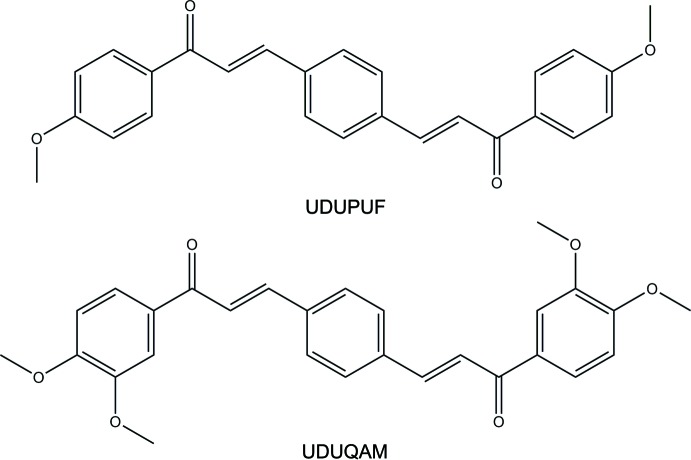
Synthesis and crystallization
A mixture of the corresponding methoxyacetophenone (0.02 mol) and terephthaldialdehyde (0.01 mol) was dissolved in methanol (20 ml). A catalytic amount of NaOH was added to the solution dropwise with vigorous stirring. The reaction mixtures were stirred for about 5–6 h at room temperature. The resultant crude products were filtered, washed successively with distilled water and recrystallized from ethanol to obtain the title compounds. Yellow blocks [(I) and (III)] and yellow needles (II) were recrystallized using the solvents noted below.
(2 E ,2′ E )-3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C26H22O4 (I)
Solvent for growing crystals: acetone; yield 85%, m.p. 429–431 K. FT–IR [ATR (solid) cm−1]: 3010 (Ar, C—H, ν), 2945 (methyl, C—H, νs), 2842 (methyl, C—H, ν), 1658 (C=O, ν), 1598, 1417(Ar, C=C, ν), 1245, 1055 (C—O, ν). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ ppm 7.677–7.632 (m, 8H, 5CH, 8CH, 11CH, 12CH), 7.536–7.504 (t, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz 3CH), 7.496–7.437 (d, 2H, J = 15.9 Hz, 9CH), 7.095–7.065 (t, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, 4CH), 7.048–7.031 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, 2CH), 3.944 (s, 6H, 13CH3). 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ ppm 192.61 (C7), 158.23 (C1), 141.48 (C9), 136.95 (C10), 133.09 (C3), 130.47 (C5), 129.17 (C6), 128.84 (C11, C12), 127.91 (C4), 120.84 (C8), 111.69 (C2), 55.80 (C13).
(2 E ,2′ E )-3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1-(3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C26H22O4 (II)
Solvent for growing crystals: chloroform and methanol; yield 85%, m.p. 444–446 K. FT–IR [ATR (solid) cm−1]: 3074 (Ar, C—H, ν), 2952 (methyl, C—H, νs), 2839 (methyl, C—H, ν), 1658 (C=O, ν), 1582, 1414 (Ar, C=C, ν), 1259, 1022 (C—O, ν). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ ppm 7.855–7.823 (d, 2H, J = 15.7 Hz, 8CH), 7.722 (s, 4H, 11CH, 12CH) , 7.650–7.635 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, 5CH), 7.606–7.574 (m, 2H, 1CH, 9CH), 7.473–441 (t, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, 4CH), 7.189–7.172 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, 3CH), 3.924 (s, 6H, 13CH3). 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ ppm 189.99 (C7), 159.99 (C2), 143.57 (C9), 139.46 (C10), 136.92 (C6), 129.65 (C5), 128.98 (C11, C12), 123.14 (C8), 121.08 (C3), 119.45 (C4), 112.96 (C1), 55.53 (C13)
(2 E ,2′ E )-3,3′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C28H26O6 (III)
Solvent for growing crystals: acetone; yield 85%, m.p. 479–481 K. FT–IR [ATR (solid) cm−1]: 3018 (Ar, C—H, ν), 2962 (methyl, C—H, νs), 2836 (methyl, C—H, ν), 1651 (C=O, ν), 1592, 1418 (Ar, C=C, ν), 1240, 1017 (C—O, ν). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ ppm 7.857–7.826 (d, 2H, J = 15.6 Hz, 8CH), 7.740–7.720 (m, 6H, 5CH, 11CH, 12CH), 7.666 (s, 2H, 1CH), 7.651–7.619 (d, 2H, J = 15.6 Hz, 9CH), 6.984–6.967 (d, 2H, J = 8.4 Hz, 4CH), 4.012–4.009 (d, 12H, 13CH3, 14CH3). 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ ppm 188.34 (C7), 153.47 (C3), 149.37 (C2), 142.80 (C9), 136.94 (C10), 131.22 (C6), 128.89 (C11, C12), 123.11 (C5), 122.62 (C8), 110.82 (C4), 110.01 (C1), 56.15 (C14), 66.10 (C13)
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. In (I), (II) and (III), the C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically [C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å] and refined using a riding model with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C-methyl) and 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | (III) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | |||
| Chemical formula | C26H22O4 | C26H22O4 | C28H26O6 |
| M r | 398.43 | 398.43 | 458.49 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 294 | 294 | 294 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 7.1078 (11), 24.544 (4), 6.0449 (9) | 5.2626 (5), 15.6157 (14), 12.4824 (11) | 6.9595 (6), 21.0272 (17), 8.3297 (7) |
| β (°) | 101.898 (2) | 98.760 (2) | 103.602 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 1031.9 (3) | 1013.83 (16) | 1184.77 (17) |
| Z | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.39 × 0.35 × 0.18 | 0.90 × 0.48 × 0.09 | 0.35 × 0.27 × 0.16 |
| Data collection | |||
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector | Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector | Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.883, 0.985 | 0.874, 0.992 | 0.890, 0.985 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 8322, 2183, 1705 | 17791, 2458, 1574 | 12532, 3165, 2328 |
| R int | 0.024 | 0.043 | 0.030 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.634 | 0.662 | 0.683 |
| Refinement | |||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.040, 0.119, 1.03 | 0.044, 0.132, 1.03 | 0.049, 0.136, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 2183 | 2458 | 3165 |
| No. of parameters | 137 | 137 | 156 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.19, −0.14 | 0.14, −0.14 | 0.20, −0.16 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II, III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678IIIsup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678Isup5.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678IIsup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678IIIsup7.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
AS, HCK and LYT thank the Malaysian Government for MyBrain15 (MyPhD) scholarships. The authors thank Vidya Vikas Research & Development Centre for the facilities and encouragement.
supplementary crystallographic information
(I) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Crystal data
| C26H22O4 | F(000) = 420 |
| Mr = 398.43 | Dx = 1.282 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.1078 (11) Å | Cell parameters from 3004 reflections |
| b = 24.544 (4) Å | θ = 2.9–26.4° |
| c = 6.0449 (9) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 101.898 (2)° | T = 294 K |
| V = 1031.9 (3) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 2 | 0.39 × 0.35 × 0.18 mm |
(I) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2183 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1705 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.024 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.8°, θmin = 1.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.883, Tmax = 0.985 | k = −24→31 |
| 8322 measured reflections | l = −7→7 |
(I) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.119 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0541P)2 + 0.2315P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2183 reflections | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 137 parameters | Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
(I) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
(I) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.51518 (16) | 0.40818 (5) | 0.74340 (18) | 0.0615 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.57299 (19) | 0.32593 (5) | 0.2133 (2) | 0.0652 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.7420 (2) | 0.33535 (6) | 0.3621 (3) | 0.0492 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.9148 (3) | 0.31024 (8) | 0.3517 (4) | 0.0689 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.9237 | 0.2877 | 0.2307 | 0.083* | |
| C3 | 1.0731 (3) | 0.31908 (9) | 0.5223 (4) | 0.0802 (6) | |
| H3A | 1.1891 | 0.3026 | 0.5138 | 0.096* | |
| C4 | 1.0640 (3) | 0.35160 (8) | 0.7040 (4) | 0.0731 (6) | |
| H4A | 1.1715 | 0.3565 | 0.8194 | 0.088* | |
| C5 | 0.8930 (2) | 0.37687 (7) | 0.7125 (3) | 0.0545 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.8854 | 0.3988 | 0.8357 | 0.065* | |
| C6 | 0.7315 (2) | 0.37030 (6) | 0.5413 (2) | 0.0420 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.5545 (2) | 0.40138 (6) | 0.5584 (2) | 0.0426 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.4371 (2) | 0.42573 (6) | 0.3525 (2) | 0.0430 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.4840 | 0.4266 | 0.2198 | 0.052* | |
| C9 | 0.2652 (2) | 0.44645 (6) | 0.3551 (2) | 0.0416 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.2239 | 0.4435 | 0.4909 | 0.050* | |
| C10 | 0.13276 (19) | 0.47340 (5) | 0.1704 (2) | 0.0379 (3) | |
| C11 | −0.0569 (2) | 0.48284 (6) | 0.1921 (2) | 0.0417 (3) | |
| H11A | −0.0958 | 0.4713 | 0.3222 | 0.050* | |
| C12 | 0.18710 (19) | 0.49116 (6) | −0.0255 (2) | 0.0413 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.3122 | 0.4854 | −0.0442 | 0.050* | |
| C13 | 0.5741 (4) | 0.29130 (8) | 0.0256 (3) | 0.0783 (6) | |
| H13A | 0.4472 | 0.2896 | −0.0672 | 0.117* | |
| H13B | 0.6140 | 0.2554 | 0.0785 | 0.117* | |
| H13C | 0.6619 | 0.3054 | −0.0614 | 0.117* |
(I) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0571 (7) | 0.0849 (9) | 0.0427 (6) | 0.0192 (6) | 0.0106 (5) | 0.0041 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0741 (8) | 0.0619 (8) | 0.0550 (7) | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0104 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0528 (9) | 0.0429 (8) | 0.0539 (9) | 0.0073 (7) | 0.0153 (7) | 0.0099 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0705 (12) | 0.0593 (11) | 0.0838 (13) | 0.0179 (9) | 0.0322 (11) | 0.0019 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0479 (11) | 0.0703 (13) | 0.1266 (19) | 0.0173 (9) | 0.0276 (12) | 0.0082 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0414 (9) | 0.0636 (12) | 0.1088 (16) | 0.0044 (8) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0043 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0437 (8) | 0.0469 (9) | 0.0693 (11) | 0.0002 (7) | 0.0032 (7) | 0.0037 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0406 (7) | 0.0372 (7) | 0.0488 (8) | 0.0027 (6) | 0.0107 (6) | 0.0094 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0398 (7) | 0.0430 (8) | 0.0448 (8) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0084 (6) | 0.0031 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0436 (8) | 0.0441 (8) | 0.0421 (8) | 0.0055 (6) | 0.0108 (6) | 0.0051 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0436 (8) | 0.0444 (8) | 0.0369 (7) | 0.0047 (6) | 0.0082 (6) | 0.0003 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0388 (7) | 0.0374 (7) | 0.0371 (7) | 0.0033 (5) | 0.0071 (5) | −0.0034 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0422 (7) | 0.0478 (8) | 0.0370 (7) | 0.0042 (6) | 0.0127 (6) | 0.0026 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0339 (7) | 0.0485 (8) | 0.0430 (7) | 0.0043 (6) | 0.0116 (6) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C13 | 0.1169 (18) | 0.0615 (12) | 0.0537 (11) | 0.0150 (11) | 0.0114 (11) | −0.0064 (9) |
(I) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C7 | 1.2187 (17) | C7—C8 | 1.474 (2) |
| O2—C1 | 1.364 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.3267 (19) |
| O2—C13 | 1.419 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.387 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.4616 (19) |
| C1—C6 | 1.396 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.378 (3) | C10—C12 | 1.3897 (19) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C10—C11 | 1.4002 (19) |
| C3—C4 | 1.370 (3) | C11—C12i | 1.3760 (19) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.375 (2) | C12—C11i | 1.3761 (19) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.387 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.4932 (19) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C1—O2—C13 | 118.66 (14) | C9—C8—C7 | 120.50 (13) |
| O2—C1—C2 | 124.22 (16) | C9—C8—H8A | 119.8 |
| O2—C1—C6 | 115.79 (13) | C7—C8—H8A | 119.8 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.87 (16) | C8—C9—C10 | 127.89 (13) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.34 (18) | C8—C9—H9A | 116.1 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.3 | C10—C9—H9A | 116.1 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.3 | C12—C10—C11 | 118.03 (13) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.72 (17) | C12—C10—C9 | 122.99 (12) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.1 | C11—C10—C9 | 118.97 (12) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.1 | C12i—C11—C10 | 121.57 (12) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.73 (19) | C12i—C11—H11A | 119.2 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.6 | C10—C11—H11A | 119.2 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.6 | C11i—C12—C10 | 120.40 (12) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.43 (18) | C11i—C12—H12A | 119.8 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.3 | C10—C12—H12A | 119.8 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.3 | O2—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.81 (14) | O2—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.92 (14) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 123.27 (14) | O2—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C8 | 121.49 (13) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 119.30 (13) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.12 (12) | ||
| C13—O2—C1—C2 | −4.7 (2) | C5—C6—C7—O1 | −36.6 (2) |
| C13—O2—C1—C6 | 179.21 (14) | C1—C6—C7—O1 | 143.60 (15) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | −174.24 (17) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 140.06 (15) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.7 (3) | C1—C6—C7—C8 | −39.8 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.8 (3) | O1—C7—C8—C9 | −13.5 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.5 (3) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 169.90 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.4 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 178.03 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 2.8 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C12 | −13.8 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −177.02 (15) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 167.44 (15) |
| O2—C1—C6—C5 | 172.83 (13) | C12—C10—C11—C12i | 0.1 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −3.4 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12i | 178.90 (13) |
| O2—C1—C6—C7 | −7.4 (2) | C11—C10—C12—C11i | −0.1 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 176.38 (14) | C9—C10—C12—C11i | −178.84 (13) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x, −y+1, −z.
(II) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Crystal data
| C26H22O4 | F(000) = 420 |
| Mr = 398.43 | Dx = 1.305 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.2626 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 2940 reflections |
| b = 15.6157 (14) Å | θ = 2.6–27.7° |
| c = 12.4824 (11) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 98.760 (2)° | T = 294 K |
| V = 1013.83 (16) Å3 | Needle, yellow |
| Z = 2 | 0.90 × 0.48 × 0.09 mm |
(II) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2458 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1574 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.043 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.1°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012) | h = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.874, Tmax = 0.992 | k = −20→20 |
| 17791 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
(II) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.132 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0567P)2 + 0.138P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2458 reflections | Δρmax = 0.14 e Å−3 |
| 137 parameters | Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
(II) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
(II) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 1.3466 (2) | 0.50160 (7) | 0.83740 (9) | 0.0753 (4) | |
| O2 | 2.0704 (2) | 0.69588 (8) | 1.00094 (10) | 0.0771 (4) | |
| C1 | 1.6959 (3) | 0.63162 (9) | 0.89251 (12) | 0.0502 (4) | |
| H1A | 1.6962 | 0.5856 | 0.9399 | 0.060* | |
| C2 | 1.8795 (3) | 0.69465 (10) | 0.91308 (12) | 0.0552 (4) | |
| C3 | 1.8786 (3) | 0.76279 (11) | 0.84322 (15) | 0.0680 (5) | |
| H3A | 2.0034 | 0.8052 | 0.8572 | 0.082* | |
| C4 | 1.6943 (3) | 0.76859 (11) | 0.75284 (16) | 0.0723 (5) | |
| H4A | 1.6945 | 0.8150 | 0.7062 | 0.087* | |
| C5 | 1.5086 (3) | 0.70582 (10) | 0.73089 (13) | 0.0583 (4) | |
| H5A | 1.3841 | 0.7100 | 0.6697 | 0.070* | |
| C6 | 1.5086 (3) | 0.63679 (9) | 0.80022 (11) | 0.0461 (3) | |
| C7 | 1.3200 (3) | 0.56519 (9) | 0.78002 (11) | 0.0499 (4) | |
| C8 | 1.1041 (3) | 0.57169 (10) | 0.69022 (12) | 0.0525 (4) | |
| H8A | 1.0879 | 0.6207 | 0.6473 | 0.063* | |
| C9 | 0.9345 (3) | 0.51020 (9) | 0.66922 (11) | 0.0505 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.9579 | 0.4629 | 0.7149 | 0.061* | |
| C10 | 0.7126 (2) | 0.50652 (9) | 0.58281 (10) | 0.0450 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.6491 (3) | 0.57310 (9) | 0.50998 (11) | 0.0514 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.7478 | 0.6228 | 0.5161 | 0.062* | |
| C12 | 0.5587 (3) | 0.43363 (10) | 0.57116 (11) | 0.0522 (4) | |
| H12A | 0.5971 | 0.3884 | 0.6194 | 0.063* | |
| C13 | 2.1228 (4) | 0.61900 (12) | 1.05960 (15) | 0.0766 (6) | |
| H13A | 2.2657 | 0.6275 | 1.1163 | 0.115* | |
| H13B | 2.1640 | 0.5748 | 1.0117 | 0.115* | |
| H13C | 1.9743 | 0.6024 | 1.0908 | 0.115* |
(II) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0691 (8) | 0.0679 (7) | 0.0765 (8) | −0.0179 (6) | −0.0289 (6) | 0.0158 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0662 (8) | 0.0728 (8) | 0.0805 (8) | −0.0176 (6) | −0.0268 (6) | −0.0033 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0443 (8) | 0.0523 (8) | 0.0509 (8) | −0.0004 (6) | −0.0027 (6) | −0.0046 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0451 (8) | 0.0557 (9) | 0.0609 (9) | −0.0035 (7) | −0.0040 (7) | −0.0106 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0536 (10) | 0.0573 (10) | 0.0894 (12) | −0.0104 (8) | −0.0009 (9) | −0.0014 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0619 (11) | 0.0631 (10) | 0.0882 (13) | −0.0042 (8) | −0.0010 (9) | 0.0156 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0494 (9) | 0.0604 (9) | 0.0612 (9) | 0.0040 (7) | −0.0042 (7) | 0.0039 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0369 (7) | 0.0511 (8) | 0.0480 (7) | 0.0035 (6) | −0.0007 (6) | −0.0063 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0418 (8) | 0.0558 (8) | 0.0486 (8) | 0.0010 (6) | −0.0044 (6) | −0.0040 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0435 (8) | 0.0583 (8) | 0.0513 (8) | 0.0010 (7) | −0.0072 (6) | −0.0015 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0450 (8) | 0.0561 (8) | 0.0464 (7) | 0.0026 (6) | −0.0063 (6) | −0.0029 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0366 (7) | 0.0524 (8) | 0.0432 (7) | 0.0042 (6) | −0.0031 (6) | −0.0071 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0442 (8) | 0.0511 (8) | 0.0550 (8) | −0.0035 (6) | −0.0048 (7) | −0.0032 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0453 (8) | 0.0549 (8) | 0.0516 (8) | 0.0015 (6) | −0.0076 (6) | 0.0035 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0648 (11) | 0.0864 (13) | 0.0689 (11) | −0.0082 (9) | −0.0214 (9) | 0.0006 (9) |
(II) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C7 | 1.2199 (17) | C7—C8 | 1.4729 (18) |
| O2—C2 | 1.3698 (17) | C8—C9 | 1.310 (2) |
| O2—C13 | 1.411 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.376 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.4652 (17) |
| C1—C6 | 1.3998 (18) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9300 | C10—C11 | 1.3882 (19) |
| C2—C3 | 1.375 (2) | C10—C12 | 1.392 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.374 (2) | C11—C12i | 1.3765 (18) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.382 (2) | C12—C11i | 1.3766 (18) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.382 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.491 (2) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C2—O2—C13 | 117.70 (12) | C9—C8—C7 | 121.65 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.92 (14) | C9—C8—H8A | 119.2 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 120.0 | C7—C8—H8A | 119.2 |
| C6—C1—H1A | 120.0 | C8—C9—C10 | 128.20 (14) |
| O2—C2—C3 | 115.34 (13) | C8—C9—H9A | 115.9 |
| O2—C2—C1 | 124.61 (14) | C10—C9—H9A | 115.9 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.05 (14) | C11—C10—C12 | 117.76 (12) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.36 (15) | C11—C10—C9 | 122.57 (13) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.8 | C12—C10—C9 | 119.67 (13) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.8 | C12i—C11—C10 | 120.65 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.36 (16) | C12i—C11—H11A | 119.7 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.8 | C10—C11—H11A | 119.7 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.8 | C11i—C12—C10 | 121.59 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.78 (14) | C11i—C12—H12A | 119.2 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 120.1 | C10—C12—H12A | 119.2 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 120.1 | O2—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.53 (13) | O2—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 122.86 (12) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 117.59 (13) | O2—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C8 | 120.62 (13) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 119.81 (12) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.57 (13) | ||
| C13—O2—C2—C3 | −164.12 (17) | C1—C6—C7—O1 | −6.5 (2) |
| C13—O2—C2—C1 | 16.2 (2) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −7.6 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—O2 | 179.81 (14) | C1—C6—C7—C8 | 173.97 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.2 (2) | O1—C7—C8—C9 | 0.2 (2) |
| O2—C2—C3—C4 | −179.41 (16) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 179.71 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.3 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −179.20 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.3 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.7 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.0 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C12 | 177.64 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.5 (2) | C12—C10—C11—C12i | −0.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −177.93 (16) | C9—C10—C11—C12i | 178.90 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.5 (2) | C11—C10—C12—C11i | 0.4 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 177.94 (14) | C9—C10—C12—C11i | −178.91 (14) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | 171.91 (15) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
(III) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Crystal data
| C28H26O6 | F(000) = 484 |
| Mr = 458.49 | Dx = 1.285 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.9595 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 3549 reflections |
| b = 21.0272 (17) Å | θ = 2.7–28.5° |
| c = 8.3297 (7) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 103.602 (2)° | T = 294 K |
| V = 1184.77 (17) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 2 | 0.35 × 0.27 × 0.16 mm |
(III) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3165 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2328 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.030 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 29.0°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012) | h = −9→8 |
| Tmin = 0.890, Tmax = 0.985 | k = −28→26 |
| 12532 measured reflections | l = −11→11 |
(III) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.136 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0557P)2 + 0.2808P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3165 reflections | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 156 parameters | Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
(III) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
(III) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.26810 (16) | 0.04480 (7) | 0.05640 (13) | 0.0667 (4) | |
| O2 | −0.37696 (15) | 0.15896 (5) | 0.01870 (14) | 0.0560 (3) | |
| O3 | −0.33472 (18) | 0.22511 (6) | 0.28240 (17) | 0.0694 (4) | |
| C1 | −0.04399 (19) | 0.11677 (6) | 0.10365 (16) | 0.0377 (3) | |
| H1A | −0.0610 | 0.0919 | 0.0090 | 0.045* | |
| C2 | −0.1959 (2) | 0.15447 (6) | 0.12601 (17) | 0.0399 (3) | |
| C3 | −0.1726 (2) | 0.19126 (7) | 0.2696 (2) | 0.0459 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.0049 (2) | 0.19044 (7) | 0.3851 (2) | 0.0525 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.0217 | 0.2154 | 0.4796 | 0.063* | |
| C5 | 0.1585 (2) | 0.15265 (7) | 0.36105 (18) | 0.0469 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.2779 | 0.1525 | 0.4398 | 0.056* | |
| C6 | 0.13686 (19) | 0.11510 (6) | 0.22134 (16) | 0.0369 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.2924 (2) | 0.07224 (7) | 0.18910 (16) | 0.0413 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.4765 (2) | 0.06233 (7) | 0.31697 (16) | 0.0419 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.4879 | 0.0794 | 0.4218 | 0.050* | |
| C9 | 0.62488 (19) | 0.02971 (7) | 0.28517 (16) | 0.0385 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.6062 | 0.0140 | 0.1782 | 0.046* | |
| C10 | 0.81526 (18) | 0.01514 (6) | 0.39711 (15) | 0.0348 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.8724 (2) | 0.03954 (7) | 0.55600 (16) | 0.0422 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.7872 | 0.0664 | 0.5947 | 0.051* | |
| C12 | 0.9466 (2) | −0.02452 (7) | 0.34276 (16) | 0.0429 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.9117 | −0.0412 | 0.2364 | 0.051* | |
| C13 | −0.4046 (3) | 0.12540 (11) | −0.1316 (2) | 0.0727 (6) | |
| H13A | −0.5375 | 0.1316 | −0.1950 | 0.109* | |
| H13B | −0.3816 | 0.0809 | −0.1092 | 0.109* | |
| H13C | −0.3135 | 0.1409 | −0.1929 | 0.109* | |
| C14 | −0.3309 (3) | 0.25570 (12) | 0.4350 (3) | 0.0920 (8) | |
| H14A | −0.4595 | 0.2727 | 0.4331 | 0.138* | |
| H14B | −0.2360 | 0.2896 | 0.4516 | 0.138* | |
| H14C | −0.2948 | 0.2255 | 0.5234 | 0.138* |
(III) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0427 (6) | 0.1049 (10) | 0.0443 (6) | 0.0272 (6) | −0.0066 (5) | −0.0257 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0389 (6) | 0.0653 (7) | 0.0565 (6) | 0.0185 (5) | −0.0031 (5) | −0.0026 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0576 (7) | 0.0680 (8) | 0.0820 (9) | 0.0234 (6) | 0.0149 (6) | −0.0190 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0349 (7) | 0.0413 (7) | 0.0355 (6) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0056 (5) | 0.0013 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0344 (7) | 0.0387 (7) | 0.0443 (7) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0048 (5) | 0.0051 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0434 (8) | 0.0380 (7) | 0.0578 (9) | 0.0059 (6) | 0.0149 (7) | −0.0026 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0523 (9) | 0.0492 (9) | 0.0544 (9) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0092 (7) | −0.0169 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0378 (7) | 0.0522 (8) | 0.0469 (8) | −0.0014 (6) | 0.0024 (6) | −0.0087 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0308 (6) | 0.0414 (7) | 0.0372 (6) | 0.0006 (5) | 0.0052 (5) | 0.0015 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0306 (7) | 0.0553 (8) | 0.0357 (6) | 0.0048 (6) | 0.0030 (5) | −0.0022 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0327 (7) | 0.0572 (8) | 0.0325 (6) | 0.0042 (6) | 0.0010 (5) | −0.0027 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0303 (7) | 0.0504 (8) | 0.0316 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0010 (5) | 0.0006 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0274 (6) | 0.0443 (7) | 0.0306 (6) | −0.0005 (5) | 0.0026 (5) | 0.0037 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0323 (7) | 0.0559 (8) | 0.0365 (7) | 0.0091 (6) | 0.0040 (5) | −0.0049 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0358 (7) | 0.0574 (9) | 0.0316 (6) | 0.0054 (6) | 0.0004 (5) | −0.0066 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0523 (11) | 0.0953 (14) | 0.0582 (10) | 0.0179 (10) | −0.0117 (8) | −0.0150 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0722 (14) | 0.0934 (16) | 0.1191 (19) | 0.0054 (12) | 0.0398 (13) | −0.0499 (15) |
(III) (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis[1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one] . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C7 | 1.2229 (17) | C8—C9 | 1.318 (2) |
| O2—C2 | 1.3660 (16) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| O2—C13 | 1.410 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.4621 (16) |
| O3—C3 | 1.3593 (18) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| O3—C14 | 1.419 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.3877 (18) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3688 (19) | C10—C12 | 1.3893 (19) |
| C1—C6 | 1.4022 (18) | C11—C12i | 1.3781 (18) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9300 | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.401 (2) | C12—C11i | 1.3780 (18) |
| C3—C4 | 1.376 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.384 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3848 (19) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.4807 (19) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.4756 (17) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C2—O2—C13 | 117.30 (12) | C7—C8—H8A | 119.4 |
| C3—O3—C14 | 117.82 (15) | C8—C9—C10 | 128.07 (12) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.95 (13) | C8—C9—H9A | 116.0 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 119.5 | C10—C9—H9A | 116.0 |
| C6—C1—H1A | 119.5 | C11—C10—C12 | 118.04 (11) |
| O2—C2—C1 | 125.04 (13) | C11—C10—C9 | 122.96 (12) |
| O2—C2—C3 | 115.10 (12) | C12—C10—C9 | 119.00 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.85 (12) | C12i—C11—C10 | 120.96 (13) |
| O3—C3—C4 | 125.24 (14) | C12i—C11—H11A | 119.5 |
| O3—C3—C2 | 115.11 (13) | C10—C11—H11A | 119.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.65 (13) | C11i—C12—C10 | 121.00 (12) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.21 (14) | C11i—C12—H12A | 119.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.9 | C10—C12—H12A | 119.5 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.9 | O2—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.91 (13) | O2—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.5 | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.5 | O2—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.41 (12) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 124.03 (12) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 117.55 (12) | O3—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C8 | 119.85 (12) | O3—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 119.98 (12) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.17 (12) | O3—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 121.13 (12) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 119.4 | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C13—O2—C2—C1 | −4.5 (2) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.1 (2) |
| C13—O2—C2—C3 | 176.83 (15) | C2—C1—C6—C7 | 178.99 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2—O2 | −179.73 (13) | C5—C6—C7—O1 | −173.70 (15) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.1 (2) | C1—C6—C7—O1 | 7.3 (2) |
| C14—O3—C3—C4 | −8.5 (3) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 6.5 (2) |
| C14—O3—C3—C2 | 170.79 (17) | C1—C6—C7—C8 | −172.50 (13) |
| O2—C2—C3—O3 | 1.14 (19) | O1—C7—C8—C9 | 7.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—O3 | −177.63 (13) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −172.95 (14) |
| O2—C2—C3—C4 | −179.52 (14) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −179.46 (13) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.7 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −5.6 (2) |
| O3—C3—C4—C5 | 178.13 (15) | C8—C9—C10—C12 | 174.89 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.1 (2) | C12—C10—C11—C12i | −0.4 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.0 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12i | −179.97 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.7 (2) | C11—C10—C12—C11i | 0.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.35 (14) | C9—C10—C12—C11i | 179.98 (13) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+2, −y, −z+1.
References
- Abdel Ghani, S. B., Weaver, L., Zidan, Z. H., Ali, H. M., Keevil, C. W. & Brown, R. C. D. (2008). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 518–522. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2012). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chandra Shekhara Shetty, T., Raghavendra, S., Chidan Kumar, C. S. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2016). Appl. Phys. B, 122, 205.
- Gaur, R. & Mishra, L. (2013). RSC Adv. 3, 12210–12219.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Harrison, W. T. A., Ravindra, H. J., Kumar, M. R. S. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3702.
- Harrison, W. T. A., Ravindra, H. J., Suresh Kumar, M. R. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2007a). Acta Cryst. E63, o3067.
- Harrison, W. T. A., Ravindra, H. J., Suresh Kumar, M. R. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2007b). Acta Cryst. E63, o3068.
- Husain, A., Ahmad, A., Mkhalid, I. A. I., Mishra, R. & Rashid, M. (2013). Med. Chem. Res. 22, 1578–1586.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Ruzié, C., Krayer, M. & Lindsey, J. S. (2009). Org. Lett. 11, 1761–1764. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y., Qin, G., Wang, W., Bian, W., Shuang, S. & Dong, C. (2011). J. Lumin. 131, 1672–1676.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II, III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678IIIsup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678Isup5.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678IIsup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017007460/hb7678IIIsup7.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report








