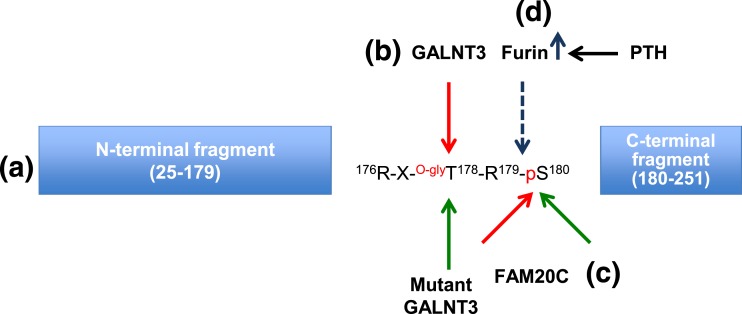
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the processing of FGF23. (a) FGF23 domains (N terminal and C terminal) are produced after specific cleavage. (b) Glycosylation (GALNT3) (red arrow) at T178 stabilizes FGF23, whereas GALNT3 inactivation (green arrow) increases FGF23 cleavage. (c) Phosphorylation by FAM20C (red arrow) increases FGF23 cleavage, whereas inhibition of phosphorylation at S180 [mutant FAM20C (green arrow)] stabilizes iFGF23. (d) Furin/subtilisin-like convertase identified by Knab et al. (4), is upregulated by PTH treatment and stimulates cleavage of FGF23 at R179/S180.